
In the world of fabrication, having a clear understanding of your machinery is essential for optimal performance. Knowing how various components interact can significantly enhance the efficiency of your projects. This section aims to provide insights into the intricate design of a specific welding device.
By exploring the essential elements that make up this equipment, users can better appreciate its functionality. Whether you are a novice or an experienced technician, familiarizing yourself with the configuration can lead to improved maintenance and troubleshooting skills. Additionally, grasping the layout of these mechanisms paves the way for informed upgrades and replacements.
Ultimately, this knowledge empowers users to harness the full potential of their tools, ensuring that every welding task is executed with precision. Join us as we delve into the specifics, providing clarity and guidance for your welding endeavors.
Understanding Lincoln 140 MIG Welder
This section aims to explore the essential components and functionality of a popular welding machine, highlighting its significance in various applications. By breaking down the key elements, users can better appreciate how this equipment operates and the advantages it offers for both novice and experienced welders.
Key Components: The machine consists of several critical elements, including the power source, feed mechanism, and control settings. Each part plays a vital role in ensuring optimal performance and quality of the welds produced.
Functionality: Understanding how these components interact is crucial for effective operation. Proper knowledge allows for adjustments to be made, enhancing the overall welding experience and ensuring that the desired results are achieved.
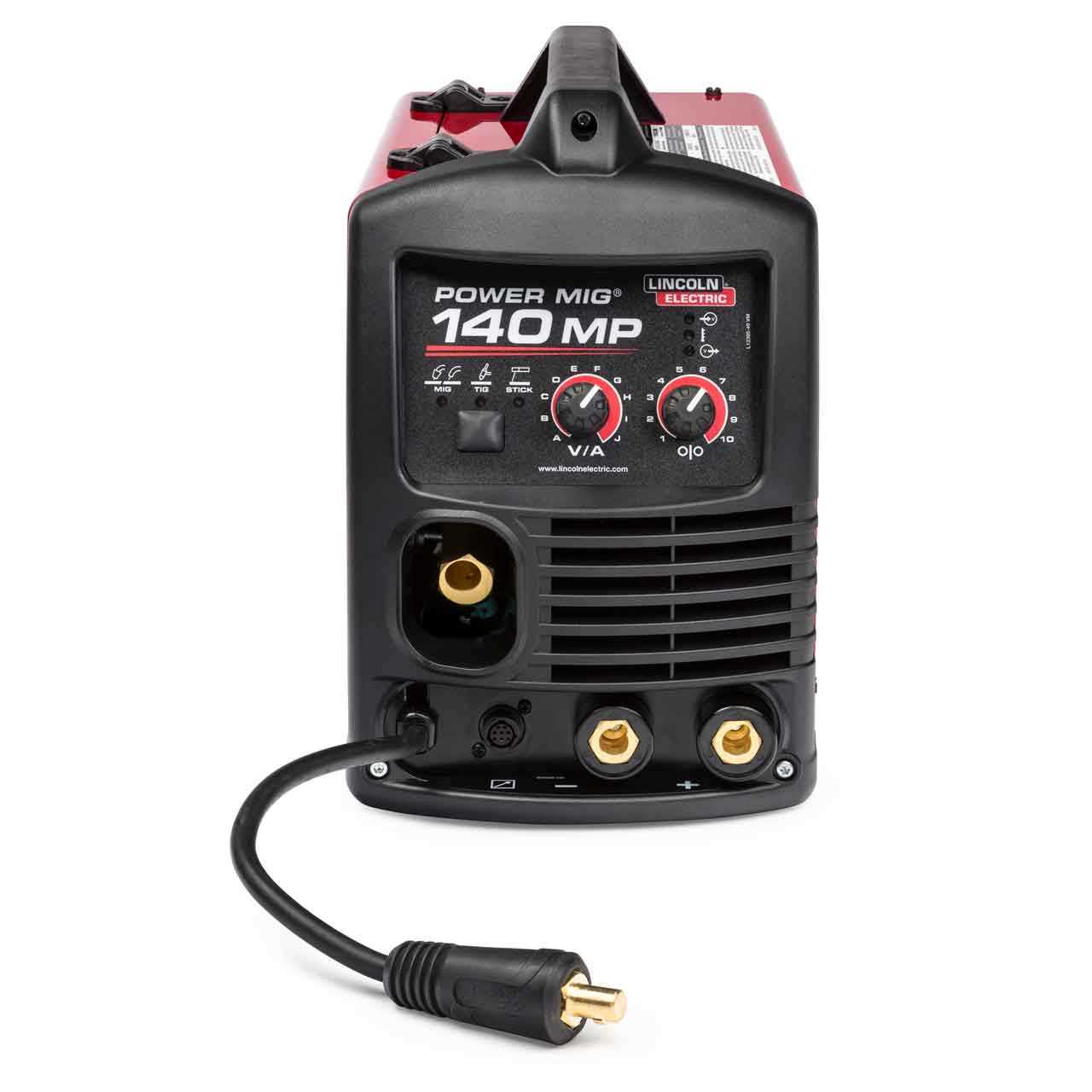
Components of the Lincoln 140 Welder
This section explores the essential elements that contribute to the functionality and efficiency of a popular welding machine. Understanding these components is crucial for both maintenance and optimal performance.
Power Source: The primary energy supply that powers the device, typically delivering the necessary voltage and current for effective operations.
Control Panel: This interface allows the operator to adjust settings such as voltage and wire feed speed, ensuring precise control during the welding process.
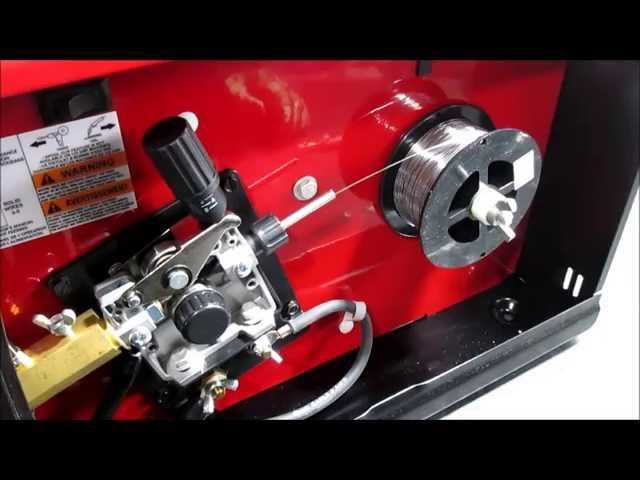
Feed Mechanism: A critical system responsible for supplying the filler material to the welding area, allowing for a consistent and smooth flow.
Ground Clamp: This component establishes a connection to the workpiece, ensuring proper electrical grounding to prevent hazards and enhance performance.
Gas Supply System: Essential for shielding the weld from contamination, this setup includes regulators and hoses that deliver the required shielding gas.
Cooling System: Prevents overheating of the machine during extended use, maintaining optimal operating temperatures for reliability and longevity.
Protective Housing: The outer casing that shields internal components from damage, ensuring durability and safety during operations.
Importance of Wiring Diagrams
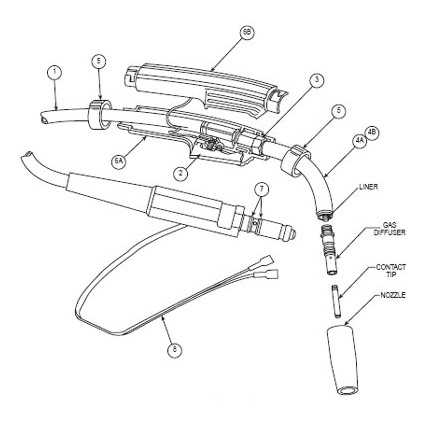
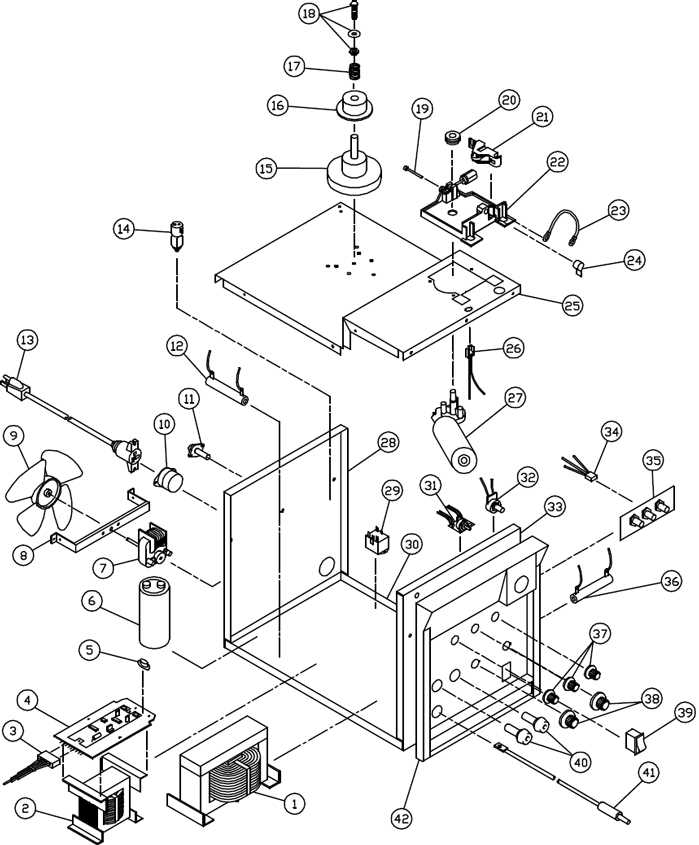
Wiring schematics are essential tools that facilitate the understanding and maintenance of electrical systems. They serve as a visual guide, detailing the connections and components within a setup.
- Clarity: These diagrams provide clear representation, making it easier to identify how parts are interconnected.
- Efficiency: With a schematic at hand, troubleshooting becomes quicker, allowing for faster repairs and adjustments.
- Safety: Understanding wiring layouts helps prevent accidents by ensuring that proper protocols are followed during maintenance.
- Training: New users can learn more effectively by studying visual aids, enhancing their comprehension of complex systems.
- Documentation: Schematics serve as vital records, providing a reference for future modifications or repairs.
In summary, these illustrations play a crucial role in the effective management of electrical projects, promoting safety and efficiency.
Common Parts Replacement Guide
This section provides a comprehensive overview of essential components commonly requiring replacement in welding equipment. Understanding these elements can help users maintain optimal performance and extend the lifespan of their machines.
Identifying Worn Components
Recognizing the signs of wear is crucial for ensuring efficient operation. Common indicators include inconsistent performance, unusual noises, or overheating. Regular inspections can help identify which components may need replacement.
Replacement Options
When it comes to replacing worn components, choosing the right parts is essential. Below is a table outlining frequently replaced items, their purposes, and recommended replacements.
| Component | Function | Replacement Options |
|---|---|---|
| Contact Tip | Directly transfers the arc and melts filler material. | Copper, brass |
| Nozzle | Focuses and directs the gas flow. | Ceramic, steel |
| Gas Diffuser | Evenly distributes shielding gas. | Aluminum, stainless steel |
| Electrode | Conducts electrical current to create the arc. | Solid wire, flux-cored wire |
| Drive Roll | Feeds the filler material into the weld pool. | Steel, aluminum |
By proactively replacing these components, users can ensure their equipment functions effectively, ultimately leading to higher quality results and greater efficiency.
Essential Safety Equipment Needed
When engaging in metalworking activities, prioritizing personal safety is crucial. Proper protective gear ensures that individuals can operate equipment effectively while minimizing the risk of injury. This section outlines the essential safety equipment required for a secure working environment.
Key Protective Gear
The following items are fundamental for safeguarding against hazards encountered during metalworking tasks:
| Equipment | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Safety Goggles | Protects eyes from sparks and debris. |
| Welding Helmet | Shields face and eyes from intense light and heat. |
| Gloves | Prevents burns and cuts while handling materials. |
| Respirator | Filters harmful fumes and particles from the air. |
| Protective Clothing | Resists flames and protects skin from sparks. |
Additional Precautions

In addition to personal protective gear, maintaining a clean and organized workspace is essential. Proper ventilation, fire extinguishers, and first aid kits should also be readily accessible to further enhance safety.
How to Read a Parts Diagram

Understanding a schematic representation of components can greatly enhance your ability to maintain and repair equipment. These visual aids serve as a map, guiding you through the various elements and their relationships. Here are some key points to keep in mind when interpreting such visuals.
- Identify the Key: Most illustrations will include a legend or key that explains symbols and labels used throughout the schematic. Familiarize yourself with these to grasp the overall layout.
- Examine the Layout: Take note of how components are organized. Often, similar parts are grouped together, which can help you understand their functions and connections.
- Follow the Flow: Look for arrows or lines that indicate the flow of energy or materials. This will provide insight into how each component interacts within the system.
- Check for Annotations: Descriptive notes or annotations can provide additional context, highlighting important information that may not be immediately obvious from the image alone.
- Practice with Examples: Start with simpler representations before tackling more complex ones. Familiarizing yourself with the format will build your confidence and comprehension skills.
By following these steps, you can enhance your understanding of technical illustrations, making it easier to troubleshoot and service your equipment effectively.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity

Proper upkeep is essential to ensure the extended lifespan of your equipment. Regular attention not only enhances performance but also prevents premature wear and costly repairs. Adopting a systematic maintenance routine can significantly improve reliability and efficiency.
Routine Inspection

Conduct frequent examinations of all components. Look for signs of wear, damage, or loose connections. Timely identification of potential issues can save you from more significant problems down the road.
Cleaning and Lubrication
Keep your machine clean and free of debris. Regular cleaning prevents build-up that can affect operation. Additionally, ensure that moving parts are adequately lubricated to reduce friction and prolong functionality.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
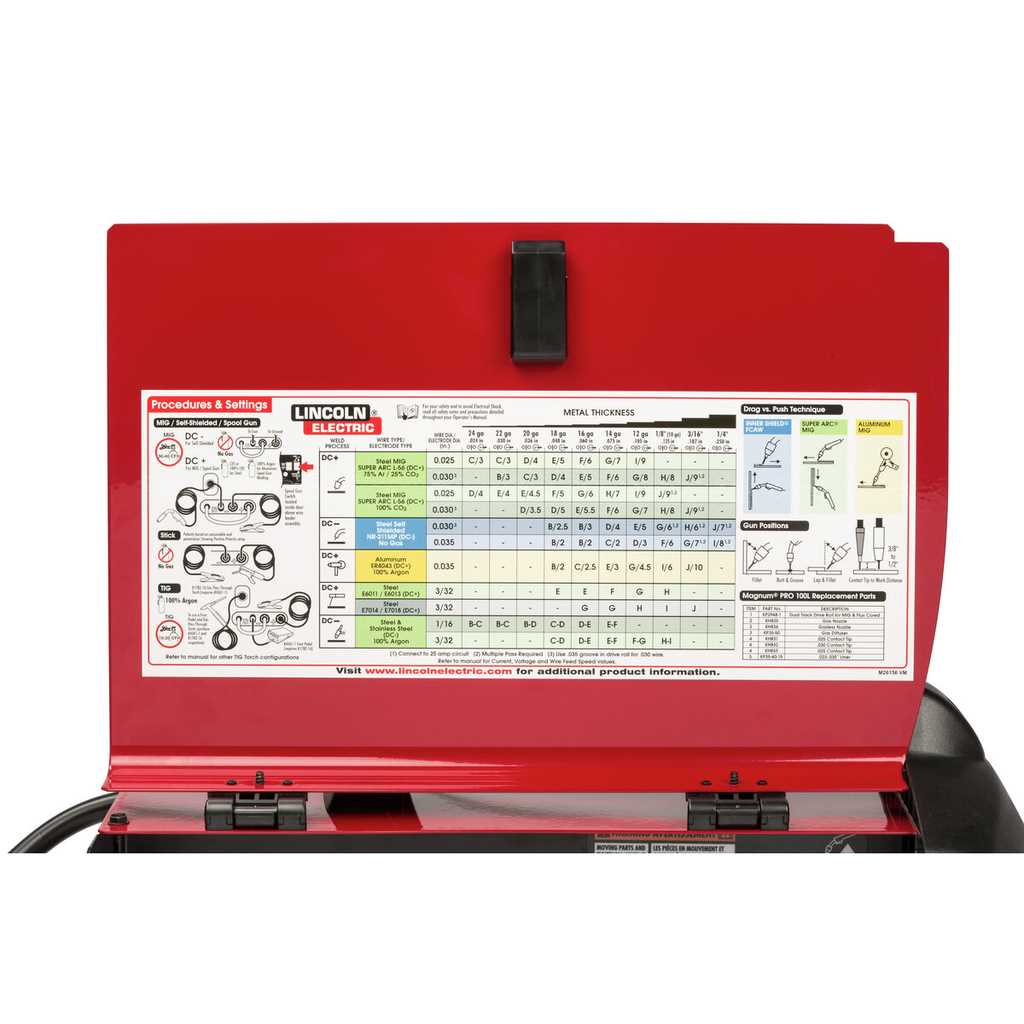

Addressing frequent problems can significantly enhance the performance and longevity of your equipment. Understanding typical malfunctions and their remedies is essential for efficient operation. This section outlines common challenges users may encounter and offers practical solutions to rectify them.
Common Problems and Solutions

| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| No Arc | Power supply issues | Check connections and ensure the unit is plugged in and switched on. |
| Inconsistent Wire Feed | Incorrect tension or blockage | Adjust the feed roller tension and clear any obstructions in the wire path. |
| Poor Weld Quality | Improper settings or dirty surfaces | Verify voltage and wire speed settings; clean the work surface thoroughly. |
| Overheating | Continuous operation or insufficient ventilation | Allow the machine to cool down and ensure adequate airflow around the unit. |
Preventive Measures

To minimize issues, regular maintenance is crucial. Periodically inspect all components, clean the feed mechanism, and ensure proper storage conditions. Following these practices can help maintain optimal functionality and reduce downtime.
Upgrading Lincoln 140 Components
Enhancing the functionality and performance of your welding machine can significantly improve your projects. By focusing on key elements, you can achieve better efficiency and results. Here are several components worth considering for upgrades:
- Power Supply: Upgrading to a higher capacity can provide more consistent performance.
- Electrode Holder: A more robust holder can improve the stability and control during use.
- Ground Clamp: A superior clamp ensures better conductivity, reducing the risk of interruptions.
When selecting parts, it’s essential to ensure compatibility with your existing setup to maximize the ultimate benefits of each enhancement.
- Research available components from reputable manufacturers.
- Consult user reviews and forums for insights on performance improvements.
- Consider installation ease and the potential need for professional assistance.
Welding Techniques for Beginners

Starting with metal joining processes can be both exciting and overwhelming. Understanding fundamental methods is essential for anyone looking to master this craft. With various approaches available, beginners should focus on the basics to develop their skills effectively. This section outlines key techniques that will provide a solid foundation for aspiring welders.
Arc Welding Basics

One of the most accessible methods for novices is arc joining. This technique involves using an electric current to create an arc between the metal and the electrode. The heat generated melts both the electrode and the base material, allowing them to fuse together. Beginners should practice maintaining a consistent distance between the electrode and the workpiece to ensure a smooth and even weld.
Gas Welding Fundamentals
Another important technique is gas joining, which utilizes a flame produced by burning a mixture of oxygen and fuel gas. This method is ideal for beginners due to its simplicity and versatility. Properly controlling the flame is crucial for achieving the desired temperature and ensuring strong joints. Practicing different joint types, such as butt and lap joints, will help develop the necessary hand-eye coordination and precision.
Recommended Accessories for Efficiency
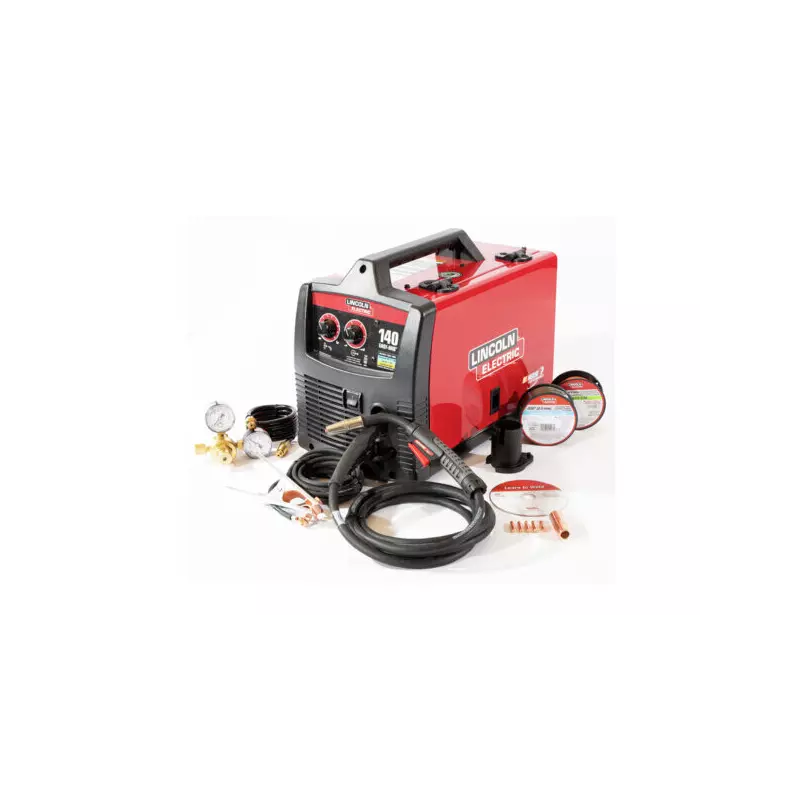

To enhance your metalworking projects and ensure optimal performance, incorporating the right tools and attachments can make a significant difference. These additions not only improve the quality of your work but also streamline the process, allowing for greater precision and ease.
- Welding Helmet: A reliable protective face shield is essential to safeguard your eyes and skin from harmful rays and sparks.
- Gloves: High-quality heat-resistant gloves provide protection while maintaining dexterity for intricate tasks.
- Fume Extractor: Investing in a fume extraction system helps maintain a clean workspace by removing hazardous fumes and particles.
- Welding Cart: A sturdy cart allows for easy transport of your equipment and keeps everything organized, improving mobility and access.
- Spare Nozzles and Tips: Having a variety of nozzles and tips on hand can accommodate different thicknesses and types of materials, enhancing versatility.
By equipping yourself with these essential tools, you can significantly boost your productivity and the quality of your output, ensuring successful projects every time.
Finding Quality Replacement Parts

Ensuring optimal performance and longevity of your equipment relies heavily on sourcing high-quality components. The right replacements can significantly enhance functionality and reduce the likelihood of future issues. Here are several tips to help you locate reliable options:
- Research Authorized Dealers: Start by identifying official distributors or retailers known for their credibility. They typically offer original or certified alternatives.
- Read Customer Reviews: Look for feedback from previous buyers to gauge the reliability and performance of the components you are considering.
- Check Warranty Information: Quality replacements often come with warranties that guarantee their durability. Verify the terms before purchasing.
- Compare Prices: While lower prices can be tempting, ensure that cost-cutting does not compromise quality. Compare options across various sellers.
- Consult User Manuals: Reference the documentation that came with your equipment. This can provide valuable information on compatible replacements.
By following these guidelines, you can confidently invest in components that will support your equipment’s performance and reliability over time.
Comparing Lincoln Models and Features
When exploring various welding machines, understanding the differences in models and their respective functionalities is crucial for making an informed choice. Each variant offers unique attributes tailored to specific applications, from lightweight options for home projects to robust models designed for industrial tasks. This section delves into the key features and performance metrics that distinguish these machines, helping users identify which model best meets their requirements.
Performance Capabilities: The range of output power varies significantly among different machines, affecting the thickness of materials they can effectively weld. Higher-powered units typically accommodate thicker metals, while entry-level models are ideal for lighter gauge work.
Portability: Weight and design play a vital role in usability, especially for those who need to move their equipment frequently. Some models prioritize compactness, making them suitable for mobile use, while others may be more cumbersome but offer enhanced stability during operation.
Control Features: Advanced settings and digital displays are increasingly common, allowing for precise adjustments to voltage and wire feed speed. Users seeking greater control over their welding process will benefit from these sophisticated features, enhancing the quality of their welds.
Compatibility with Consumables: Different machines may require specific types of wires and gas mixtures. Understanding these requirements can prevent frustration and ensure optimal performance, as using the correct materials directly impacts the welding outcome.
Durability and Maintenance: The longevity of welding equipment is often tied to the materials used in construction and the ease of maintenance. Models that are designed for frequent use typically feature more durable components, while others might require regular servicing to ensure peak performance.
In conclusion, evaluating the various features across models allows users to select the best-suited machine for their welding tasks, balancing performance, portability, and user-friendliness to achieve desired results.