When it comes to maintaining and repairing an automobile, having a clear visual representation of its structure is crucial. A detailed illustration serves as a valuable resource, guiding enthusiasts and professionals alike in identifying various elements within the vehicle. Such diagrams enhance the understanding of how different sections interact, contributing to better maintenance practices.
In this exploration, we delve into the intricacies of a specific model’s configuration. By examining the arrangement of essential components, users can gain insight into the functionality of their vehicle. This knowledge not only aids in troubleshooting but also empowers owners to make informed decisions regarding repairs and upgrades.
Whether you are an experienced mechanic or a passionate car owner, familiarizing yourself with the layout can significantly improve your approach to vehicle care. Having access to accurate representations of the automobile’s anatomy can simplify the process of diagnostics and maintenance, ensuring longevity and optimal performance.
This section outlines the essential components and assemblies of a specific vehicle model, providing insights into their functions and interrelationships. Understanding these elements can enhance maintenance practices and facilitate troubleshooting for vehicle owners and technicians alike.
1. Introduction to Vehicle Components
This part introduces the significance of recognizing various elements within a vehicle and how they contribute to overall performance.
2. Engine Assembly Overview

- Key functions of the engine
- Common components included
3. Transmission System Insights
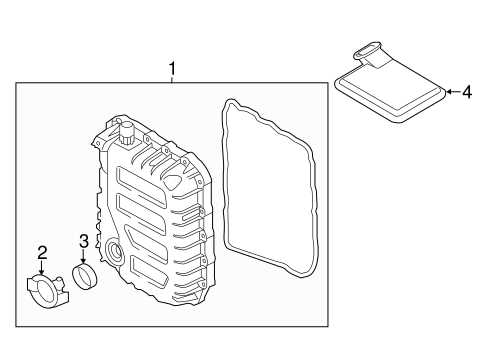
- Importance of the transmission
- Types of transmission used
4. Electrical Systems Breakdown
- Overview of wiring and connectors
- Functions of the battery and alternator
5. Suspension and Steering Details
- Role of the suspension system
- Components involved in steering
6. Brake Mechanism Explanation
- Understanding the braking system
- Components that enhance safety
7. Exhaust System Components
- Purpose of the exhaust system
- Key parts within the system
8. Fuel System Functionality
- Overview of fuel delivery
- Important components of the system
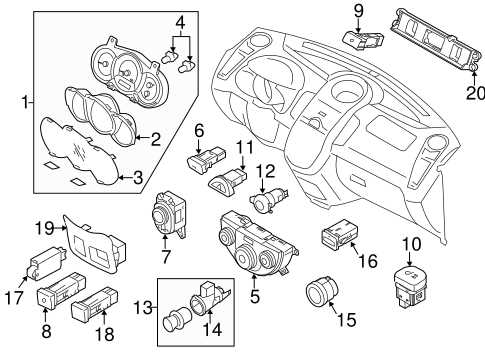
9. Interior Assembly Elements
- Significance of cabin components
- Key features for comfort and control
10. Exterior Features and Accessories
- Overview of body elements
- Functional and aesthetic accessories
Key Components in Vehicle Assembly
The assembly of a motor vehicle involves various essential elements that work in harmony to ensure optimal performance and safety. Each component plays a significant role, contributing to the overall functionality and reliability of the automobile. Understanding these integral parts is crucial for maintenance and repair, as well as for appreciating the complexities involved in modern vehicle construction.
Core Structural Elements
At the heart of any vehicle’s design are its core structural elements, which provide stability and support. The chassis serves as the foundation, connecting various systems and components. This framework is reinforced by additional supports, ensuring durability under stress. The body panels, crafted from lightweight materials, not only contribute to the vehicle’s aesthetic appeal but also play a vital role in aerodynamics.
Essential Functional Systems
In addition to structural components, numerous functional systems are crucial for vehicle operation. The powertrain, comprising the engine and transmission, is responsible for propelling the vehicle. Complementing this system are the braking and suspension mechanisms, which enhance safety and comfort. Furthermore, the electrical system integrates lighting, infotainment, and various controls, showcasing the sophistication of contemporary automotive engineering.
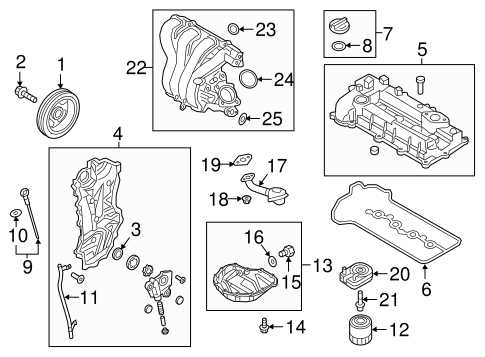
Understanding the Engine Layout
The arrangement of components within an automobile’s engine compartment is crucial for optimal performance and functionality. A well-organized layout facilitates effective operation and simplifies maintenance tasks, enhancing the overall driving experience. Each element plays a significant role, contributing to the engine’s efficiency and reliability.
In general, the engine layout comprises various parts that work in unison. Below is a table outlining key components typically found in an engine layout, along with their respective functions:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Cylinder Block | Houses the cylinders and provides structural support. |
| Pistons | Convert fuel energy into mechanical power. |
| Crankshaft | Transforms linear motion of pistons into rotational motion. |
| Camshaft | Controls the timing of valve openings and closings. |
| Intake Manifold | Distributes the air-fuel mixture to the cylinders. |
| Exhaust Manifold | Collects exhaust gases from the cylinders. |
| Oil Pan | Holds engine oil and provides lubrication to moving parts. |
A comprehensive understanding of these elements allows for better insight into engine functionality, ultimately aiding in maintenance and troubleshooting efforts.
Transmission System Breakdown
The transmission system is a crucial component of any vehicle, responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels. This system consists of various elements that work together to ensure smooth shifting and optimal performance. Understanding the intricacies of this system can help in diagnosing issues and performing maintenance effectively.
Components of the Transmission System
Several key components make up the transmission system, each playing a vital role in its operation. These parts must function harmoniously to facilitate the vehicle’s movement and ensure a reliable driving experience.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Gearbox | The mechanism that contains gears, allowing the driver to select the appropriate gear for speed and torque. |
| Clutch | A device that engages and disengages the engine from the transmission, allowing for smooth gear changes. |
| Torque Converter | A fluid coupling that transmits power from the engine to the transmission, enabling automatic shifting. |
| Shift Linkage | The system that connects the gear shifter to the transmission, allowing the driver to select different gears. |
| Transmission Fluid | A special fluid that lubricates and cools the transmission components, ensuring efficient operation. |
Common Issues in Transmission Systems
Like any mechanical system, the transmission is prone to various problems that can affect vehicle performance. Recognizing these issues early can prevent more extensive damage and costly repairs.
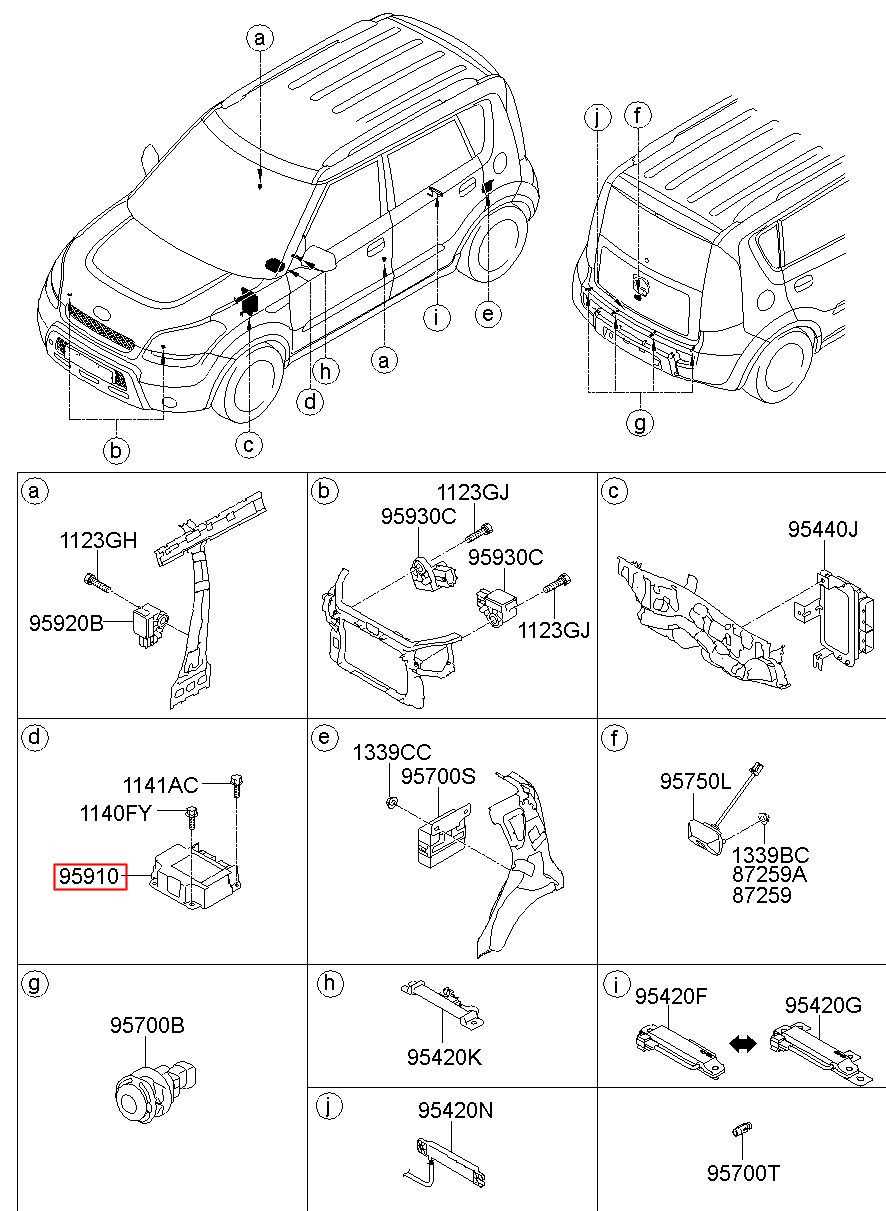
Electrical System Wiring Diagram
The electrical system within a vehicle is a complex network designed to ensure seamless communication between various components. Understanding the layout of this intricate system is crucial for troubleshooting and maintenance. The wiring schematic serves as a guide, highlighting the connections and pathways through which electrical currents flow, thus facilitating the proper functioning of critical elements such as lighting, infotainment, and safety features.
Components and Connections
This section outlines the essential components involved in the electrical network. Each part is interconnected, allowing for efficient energy distribution. Notably, the battery acts as the powerhouse, supplying energy to various systems. Moreover, fuses are strategically placed to protect against overloads, ensuring the safety of the entire electrical framework.
Understanding Circuit Pathways
Mapping the circuit pathways is vital for diagnosing issues that may arise within the electrical system. The schematic illustrates how signals travel from switches to their respective components, such as lights and sensors. Recognizing these pathways enables technicians to pinpoint malfunctions and restore functionality swiftly.
Suspension Parts and Configuration
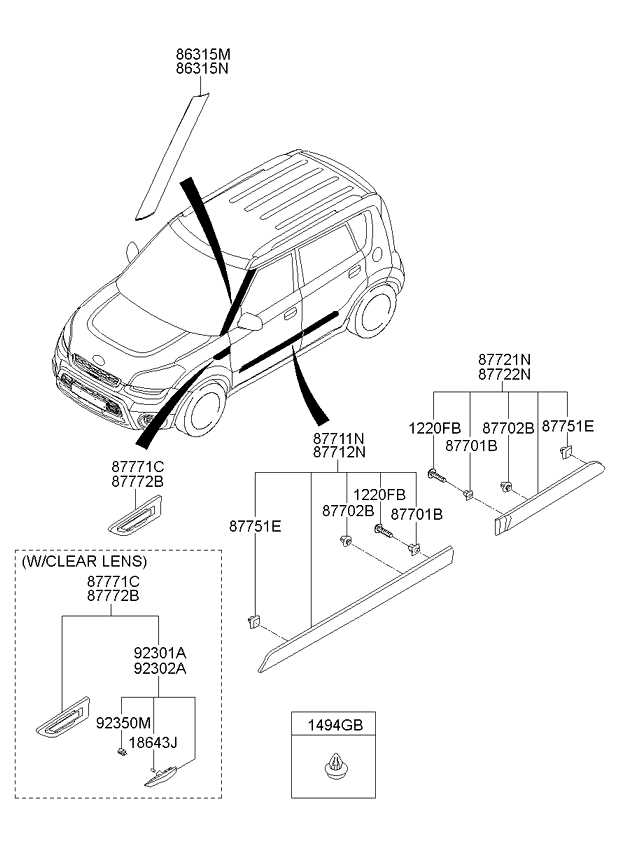
The suspension system plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth and comfortable ride by maintaining tire contact with the road while absorbing shocks from uneven surfaces. This system consists of various components that work together to enhance vehicle stability, handling, and overall performance.
Key elements of the suspension assembly include springs, shock absorbers, struts, and control arms. Each of these components serves a distinct purpose, contributing to the vehicle’s ability to navigate different terrains and manage weight distribution effectively. The arrangement and design of these elements can significantly influence ride quality and responsiveness during acceleration and braking.
Additionally, the configuration of the suspension system may vary between different models, allowing for customization based on driving conditions and preferences. Proper maintenance and timely replacement of worn or damaged components are essential for preserving the integrity of the suspension, ensuring optimal safety and driving enjoyment.
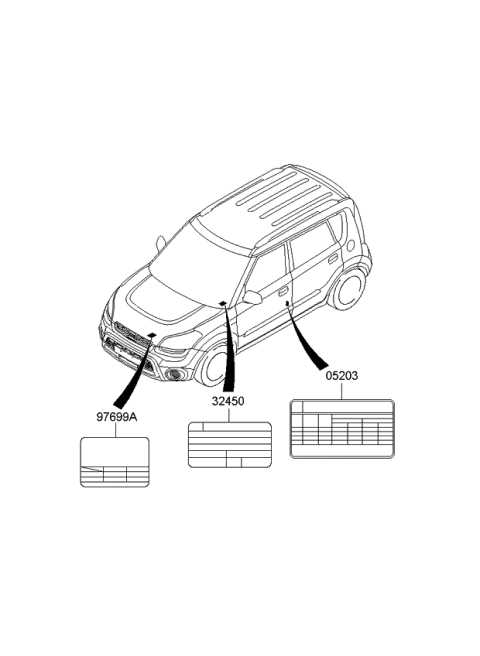
Interior Features and Components
The interior of a modern compact vehicle is designed to enhance comfort, functionality, and style. It incorporates various elements that contribute to the overall driving experience, making it both enjoyable and practical for everyday use. From seating arrangements to technological innovations, each component plays a vital role in ensuring convenience and satisfaction for occupants.
Comfort and Seating Arrangements
Seating options are crafted with an emphasis on ergonomics and aesthetics, offering ample support for both short commutes and long journeys. Materials used for upholstery are selected not only for durability but also for visual appeal, providing a welcoming atmosphere within the cabin. Configurations often include adjustable front seats and a spacious rear area, accommodating passengers with ease.
Technology and Connectivity
Advanced technological features are integrated into the interior, enhancing connectivity and entertainment. Infotainment systems provide access to navigation, audio, and communication services, all managed through intuitive interfaces. Additionally, the inclusion of USB ports and Bluetooth connectivity ensures that drivers and passengers stay connected while on the move, making journeys more enjoyable and efficient.
Braking System Parts Explained
The braking mechanism of a vehicle is crucial for ensuring safe operation and effective stopping power. This system comprises various components that work together to slow down or halt the vehicle’s motion. Understanding these elements can enhance your comprehension of vehicle maintenance and repair.
At the core of the braking system are the following main components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Brake Pedal | The interface between the driver and the braking system, initiating the braking process when pressed. |
| Master Cylinder | This device converts the force from the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure, distributing it to the brake calipers. |
| Brake Lines | Flexible tubes that carry hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the brake calipers, enabling effective braking action. |
| Brake Calipers | These components house the brake pads and apply pressure to them against the brake rotors to create friction. |
| Brake Pads | Friction materials that press against the rotors to slow down the vehicle when the brake calipers are engaged. |
| Brake Rotors | Discs that the brake pads clamp onto to create the necessary friction for stopping the vehicle. |
Each element plays a pivotal role in the overall function of the braking system, contributing to the safety and control of the vehicle during operation.
Maintenance and Replacement Parts
Regular upkeep and timely substitutions are essential for the longevity and efficiency of any vehicle. Understanding which components require periodic checks and replacements can help maintain optimal performance. By staying informed about various components and their roles, owners can ensure their vehicles run smoothly and reliably.
Below is a table outlining common components that may need attention during regular maintenance or replacement:
| Component | Purpose | Maintenance Interval |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Filter | Removes contaminants from engine oil | Every 5,000 – 7,500 miles |
| Air Filter | Ensures clean air intake for combustion | Every 15,000 – 30,000 miles |
| Brake Pads | Facilitates safe stopping power | Every 30,000 – 70,000 miles |
| Battery | Powers electrical systems and starts the engine | Every 3 – 5 years |
| Tires | Supports the vehicle and provides traction | Every 25,000 – 50,000 miles |
Staying proactive about these components can significantly enhance the driving experience and minimize unexpected breakdowns. Regular inspections and timely replacements contribute to safety and comfort on the road.
Safety Features and Specifications
This section provides an overview of the essential safety attributes and specifications associated with the vehicle. Understanding these aspects is crucial for ensuring a secure driving experience. The integration of advanced safety systems enhances overall vehicle reliability and provides peace of mind for both drivers and passengers.
Key Safety Attributes
The vehicle incorporates a range of safety technologies designed to mitigate risks during travel. These features are tailored to protect occupants and reduce the likelihood of accidents. Below are some of the prominent safety characteristics:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Airbags | Equipped with multiple airbags strategically placed to provide cushioning in the event of a collision. |
| Anti-lock Braking System | This system prevents wheel lock-up during braking, enhancing steering control during emergency stops. |
| Electronic Stability Control | Aids in maintaining vehicle control during slippery conditions by adjusting brake force and engine power. |
| Traction Control | Helps prevent wheel spin during acceleration, improving stability on various road surfaces. |
Safety Ratings
The vehicle has undergone rigorous testing to evaluate its safety performance. These assessments provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of its safety features. Understanding safety ratings can guide potential buyers in making informed decisions.