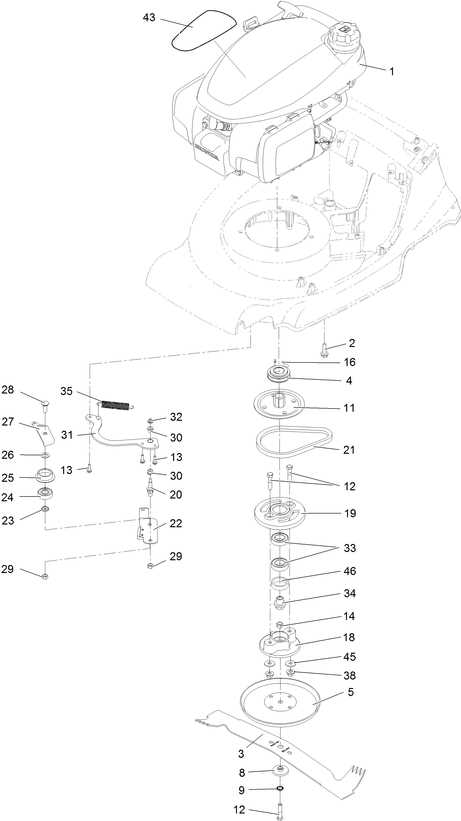
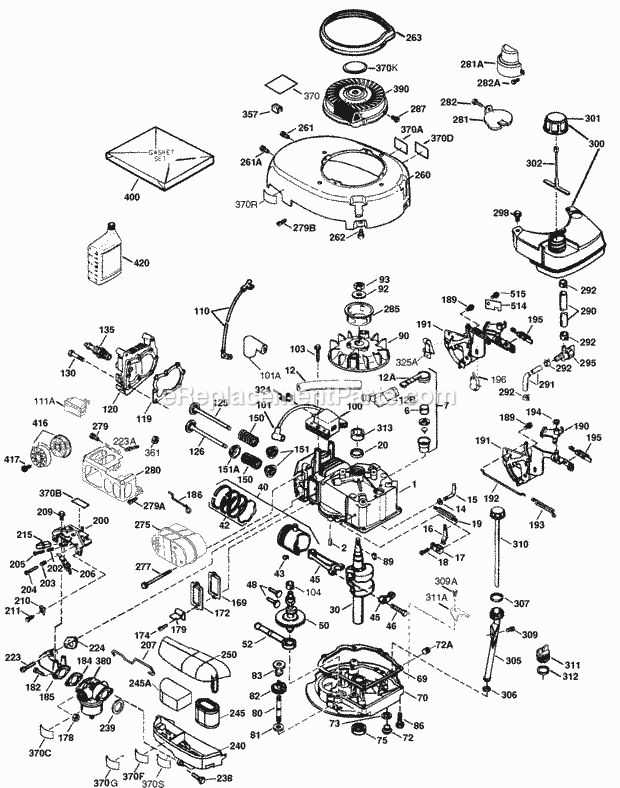
When working with outdoor equipment that involves mechanical functionality, it’s essential to grasp the inner workings and how various elements connect to ensure efficient performance. This guide aims to provide insight into the key mechanisms that drive these powerful tools, helping you maintain, troubleshoot, and optimize their operation.
Each component plays a vital role in the overall functionality, contributing to smooth operation and longevity. From the system responsible for igniting the core power source to those that ensure consistent movement, understanding these elements allows for easier maintenance and improved reliability. By familiarizing yourself with these structures, you can more effectively handle repairs and ensure peak performance of your machine.
Essential Components of a Riding Mower Engine
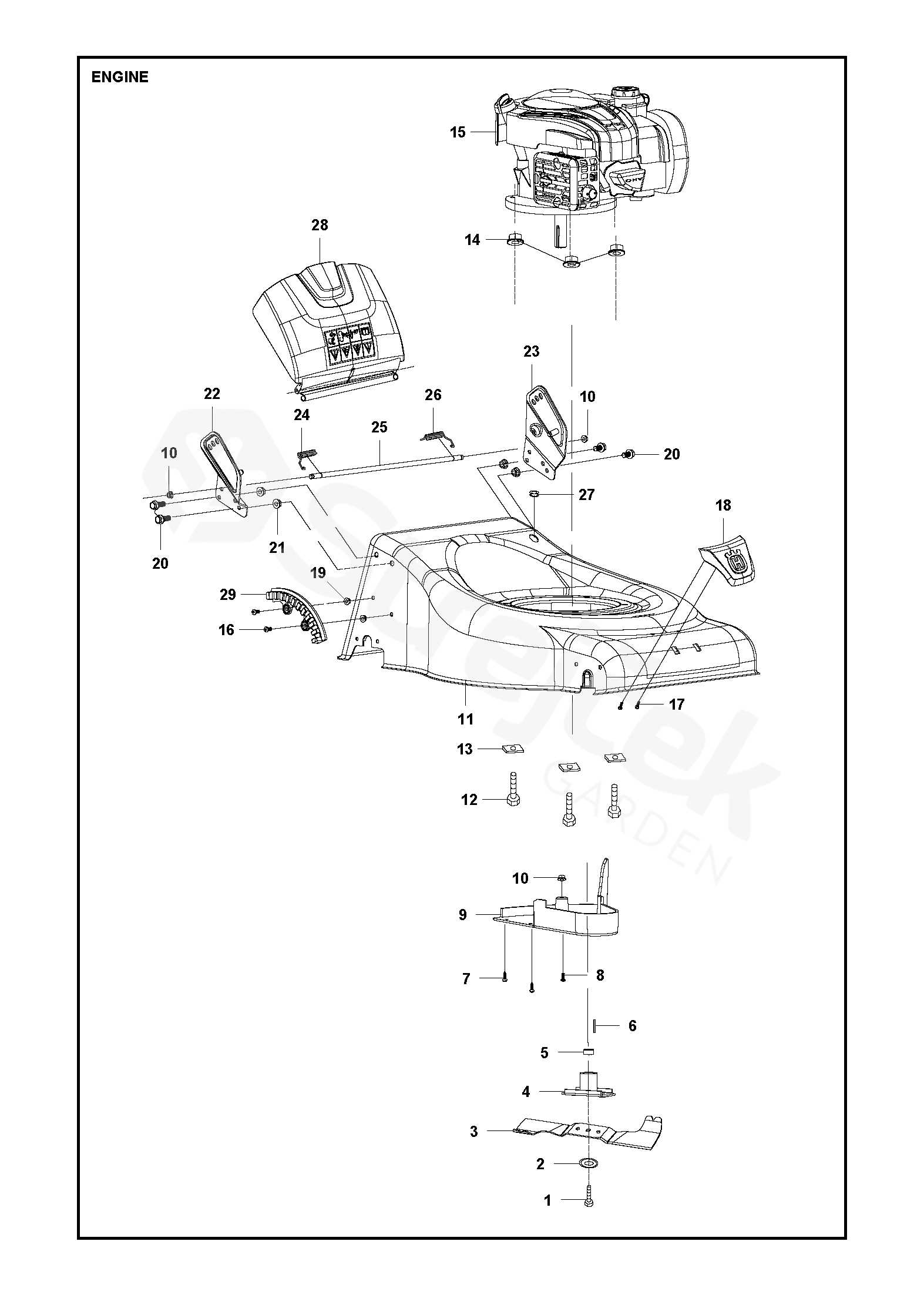
Understanding the key elements that make up a motorized cutting device helps in maintaining its efficiency and prolonging its life. Below is a breakdown of the primary mechanical parts responsible for smooth functionality, each playing a critical role in its operation.
Core Mechanical Elements
- Cylinder Block: The main structure housing vital components, ensuring the proper combustion process.
- Crankshaft: Converts linear motion from the piston into rotational force, driving the machine’s movement.
- Piston: Moves inside the cylinder, helping to compress fuel for ignition and power generation.
- Valves: Regulate the intake of fuel and expulsion of exhaust gases, ensuring smooth performance.
Fuel and Ignition System

- Carburetor: Mixes air with fuel in the correct ratio, providing the necessary blend f
Internal Mechanisms Behind Lawn Mower Power
The core systems within power equipment play a crucial role in driving its overall functionality. These mechanisms are designed to work in harmony, ensuring efficient energy conversion and smooth operation. By understanding how each component interacts, one can better grasp how mechanical force is generated and maintained throughout use.
Energy Conversion Process
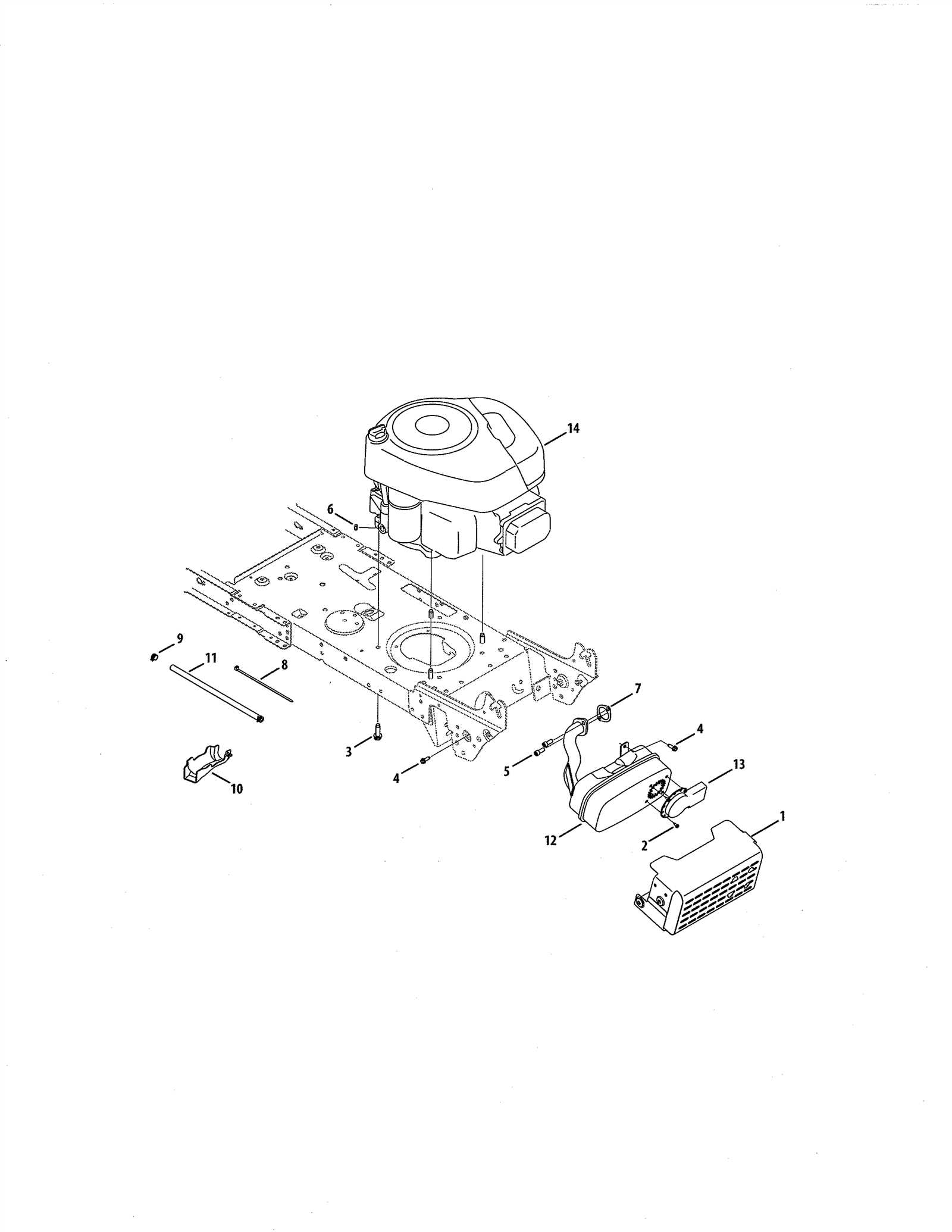
At the heart of the power system is the energy conversion process, which transforms fuel or electrical input into kinetic energy. This transformation is facilitated through a series of intricate components, each contributing to the overall movement and strength of the machinery. Elements such as combustion chambers or electrical systems initiate this process, allowing energy to flow and power the key components.
Movement Control and Efficiency
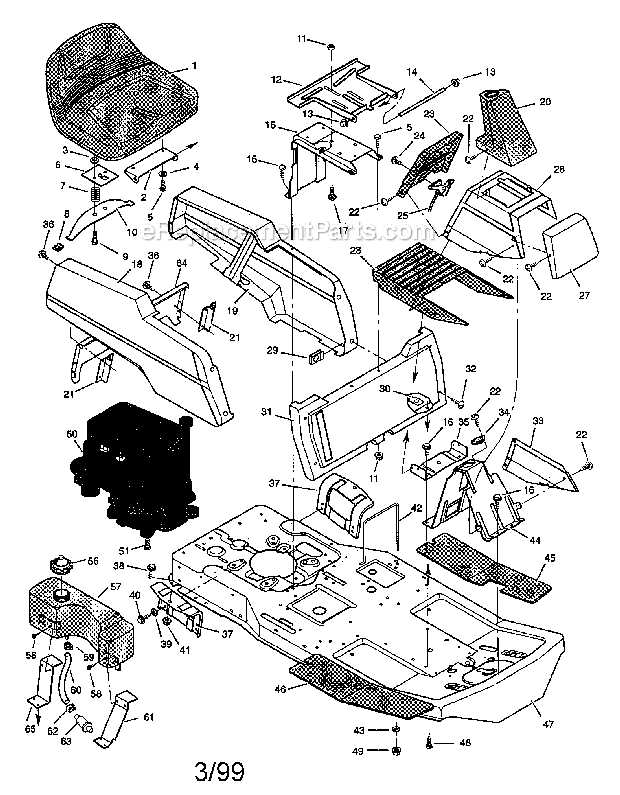
Movement control is critical for managing how efficiently energy is transferred to the machine’s active parts. Systems involving gears, pulleys, and shafts work together to regulate speed, torque, and stability. Proper coordination between these elements not only ensures smooth operation but also prolongs the lifespan of the equipment by preventing unnecessary strain on the system.
Understanding the Role of the Carburetor
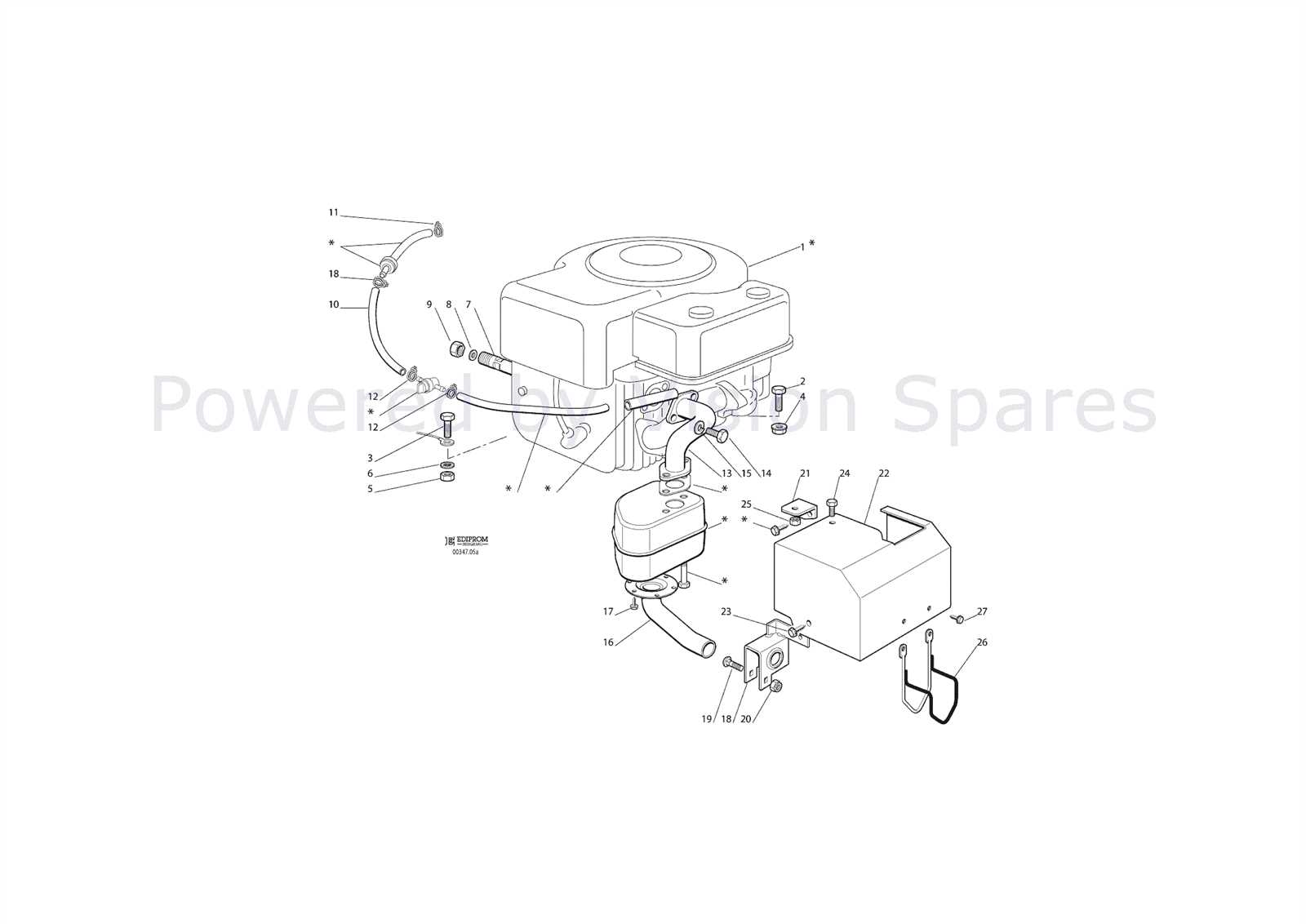
The carburetor plays a vital role in maintaining the balance of air and fuel, ensuring efficient combustion. Its primary function is to mix these elements in the correct proportions to optimize performance. Without proper regulation, an imbalance can lead to poor output or even mechanical issues. This component, though small, has a significant impact on the overall functionality of the entire system.
How the Carburetor Controls Air and Fuel Flow

At the core of the carburetor’s operation is its ability to regulate the air intake and fuel delivery. By adjusting the ratio based on demand, it ensures a smooth flow for various conditions. Whether at idle or high performance, this system automatically adjusts to meet requirements, providing the necessary mix for different settings.
Importance of Regular Maintenance

Maintaining the carburetor is essential for consistent efficiency. Over time, debris and residue can accumulate, affecting its ability to function. Regular cleaning and inspection help prevent clogging and ensure smooth operations. Proper upkeep prolongs the life of this critical component and prevents potential disruptions.
Crankshaft Function in Lawn Mower Engines

The crankshaft plays a vital role in converting the motion generated within a small motor into usable mechanical energy. It translates the linear movement created by combustion into rotational force, which powers the mechanical components. This rotation is essential for driving other elements that rely on continuous motion, ensuring smooth operation of the entire system.
How the Crankshaft Transforms Motion
The crankshaft is connected to the pistons through connecting rods. As the pistons move up and down during the combustion cycle, the crankshaft converts this vertical motion into a rotational movement. This transformation allows the energy produced to be directed toward moving mechanical parts like the transmission system and cutting mechanisms. The smoother the rotation, the more efficiently the entire process functions.
Key Components Attached to the Crankshaft
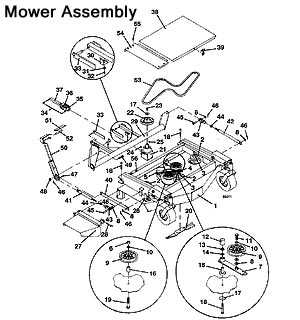
Several essential elements are directly connected to the crankshaft, influencing its performance and ensuring a balanced rotation. These include the flywheel, bearings, and the pulley system, which together provide balance, reduce vibration, and distribute the energy to the necessary components.
Component Detailed Look at Piston and Cylinder 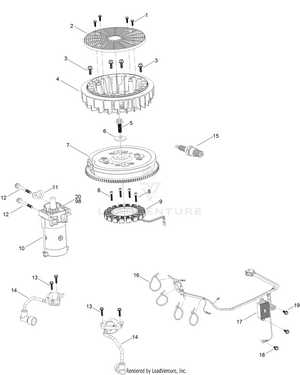
In this section, we will explore the essential relationship between the piston and the cylinder, two integral components that drive the mechanical force. These elements work together in a dynamic way, creating the necessary compression and combustion processes that generate power. Understanding their interaction is crucial to grasping how power is transmitted efficiently within the system.
The piston is designed to move up and down within the cylinder, controlled by precise timing and synchronization. As the piston moves, it alters the volume inside the cylinder, creating pressure variations. This motion is a critical part of energy conversion, transforming chemical reactions into mechanical action. The cylinder, serving as a guiding chamber, ensures that the piston follows the correct path without deviation, maintaining stability and preventing mechanical failures.
Proper lubrication and maintenance are vital for the longevity of both components. Any imbalance or wear can affect their performance, leading to inefficiencies or even breakdowns. By paying attention to the condition of the piston and cylinder, one can ensure the smooth operation of the entire system, maximizing durability and output.
The Importance of the Flywheel
The flywheel is a crucial component that plays a significant role in the overall functionality of various machines. It serves as a mechanical device designed to store rotational energy, which contributes to smoother operation and stability during performance. By maintaining momentum, it ensures that the system runs efficiently and effectively, minimizing fluctuations that could lead to operational issues.
In addition to its energy-storing capabilities, the flywheel also aids in the regulation of speed and enhances the durability of the machine. By providing a consistent rotational force, it helps to reduce vibrations and stress on other components, ultimately prolonging their lifespan. Moreover, a well-designed flywheel can improve the responsiveness of the system, allowing for quicker adjustments and enhanced performance.
Overall, the flywheel is an integral part that contributes to the seamless operation of machinery. Its ability to balance energy and provide stability makes it an essential element for anyone seeking reliability and efficiency in their equipment.
How the Ignition System Works

The ignition system plays a crucial role in initiating the combustion process within the machinery. It is responsible for creating a spark that ignites the fuel-air mixture, allowing for efficient power generation. Understanding the functionality of this system is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Components
The ignition assembly consists of several vital elements, including the spark plug, ignition coil, and distributor. Each component works in harmony to ensure that a strong spark is delivered at the right moment, promoting optimal performance.
Operational Mechanism
When the unit is activated, electrical energy flows from the battery to the ignition coil, where it is transformed into a higher voltage. This high voltage travels to the spark plug, creating a spark that ignites the fuel mixture. The timing of this process is critical, as it directly influences the efficiency and power output of the machinery.
Role of Valves in Engine Operation
The functioning of a mechanical system relies heavily on specific components that manage the flow of gases within its structure. These elements play a critical role in regulating the timing and direction of air and exhaust, which is essential for optimal performance. By understanding their significance, one can appreciate how they contribute to the overall efficiency of the machinery.
Gas Flow Regulation
Valves are vital for controlling the intake and release of gases. They open and close at precise intervals, allowing fresh air to enter while expelling exhaust fumes. This controlled movement ensures that the system operates smoothly, preventing any interruptions that could lead to reduced functionality.
Impact on Performance
The efficiency of a mechanical unit is significantly influenced by the condition and operation of these components. Well-functioning valves enhance the power output and fuel efficiency, while any malfunction can lead to decreased performance and potential damage. Therefore, regular maintenance and timely replacement of these elements are crucial for sustaining high performance levels.
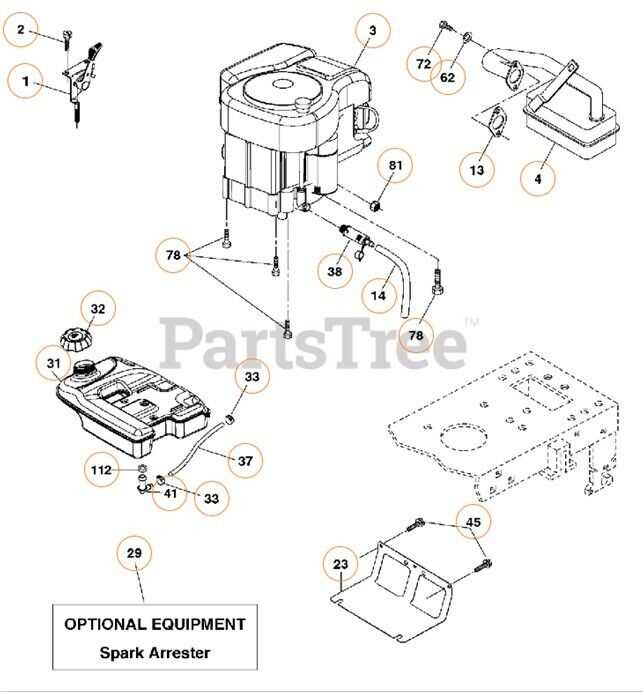
Fuel Line Connections and Their Functions
Understanding the various components involved in fuel transportation is crucial for optimal functionality. These connections play a significant role in delivering the necessary liquid to the combustion chamber, ensuring efficient operation of the machinery. Each segment of the line is designed to serve specific purposes that enhance performance and reliability.
Key Components
The primary elements involved in the transfer of fuel include hoses, fittings, and valves. Each part contributes to the overall system, enabling smooth and uninterrupted flow. Below is a summary of these components:
Component Function Fuel Hose Transfers fuel from the tank to the combustion area. Fuel Fittings Connects hoses securely to prevent leaks. Shut-off Valve Controls the flow of fuel, allowing for maintenance without draining the tank. Importance of Proper Connections
Ensuring that all connections are secure and functioning correctly is vital for preventing leaks and maintaining performance. Regular inspection of these components can help identify wear and tear, ensuring that the entire system operates efficiently.
Air Filter and Its Maintenance
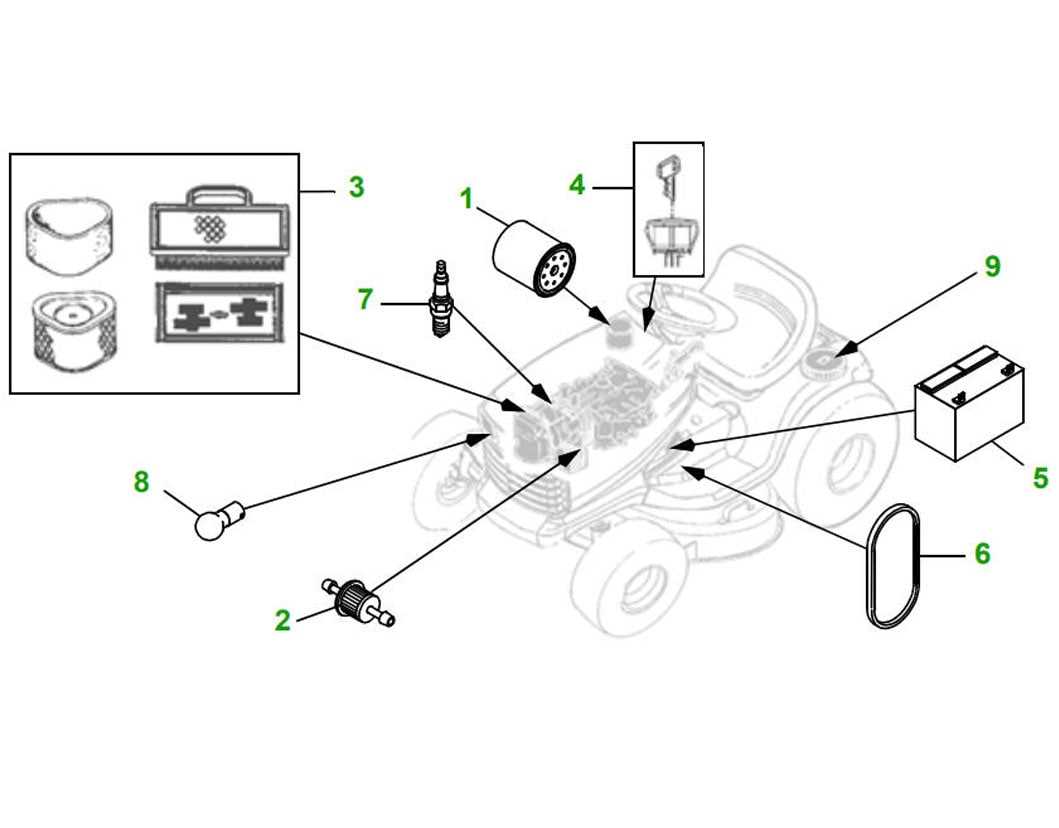
The air filtration system plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and longevity of your machinery. By preventing dirt, debris, and contaminants from entering the combustion chamber, a clean filter helps maintain efficiency and reduces wear on internal components. Regular upkeep of this element is essential for smooth operation and overall functionality.
Importance of a Clean Filter
A properly maintained air filtration system contributes to various benefits, including:
- Improved fuel efficiency
- Enhanced engine performance
- Extended lifespan of internal components
- Reduction of harmful emissions
Maintenance Guidelines

To ensure the longevity of the air filter, follow these maintenance practices:
- Check the filter regularly for dirt and debris.
- Replace the filter as recommended by the manufacturer, typically every 100 hours of operation or annually.
- Use compressed air to clean reusable filters, ensuring all particles are removed.
- Inspect the filter housing for cracks or damage, which can lead to contamination.
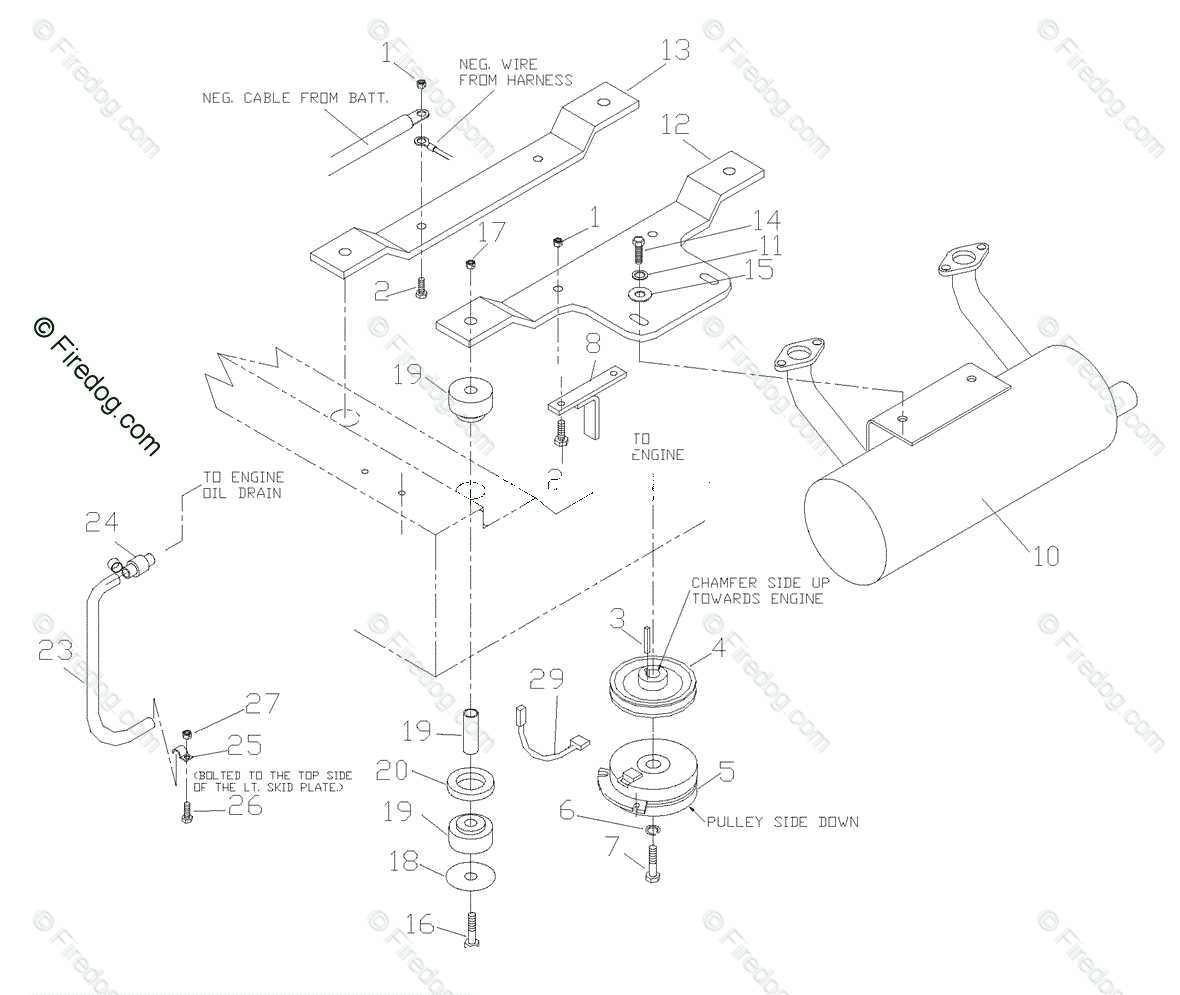
Analyzing the Exhaust System Components
The exhaust system plays a critical role in the performance and efficiency of a power-generating machine. Understanding its various elements can help in diagnosing issues and ensuring optimal operation. This section delves into the key components that make up this vital system, highlighting their functions and importance.
- Exhaust Manifold: This component collects exhaust gases from the combustion chamber and directs them to the exhaust pipe. It is essential for maintaining proper engine pressure.
- Exhaust Pipe: The pipe channels exhaust gases away from the machine. Its design impacts flow efficiency and can influence engine performance.
- Silencer: Also known as a muffler, this part reduces noise generated by the escaping gases. It helps in maintaining a quieter operational environment.
- Exhaust Gasket: This seal prevents leaks between the manifold and the cylinder head. Proper sealing is crucial for maintaining performance and efficiency.
- Heat Shield: This protective cover guards surrounding components from excessive heat produced by the exhaust. It enhances safety and prevents damage.
Regular inspection and maintenance of these components are vital for ensuring smooth operation. Addressing any wear or damage promptly can lead to improved efficiency and longevity of the entire system.
Engine Cooling System and Efficiency
The thermal management of a power unit is crucial for optimal operation and longevity. Effective cooling mechanisms ensure that the internal components remain within their ideal temperature range, preventing overheating and maintaining performance. This section explores the significance of these systems and their influence on the overall functionality of the unit.
Cooling Mechanisms play a vital role in dissipating excess heat generated during operation. Common methods include air and liquid cooling, each with its own advantages. Air cooling utilizes the flow of air to regulate temperature, while liquid cooling involves circulating a coolant to absorb and carry heat away from the core components. Both approaches aim to enhance the efficiency of the system by maintaining consistent operating temperatures.
Moreover, efficiency in thermal management directly impacts fuel consumption and power output. When a unit runs within its optimal temperature range, it operates more effectively, leading to reduced energy waste and enhanced performance. Conversely, inadequate cooling can result in power loss and increased wear on components, ultimately affecting the lifespan of the machinery.
In conclusion, the design and functionality of cooling systems are integral to maintaining the efficiency and reliability of any mechanical unit. By understanding and optimizing these systems, users can ensure better performance and prolong the service life of their equipment.