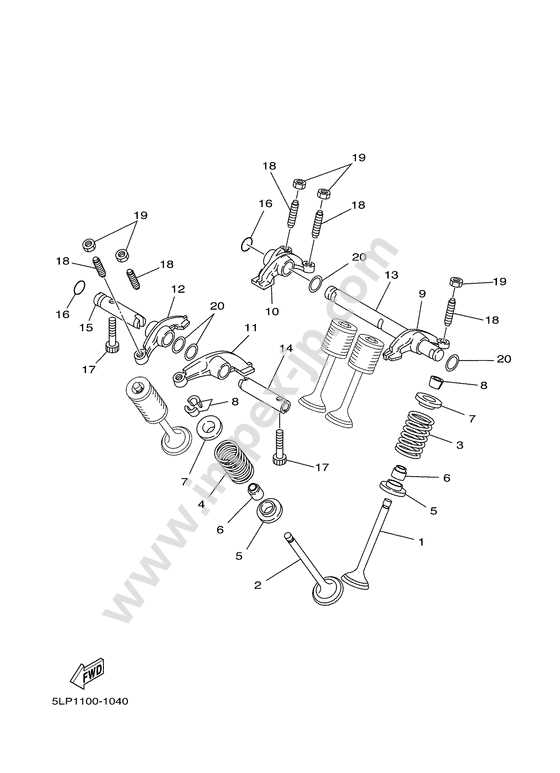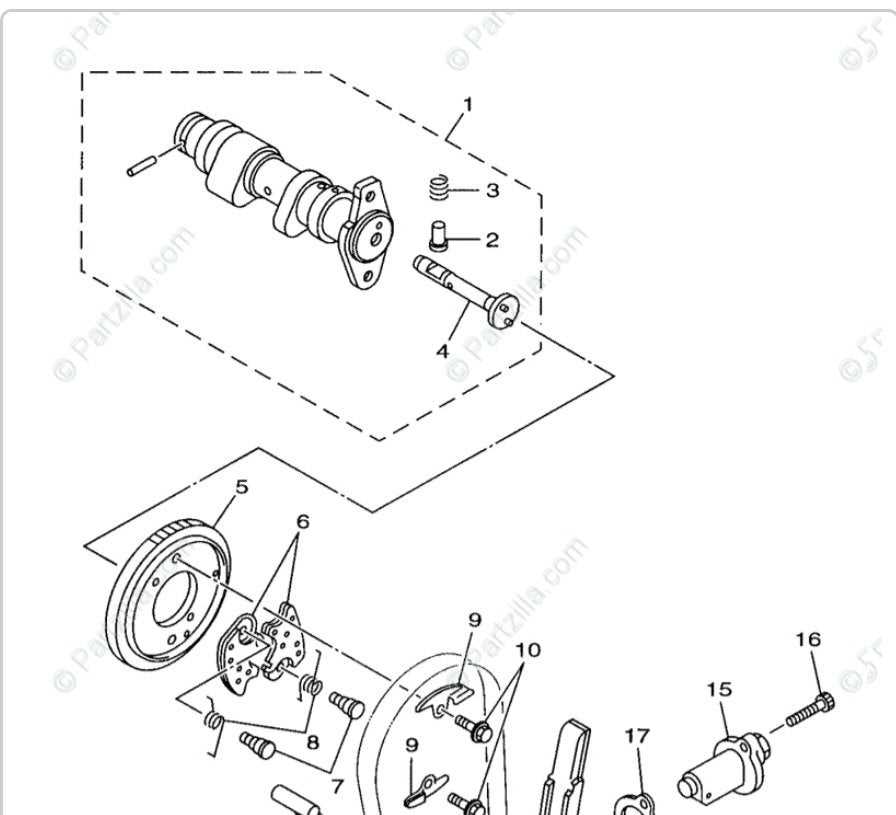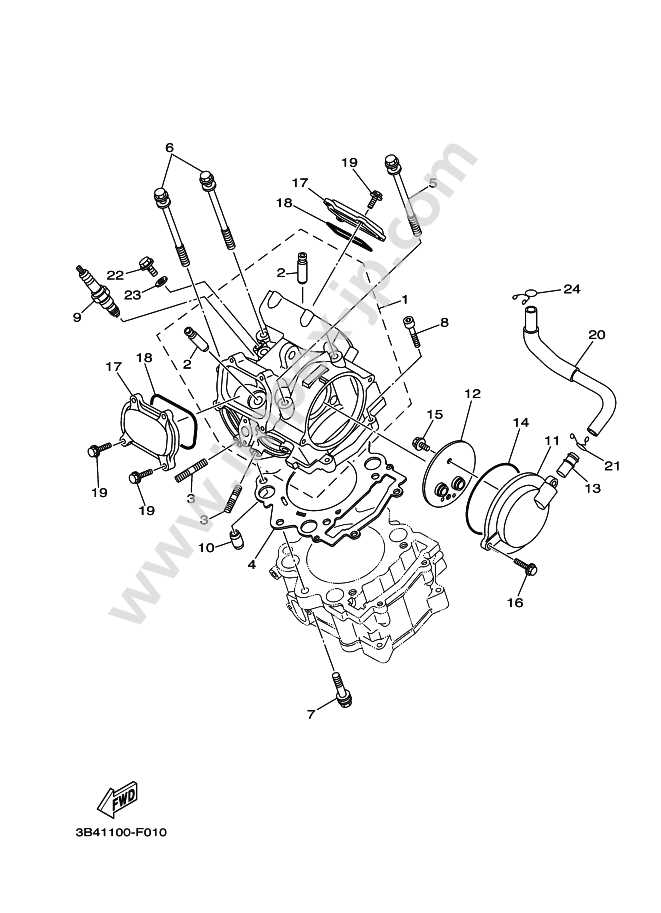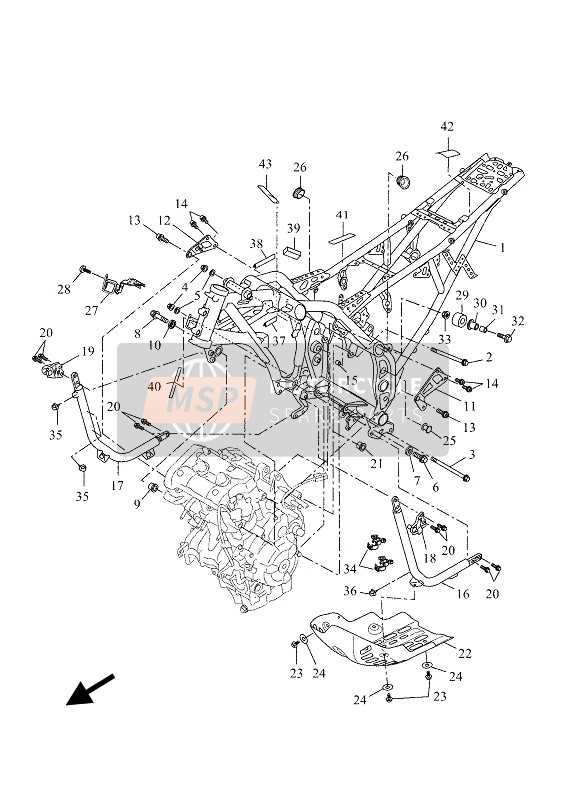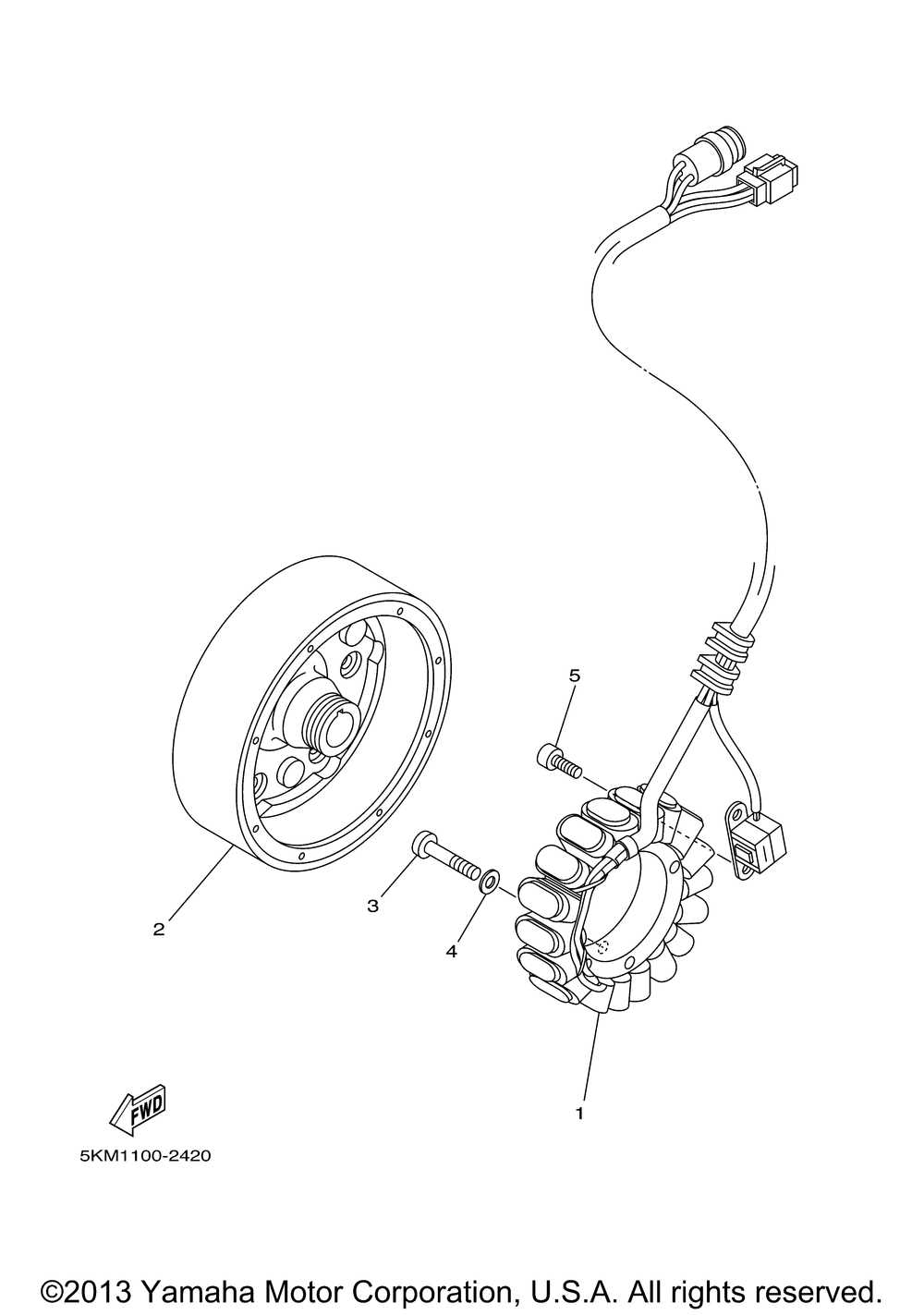
Understanding the configuration of essential elements is crucial for maintaining and optimizing the performance of any utility vehicle. By familiarizing yourself with the layout, you can efficiently troubleshoot, perform upgrades, and ensure smooth operation across diverse terrains.
This section provides detailed insights into the interconnected mechanisms that form the foundation of off-road vehicles. With a clear breakdown of individual elements, users gain the knowledge needed to handle repairs, replacements, and customizations with confidence.
Whether you’re an experienced technician or a first-time enthusiast, having a clear visualization of the internal systems is invaluable. This resource aims to simplify complex mechanical structures, making the information accessible for every level of expertise.
Yamaha Grizzly 660 Parts Diagram
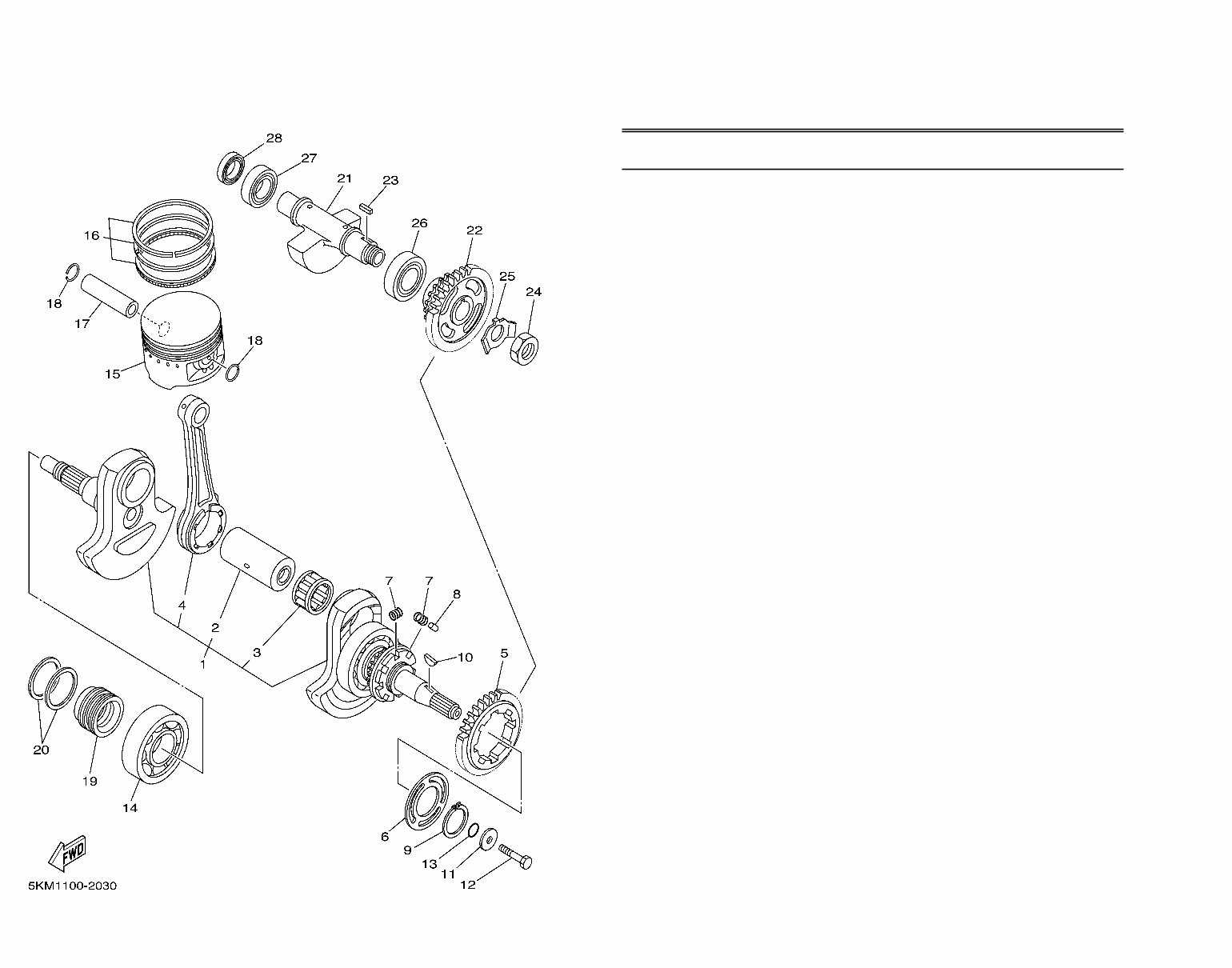
Understanding the layout of individual components is essential for maintaining a vehicle’s reliability and performance. A clear visualization of how elements are connected helps in both routine inspections and troubleshooting any unexpected issues. Whether addressing mechanical adjustments or planning future upgrades, having an overview of every element’s placement ensures efficiency.
Component Categories and Their Functions
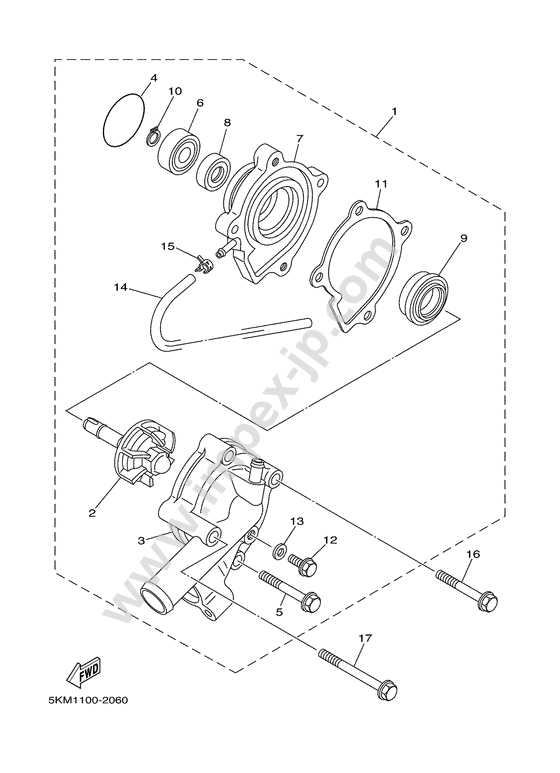
Each part within the system serves a specific role, ensuring the smooth operation of the whole. Elements such as power sources, transmission units, and control mechanisms are intricately linked. Identifying these categories simplifies the process of isolating malfunctions or enhancing performance.
Key Assemblies Overview
Main assemblies include essential areas like the drivetrain, suspension, and braking system. Familiarity with these groups allows owners to focus on the correct segment when addressing operational concerns. Additionally, understanding auxiliary systems ensures that non-critical but important features continue to function optimally.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Header | Collects exhaust gases from the engine’s cylinders and directs them to the exhaust pipe. |
| Exhaust Pipe | Channels exhaust gases away from the engine towards the rear of the vehicle. |
| Muffler | Reduces noise from exhaust gases and helps manage back pressure. |
| Catalytic Converter | Converts harmful emissions into less harmful substances before they exit the exhaust. |
| Exhaust Tip | Finishes the exhaust system, providing an aesthetic touch while directing gases away from the vehicle. |
Fuel Tank and Delivery System
The fuel reservoir and distribution mechanism play a crucial role in the operation of any vehicle. This system is designed to store and deliver fuel efficiently to the engine, ensuring optimal performance. Understanding its components and functionality is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting.
Components of the Fuel System include the tank, fuel pump, filter, and injectors. The tank serves as a storage unit, while the pump transfers fuel from the tank to the engine. A filter ensures that impurities are removed, protecting the engine from potential damage.
Fuel Delivery Process begins when the pump activates, drawing fuel from the tank. The filtered fuel then travels through lines to the injectors, where it is atomized and mixed with air for combustion. This process is vital for achieving the correct air-fuel ratio, leading to efficient engine operation.
Maintenance Considerations include regularly checking the tank for leaks, ensuring the pump operates correctly, and replacing filters as needed. Keeping the fuel system clean and functional is vital for the longevity of the engine and overall vehicle performance.
Handlebars and Control Layout
The configuration of the steering mechanism and associated controls plays a crucial role in the overall functionality and user experience of all-terrain vehicles. This section explores the arrangement of the handlebars and the essential controls that enhance rider comfort and safety.
Handlebars serve as the primary interface between the rider and the vehicle, allowing for precise maneuverability. The design typically features an ergonomic shape, providing a comfortable grip for extended rides. The width and height of the handlebars can vary, catering to different riding styles and preferences.
Control Layout includes various switches and levers strategically placed for easy access. These controls typically manage essential functions such as acceleration, braking, and lighting. An intuitive arrangement ensures that riders can operate the vehicle effectively without taking their focus off the terrain.
Overall, a well-designed handlebar and control setup significantly contribute to the performance and enjoyment of the riding experience.
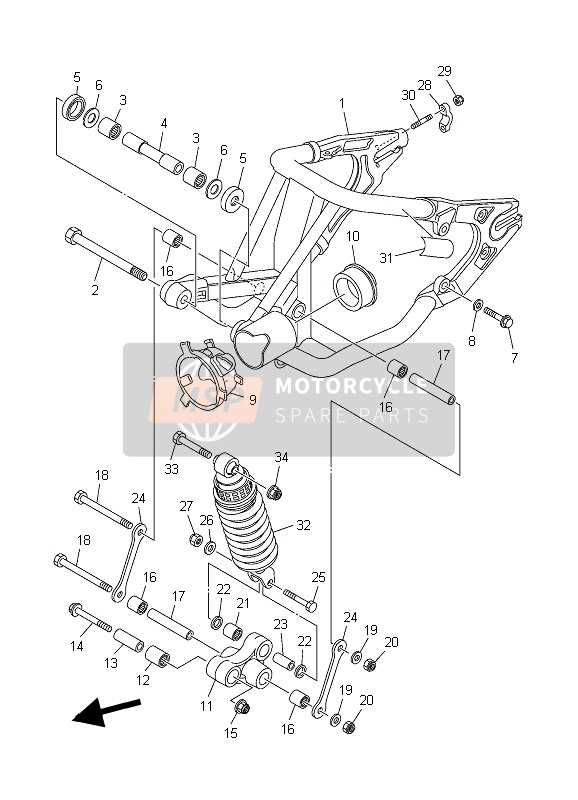
Tires, Wheels, and Axles
When it comes to enhancing the performance and handling of all-terrain vehicles, the components related to traction and stability play a crucial role. Understanding the various elements that contribute to this aspect can greatly improve overall efficiency and safety while navigating diverse terrains.
Types of Tires
Choosing the right tires is essential for optimal performance. Different types cater to specific conditions:
- All-Terrain Tires: Versatile options designed for a mix of surfaces.
- Mud Tires: Aggressive tread patterns for muddy and soft ground.
- Sand Tires: Designed for excellent flotation and traction on sandy surfaces.
Wheels and Their Importance
Wheels significantly influence the handling and aesthetics of the vehicle. Key factors include:
- Material: Aluminum and steel options offer different strengths and weights.
- Size: Larger wheels can improve ground clearance but may impact acceleration.
- Design: Aesthetic choices can reflect personal style while providing functionality.
Axles and Their Functions
Axles are vital for supporting the weight of the vehicle and facilitating movement. Important aspects to consider:
- Strength: Heavy-duty axles are necessary for rugged use and demanding conditions.
- Type: Independent and solid axles each have their advantages in terms of handling and durability.
- Maintenance: Regular checks and lubrication can prevent premature wear and ensure smooth operation.
Cooling System and Radiator Structure
The cooling system is an essential component that ensures the optimal functioning of the engine by regulating its temperature. A well-designed cooling mechanism prevents overheating, which can lead to engine damage and performance issues. The radiator plays a crucial role in this system by dissipating heat absorbed from the engine.
The structure of the cooling system typically consists of several key elements:
- Radiator: The primary component that facilitates heat exchange, allowing coolant to cool down before returning to the engine.
- Coolant: A mixture of water and antifreeze that circulates through the system, absorbing heat and transferring it away from the engine.
- Thermostat: A valve that regulates the flow of coolant based on temperature, ensuring the engine operates within a specific range.
- Water Pump: Responsible for circulating coolant throughout the system, maintaining a constant flow to prevent hot spots.
- Hoses: Flexible tubes that connect the various components of the cooling system, allowing coolant to flow freely.
Each of these components works in harmony to maintain the engine’s temperature. Regular maintenance and inspection of the cooling system are vital to ensure all parts function correctly and efficiently.