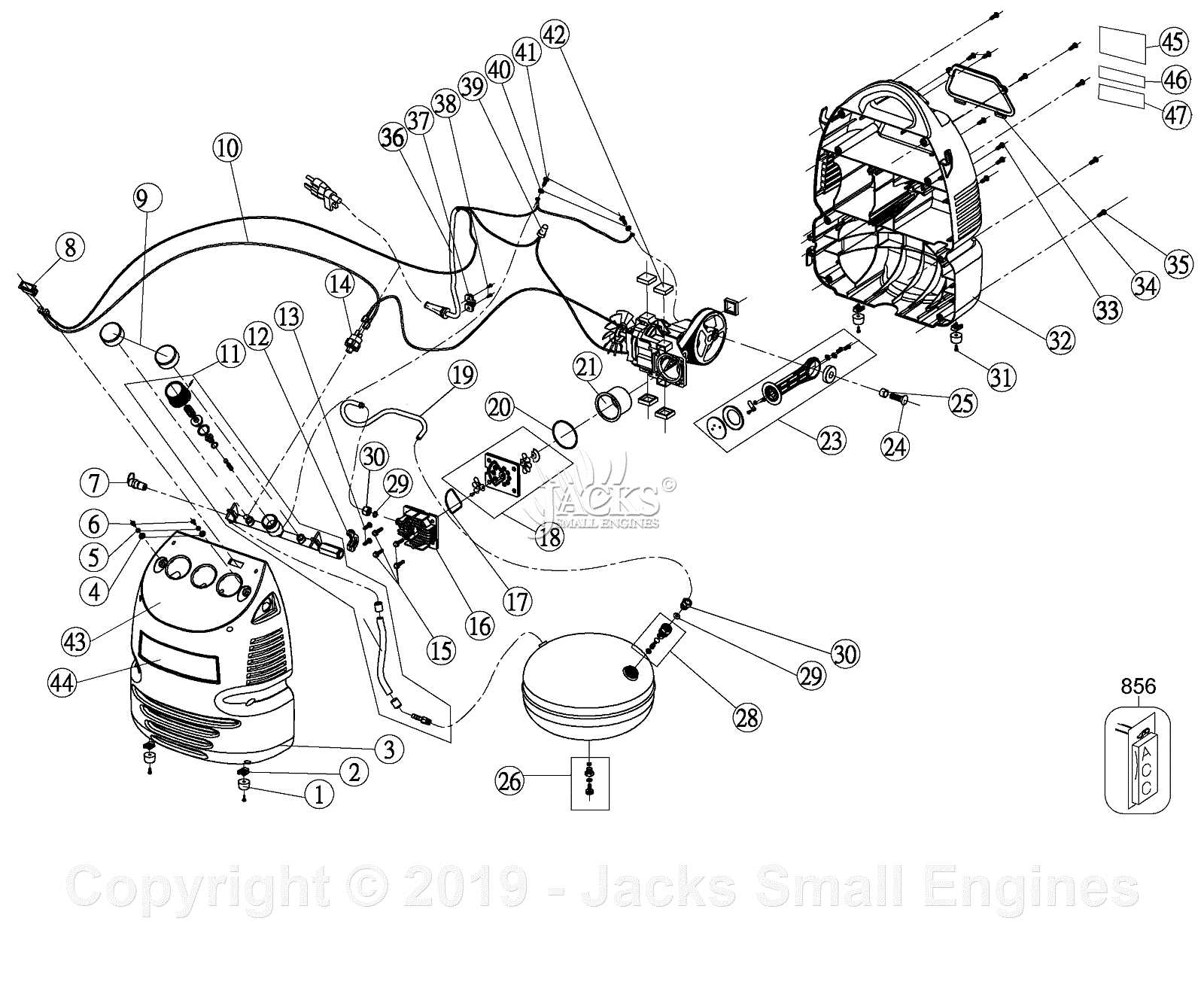
When dealing with complex mechanical devices, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of how each element works together. Whether you’re maintaining a machine for personal or professional use, recognizing the key elements that contribute to its functionality is crucial for ensuring its longevity and efficiency. This guide provides insight into the internal mechanisms and how they support overall operation.
By breaking down the various elements involved, we aim to help you gain a comprehensive understanding of their roles and how they interact. Each section is dedicated to exploring the function of different parts, highlighting their importance in maintaining optimal performance. With a clear grasp of these details, troubleshooting and repair become significantly more manageable.
Delving into the structure and connections, this guide will also provide visual references, aiding in identifying and understanding each component. This information will empower users to perform basic maintenance, improving both safety and operational efficiency.
Understanding the Key Components of the Compressor
In any air-powered system, there are several essential elements that work together to ensure efficient operation. These components serve different roles, from controlling pressure levels to ensuring proper air flow. A solid grasp of how these elements interact can help you maintain and troubleshoot your equipment effectively.
Motor is the driving force behind the device, converting electrical energy into mechanical power. It is critical for generating the necessary motion that powers the entire system.
The tank serves as a storage unit, holding the pressurized air. This chamber ensures that air is available when needed, maintaining the pressure levels required for various tasks.
Pressure switches monitor and regulate the internal air levels, automatically turning the motor on or off to maintain consistent pressure. Without these, the system would either lose efficiency or risk damage from over-pressurization.
Another key part is the
How the Air Tank Functions
The air tank plays a crucial role in maintaining and distributing compressed air for various applications. It stores the pressurized air, ensuring that there is a steady supply available for tools or systems when needed. The tank also helps regulate pressure levels, preventing sudden drops or spikes that could affect performance. By keeping a reserve of air at a set pressure, the system can operate more efficiently and consistently.
Inside the tank, compressed air is stored until it is required. As the air is compressed, it is forced into the tank, where it is held under pressure. The tank’s design allows it to handle high pressure levels safely, with built-in mechanisms that prevent over-pressurization. These features ensure that the air stored is always at optimal levels for efficient use.
Release mechanisms are also in place to ensure controlled flow from the tank to the system. Valves and regulators control the release
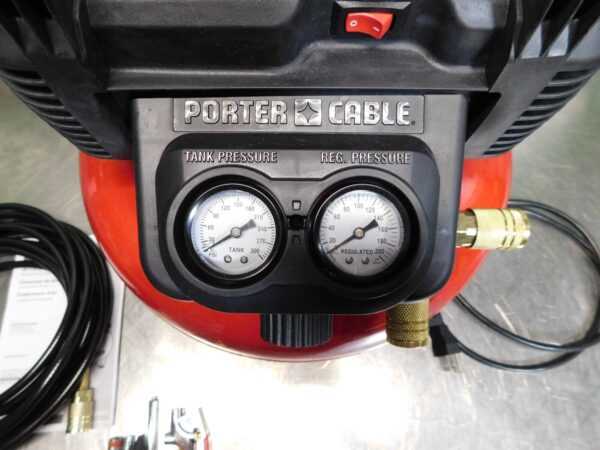
The Role of the Pressure Switch
The pressure switch plays a crucial role in regulating the overall functionality of air delivery systems. It is responsible for monitoring internal pressure levels, ensuring that they remain within a safe and efficient range. When pressure exceeds or drops below the desired thresholds, the switch automatically engages or disengages the system to maintain balance.
The proper functioning of this component is vital for optimal performance and safety. Below are some of the key functions and mechanisms by which the switch operates:
- Monitoring Pressure Levels: Continuously senses the pressure inside the tank and reacts to changes.
- Automatic Shutoff: Stops the system when the pressure reaches a predefined upper limit to prevent overloading.
- System Activation: Triggers the system to restart when the pressure drops below the minimum required level.
- Prevents Damage: Protects
Importance of the Regulator in Airflow Control

Maintaining consistent air pressure is essential for optimal performance in pneumatic systems. One critical component that ensures proper adjustment of the output pressure is the regulator. By precisely modulating the flow of air, the regulator plays a vital role in ensuring that tools and equipment receive the correct amount of pressure for efficient and safe operation.
Precision in Air Distribution
When working with air-powered tools, precise pressure control is crucial. The regulator allows for adjustments to be made according to the specific needs of each task. This control helps prevent over-pressurization, which can damage tools or reduce their lifespan. Proper regulation also avoids under-pressurization, which can lead to inefficient operation and inconsistent results.
Protecting Equipment and Enhancing Safety

A well-maintained regulator not only optimizes performance but also protects the overall system. By ensuring that air pressure stays within the desired range, it prevents sudden pressure spikes, reducing the risk of equipment failure. Additionally, a correctly set regulator enhances safety, minimizing potential hazards that can arise from unstable air pressure levels.
Purpose of the Safety Valve
The safety valve plays a crucial role in preventing potential damage by releasing excess pressure from the system. This component is designed to maintain safe operation by ensuring that pressure levels do not exceed the designated limits, thereby protecting both the equipment and the user from potential hazards. It acts as a fail-safe mechanism that automatically activates when internal pressure becomes too high.
How the Safety Mechanism Works
The valve is set to open at a pre-determined threshold, allowing the controlled release of air when pressure reaches unsafe levels. Once the internal pressure drops to a safe range, the valve closes, ensuring continued functionality of the system. This process is automatic, requiring no intervention from the operator.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular inspections and maintenance of the valve are essential to ensure its proper operation. Over time, debris or corrosion can affect its sensitivity, which may lead to malfunction. Keeping the valve clean and functional helps prevent dangerous situations and ensur
Exploring the Drain Valve Operation
The drain valve is a critical component that plays a significant role in maintaining optimal performance in air handling systems. Understanding its function helps ensure longevity and efficiency. This section delves into the mechanics of this essential feature, outlining its purpose, operation, and maintenance.
At its core, the drain valve serves to expel moisture that accumulates within the system. This moisture can lead to various issues if not properly managed. Here’s a closer look at its operation:
- Moisture Accumulation: During operation, air handling systems generate humidity, which condenses and collects inside the unit.
- Function of the Valve: The drain valve allows for the release of this accumulated moisture, preventing potential damage and ensuring efficient performance.
- Manual vs. Automatic: Some systems feature manual valves that require user intervention, while others have automatic mechanisms that facilitate drainage without user input.
Proper maintenance of the drain valve is essential for uninterrupted operation. Here are key maintenance tips:
- Regularly inspect the valve for any signs of wear or damage.
- Ensure that the valve is functioning correctly by testing it periodically.
- Clear any debris or buildup that may obstruct the drainage process.
By understanding and maintaining the drain valve, users can enhance the reliability and efficiency of their air management systems, ensuring optimal functionality over time.
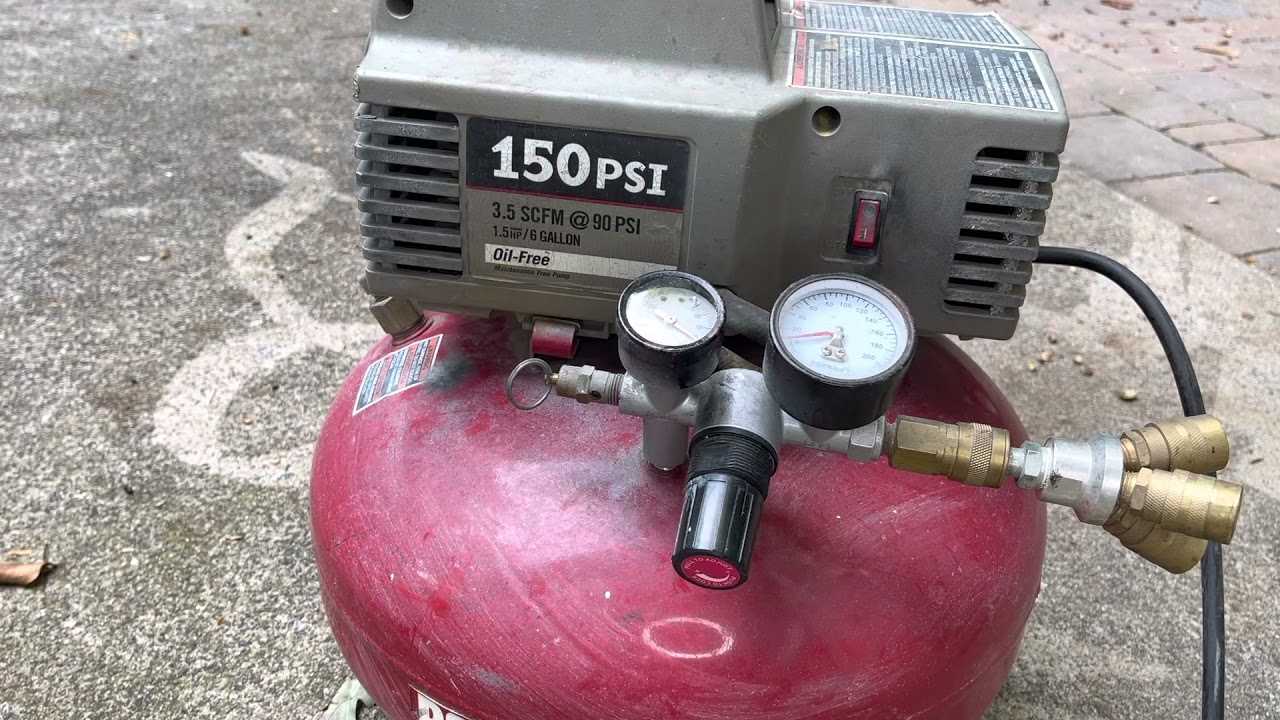
What the Gauge Tells You

The reading on a pressure indicator is crucial for understanding the performance and efficiency of your device. This instrument provides valuable insights into the operational state, allowing users to make informed decisions regarding functionality and maintenance. By interpreting the values displayed, one can ensure optimal performance and longevity of the equipment.
Understanding Pressure Readings

The pressure measurement is typically expressed in pounds per square inch (PSI). A higher PSI indicates greater pressure, which is essential for tasks that require significant power. Conversely, a low reading may suggest inadequate performance for demanding applications. Regular monitoring can help identify potential issues before they escalate, ensuring the device operates smoothly.
Maintaining Optimal Levels
Maintaining the correct pressure levels is vital for efficiency and safety. Excessive pressure can lead to equipment failure or safety hazards, while insufficient pressure may hinder performance. Regular checks of the pressure gauge can prevent these problems, allowing users to adjust settings as needed to match specific tasks and materials.
Analyzing the Motor and Pump System

The functionality of any air pressurization unit relies heavily on the interaction between its motor and pump assembly. This integral system is designed to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, facilitating the compression of air. Understanding the mechanics involved can provide insight into enhancing performance and addressing common issues.
Motor Characteristics
The motor is the powerhouse of the system, responsible for driving the pump. A key factor in its efficiency is the horsepower rating, which directly influences the speed and torque produced. When assessing this component, one should consider the design, such as whether it is a direct drive or belt-driven model. Regular maintenance is essential to prolong its lifespan, including checking for signs of wear or overheating.
Pump Functionality

The pump’s role is to compress air effectively, creating the necessary pressure for various applications. There are different types of pump designs, such as single-stage or two-stage, each suited for specific tasks. Understanding the compression ratio is crucial as it impacts the output pressure and overall efficiency. Ensuring that the intake filter remains clean and unobstructed is vital for optimal performance and longevity.
The Role of the Check Valve in Airflow
The check valve plays a crucial role in managing the flow of air within a system, ensuring that the medium moves in the desired direction while preventing backflow. This component is essential for maintaining pressure stability and optimizing the efficiency of the overall setup.
When air is pumped through a system, the check valve allows it to pass in one direction only. This function is vital for preventing any reverse flow that could disrupt pressure levels and potentially damage other components. By creating a one-way barrier, the valve contributes to a consistent and reliable airflow, which is fundamental for various applications.
Additionally, the check valve helps to minimize the risk of air leakage. When the pressure in the system decreases, the valve closes automatically, preventing any unwanted air from escaping. This action not only maintains pressure but also enhances the performance and longevity of the equipment.
In summary, the check valve is an indispensable element in airflow management, ensuring that air travels efficiently and effectively throughout the system while safeguarding against backflow and leaks.
Understanding the Function of the Power Cord
The power cord serves as a vital component in connecting an electrical device to a power source, enabling it to operate effectively. This essential element transmits electrical energy, ensuring that the machinery receives the necessary voltage to function correctly. A thorough comprehension of its role can enhance the overall performance and safety of the equipment.
Components and Structure
Typically, the power cord consists of multiple conductive wires encased in an insulating material. This design prevents electrical shorts and protects users from potential hazards. The quality of the wiring and insulation directly impacts the device’s efficiency and durability.
Importance of Proper Maintenance
Maintaining the integrity of the electrical cord is crucial for safety and functionality. Regular inspections for wear and damage can prevent malfunctions and electrical failures. Replacing a frayed or damaged cord promptly is essential to ensure safe operation. Understanding the significance of this component can lead to improved longevity and reliability of the equipment.
Impact of Filters on Compressor Performance

Filters play a crucial role in ensuring the efficient operation of air-moving devices. They serve to remove impurities and contaminants from the intake air, significantly influencing overall functionality and longevity. Understanding the importance of these components can lead to enhanced performance and reduced maintenance costs.
Key Benefits of Utilizing Filters

- Enhanced Air Quality: Clean air leads to improved output quality, minimizing the risk of defects in the final product.
- Prolonged Lifespan: By preventing dust and debris from entering the system, filters help extend the lifespan of internal mechanisms.
- Improved Efficiency: A clean intake reduces the energy consumption required for operation, translating to lower utility costs.
Types of Filters and Their Impact
- Particulate Filters: These capture larger particles, preventing them from causing wear and tear on internal components.
- Activated Carbon Filters: They effectively remove odors and volatile organic compounds, ensuring cleaner air output.
- HEPA Filters: High-efficiency particulate air filters trap even the smallest particles, making them ideal for applications requiring strict air quality standards.
Maintenance Tips for Key Parts
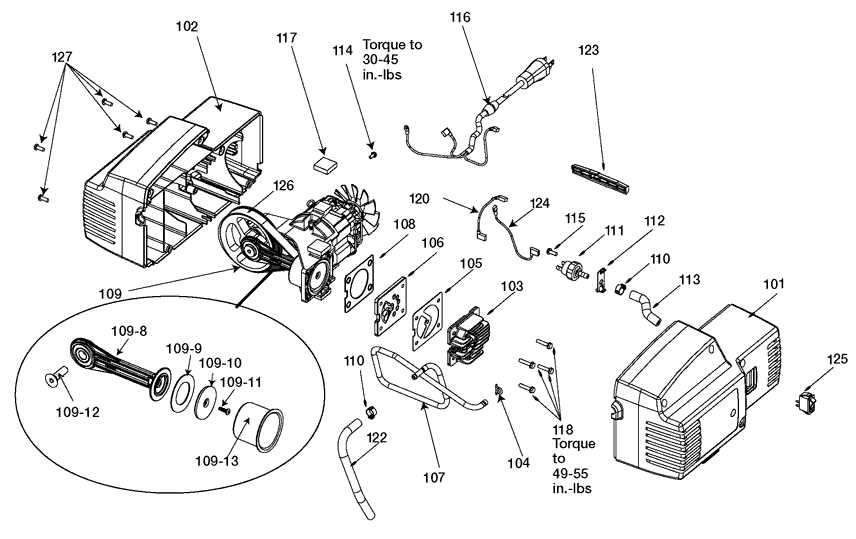
Regular upkeep of essential components ensures optimal performance and longevity of your equipment. By focusing on a few critical elements, you can prevent costly repairs and enhance efficiency. Here are some practical suggestions for maintaining these vital sections.
Routine Inspection
- Check for any signs of wear or damage.
- Inspect seals and gaskets for leaks.
- Ensure that connections are secure and free from corrosion.
Cleaning Practices
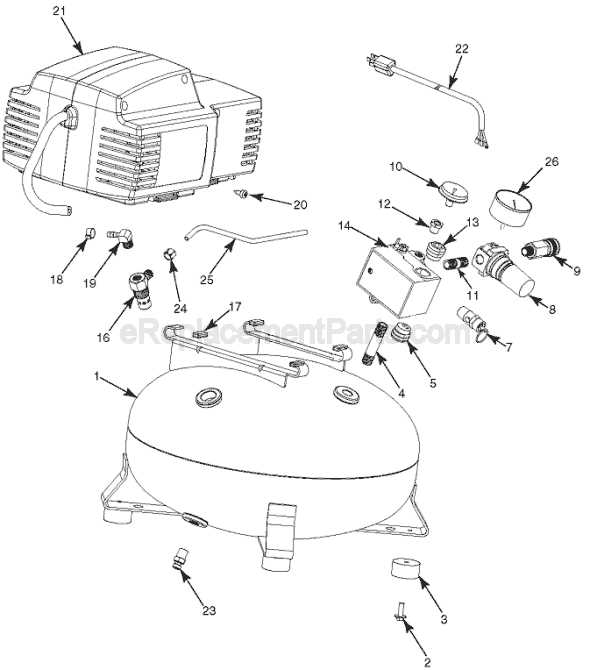
- Clean air filters regularly to promote airflow.
- Remove debris from external surfaces to prevent overheating.
- Use a soft brush to clear out any dust buildup in vents.
By implementing these maintenance strategies, you can significantly extend the lifespan of your machinery and maintain its peak performance.