
Understanding the internal structure of any mechanical system can significantly enhance the process of maintenance and repair. When working with complex machinery, it becomes crucial to identify how various elements are interconnected. This allows for easier troubleshooting and efficient replacements, ensuring long-term performance and reliability.
In this section, we’ll dive into the arrangement of essential components within a high-performance machine. The layout reveals how various mechanisms cooperate to deliver optimal function. By studying the detailed arrangement of each element, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of the overall engineering design and its operational strategy.
With clear visuals and explanations, navigating through intricate mechanical systems becomes more straightforward. Whether you’re conducting regular checks or involved in more substantial upgrades, understanding how each element fits into the larger system will save both time and effort in achieving your desired outcome.
Exploring the Components of Yamaha FZ1
When it comes to understanding the mechanical structure of this popular two-wheeler, it’s essential to dive into the key systems that make it function smoothly. Each element plays a crucial role in ensuring performance, stability, and safety. This section focuses on the major components, breaking them down for easy comprehension and maintenance.
Key Mechanical Systems

The vehicle’s mechanical makeup consists of several primary systems that work together harmoniously. Below is a breakdown of the critical areas that require attention during regular inspection:
- Engine and power delivery system
- Suspension and handling components
- Braking mechanisms and safety features
Regular Maintenance Checklist
Ensuring optimal performance over time depends on consistent care. The following list highlights key areas to focus on during routine maintenance:
- Fluid levels, including oil and coolant
- Brake pad and disc wear
- Tire pressure and tread health
- Chain tension and lubrication
Understanding Key Engine Elements
When analyzing the structure of a motor, it’s important to focus on the essential components that contribute to its smooth operation. Each piece plays a significant role in ensuring the efficient conversion of energy and the overall functionality of the system. A clear understanding of these elements is crucial for maintenance and troubleshooting.
Core Functional Components
The engine is comprised of several key elements that work together to generate motion. Cylinders form the heart of the system, providing the space where fuel combustion occurs. The pistons, which move within the cylinders, are responsible for converting energy into mechanical movement. The balance between these elements is critical for performance and reliability.
Supporting Systems
In addition to the core components, the motor relies on various supporting systems. The cooling mechanism prevents overheating, while the fuel delivery system ensures a steady supply of fuel to the cylinders. Each of these
Chassis Structure and Frame Details
The overall design of the framework is essential for ensuring both stability and agility in various riding conditions. The construction of the frame supports the entire mechanical system, providing a balance between durability and flexibility, which is crucial for handling and performance. The structural components are carefully designed to absorb vibrations, improving comfort and control during operation.
One of the key elements is the integration of high-strength materials that contribute to the overall rigidity without significantly increasing weight. This balance helps maintain maneuverability while offering a sturdy base for the engine and suspension systems. The layout and alignment of the components are optimized to distribute weight efficiently, enhancing the vehicle’s dynamics on the road.
Attention to detail in the connection points and reinforcement areas ensures that the framework can withstand the stresses of different terrains and speeds. The choice of materials and the design approach reflect a focus on safety, efficiency, and longevity, making it an integral part of the vehicle’s performance capabilities.
Electrical System Breakdown
The electrical setup of any modern machine is complex, involving multiple interconnected components working together to ensure proper functionality. Understanding the layout and how various elements interact is key to diagnosing issues or planning upgrades. This section outlines the main aspects of the system, breaking it down into core elements that contribute to the smooth operation of the entire vehicle.
- Power generation and distribution
- Control units and sensors
- Wiring and connectors
- Lighting and signaling mechanisms
Each of these sections plays a vital role in maintaining the overall integrity of the vehicle’s electrical functionality. Below is a more detailed look into how each component fits into the bigger picture.
Fuel Delivery System Overview
The fuel delivery mechanism is a critical component responsible for ensuring a consistent flow of fuel to the engine. It involves several interconnected elements working together to maintain efficient combustion and performance. Understanding how this system operates is key to diagnosing potential issues and performing maintenance effectively.
- Fuel Tank: The primary reservoir for storing fuel before it is distributed to the engine. Its size and placement impact the overall balance and fuel capacity of the vehicle.
- Pump: This device moves fuel from the tank through the system, maintaining proper pressure to meet the engine’s demands. It is often electric in modern designs.
- Filter: A vital component that removes impurities from the fuel, ensuring only clean fuel reaches the engine. Regular filter changes prevent clogging and extend the system’s life.
- Injectors: These devices spray fuel into the engine’s combustion chamber. The amount and timing of the fuel injection are crucial for optimal engine performance.
Proper maintenance of each part of the fuel delivery system ensures that the engine receives the right fuel mixture at the right time, promoting smooth operation and reducing wear on the system.
Brake System Parts and Layout
The braking mechanism is crucial for ensuring safety and control during operation. Understanding its composition and arrangement helps in maintaining optimal functionality and performance. Each component plays a specific role, contributing to the overall effectiveness of the system.
Key elements of the braking system include:
- Brake Lever: This component is operated by the rider and is essential for engaging the braking action.
- Brake Master Cylinder: It converts the force from the lever into hydraulic pressure, which activates the brakes.
- Brake Lines: These tubes carry hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the calipers, facilitating the transfer of pressure.
- Brake Caliper: This unit houses the brake pads and applies pressure to the rotor to slow down or stop the vehicle.
- Brake Pads: Friction materials that grip the rotor, providing the necessary stopping power.
- Brake Rotors: These discs are attached to the wheel and provide a surface for the pads to clamp against.
Understanding the configuration and function of these components aids in troubleshooting and enhancing performance. Regular inspection and maintenance ensure that each part operates efficiently, contributing to a reliable braking system.
Suspension Setup and Components
Properly configuring the suspension system is crucial for achieving optimal performance and handling characteristics in any motorcycle. This setup encompasses a variety of elements that work together to enhance stability, comfort, and control during rides. Understanding the key components and their adjustments is essential for riders seeking to improve their machine’s responsiveness to various terrains and riding styles.
Key Elements of Suspension
- Forks: The front forks play a significant role in absorbing shocks and maintaining traction. Different types of forks, such as telescopic and inverted, offer distinct advantages in terms of performance and feel.
- Shock Absorber: The rear shock absorber is vital for stabilizing the bike during acceleration and cornering. Its damping characteristics can greatly affect ride quality and control.
- Springs: Both front and rear springs are fundamental in determining ride height and weight distribution. Stiffer springs can enhance performance on smooth surfaces, while softer springs provide comfort on rough roads.
Adjustment Options
- Preload: Adjusting the preload affects the initial compression of the spring, allowing customization for rider weight and cargo.
- Damping: Fine-tuning the damping settings controls the rate at which the suspension compresses and rebounds, impacting handling and comfort.
- Ride Height: Modifying the ride height can alter the bike’s center of gravity, influencing its stability and cornering capabilities.
Understanding and adjusting these components can lead to significant improvements in performance and rider confidence, making the journey more enjoyable and controlled.
Transmission and Gearbox Mechanism
The transmission and gearbox mechanism plays a crucial role in converting engine power into usable torque for driving. This system ensures smooth acceleration and deceleration by allowing the rider to select appropriate gear ratios. Understanding its components and functionality is essential for anyone involved in maintenance or repair tasks.
Key Components
- Gear Selector: Enables the user to change gears based on speed and power requirements.
- Transmission Housing: Contains the gear sets and lubricates the system to reduce friction.
- Output Shaft: Transfers power from the gearbox to the rear wheel.
- Clutch Assembly: Engages and disengages the engine from the transmission, allowing for smooth gear changes.
Working Principles
The gearbox operates on the principle of gear ratios, which determine the relationship between the input and output speeds. By shifting through various gears, the rider can optimize performance for different riding conditions. A higher gear ratio provides more torque, while a lower ratio enhances speed. This mechanism also includes:
- Synchronizers: Facilitate smooth engagement of gears.
- Bearings: Support rotating shafts and reduce friction.
- Lubrication System: Maintains optimal operating temperature and prolongs component life.
Understanding these elements and their interactions enhances the overall performance and reliability of the transmission system.
Cooling System Parts Guide
The efficiency of any engine largely depends on its ability to maintain optimal operating temperatures. A well-functioning cooling assembly is essential for preventing overheating and ensuring longevity. This section will delve into the various components of the cooling assembly, explaining their roles and importance in maintaining engine performance.
Radiator: The radiator serves as the primary heat exchanger, allowing coolant to release heat into the atmosphere. It consists of a series of tubes and fins that maximize surface area for efficient heat dissipation.
Water Pump: This component is crucial for circulating coolant throughout the engine and radiator. A reliable water pump ensures that the coolant flows properly, preventing hot spots and maintaining a consistent temperature.
Thermostat: The thermostat regulates the flow of coolant based on the engine temperature. It opens and closes at specific temperature thresholds, allowing the engine to reach optimal operating conditions quickly.
Hoses: These flexible tubes transport coolant between the engine, radiator, and other components. Quality hoses are vital to prevent leaks and ensure a steady flow of coolant.
Coolant Reservoir: This container holds excess coolant and allows for expansion as temperatures rise. It ensures that the system remains filled and can accommodate variations in coolant volume.
Cooling Fan: Often electric, the cooling fan draws air through the radiator when the vehicle is stationary or at low speeds, enhancing heat dissipation when needed most.
Understanding these essential elements will help in recognizing their functions and the significance of maintaining a well-operating cooling assembly. Regular checks and timely replacements can prevent costly repairs and enhance the overall reliability of the engine.
Body Panels and Fairing Design
The aesthetics and functionality of a motorcycle are significantly influenced by the design of its body panels and fairings. These components serve both protective and aerodynamic purposes, contributing to the overall performance and visual appeal of the vehicle. Effective fairing design not only enhances airflow but also reduces drag, allowing for a smoother ride.
Body panels are crucial for safeguarding the internal mechanisms while providing a cohesive look to the bike. Various materials, such as plastics and composites, are utilized to achieve a balance between weight and durability. The ergonomic design of these panels is essential for rider comfort and ease of handling.
Moreover, the integration of fairings plays a pivotal role in shaping the motorcycle’s profile. Streamlined designs can lead to improved stability at higher speeds, making them essential for sport-oriented models. Customizable features in fairing design allow riders to personalize their machines, reflecting individual styles while maintaining performance efficiency.
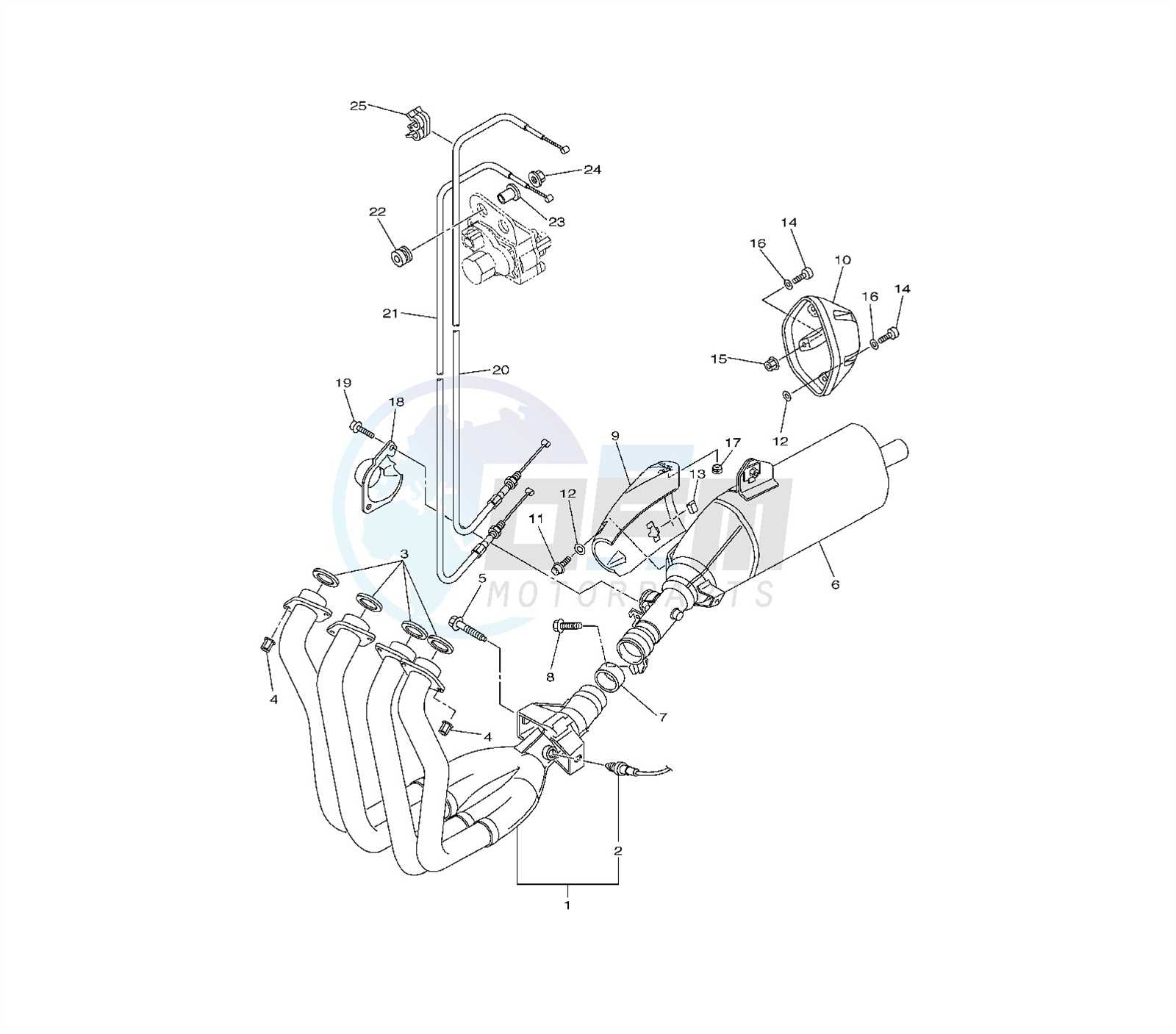
Exhaust System Configuration
The exhaust system plays a crucial role in optimizing engine performance and ensuring efficient gas expulsion. A well-designed configuration not only enhances power delivery but also contributes to the overall acoustic character of the machine. Understanding the components and their arrangement can help in achieving the desired balance between performance and sound.
Key Components
In the typical exhaust assembly, several essential elements work in harmony. The main components include headers, mufflers, and intermediate pipes, each serving a specific function. Headers facilitate the exit of exhaust gases from the engine, while mufflers control noise levels and improve sound quality. The arrangement of these parts influences backpressure and, consequently, engine efficiency.
Table of Components
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Headers | Channel exhaust gases away from the engine |
| Muffler | Reduces noise and modifies sound profile |
| Intermediate Pipes | Connect headers to the muffler and facilitate gas flow |
| Exhaust Tips | Direct exhaust gases out of the vehicle, enhancing aesthetics |
By optimizing the arrangement and specifications of these elements, enthusiasts can significantly enhance the performance and sound of their machines. Proper tuning and configuration can lead to noticeable improvements in power delivery and overall riding experience.
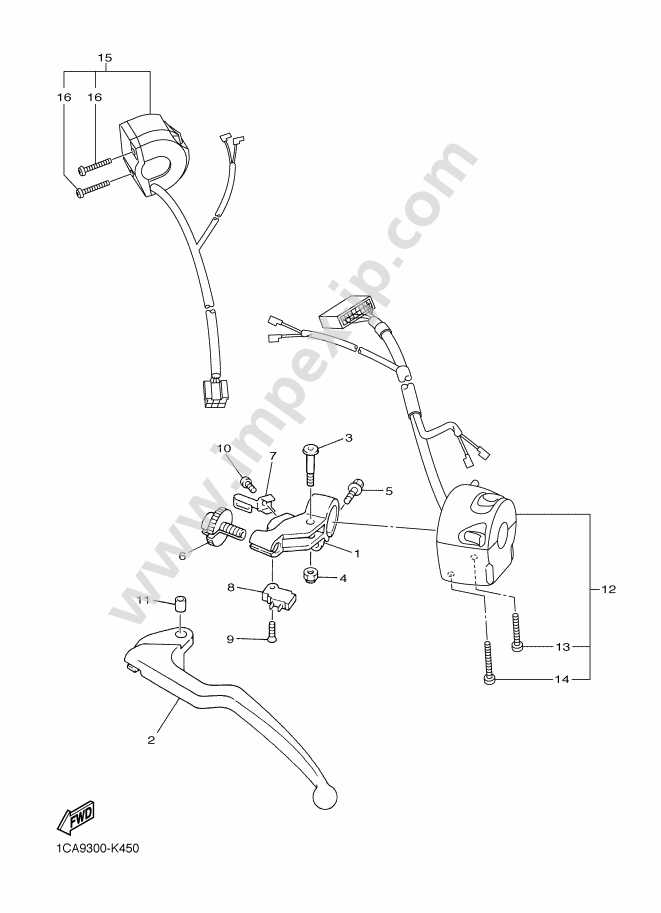
Handlebar and Control Mechanisms
The handlebar assembly and control systems play a vital role in ensuring a smooth and responsive riding experience. These components not only influence the maneuverability of the vehicle but also integrate various functionalities essential for safe operation. Understanding their design and arrangement can enhance both performance and comfort for the rider.
| Component | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Handlebar | The primary interface for steering and control. | Provides leverage for turning and stabilizing the vehicle. |
| Grips | Rubber or foam coverings on the handlebar ends. | Enhances comfort and control while riding. |
| Throttle | Control mechanism for regulating engine power. | Adjusts acceleration and speed based on rider input. |
| Brake Levers | Levers used to engage the braking system. | Allows the rider to reduce speed or stop safely. |
| Clutch Lever | Lever for disengaging the engine from the transmission. | Facilitates gear changes and smooth operation. |
| Switches | Control elements for lights, horn, and other features. | Enables the rider to operate various electrical systems. |