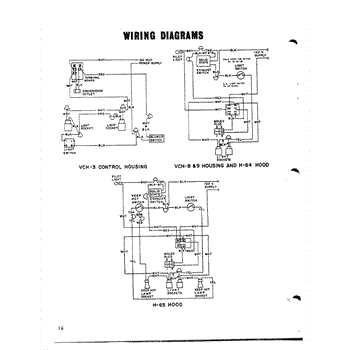
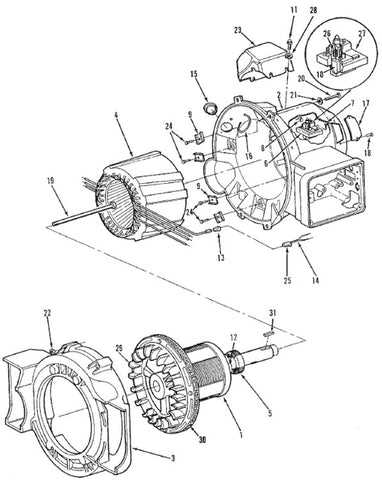
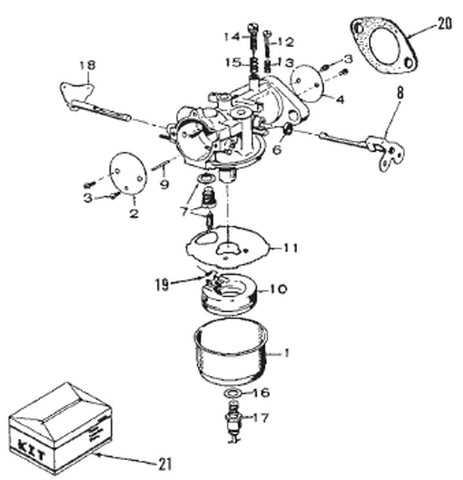
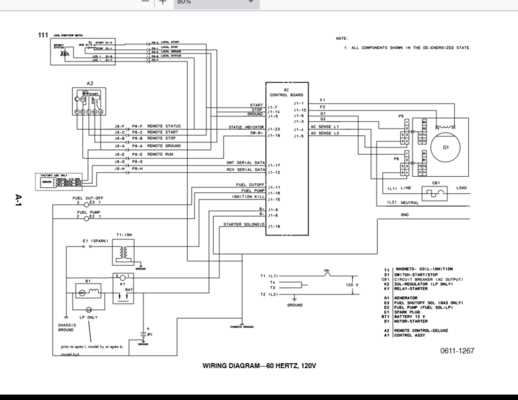
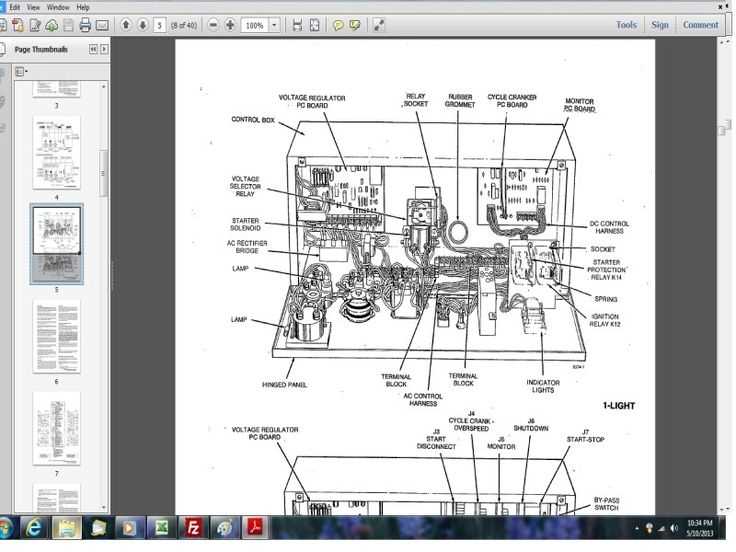
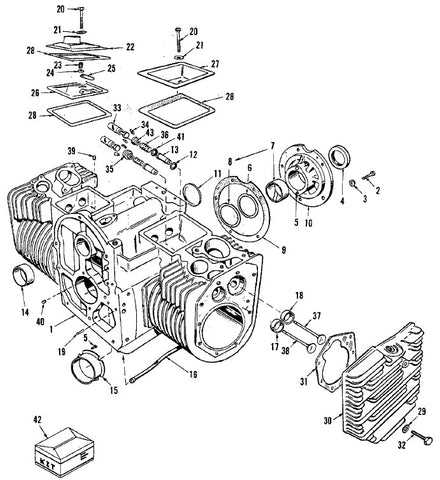
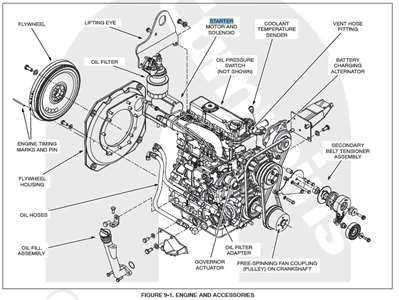
Control Panel: Allows monitoring and adjustments, ensuring proper functionality of the entire electrical circuit.
Cooling System Parts Explained
The cooling system is crucial for maintaining optimal operating temperatures in various machinery. Understanding its components is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. Each element plays a specific role in ensuring the system functions efficiently, preventing overheating and prolonging the lifespan of the equipment.
Radiator: This component dissipates heat from the coolant, allowing it to cool before recirculating back into the engine. A properly functioning radiator is vital for maintaining the right temperature balance.
Water Pump: The water pump circulates coolant throughout the system, ensuring that all parts receive adequate cooling. Its efficiency directly impacts the overall performance of the cooling system.
Thermostat: The thermostat regulates the flow of coolant based on temperature. It opens and closes to maintain the engine at the optimal temperature, ensuring efficiency and preventing overheating.
Hoses: These flexible tubes transport coolant between the engine, radiator, and other components. They must be in good condition to prevent leaks and ensure proper circulation of the cooling fluid.
Cooling Fan: The cooling fan aids in airflow across the radiator, particularly when the vehicle is stationary or moving slowly. Its operation helps enhance the cooling effect of the radiator.
Expansion Tank: This tank accommodates the expansion of coolant as it heats up. It also provides a reserve of coolant, which is essential for maintaining the system’s pressure and preventing air pockets.
Understanding each of these elements allows for better care and maintenance of the cooling system, ultimately ensuring reliable performance and efficiency.
Exploring the Ignition System
The ignition system plays a crucial role in the overall performance of combustion engines, ensuring that the fuel-air mixture is ignited at the right moment. This intricate assembly consists of various components that work together to produce the spark necessary for combustion, thus enabling the engine to function efficiently. Understanding the workings of this system is essential for maintaining optimal operation and troubleshooting any potential issues.
At the core of the ignition setup is the spark plug, which generates the electrical discharge needed to ignite the fuel mixture. It is essential for the spark plug to be in good condition, as any wear or damage can lead to misfiring or poor engine performance. Alongside the spark plug, the ignition coil amplifies the low voltage from the battery to a higher voltage, ensuring that a strong spark is produced.
Additionally, the ignition timing is a critical factor, determining when the spark occurs in relation to the engine’s cycle. If the timing is off, it can lead to inefficient combustion, reduced power output, and increased emissions. Properly adjusting the timing ensures that the engine operates smoothly and efficiently.
Another vital element is the distributor, which directs the high-voltage current from the ignition coil to the correct spark plug at the appropriate time. This component ensures that each cylinder receives the necessary spark to initiate combustion. Regular inspection and maintenance of the ignition system components can significantly enhance the performance and longevity of the engine.
Exhaust System and Its Function

The exhaust system is a crucial component of any engine, designed to manage the gases produced during combustion. Its primary role is to channel these gases away from the engine, reducing harmful emissions and enhancing overall performance. Proper functioning of this system is vital for maintaining engine efficiency and prolonging its lifespan.
This system typically consists of several parts working together to achieve its goals. Key components include the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, muffler, and various pipes that connect these elements. Each part plays a specific role, contributing to the effective removal and treatment of exhaust gases.
| Component |
Function |
| Exhaust Manifold |
Collects exhaust gases from the engine and directs them to the exhaust pipe. |
| Catalytic Converter |
Reduces harmful emissions by converting toxic gases into less harmful substances. |
| Muffler |
Reduces noise produced by the engine and exhaust gases. |
| Exhaust Pipes |
Transport exhaust gases from the engine to the outside environment. |
Regular maintenance of the exhaust system is essential to ensure optimal performance. Neglecting this aspect can lead to increased emissions, decreased fuel efficiency, and potential engine damage. Therefore, understanding the function and importance of each component can help in diagnosing issues and maintaining a well-functioning system.
Oil Circulation and Lubrication
Effective circulation and lubrication of oil are crucial for maintaining optimal performance and longevity of engine systems. A well-designed lubrication system ensures that all moving components receive adequate oil flow, minimizing friction and wear during operation. This process not only protects the internal parts but also helps in dissipating heat generated by the engine, contributing to overall efficiency.
The lubrication process typically involves several key components:
- Oil Pump: This device is responsible for drawing oil from the sump and circulating it throughout the engine. It generates the necessary pressure to ensure oil reaches all critical areas.
- Oil Filter: It removes impurities and contaminants from the oil, ensuring that clean oil circulates through the system, which helps prolong the life of engine parts.
- Oil Cooler: This component helps regulate the temperature of the oil, preventing overheating and maintaining viscosity, which is essential for effective lubrication.
- Oil Sump: The reservoir where the oil collects, allowing for sedimentation of contaminants and ensuring a stable supply of oil to the pump.
Lubrication can be categorized into different types, including:
- Wet Sump System: Oil is stored in the oil pan, and the pump draws oil directly from this reservoir.
- Dry Sump System: Oil is stored in an external tank, with the pump scavenging oil from the engine, allowing for better oil management and performance under extreme conditions.
Maintaining proper oil levels and quality is essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of the engine. Regular oil changes and monitoring for signs of contamination can significantly enhance the efficiency and performance of the lubrication system.
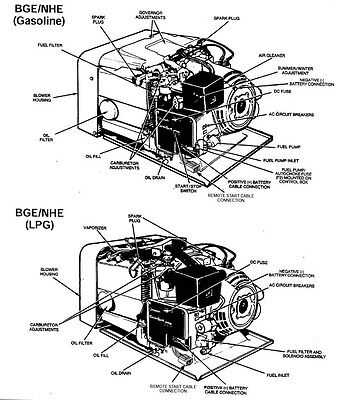
Common Wear Parts to Replace
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of any engine or generator. Over time, certain components may experience wear and tear, necessitating their replacement. Identifying these parts early can help prevent larger issues and maintain efficiency.
- Filters: Air and fuel filters can become clogged, affecting performance and efficiency. Replacing them regularly helps maintain clean airflow and fuel supply.
- Belts: Drive belts may stretch or fray with use. Inspecting and replacing worn belts can prevent power transmission issues.
- Spark Plugs: Over time, spark plugs can degrade, leading to poor ignition and reduced engine performance. Regular replacement ensures smooth operation.
- Battery: A weak or dead battery can hinder starting capabilities. Regular checks and timely replacement can prevent unexpected failures.
- Lubricants: Oil and lubrication fluids break down over time. Regular oil changes help reduce friction and keep components functioning optimally.
By keeping an eye on these common wear items, you can help ensure reliable operation and extend the lifespan of your machinery.
How the Voltage Regulator Operates
The voltage regulator is a crucial component in electrical systems, responsible for maintaining a stable voltage output despite variations in load conditions or input voltage. This ensures that connected devices receive a consistent level of electrical power, which is essential for their proper functioning and longevity.
Basic Principles of Operation
The operation of a voltage regulator relies on feedback mechanisms that continuously monitor the output voltage. When the output deviates from the desired level, the regulator adjusts the current flow to correct the voltage. This process can be described in the following steps:
- Input Voltage Sensing: The regulator constantly measures the output voltage.
- Comparison: It compares the sensed voltage with a predetermined reference voltage.
- Adjustment: If a discrepancy is detected, the regulator modifies the amount of current supplied to the load.
- Feedback Loop: The adjustments are continuously monitored, creating a feedback loop that stabilizes the output voltage.
Types of Voltage Regulators
There are several types of voltage regulators, each designed to meet specific requirements:
- Linear Regulators: Provide a smooth output voltage by dissipating excess power as heat.
- Switching Regulators: Use rapid switching to control the output voltage, making them more efficient than linear types.
- Shunt Regulators: Maintain a constant voltage by diverting excess current away from the load.
Understanding the operation and types of voltage regulators is vital for ensuring reliable performance in various electrical applications.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Ensuring the durability of your equipment requires consistent care and attention. Implementing routine maintenance practices can significantly enhance the performance and lifespan of your machinery. By adhering to recommended guidelines and being proactive, you can prevent common issues and extend operational efficiency.
Regular Inspections
Conducting frequent inspections is essential for identifying wear and tear before they escalate into serious problems. Look for signs of damage, leaks, or unusual noises that may indicate underlying issues. Keeping a log of inspections can help track changes and aid in timely interventions.
Cleaning and Lubrication
Maintaining cleanliness is vital for optimal functionality. Regularly remove dirt and debris from surfaces, particularly around moving parts. Additionally, ensure that all components are adequately lubricated to reduce friction and prevent premature wear.
| Maintenance Activity |
Frequency |
Benefits |
| Visual Inspection |
Monthly |
Identifies potential issues early |
| Cleaning |
Every 3 Months |
Prevents build-up that can hinder performance |
| Lubrication |
Every 6 Months |
Reduces wear and extends life |
| System Check |
Annually |
Ensures overall functionality and safety |