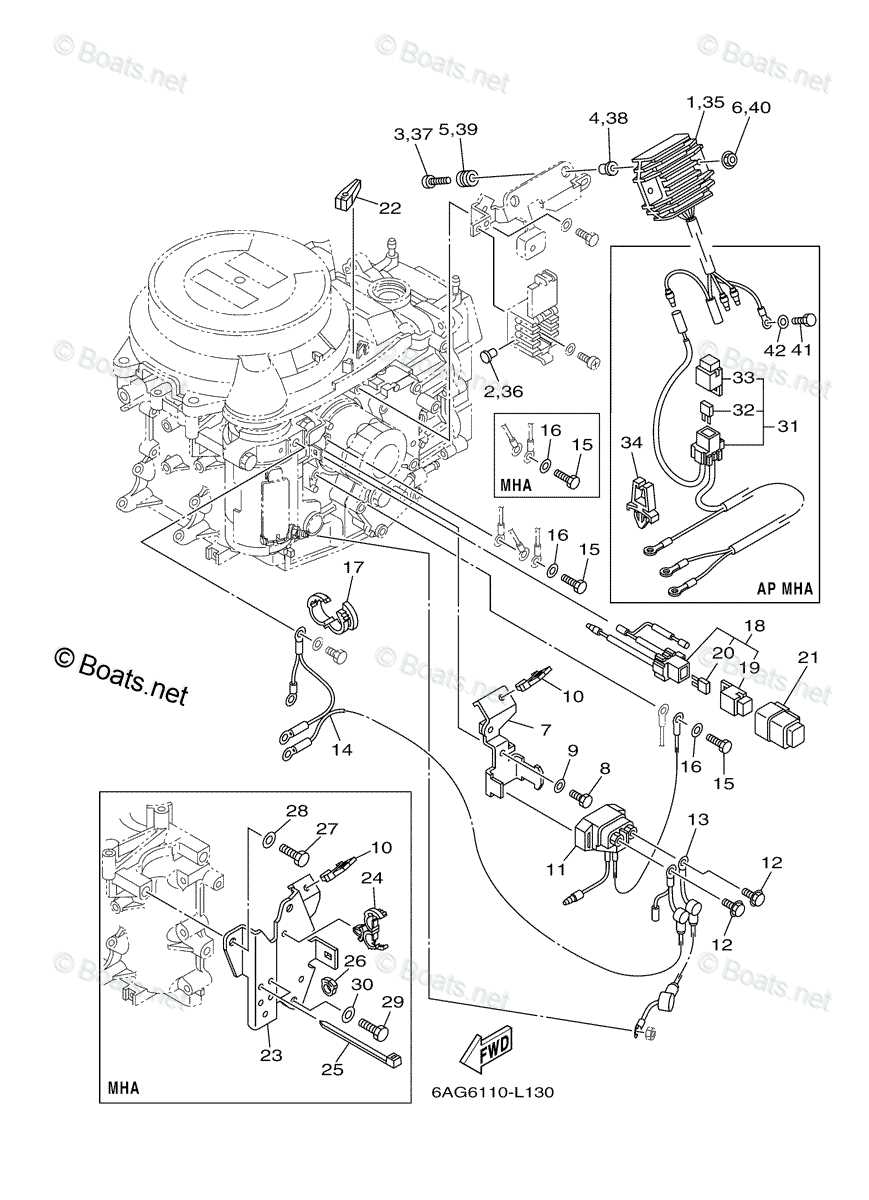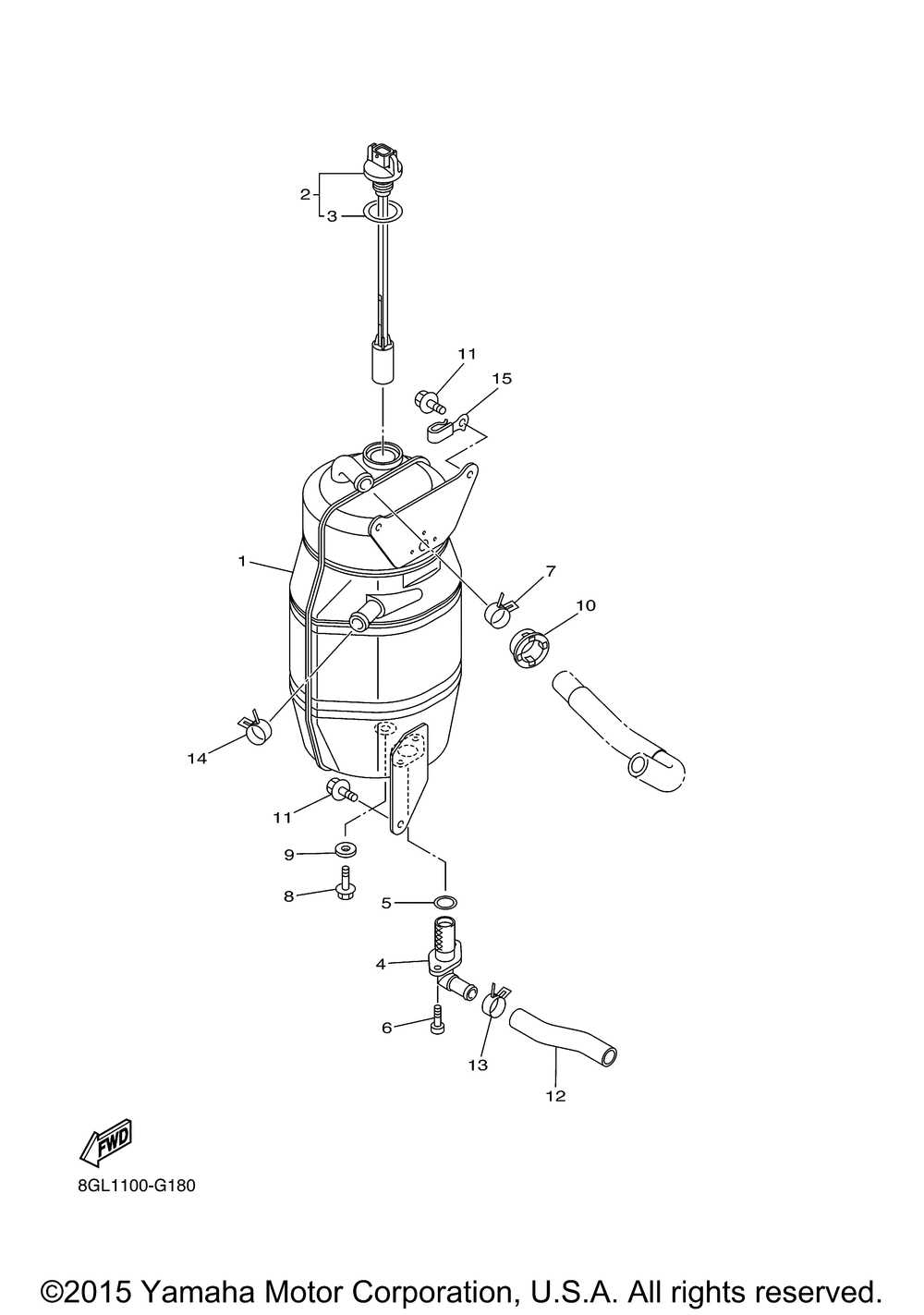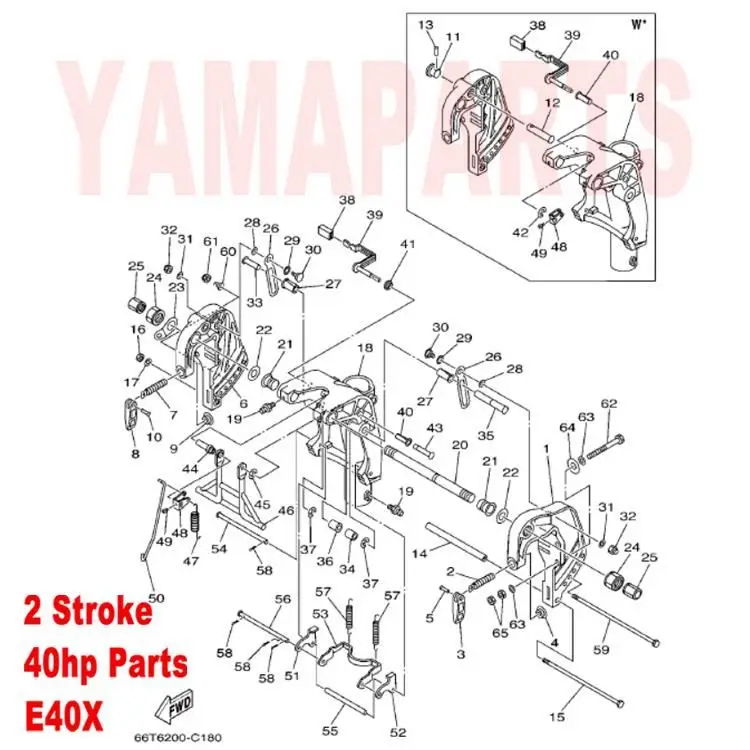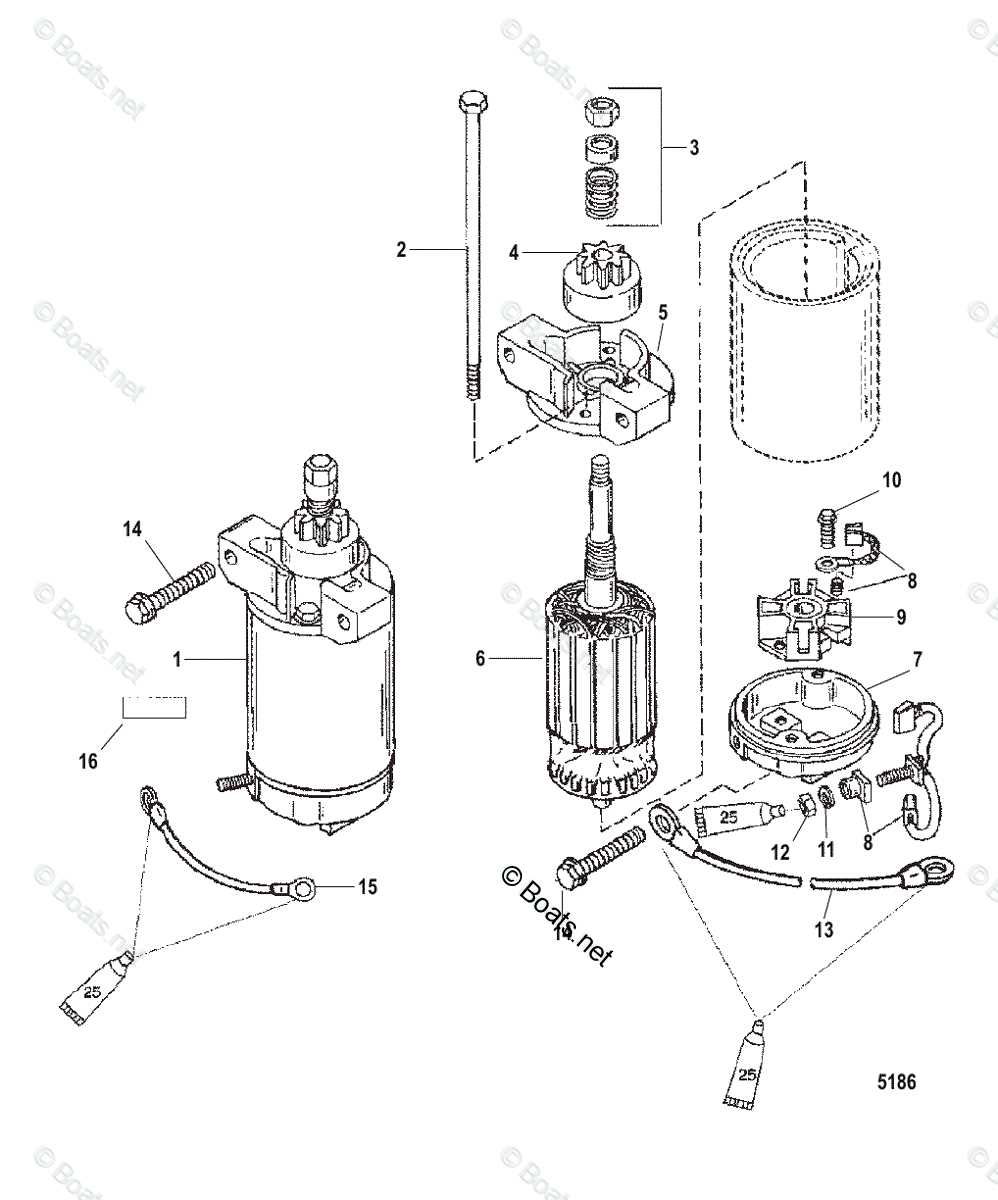
In this section, we will explore the essential elements that make up an efficient and powerful marine propulsion system. Each unit is designed with precision to ensure optimal performance and durability in various water conditions. The focus will be on the internal and external components that contribute to the smooth operation and longevity of the engine.
Understanding the arrangement and function of different mechanical systems is crucial for maintaining and repairing your engine. We will break down the individual sections, highlighting the roles of key components involved in powering the boat. This guide will provide a clear overview, allowing for better insight into how everything fits together and works seamlessly.
Yamaha 40 hp 2 Stroke Engine Components
This section provides a detailed overview of the key elements that make up the power system of a small marine propulsion unit. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the engine. Understanding these components is essential for maintenance and efficient operation.
| Component | Function | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Piston | Responsible for converting fuel energy into mechanical power by moving inside the cylinder. | ||||||||||||||
| Cylinder Head | Houses various parts crucial for combustion and helps in sealing the combustion chamber. | ||||||||||||||
| Crankshaft | Transforms the linear motion of the pistons into rotational movement, driving the propeller. |
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Housing | The outer structure that protects internal components and supports the assembly. |
| Shaft | A rotating element that transmits power from the engine to the propeller. |
| Gears | Interlocking pieces that modify the torque and speed transmitted to the output shaft. |
| Bearings | Support rotating shafts and reduce friction between moving parts. |
| Seal | Prevents fluid leaks and keeps contaminants out of the gearbox. |
| Clutch | Engages and disengages the power flow to control movement. |
Exhaust System Structure and Maintenance
The exhaust system plays a critical role in the overall functionality and efficiency of an engine. It is designed to expel combustion gases safely and effectively while minimizing noise and emissions. Understanding its components and ensuring regular maintenance can significantly enhance performance and longevity.
Key Components
- Exhaust Manifold: This part collects gases from the engine and directs them into the exhaust system.
- Silencer: Also known as a muffler, it reduces noise produced by the engine’s exhaust.
- Exhaust Pipe: It channels the gases from the manifold to the outside environment.
- Catalytic Converter: This component helps reduce harmful emissions by converting them into less harmful substances.
Maintenance Tips
- Regular Inspections: Check for any signs of leaks, corrosion, or damage to components.
- Cleaning: Remove any buildup of soot or debris from the exhaust system to maintain optimal airflow.
- Fastener Tightness: Ensure all connections and bolts are secure to prevent leaks and ensure proper function.
- Professional Servicing: Schedule periodic professional checks to assess the system’s condition and functionality.
Oil Pump and Lubrication Process
The efficiency of an engine significantly relies on its lubrication system. This system ensures that all moving components operate smoothly and minimizes wear over time. Proper lubrication is essential for maintaining optimal performance and longevity of the engine, preventing overheating and reducing friction among parts.
In this section, we will explore the functionality of the lubrication mechanism and the crucial role of the oil pump in this process.
- Oil Pump Functionality: The oil pump is responsible for circulating oil throughout the engine. It draws oil from the reservoir and delivers it to various components, ensuring adequate lubrication.
- Types of Oil Pumps:
- Gear pumps
- Rotary vane pumps
- Diaphragm pumps
- Lubrication Process: The lubrication system typically operates as follows:
- The oil is drawn from the crankcase or oil reservoir.
- The oil pump pressurizes the oil and sends it to the engine parts.
- Oil lubricates critical components such as bearings, pistons, and crankshafts.
- Excess oil returns to the reservoir, allowing for continuous circulation.
- Importance of Regular Maintenance: Regular checks and maintenance of the lubrication system are vital. This includes:
- Inspecting oil levels and quality
- Replacing worn or damaged oil pumps
- Using the recommended oil type for optimal performance
Steering Mechanism and Control Cables
The steering system plays a crucial role in the operation of any marine vessel, providing the ability to navigate and control direction effectively. This mechanism is essential for achieving precise handling and ensuring a smooth ride across various water conditions. Understanding the components involved is vital for proper maintenance and troubleshooting.
Components of the Steering System
The primary elements of the steering system include the helm, cables, and the actuator. The helm serves as the operator’s interface, allowing for easy maneuvering. The cables connect the helm to the actuator, translating the operator’s movements into directional changes. Regular inspection of these components is necessary to ensure optimal functionality and prevent steering issues.
Importance of Control Cables

Control cables are critical for the reliable transmission of signals between the helm and the steering mechanism. They must be durable and resistant to wear and corrosion, as they are often exposed to harsh marine environments. Proper adjustment and maintenance of these cables are essential to guarantee responsive steering and enhance overall safety while navigating.
Gaskets and Seals Placement in Yamaha Engines
Effective assembly of components in marine power units relies significantly on the strategic positioning of gaskets and seals. These elements play a crucial role in preventing leaks and ensuring optimal performance by maintaining proper pressure and fluid containment throughout the engine.
Types of Gaskets and Seals
- Base gaskets: Essential for sealing the contact surfaces between the engine block and cylinder head.
- Exhaust gaskets: Critical for sealing the exhaust manifold to prevent gas leaks.
- Oil seals: Important for maintaining oil pressure and preventing oil from leaking out of various engine sections.
- Water pump gaskets: Ensure a secure fit between the water pump and engine, preventing coolant leaks.
Proper Installation Techniques
- Clean all surfaces thoroughly to remove any debris or old gasket material before applying new seals.
- Ensure that the gasket is properly aligned with the bolt holes and surfaces to avoid misalignment.
- Apply the correct torque specifications to the fasteners to secure the gaskets in place without over-compressing them.
- Inspect for any signs of wear or damage during reassembly to ensure longevity and reliability.
Maintenance Tips for Key Engine Components
Regular upkeep of essential engine elements is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. By focusing on specific areas, you can prevent issues and enhance the overall efficiency of the machinery.
- Cooling System:
- Check coolant levels regularly to avoid overheating.
- Inspect hoses for any signs of wear or leaks.
- Flush the cooling system as recommended to remove debris.
- Fuel System:
- Use high-quality fuel to prevent clogging and build-up.
- Regularly replace fuel filters to ensure clean fuel supply.
- Inspect fuel lines for cracks or damage.
- Ignition System:
- Check spark plugs for wear and replace them as needed.
- Inspect ignition coils for proper function.
- Ensure all electrical connections are secure and corrosion-free.
- Lubrication:
- Change oil and filters at regular intervals to maintain engine health.
- Use the appropriate type of oil as specified in the manual.
- Check for oil leaks and address them immediately.
By adhering to these maintenance suggestions, you can significantly prolong the life of your engine and maintain its peak performance.