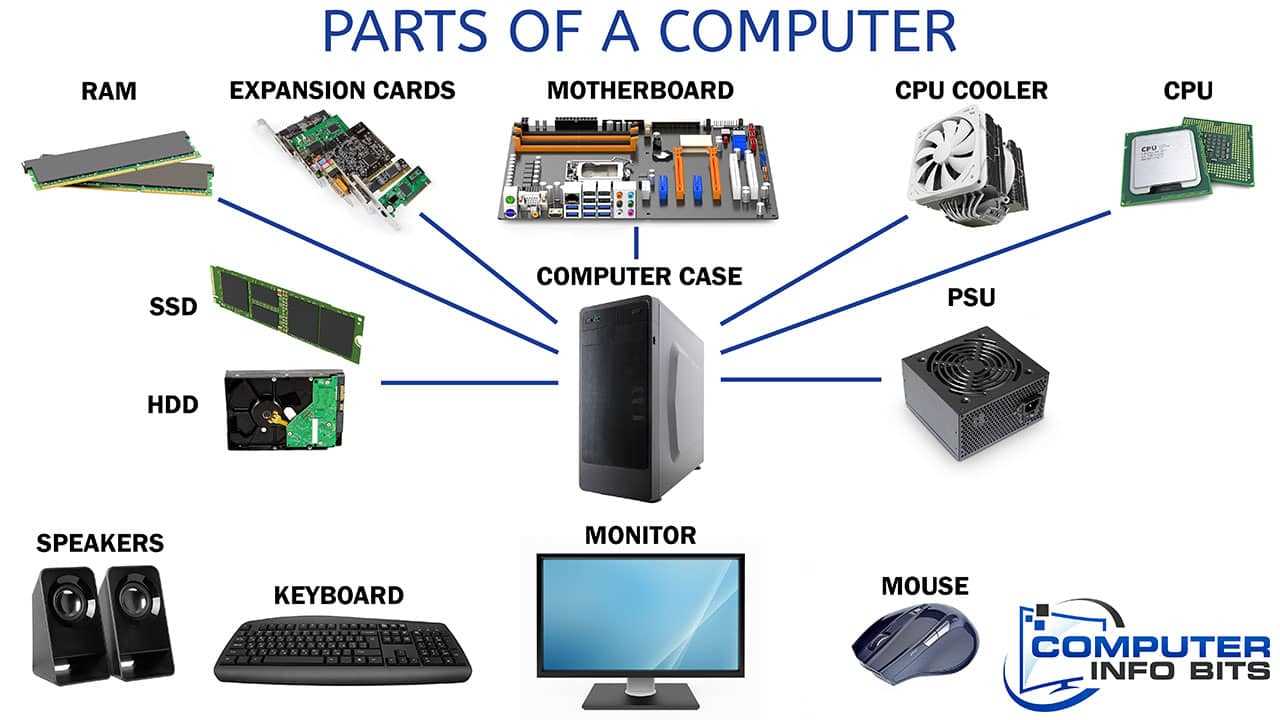
The intricate framework of a computer system is a marvel of modern engineering, where each component plays a crucial role in ensuring seamless operation. From processing information to storing data, these interconnected elements collaborate to bring the user experience to life. Grasping the relationships between these various units is essential for anyone looking to deepen their knowledge of computing.
In this exploration, we will delve into the essential components that constitute a computer’s architecture. By examining their functions and interactions, readers will gain insights into how these elements synergize to perform complex tasks. Whether you’re a novice eager to learn or an enthusiast aiming to refine your understanding, this section will illuminate the fundamental concepts that underpin computing technology.
Furthermore, appreciating the structure and functionality of each unit will empower individuals to make informed decisions when upgrading or building their own systems. Understanding these core concepts not only enhances technical skills but also fosters a greater appreciation for the technology that has become integral to our daily lives. Join us as we embark on this enlightening journey into the heart of computer systems.
Understanding the Basic PC Components
Every computer is built on a foundation of essential elements that work together seamlessly. Grasping the roles of these components is crucial for anyone looking to assemble or upgrade their system effectively.
Core Components
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): Often referred to as the brain, it executes instructions and processes data.
- Motherboard: The main circuit board that connects all components, allowing them to communicate.
- Random Access Memory (RAM): Temporary storage that provides space for active tasks and processes.
- Storage Devices: Includes hard drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs) for long-term data storage.
Peripheral Components
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): Converts electricity from the wall into usable power for the computer.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): Handles rendering of images and video, essential for gaming and graphic design.
- Cooling Systems: Keeps the internal temperature down to prevent overheating and ensure performance.
Essential Hardware for Computer Build
Creating a functional computing system requires various components that work harmoniously to deliver optimal performance. Understanding these crucial elements is key to assembling a reliable machine tailored to your needs.
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): The brain of the computer, responsible for executing instructions and processing data.
- Motherboard: The main circuit board that connects all components, allowing communication between them.
- Memory (RAM): Temporary storage that enables quick access to data for active processes.
- Storage Drive: Where your data and applications are permanently stored, available in HDD or SSD formats.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): Converts electrical power from an outlet to usable power for your system.
- Graphics Card: Handles rendering images and video, crucial for gaming and graphic design tasks.
Each element plays an integral role, ensuring the system runs smoothly and efficiently. Selecting high-quality components will ultimately enhance your overall experience.
Visual Guide to PC Parts Layout
This section provides an insightful overview of the various components that make up a computer system. Understanding the arrangement and functionality of these elements is essential for anyone looking to build or upgrade their own machine. By visualizing how these items fit together, one can better appreciate their individual roles and the overall operation of the system.
Component Arrangement Overview
The layout of a computer includes several key items, each playing a vital role in performance and connectivity. Here’s a brief look at the main elements and their typical positioning within a setup.
| Component | Description | Typical Location |
|---|---|---|
| Central Processing Unit (CPU) | The brain of the system, executing instructions and processing data. | Motherboard socket |
| Random Access Memory (RAM) | Temporary storage for data and instructions currently in use. | Motherboard slots |
| Storage Drive | Permanent storage for the operating system, applications, and files. | Drive bays or M.2 slots |
| Power Supply Unit (PSU) | Provides electrical power to all components. | Bottom or top of the case |
| Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) | Handles rendering images and video for display. | PCIe slot on the motherboard |
Connecting Elements
To ensure seamless communication among these components, various connectors and cables are utilized. Recognizing the importance of proper connections enhances the overall efficiency and performance of the system. This visual understanding lays the groundwork for successful assembly and troubleshooting.
Key Functions of Each Component
Understanding the essential roles played by various elements within a computer system is crucial for both building and troubleshooting. Each component contributes to the overall functionality, ensuring that tasks are processed efficiently and effectively. This section delves into the primary functions of these critical components, highlighting their significance in the overall architecture.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The CPU is often referred to as the brain of the computer. It executes instructions from programs and manages data processing tasks. Its performance directly affects the speed and efficiency of the entire system.
Memory (RAM)
Random Access Memory temporarily stores data that the CPU needs while performing tasks. This allows for quick access and enhances multitasking capabilities, significantly improving overall system responsiveness.
| Component | Key Function |
|---|---|
| CPU | Executes instructions and manages data processing |
| RAM | Stores temporary data for quick access |
| Motherboard | Connects all components and facilitates communication |
| Storage (HDD/SSD) | Holds permanent data and programs |
| Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) | Renders images and videos, enhancing visual performance |
Importance of Motherboard in PCs
The motherboard serves as the backbone of a computer, integrating various components and facilitating communication among them. Its significance lies not only in providing physical connections but also in ensuring that all elements work harmoniously to deliver optimal performance.
Key Functions of the Motherboard
- Connection Hub: It connects the CPU, RAM, storage devices, and other peripherals, enabling them to function as a cohesive unit.
- Power Distribution: The motherboard distributes electrical power from the power supply to all connected components.
- Data Transfer: It manages data transfer between various hardware, ensuring speed and efficiency.
- Expansion Capabilities: The motherboard provides slots for additional cards and devices, allowing users to upgrade their systems as needed.
Impact on Performance and Compatibility
A well-designed motherboard influences overall system performance significantly. It determines compatibility with different processors, memory types, and expansion cards. Investing in a high-quality motherboard can enhance stability, enable better cooling solutions, and support advanced features such as overclocking.
In summary, the motherboard plays a crucial role in the functionality and reliability of a computer system, making it a vital component in any build.
Choosing the Right Power Supply
Selecting an appropriate power source is crucial for ensuring your system operates efficiently and reliably. A well-matched supply not only provides the necessary energy but also contributes to the longevity of your components.
When evaluating options, consider the following key factors:
- Wattage: Determine the total wattage required by all components to ensure adequate power delivery.
- Efficiency Rating: Look for units with higher efficiency ratings (such as 80 PLUS) to reduce energy waste and heat generation.
- Modularity: Decide between non-modular, semi-modular, or fully modular designs for better cable management and airflow.
- Connectors: Ensure the supply has the right connectors for your components, including the motherboard and graphics card.
- Brand Reputation: Opt for reputable manufacturers known for reliability and quality customer support.
By taking these elements into account, you can make an informed decision that meets your system’s demands and enhances overall performance.
Graphics Cards: A Closer Look
Graphics cards serve as the vital engine behind visual processing in computers, translating data into images and animations. Their importance in gaming, design, and other graphic-intensive applications cannot be overstated. Understanding their functionality and components helps users make informed choices for optimal performance.
Modern graphics units are equipped with various features that enhance their capabilities. Below is a table outlining key specifications and considerations:
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| GPU Architecture | The underlying design that affects performance and efficiency. |
| VRAM | Dedicated memory that stores textures and frame data for quick access. |
| Clock Speed | The frequency at which the GPU operates, influencing speed and responsiveness. |
| Cooling Solutions | Methods used to dissipate heat, crucial for maintaining performance under load. |
| Connectivity Options | Types of ports available for connecting displays and additional peripherals. |
By delving into these specifications, users can identify the ultimate graphics card that meets their specific needs, whether for casual use or demanding tasks.
Storage Options: SSD vs HDD
When it comes to data storage, two popular technologies often come into play, each offering distinct advantages and drawbacks. Understanding their differences can help users make informed decisions based on their needs and preferences.
| Feature | SSD (Solid State Drive) | HDD (Hard Disk Drive) |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Faster data access and transfer rates | Slower performance, especially for large files |
| Durability | More resistant to physical shock | Vulnerable to damage from drops |
| Storage Capacity | Higher cost for large capacities | More affordable for larger volumes |
| Power Consumption | Lower energy usage | Higher energy consumption |
| Noise Level | Quiet operation | Can be noisy due to moving parts |
Choosing between these storage solutions ultimately depends on individual requirements such as speed, capacity, and budget considerations.
Cooling Solutions for Optimal Performance
Maintaining an efficient thermal management system is crucial for maximizing the capabilities of any computing system. Proper cooling mechanisms ensure that the internal components operate at ideal temperatures, thereby enhancing stability, longevity, and overall efficiency. This section explores various strategies to achieve optimal thermal performance.
Types of Cooling Solutions
Different methods can be employed to manage heat effectively. Here are some common cooling strategies:
- Air Cooling: Utilizes fans and heatsinks to dissipate heat.
- Liquid Cooling: Involves circulating liquid through a system to absorb and transfer heat away from components.
- Phase Change Cooling: Uses refrigerants to absorb heat through phase transitions.
Considerations for Effective Cooling

When selecting a cooling method, consider the following factors:
- Component Compatibility: Ensure the cooling solution fits with the existing hardware.
- Noise Levels: Some cooling systems can be loud; choose one that meets your noise tolerance.
- Space Availability: Assess the physical space within the case to accommodate the cooling solution.
- Maintenance Requirements: Consider how easy it is to maintain and clean the cooling system.
Implementing the right cooling solution is vital for achieving the best performance and reliability in any computing environment. Understanding the options available and their respective advantages will empower users to make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs.
Building a Balanced PC System
Creating a harmonious computing setup involves ensuring that all components work together efficiently. A well-rounded configuration not only enhances performance but also maximizes value for the user.
To achieve this balance, consider the following key elements:
- Processor: Choose a CPU that matches your workload requirements.
- Memory: Ensure sufficient RAM for multitasking and application demands.
- Storage: Opt for a mix of SSDs for speed and HDDs for capacity.
- Graphics: Select a GPU that complements your gaming or creative needs.
- Power Supply: Invest in a reliable PSU to support all components adequately.
- Cooling: Incorporate effective cooling solutions to maintain optimal temperatures.
By carefully selecting each element, you can create a system that not only meets your expectations but also provides a seamless experience across various tasks.