Brake Assembly Visual Reference Guide
This section provides an overview of the key components involved in the braking mechanism, offering a clear understanding of their arrangement and function. By exploring these elements, users can better comprehend how each part interacts within the system to ensure safe and effective vehicle operation.
Primary Components and Their Functions

The braking system consists of several critical elements, including calipers, rotors, brake pads, and hydraulic lines. Calipers apply pressure to the pads, pressing them against the rotors to slow or stop the wheels. The pads act as a buffer, preventing direct metal contact while absorbing the friction generated during braking. Hydraulic lines transfer the pressure from the brake pedal to the calipers, ensuring smooth and responsive operation.
Maintaining Optimal Performance

To keep the system working efficiently, regular inspections are essential. Pads should be checked for wear, as thin or damaged pads can compromise stopping power. The rotors must also be monitored for grooves or warping, which could affect braking smoothness. Additionally, hydraulic fluid levels should be maintained to prevent air from entering the lines, which could reduce braking efficiency. Proper maintenance ensures the system remains reliable, enhancing safety on the road.
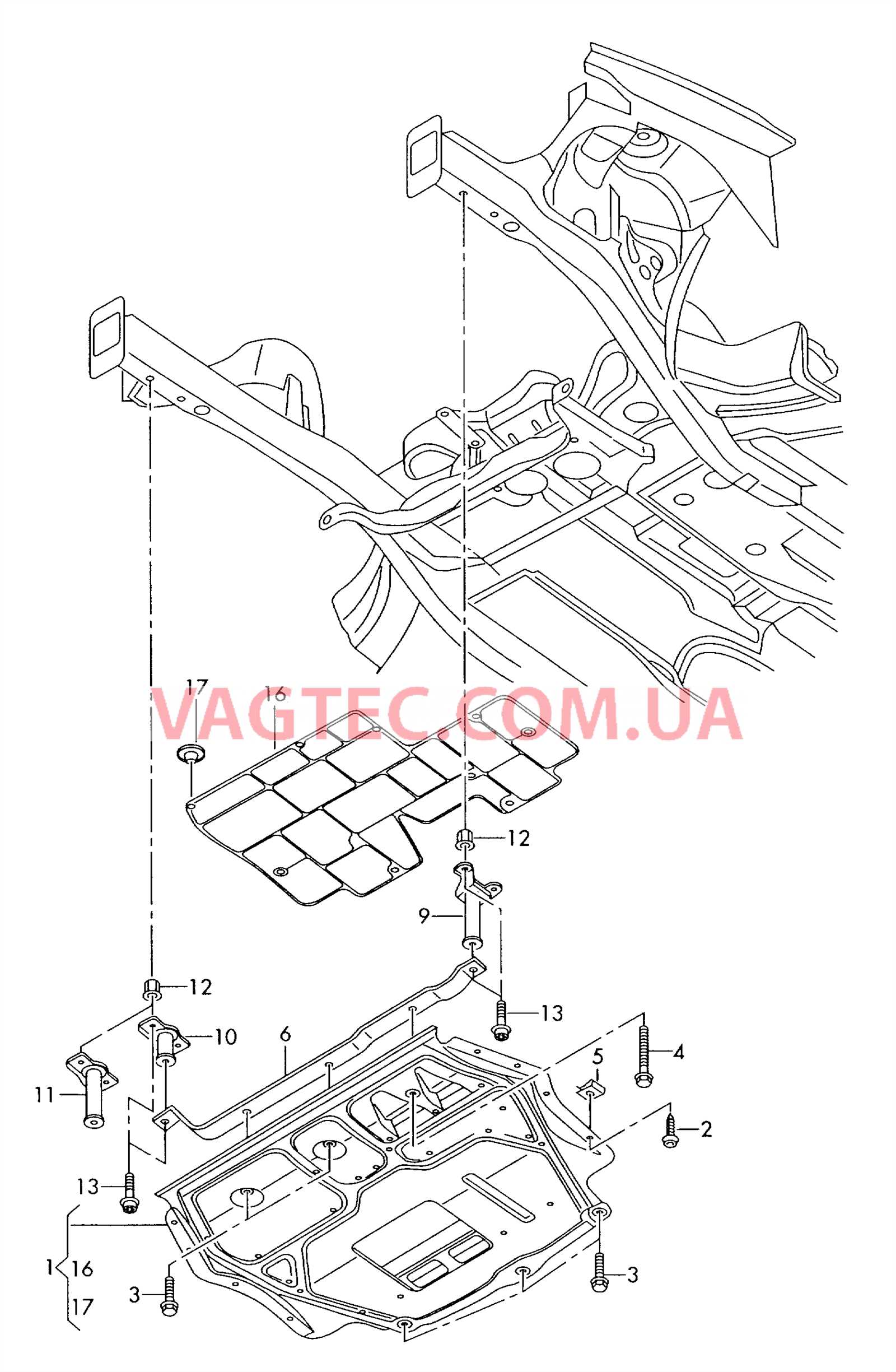
Suspension Parts Placement and Function
The arrangement of the vehicle’s suspension components plays a crucial role in ensuring stability, comfort, and precise handling. Proper alignment and coordination among these elements contribute to smooth movement across various road surfaces, absorbing shocks and maintaining tire contact with the road.
Each element within the suspension system works together to balance the forces generated during acceleration, braking, and cornering. Shock absorbers, springs, and control arms coordinate to minimize vibrations, allowing the vehicle to remain responsive and predictable under different driving conditions. The positioning of these components directly affects how well the system can adapt to changes in road conditions.
Structural elements such as bushings and linkages support flexibility while reducing noise and harshness. They help maintain alignment by compensating for minor shifts, preventing uneven tire wear and ensuring a comfortable driving experience. Understanding the function and placement of these interconnected components is essential for maintaining vehicle performance and safety over time.
Electrical System Diagram for Troubleshooting
Identifying and resolving electrical issues requires a clear understanding of how components are interconnected within the system. A detailed visual representation offers insights into connections, signal paths, and critical elements, helping technicians quickly pinpoint malfunctions and irregularities in circuits.
Key Areas of the Electrical System
The system includes essential sections such as the power distribution network, grounding points, and control modules. Each area plays a specific role in maintaining functionality and stability, ensuring seamless operation of connected devices.
Using Diagrams for Efficient Diagnostics
Analyzing wiring layouts is essential during maintenance or repairs. These diagrams help locate faults, such as short circuits, damaged fuses, or corroded terminals, guiding technicians toward the most effective solutions with minimal guesswork.
Cooling System Parts Arrangement Explained
The cooling system ensures that engine temperatures remain within optimal limits, preventing overheating during operation. This setup enables efficient heat exchange by circulating coolant through various components, helping the motor run smoothly and reliably.
Radiators are key elements that disperse heat from the coolant, maintaining a balanced engine temperature. As coolant passes through thin tubes, airflow facilitated by the fan or vehicle motion cools it down.
The thermostat plays a crucial role by regulating coolant flow. It remains closed when the engine is cold, allowing it to reach operating temperature quickly. Once warm, it opens, directing coolant towards the radiator.
To improve efficiency, water pumps ensure the fluid circulates continuously throughout the system. These pumps work in tandem with the engine, driven by a belt or chain, to maintain consistent coolant flow.
Hoses connect the radiator, engine block, and other components, ensuring coolant can
Interior Console Components and Layout
The central console plays a vital role in ensuring both convenience and functionality within the cabin. It seamlessly integrates various controls and storage spaces, enhancing the driving experience by keeping essential features easily accessible. Thoughtful placement of elements contributes to a balanced design, offering both aesthetic appeal and practical use.
Main Control Panel
This section typically houses key driving functions, including climate settings, multimedia controls, and access to essential driving modes. Designed for intuitive use, the arrangement ensures that drivers can adjust these settings without distraction, maintaining focus on the road.
Storage Compartments and Accessories
The console includes various storage solutions, such as cup holders, compartments for personal items, and charging ports. These spaces are strategically designed to offer convenient access while maintaining an uncluttered environment. Additional accessories, such as armrests, provide extra comfort during long drives.
| Component |
Description |
| Climate Control Unit |
Enables easy management of temperature and air
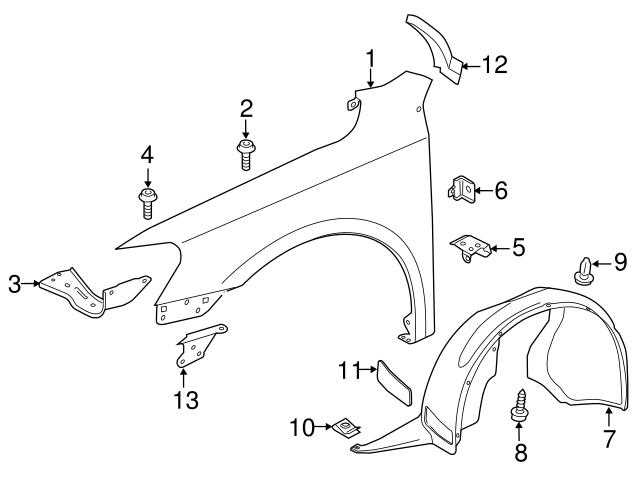
Exterior Body Parts for Easy Replacement
Maintaining the integrity of your vehicle’s exterior is essential for both aesthetic appeal and functionality. Whether due to minor accidents, wear and tear, or environmental factors, various elements of the outer shell can require attention. Understanding how to identify and replace these components can save time and money, ensuring your automobile remains in top condition.
Common Components for Replacement
Several elements comprise the outer structure of a vehicle, each serving a vital purpose. These may include bumpers, fenders, doors, and hoods. Damage to any of these areas can compromise both appearance and safety. Recognizing the signs of wear or impact is the first step toward making necessary adjustments.
Benefits of DIY Replacement

Opting for a do-it-yourself approach when replacing exterior components offers numerous advantages. It not only allows for a personalized touch but also enhances your understanding of the vehicle’s construction. Additionally, sourcing quality aftermarket or OEM alternatives can result in cost-effective solutions that maintain the vehicle’s integrity.
Exhaust System Structure and Key Elements
The exhaust system plays a crucial role in the overall performance and efficiency of a vehicle. Its primary function is to direct harmful gases away from the engine and passengers, while also minimizing noise and emissions. Understanding the composition and function of various components within this system is essential for effective maintenance and repair.
| Component |
Description |
| Exhaust Manifold |
Collects exhaust gases from the engine cylinders and channels them into the exhaust pipe. |
| Catalytic Converter |
Reduces harmful emissions by converting toxic gases into less harmful substances before they exit the system. |
| Resonator |
Enhances sound quality and can help improve engine efficiency by modifying exhaust flow. |
| Muffler |
Reduces noise produced by the exhaust gases as they exit the vehicle. |
| Exhaust Pipe |
Channels exhaust gases from the manifold through the system and out of the vehicle. |
Fuel System Diagram for Better Maintenance
A well-maintained fuel delivery mechanism is essential for the optimal performance of any vehicle. Understanding the layout and components involved in the fuel system allows for more effective upkeep and troubleshooting. This section provides an overview of the various elements that contribute to the fuel delivery process.
Key components of the fuel delivery system include:
- Fuel Tank: Stores the fuel necessary for engine operation.
- Fuel Pump: Responsible for transferring fuel from the tank to the engine.
- Fuel Filter: Removes impurities from the fuel before it reaches the engine.
- Fuel Injectors: Spray the fuel into the engine’s combustion chamber for optimal mixing with air.
- Pressure Regulator: Maintains the appropriate fuel pressure for efficient engine operation.
Regular inspection of these components can prevent costly repairs and enhance vehicle performance. For effective maintenance, consider the following practices:
- Regularly check and replace the fuel filter as needed.
- Inspect the fuel lines for any leaks or wear.
- Monitor fuel pump performance to ensure proper operation.
- Keep an eye on fuel injectors for signs of clogging or damage.
- Check fuel tank integrity to prevent contamination.
By being proactive with maintenance and understanding the essential elements of the fuel delivery system, vehicle owners can significantly improve reliability and performance.
|