
Heavy machinery used in construction and other industrial tasks is composed of various intricate systems that work together to achieve smooth operation. Familiarizing oneself with these systems can help in both the maintenance and efficient use of such machinery. It’s important to have a clear overview of how the various mechanical and hydraulic elements are organized to support the machine’s functionality.
By breaking down the key sections of these machines, one can gain insight into how power is transmitted, how control mechanisms are engaged, and how the overall structure contributes to the machine’s capacity to handle heavy workloads. Knowing the layout and interaction of these essential elements enables better troubleshooting and operational understanding.
Whether dealing with mechanical systems or hydraulic networks, understanding how each piece interacts within the larger framework is crucial for effective management. This knowledge allows for proactive maintenance and the avoidance of potential issues that could disrupt operations.
Understanding the Wheel Loader Components
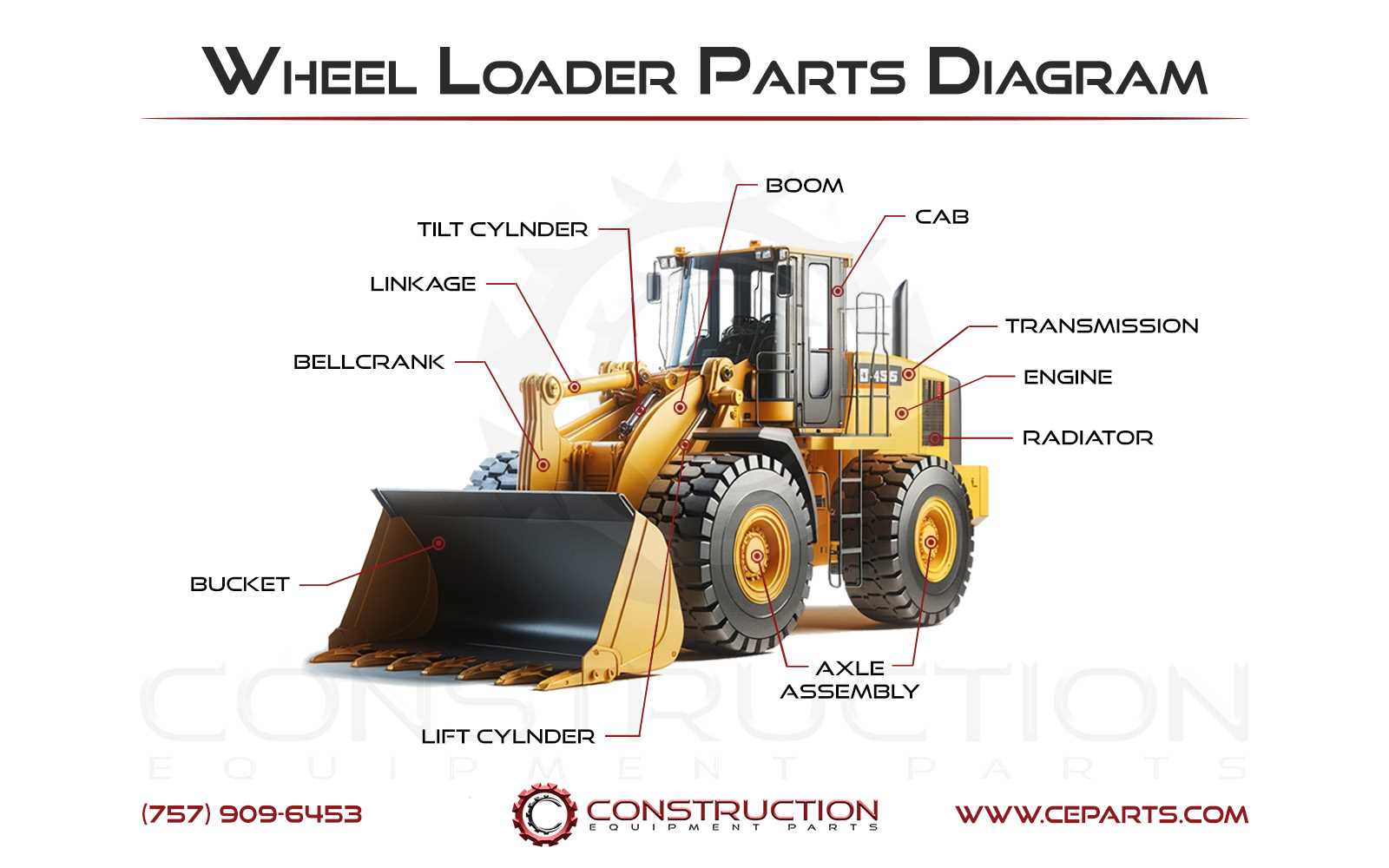
Construction machinery is composed of multiple essential systems working together to perform heavy-duty tasks. Each system plays a critical role in ensuring the machine operates smoothly and efficiently. Familiarizing yourself with these mechanisms is key to maintaining performance and ensuring the longevity of the equipment.
Main Structural Elements
- The frame supports the overall structure, providing stability and strength during operations.
- The hydraulic system controls various movements and allows for powerful handling of materials.
- The engine powers the equipment, ensuring all systems receive the necessary energy to function.
Key Operational Systems
- The control system enables precise operation, allowing the operator to manage the machine’s movements effortlessly.
- The transmission system ensures smooth shifts between different power levels, adapting to the load’s demands.
- The braking mechanism provides essential safety, ensuring controlled stops during operations.
Main Systems in a Wheel Loader
The structure of this type of heavy machinery relies on several key mechanisms, each playing a crucial role in its operation. These systems ensure efficient performance, durability, and safety during various tasks. Understanding these elements helps in maintaining smooth functionality.
- Hydraulic Mechanism – This system provides the necessary force for moving components and handling materials effectively. It powers the lifting and tilting functions.
- Engine and Powertrain – The core source of energy that drives the machine, delivering power to essential operational components.
- Control and Steering Mechanisms – Ensures precise movement and handling. This section helps the operator navigate and control the direction of movement.
- Braking System – Critical for ensuring safety, this mechanism allows for controlled stops and holds under various working conditions.
- Cooling and Filtration – Designed to prevent overheating and contamination, extending the equipment’s life and ensuring reliable performance.
Hydraulic Mechanisms and Their Functions

Hydraulic systems play a crucial role in modern machinery, offering powerful and efficient methods to transmit force through fluid pressure. These mechanisms operate by converting mechanical energy into hydraulic energy, enabling smooth and precise control over various operations in heavy-duty equipment.
Main Components of Hydraulic Systems

The core elements of any hydraulic system include pumps, valves, and cylinders. Pumps generate the necessary flow of hydraulic fluid, while valves regulate this flow, controlling the pressure and direction. Cylinders, in turn, convert the hydraulic energy back into mechanical force, driving the motion of different mechanical parts.
Applications and Benefits

Hydraulic mechanisms are favored for their ability to handle heavy loads with minimal effort, offering reliability and precise control. The flexibility of hydraulic systems allows them to adapt to different operational requirements, making them essential for tasks that demand strength and accuracy.
Steering and Control Linkages Overview

The steering and control linkages play a critical role in ensuring smooth and responsive handling of heavy equipment. These systems are designed to provide accurate control over movement, translating operator input into mechanical motion for precise maneuvering. Proper maintenance of these linkages is essential for maintaining operational efficiency and safety.
Components of the Steering Mechanism
- Steering column: Transmits directional commands from the operator to the control system.
- Pitman arm: Connects the steering box to the linkages, converting rotary motion into linear movement.
- Drag link: Transfers motion from the Pitman arm to the steering linkage, ensuring smooth operation.
Control Linkages Operation
The control linkages are responsible for delivering precise input to various operational mechanisms, ensuring accurate functionality of the equipment. These linkages include various rods and arms that relay control signals to the necessary components, enabling smooth and efficient operations.
Bucket and Loader Arm Parts Explained

The components involved in lifting and moving materials play a crucial role in heavy machinery operations. These elements are essential for handling large quantities of earth, debris, or other materials efficiently and safely. Understanding how these elements function can help improve performance and maintenance efforts.
The bucket is designed for collecting and transporting materials. It is built to withstand significant pressure and wear, making it suitable for various environments. The size and shape of the bucket can vary depending on the type of material being moved.
The loader arm serves as the mechanism that raises and lowers the bucket. These arms are constructed to support heavy loads while maintaining stability during operation. The precision of their movement is critical for safe and effective material handling.
Transmission System Layout in Wheel Loaders

The transmission system in heavy machinery plays a crucial role in ensuring effective power distribution and control. This layout is designed to optimize performance, enhancing the machine’s ability to navigate various terrains while efficiently managing load handling tasks.
Components of the Transmission System

The transmission assembly typically consists of several key elements, each serving a distinct function. These include the gearbox, torque converter, and hydraulic systems, which work together to regulate speed and torque output. The gearbox is responsible for shifting between different speeds, allowing the operator to adjust to the demands of the work environment.
Functionality and Efficiency
Proper functioning of the transmission layout is essential for maintaining high levels of efficiency and productivity. By facilitating smooth transitions between gears and providing adequate torque, the system minimizes wear on other components, ensuring longevity and reliability. Regular maintenance and checks are necessary to preserve the system’s integrity and performance.
Braking Mechanism and Key Components
The braking system is crucial for the safe operation of heavy machinery, ensuring effective control and stability during various tasks. This system comprises several essential elements that work together to provide reliable stopping power and enhance overall performance.
Essential Elements of the System

Key components include the brake pedal, which activates the braking process, and the hydraulic lines that transmit force from the pedal to the braking mechanism. Additionally, the brake calipers play a significant role in applying pressure to the braking surfaces, resulting in effective deceleration.
Maintenance and Efficiency
Regular maintenance of the braking components is vital to ensure optimal functionality and safety. Inspections should focus on the wear of friction materials and the integrity of hydraulic systems, as any deficiencies can compromise the equipment’s performance and the operator’s safety.
Axles and Wheels in a Loader
The components responsible for mobility and stability in heavy machinery play a crucial role in overall performance. These elements are essential for transferring power from the engine to the ground, ensuring effective movement and handling of loads. Their design and functionality significantly impact operational efficiency and safety.
Functionality and Design
Understanding the mechanics of these crucial elements is vital for anyone involved in the maintenance or operation of heavy machinery. The central beam, connecting the driving mechanism to the frame, must be robust to withstand heavy loads and stresses during operation. The circular components must provide not only traction but also stability while navigating various terrains.
Maintenance Considerations
Regular inspection and maintenance of these components are necessary to prevent wear and potential failure. Ensuring proper lubrication, checking for alignment, and assessing the integrity of connections can enhance durability and performance. Neglecting these factors may lead to decreased efficiency and increased operational costs.
| Component | Function | Maintenance Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Axle | Transfers power and supports the weight | Regularly check for alignment and wear |
| Wheel | Provides traction and stability | Inspect for damage and maintain proper inflation |
Engine and Cooling System Parts
This section delves into the essential components that ensure optimal performance and reliability of the machinery’s power unit and its cooling mechanism. Understanding these elements is crucial for maintenance and efficient operation, as they play a vital role in preventing overheating and ensuring smooth functionality.
Key Components of the Engine

The core of the machinery consists of several vital elements that work in harmony to generate power. These include the cylinder head, which houses critical valves and injectors, and the crankshaft, responsible for converting linear motion into rotational energy. Additionally, the oil pump circulates lubricants to minimize friction and wear among moving parts.
Cooling Mechanism Essentials
To maintain optimal operating temperatures, the radiator plays a pivotal role by dissipating heat generated during operation. Connected to the radiator, the water pump circulates coolant throughout the engine. Furthermore, the thermostat regulates the flow of coolant, ensuring the engine reaches its ideal temperature without overheating.
Maintenance Tips for Loader Components
Regular upkeep of equipment elements is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Implementing a systematic maintenance approach can prevent unexpected breakdowns and extend the lifespan of the machinery. Here are some effective strategies to consider.
| Component | Maintenance Tip |
|---|---|
| Hydraulic System | Regularly check fluid levels and inspect hoses for leaks. |
| Engine | Change oil and filters according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. |
| Transmission | Monitor fluid quality and levels; replace when necessary. |
| Tires | Maintain proper inflation and inspect for wear and damage. |
| Electrical System | Check battery terminals and wiring for corrosion or wear. |
Electrical System and Wiring Diagrams
This section focuses on the intricate design and configuration of electrical systems used in heavy machinery. Understanding these systems is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting, ensuring that all components function seamlessly together.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Battery | Stores electrical energy and provides power to start the engine and run electrical systems. |
| Alternator | Generates electricity while the engine is running, supplying power to the electrical system and recharging the battery. |
| Starter Motor | Engages the engine flywheel to initiate engine operation when the ignition is activated. |
| Wiring Harness | A collection of wires that connects various electrical components, facilitating communication and power distribution. |
| Fuses | Protects the electrical system by breaking the circuit if there is an overload or short circuit. |
| Relay | Controls the operation of larger electrical devices by using a smaller current to switch them on or off. |