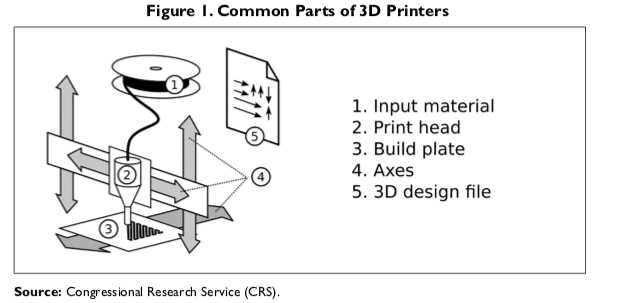
The efficient functioning of any imaging device relies on the collaboration of various elements that work together seamlessly. Each component plays a critical role in the overall process, contributing to the quality and speed of output. A comprehensive examination of these individual elements provides insight into how they interact and support the device’s operations.
By exploring the different sections of an imaging device, one can appreciate the intricate design and engineering that goes into their construction. From the mechanisms responsible for applying ink to the surfaces to the systems managing data input, every segment is essential for achieving the desired results. Understanding these elements enhances one’s ability to troubleshoot and maintain the equipment effectively.
Furthermore, gaining knowledge about the assembly can lead to better decision-making when selecting or upgrading equipment. Familiarity with the various sections empowers users to choose devices that align with their specific needs, ensuring optimal performance and satisfaction in their imaging tasks.
Exploring Ink Cartridge Functionality
The mechanism behind ink cartridges plays a crucial role in the overall performance and efficiency of a printing device. These components are responsible for delivering the required color and quality to the printed materials. Understanding their operation can enhance the user experience and maintenance of the equipment.
Ink cartridges serve as the reservoirs for the colored fluids that create images and text on various surfaces. They are designed to dispense precise amounts of ink during the printing process. This functionality relies on a combination of technology and design, ensuring that the ink is released in a controlled manner, preventing smudging and ensuring clarity.
Moreover, modern cartridges often come equipped with sensors that monitor ink levels, providing users with timely alerts when it’s time for a replacement. This feature not only aids in maintaining print quality but also helps avoid interruptions during important tasks. Understanding these functionalities can lead to more informed choices when selecting or replacing cartridges.
Ultimately, recognizing the significance of these components contributes to better upkeep and optimized usage of the entire system, leading to consistent results in all printing endeavors.
Types of Printer Connections
Understanding the various ways to link devices is essential for seamless functionality. Different methods offer unique advantages, catering to diverse user needs and technology preferences.
One popular approach involves utilizing a physical cable, ensuring a stable and reliable connection. Common interfaces include USB and parallel connections, which have been widely adopted for their straightforward setup and consistent performance.
Alternatively, wireless solutions have gained traction, enabling users to connect without the constraints of cables. Technologies like Wi-Fi and Bluetooth allow for flexible positioning and multiple device access, enhancing convenience and mobility.
Moreover, some setups utilize network connections, integrating machines into a local area network. This method supports multiple users accessing a single device, making it ideal for office environments where efficiency is paramount.
Role of the Print Head
The print head is a crucial component that significantly impacts the overall output quality. It is responsible for transferring ink onto the medium, enabling the creation of detailed images and text. The efficiency and precision of this element directly influence the clarity and vibrancy of the final result.
Functionality and Mechanism
This component operates by releasing small droplets of ink onto the surface. Utilizing advanced technology, it can produce various dot sizes, allowing for a range of tonal gradations and intricate designs. The precise control over ink placement is essential for achieving sharp lines and smooth gradients.
Importance in Quality Production
Without a well-functioning unit, the quality of the output can be compromised. Issues such as streaking or blurriness often arise from malfunctions within this essential part. Regular maintenance and timely replacement are vital to ensure that it performs optimally, thereby preserving the integrity of the printed material.
Paper Feed Mechanism Explained
The process of transporting sheets from a supply source to the printing area is a fundamental aspect of any device that produces hard copies. Understanding how this operation functions is essential for both troubleshooting and enhancing overall performance.
This mechanism typically involves various components working in unison to ensure that the media is correctly aligned and fed into the production zone. The following table outlines key elements and their respective roles in this crucial operation.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Feed Rollers | These rotate to grip and propel sheets forward into the working area. |
| Separation Pads | These prevent multiple sheets from being fed simultaneously, ensuring one sheet at a time. |
| Guide Rails | These help maintain proper alignment of the media as it moves towards the printing mechanism. |
| Media Tray | This holds the sheets securely before they are fed into the device. |
| Drive Motors | These provide the necessary power to move the rollers and other components. |
Importance of the Control Panel
The control panel serves as a critical interface, facilitating user interaction and management of device functions. It enables seamless communication between the user and the equipment, making it essential for efficient operation and troubleshooting.
Key Functions of the Control Interface
- Operational Management: Users can initiate, pause, or cancel tasks, ensuring optimal workflow.
- Settings Adjustment: Access to configuration options allows customization according to specific needs.
- Status Monitoring: Displays essential information such as error messages, ink levels, and connectivity status.
Enhancing User Experience
A well-designed control interface significantly improves user satisfaction by:
- Intuitive Navigation: Simplifying access to functions through clear layout and labeling.
- Real-Time Feedback: Providing immediate updates on operations, helping users make informed decisions.
- Error Resolution: Guiding users through troubleshooting steps to quickly resolve issues.
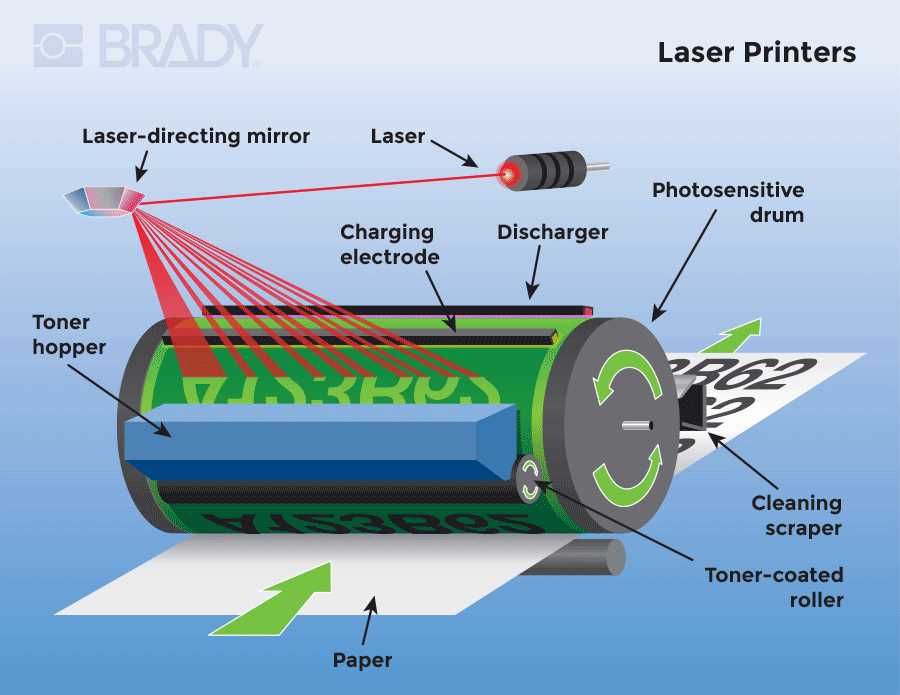
How the Power Supply Works
The power supply unit is a crucial component that converts electrical energy from a source into the appropriate voltage and current required for operation. Its primary function is to ensure that the entire system receives stable and reliable power, facilitating optimal performance.
Conversion Process
Initially, alternating current (AC) from the main supply is transformed into direct current (DC) through a series of components. This conversion process involves several stages, including rectification, filtering, and regulation, to provide the necessary power levels for various functions.
Key Components
Essential elements within the power supply unit include transformers, diodes, capacitors, and voltage regulators. Each component plays a specific role in ensuring efficient energy management and stability.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Transformer | Adjusts voltage levels |
| Diode | Rectifies AC to DC |
| Capacitor | Filters and stabilizes voltage |
| Voltage Regulator | Maintains constant voltage output |
Inside the Printer’s Housing
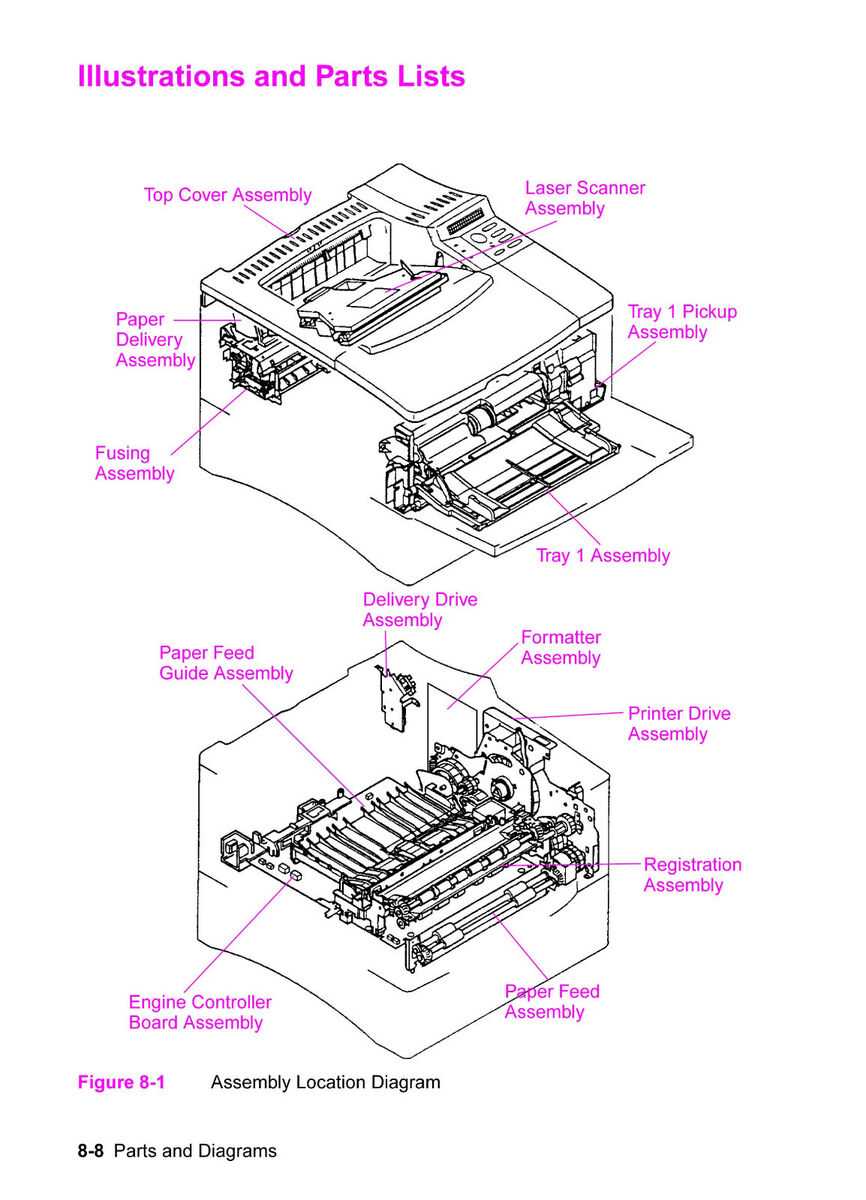
The internal structure of a printing device plays a crucial role in its functionality and performance. This complex assembly houses various elements that work in harmony to produce high-quality outputs. Understanding this framework helps users appreciate the engineering behind these machines.
At the core, one can find essential components that facilitate the movement and processing of media. The mechanical system is responsible for transporting sheets and ensuring precise alignment during operation. Meanwhile, the electronic circuitry manages data flow and communicates with external devices, enhancing overall efficiency.
Another critical aspect involves the ink delivery system, which meticulously dispenses the necessary fluids to create vivid images and text. This assembly must be well-maintained to avoid clogs and ensure consistent output quality. Overall, a deeper look into the inner workings reveals the intricate design and engineering that make these devices essential in both personal and professional settings.
Connectivity Options Overview
In today’s digital landscape, the ability to establish connections is paramount for effective functionality. Various methods enable devices to communicate with one another, enhancing overall usability and performance. Understanding these options is essential for optimizing interactions and ensuring seamless integration within a network.
This section will explore different methods available for establishing connections, focusing on their characteristics and applications. By evaluating these choices, users can make informed decisions based on their specific needs and environments.
| Connection Type | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| USB | A standard interface for direct connection between devices. | High-speed data transfer and easy plug-and-play setup. |
| Wi-Fi | Wireless technology allowing devices to connect through a network. | Convenience of wireless access and flexibility in placement. |
| Bluetooth | A short-range wireless technology for connecting nearby devices. | Energy-efficient and simple pairing process. |
| Ethernet | A wired network connection using cables for data transmission. | Stable and reliable connection with minimal interference. |
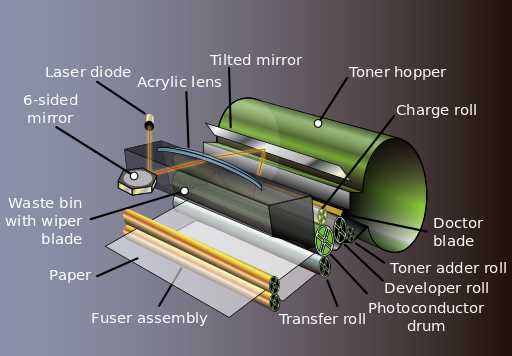
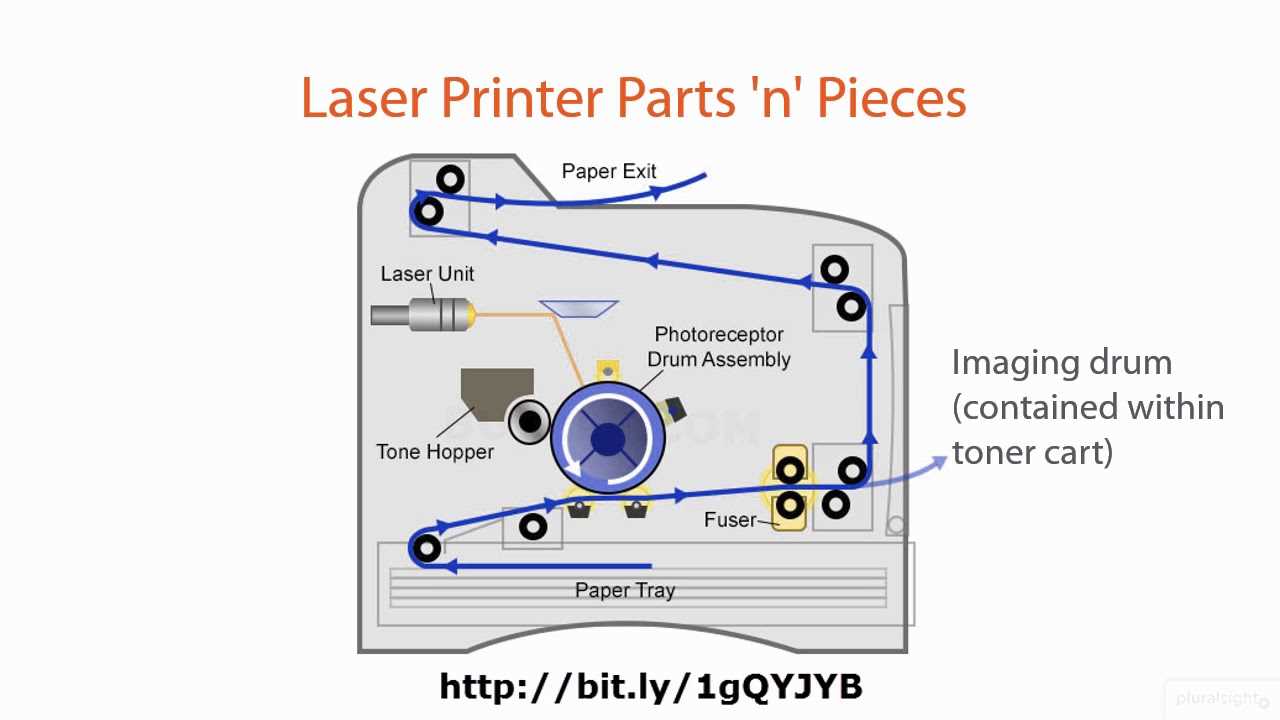
Analyzing the Print Engine
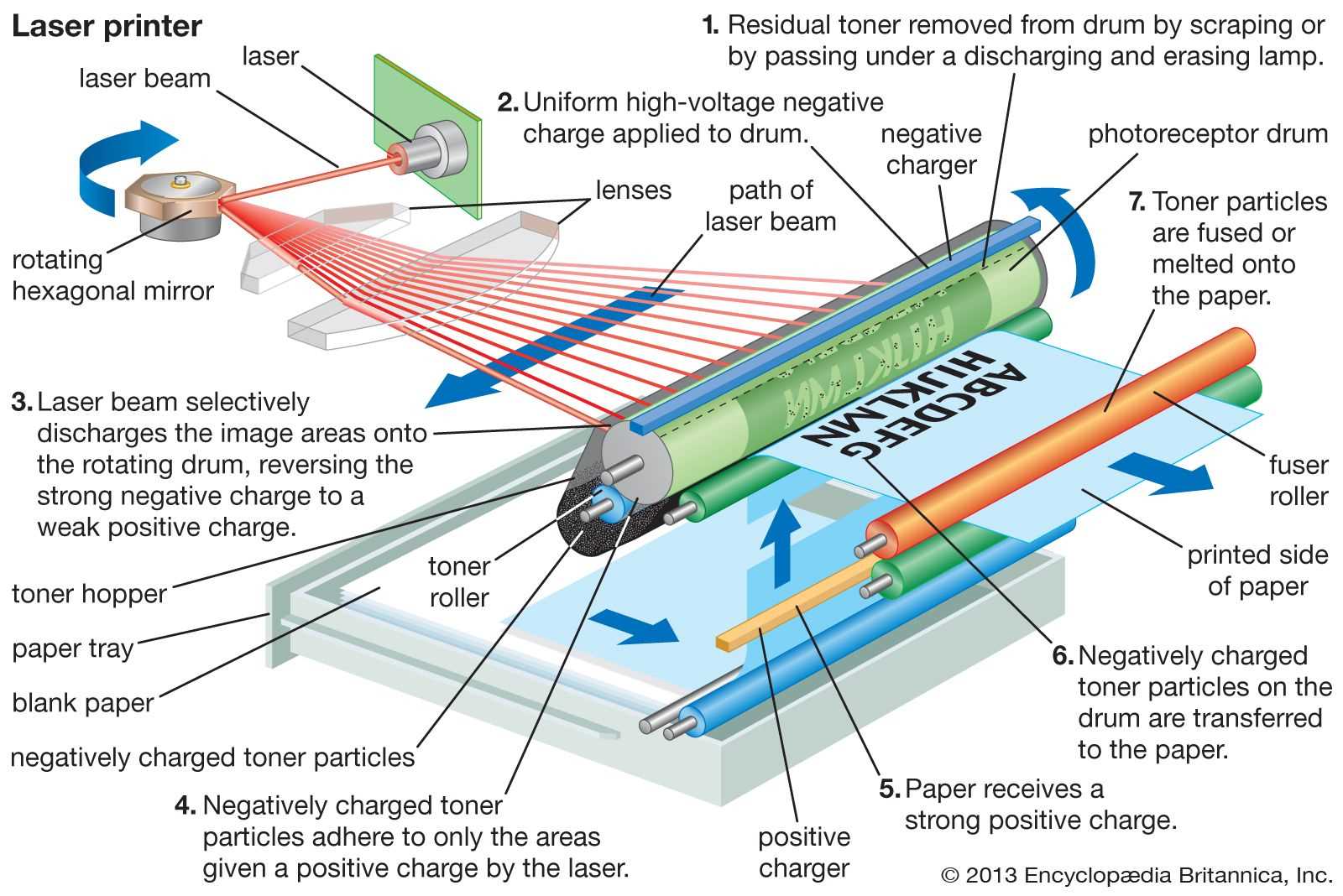
Understanding the core functionality of the printing mechanism is essential for evaluating overall performance and efficiency. This section delves into the intricate components and processes that contribute to the production of high-quality output.
The primary function of this assembly is to facilitate the transfer of ink onto the medium. Each element within the system plays a pivotal role in ensuring precision and consistency. Key components, such as the imaging unit and transfer belts, work in harmony to achieve optimal results.
Imaging Technology: The technology employed in the imaging unit significantly influences the quality of the printed material. Techniques like laser and inkjet each offer unique advantages, affecting resolution and speed.
Transfer Mechanisms: Efficient transfer systems are crucial for aligning ink with the intended surface. Understanding how these mechanisms operate can provide insights into potential enhancements in output quality.
Conclusion: Analyzing the functionality of the core mechanism reveals opportunities for innovation and improvement. A thorough comprehension of these processes is vital for anyone looking to optimize performance and enhance print quality.