
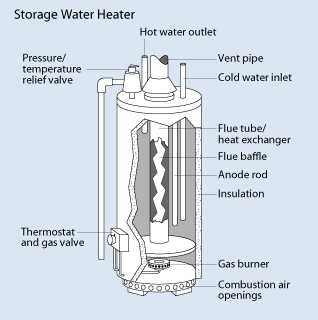
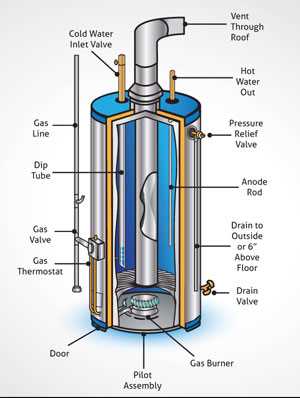
Introduction: Within the intricate workings of a system designed for heating fluids through the combustion of a specific type of fuel, lies a network of interconnected components. These elements collectively contribute to the efficient conversion of energy, ensuring the consistent supply of warmth as required.
Detailing: Each constituent part plays a crucial role in this process, from the primary mechanisms responsible for igniting the fuel to the intricate conduits that facilitate the controlled flow of resulting by-products. Understanding these elements provides insight into the operational synergy necessary for sustained functionality.
Functional Aspects: Examining the operational dynamics reveals the integration of safety mechanisms, ensuring that the operation remains both efficient and secure. The intricate balance of components underscores the importance of maintenance and periodic inspection to sustain optimal performance.
Understanding Water Heating Components
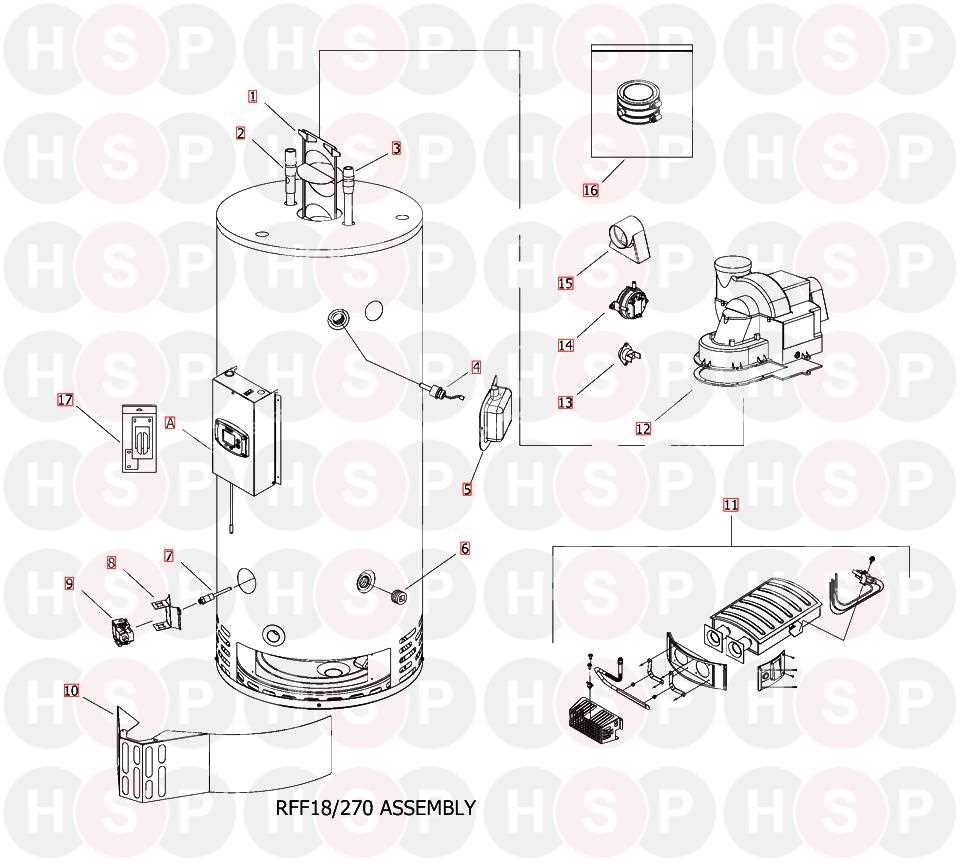
In this section, we delve into the fundamental elements that constitute a typical system for heating liquid used in residential and commercial settings. Our focus is on identifying the essential parts responsible for the process of warming fluid, essential for various applications. Let’s explore the key components that play vital roles in this thermal process.
| Heating Element |
A critical component responsible for raising the temperature of the fluid. |
| Thermostat |
Regulates the temperature of the liquid to ensure it remains within optimal ranges. |
| Insulation |
Material surrounding the system to minimize heat loss and improve efficiency. |
| Pressure Relief Valve |
Safety device designed to release excess pressure to prevent system damage. |
| Control Panel |
Interface where users manage settings and monitor operation. |
These components work in tandem to ensure effective heating and safe operation of the system, illustrating the intricate balance between functionality and safety in fluid heating applications.
Main Features of Gas Heating Systems
Modern thermal units designed for residential use offer efficient energy solutions, making them an essential part of any home. These systems are known for their durability, performance, and the ability to consistently provide warmth throughout different seasons. Understanding the main components and their operation can help in ensuring optimal functionality.
Efficiency and Energy Saving: One of the key benefits of these units is their ability to conserve energy while providing consistent warmth. Advanced models come equipped with mechanisms that optimize fuel usage, reducing unnecessary consumption and lowering costs.
Durability and Maintenance: These systems
Exploring the Role of the Burner
The combustion element is a crucial component responsible for generating the necessary energy to initiate the heating process. It plays a pivotal part in ensuring efficient performance and optimal thermal distribution. Understanding its operation is key to maintaining an efficient system.
| Component |
Function |
| Ignition System |
Starts the combustion process by sparking the fuel source. |
Functions of the Thermostat in Heaters
The thermostat plays a crucial role in ensuring that temperature regulation is maintained within the system. Its primary function is to monitor and adjust the internal conditions, allowing the device to operate efficiently without overheating or underperforming.
Temperature Control: The thermostat constantly measures the ambient heat level, ensuring that the system stays within the desired range. Once the desired temperature is reached, it signals the system to reduce or halt energy use, maintaining efficiency.
Energy Efficiency: By optimizing the system’s operation, the thermostat helps reduce energy consumption. It prevents unnecessary heating cycles, allowing the user to conserve
Heat Exchanger: Key to Efficiency
The component responsible for transferring thermal energy plays a crucial role in maximizing the performance and overall energy usage of the system. Its ability to optimize the movement of warmth from one medium to another ensures that minimal energy is wasted, making the entire operation more effective and economical.
| Feature |
Function |
| Thermal Transfer |
Facilitates the exchange of heat between two areas without direct contact. |
Pilot Light Mechanism and Its Importance
The pilot light system plays a critical role in ensuring consistent functionality and safety within heating devices. This small flame is responsible for igniting the main burner, allowing the appliance to perform efficiently. Understanding how this mechanism works can help in maintaining optimal performance and identifying potential issues before they become significant problems.
How the Pilot System Works

The mechanism operates by sustaining a small flame that is always ready to ignite the primary burner when needed. This is achieved through a thermocouple, which monitors the flame and sends a signal to the control valve. If the flame extinguishes, the thermocouple ensures that fuel flow
Pressure Relief Valve: Safety Element

The pressure relief valve serves as a critical component that prevents potential malfunctions within the system by managing excessive internal forces. Its primary role is to ensure stability and protect the overall mechanism from unforeseen damage.
Once installed, the valve is designed to automatically open when internal pressure exceeds a safe limit, allowing the release of built-up force. This function helps to maintain co
Anatomy of the Gas Control Valve
The control valve is a key component responsible for regulating the flow of energy into the system. It ensures safe and efficient operation by managing the energy supply, helping to maintain optimal conditions. Understanding its structure and functions is crucial for anyone looking to improve or repair this type of equipment.
| Component |
Function |
| Thermostat |
Common Issues with Ignition Systems
One of the most frequent problems with modern ignition setups is the failure to consistently start the flame. This can be caused by a variety of factors, making it crucial to understand the components involved and the symptoms that indicate a malfunction. Regular checks can prevent many ignition failures and ensure the system functions reliably.
Some common issues include dirty or faulty igniters, which may struggle to produce a spark. Additionally, wiring problems or loose connections can lead to intermittent performance, disrupting the ignition process. It is also important to inspect safety mechanisms, as they might prevent the ignition from operating correctly if triggered.
Maintenance Tips for Heat Exchangers
Regular upkeep of thermal transfer components is essential to ensure optimal efficiency and longevity. These devices play a critical role in transferring energy between two or more fluids. Neglecting maintenance can lead to reduced performance and costly repairs. Here are some key practices to maintain these systems effectively.
Inspect for Leaks
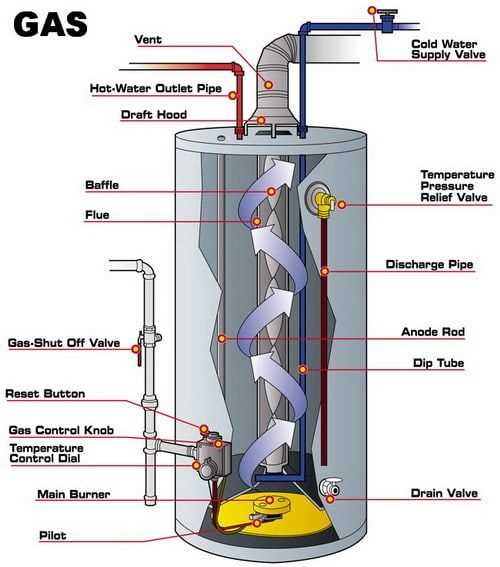
Frequent inspections are vital to identify any signs of fluid leaks. These leaks can compromise the efficiency of the system and result in wasted resources. Check connections, joints, and seals for any signs of moisture or corrosion. Addressing these issues promptly can prevent further damage and ensure smooth operation.
Clean Regularly
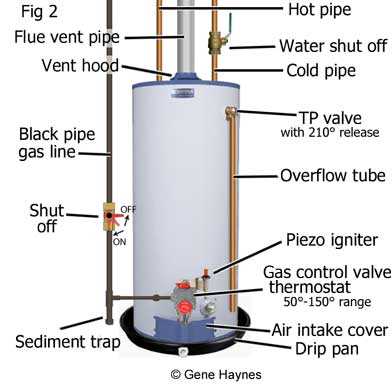
Accumulation of debris can hinder the efficiency of thermal transfer systems. Regularly cleaning the exterior and accessible interior surfaces helps maintain optimal heat exchange. Use appropriate cleaning solutions and tools to remove any buildup without damaging the materials. Schedule routine cleanings as part of your maintenance plan to keep the system running efficiently.








