| Firing Pin |
Initiates the release when triggered, playing a key role in the action process. |
Maintaining the Recoil System for Longevity
Proper upkeep of the recoil mechanism is essential for ensuring the reliability and performance of your firearm. A well-maintained system not only enhances functionality but also extends the lifespan of various components. Regular attention to this critical area can prevent potential issues and ensure smooth operation during use.
Routine Inspections: Conducting frequent checks of the recoil assembly helps identify wear and tear early. Look for signs of rust, cracks, or any abnormal movements. Addressing minor issues promptly can prevent more significant problems from developing.
Lubrication: Applying appropriate lubricant to moving parts minimizes friction and wear. Use a high-quality oil or grease designed for firearms, ensuring that all parts of the recoil mechanism are adequately coated. Regular lubrication promotes smooth operation and reduces the risk of jamming.
Cleaning: Regular cleaning of the recoil system is vital to prevent dirt and debris buildup. Utilize a soft brush and cleaning solvent to remove residues, ensuring that all components are free from contaminants. A clean system operates more efficiently and is less prone to malfunctions.
Replacement of Worn Components: Over time, certain elements of the recoil system may wear out and require replacement. Identify any parts that show significant wear and replace them with quality components to maintain optimal performance. Regular updates of worn-out elements will contribute to the overall reliability of the firearm.
By incorporating these maintenance practices into your routine, you can significantly enhance the functionality and longevity of the recoil system, ensuring consistent performance during every use.
Inspection of Barrel and Receiver Integration
Ensuring the proper alignment and fit between the barrel and receiver is crucial for the overall functionality and safety of a firearm. This section delves into the essential aspects of examining the interaction between these components, highlighting the importance of precision and attention to detail during the inspection process.
Key Aspects to Evaluate
- Alignment: Check the alignment of the barrel within the receiver to prevent misfires and ensure accurate shooting.
- Fit: Inspect the tightness of the connection between the two parts, as a loose fit can lead to operational failures.
- Wear and Tear: Look for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage on both the barrel and receiver surfaces, which may affect performance.
- Locking Mechanism: Ensure that the locking mechanisms are functioning properly to maintain the integrity of the assembly.
Inspection Procedure
- Begin with a thorough visual examination of both components.
- Use appropriate measuring tools to check for proper alignment and fit.
- Test the locking mechanism to confirm it engages smoothly and securely.
- Document any discrepancies or areas of concern for further evaluation or repair.
Following these guidelines will help maintain the reliability and safety of the firearm by ensuring that the barrel and receiver are correctly integrated.
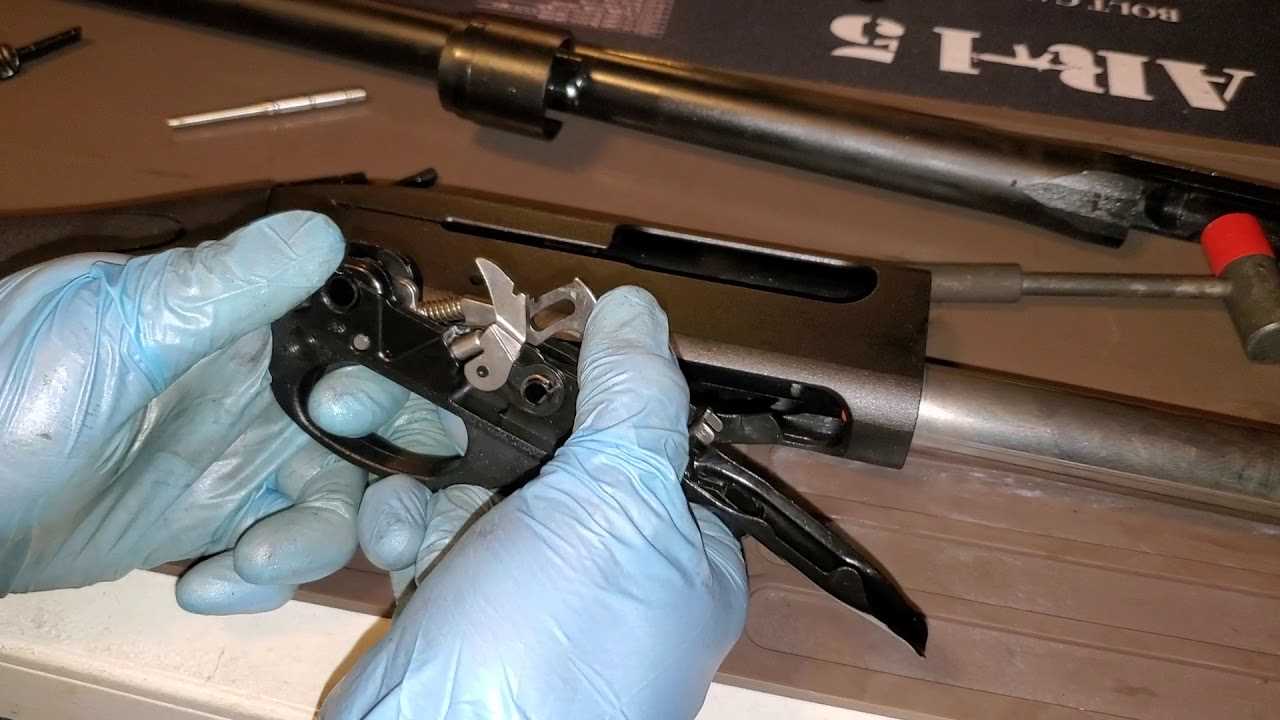
Functionality of Trigger Group Components
The trigger group is a crucial assembly that significantly influences the overall performance and safety of a firearm. Understanding the roles of its individual elements is essential for proper maintenance and effective operation. Each component within this assembly plays a specific part, ensuring smooth and reliable functionality.
Key Components and Their Roles
- Trigger: This part initiates the firing sequence when pulled, providing the shooter with control over the shot.
- Sear: The sear holds the hammer or striker in place until the trigger is activated, playing a vital role in safety mechanisms.
- Hammer: Once released by the sear, the hammer strikes the firing pin, igniting the cartridge and facilitating the discharge of the projectile.
- Disconnector: This component prevents the firearm from firing multiple rounds with a single trigger pull, enhancing safety and control.
Interaction and Coordination
The interplay between these elements is fundamental for achieving reliable operation. When the trigger is engaged, it activates the sear, which in turn releases the hammer. The disconnector ensures that only one round is fired per trigger pull, maintaining proper function during use.
Regular inspection and maintenance of these components are essential to ensure their proper functioning. Any wear or damage can lead to malfunctions, which may compromise the effectiveness and safety of the firearm.
Gas System Parts and Their Role

The gas system is a vital component that ensures efficient operation and performance. Understanding its various elements and their functions is essential for optimal maintenance and troubleshooting. Each component plays a unique role in facilitating the safe and effective operation of the overall system.
- Gas Valve: This device regulates the flow of gas, controlling the delivery to the combustion chamber. It ensures that the correct amount of fuel is available for combustion, contributing to the efficiency of the system.
- Gas Cylinder: Serving as the storage unit, it holds the gas under pressure, ready for use. The design and material of the cylinder are crucial for safety and durability.
- Regulator: This component is responsible for maintaining consistent pressure, ensuring that gas flows at a safe and manageable rate. It prevents fluctuations that could lead to operational issues.
- Burner: The burner is where the gas mixes with air and ignites, producing the flame needed for various applications. Its design affects combustion efficiency and heat output.
- Ignition System: This system initiates the combustion process. It can be electronic or manual, depending on the setup, and is essential for starting and maintaining the flame.
Understanding these components and their interactions is crucial for anyone involved in maintenance or operation. Proper knowledge allows for informed decisions regarding repairs and replacements, ultimately ensuring reliable and efficient performance.
Stock and Forend Assembly Details
The assembly of the stock and forend is crucial for maintaining the overall functionality and aesthetics of the firearm. This section delves into the components involved in this assembly, highlighting their roles and how they contribute to the operation and handling of the weapon. Understanding these elements is essential for effective maintenance and customization.
Components Overview
The key components that make up the stock and forend assembly include various structural and functional elements. Each component has a specific purpose, ensuring the weapon’s stability and comfort during use. Below is a detailed table outlining these components, their descriptions, and their significance in the overall assembly.
| Component |
Description |
Function |
| Stock |
The rear part of the firearm that provides support against the shoulder. |
Stabilizes the weapon and absorbs recoil. |
| Forend |
The front portion that is held during firing. |
Allows for a secure grip and aids in aiming. |
| Recoil Pad |
A cushioned piece attached to the stock. |
Increases comfort by reducing recoil impact. |
| Mounting Screws |
Fasteners used to secure the stock and forend. |
Ensures stability and proper alignment of components. |
Assembly Process
Correctly assembling the stock and forend requires attention to detail and an understanding of the interrelationships among components. Begin by aligning the forend with the receiver, ensuring proper fit. Secure it using mounting screws, followed by the attachment of the stock. Verify that all parts are tightly fastened to prevent movement during operation. This careful assembly ensures optimal performance and reliability of the firearm.
Exploring the Magazine Tube Components
The magazine tube serves as a crucial element in various firearm designs, playing a significant role in ammunition storage and feeding. Understanding its various components is essential for maintenance, repairs, and overall functionality. This section delves into the key elements that comprise the magazine tube system, highlighting their functions and importance.
Key Components of the Magazine Tube
- Magazine Tube: This cylindrical part houses the cartridges, ensuring they are aligned and ready for feeding into the chamber.
- Follower: Positioned at the top of the cartridges, the follower pushes rounds upward as they are fed into the action. It ensures smooth and reliable operation.
- Spring: The spring provides the necessary force to push the follower and cartridges into the chamber. Its tension is critical for reliable feeding.
- End Cap: This component secures the spring and follower within the magazine tube, preventing them from dislodging during operation.
- Barrel Connection: This part connects the magazine tube to the firearm’s action, allowing for the smooth transfer of rounds into the chamber.
Importance of Proper Maintenance
Regular inspection and maintenance of the magazine tube components are vital for ensuring optimal performance. Neglecting any of these elements can lead to malfunctions, such as failures to feed or jammed rounds. Proper cleaning, lubrication, and replacement of worn parts are essential steps to maintain reliability and safety.
Replacement Tips for Commonly Worn Parts
Over time, certain components within a mechanism may experience wear and tear, leading to decreased performance or functionality. Understanding how to effectively replace these elements can greatly enhance the longevity and efficiency of the entire system. Below are some essential guidelines to consider when addressing these common issues.
Identify Signs of Wear
Recognizing the early indicators of deterioration is crucial. Look for irregularities such as unusual noises, decreased efficiency, or visible damage. Regular inspections will help you determine which components may require immediate attention or replacement.
Choose Quality Replacements
When selecting new components, prioritize quality over cost. Opt for reputable brands known for durability and reliability. Investing in high-quality replacements can save time and resources in the long run, as they tend to have a longer lifespan compared to cheaper alternatives.
Additionally, consult manuals or guides specific to the mechanism to ensure compatibility with the new components. Following these practices will lead to a smoother replacement process and optimal functionality.
Advanced Care for Internal Systems
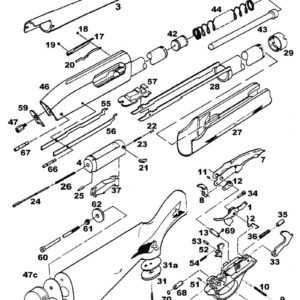
Maintaining optimal functionality of internal components is crucial for ensuring the longevity and reliability of any system. Proper attention to these elements can prevent unnecessary wear and tear, enhance performance, and minimize downtime. A comprehensive understanding of the various parts involved allows for better diagnostics and efficient troubleshooting.
Regular inspections and servicing are key to identifying potential issues before they escalate. Here are some essential practices to consider when caring for internal mechanisms:
| Practice |
Description |
| Routine Cleaning |
Remove dust and debris to prevent overheating and ensure smooth operation. |
| Lubrication |
Apply appropriate lubricants to moving parts to reduce friction and wear. |
| Periodic Testing |
Conduct performance tests to identify any anomalies in function. |
| Component Replacement |
Replace worn or damaged elements to maintain system integrity and efficiency. |
| Documentation |
Keep detailed records of maintenance activities to track performance and identify trends. |
By implementing these practices, users can ensure that their internal systems remain in peak condition, ultimately leading to improved overall performance and reliability.


