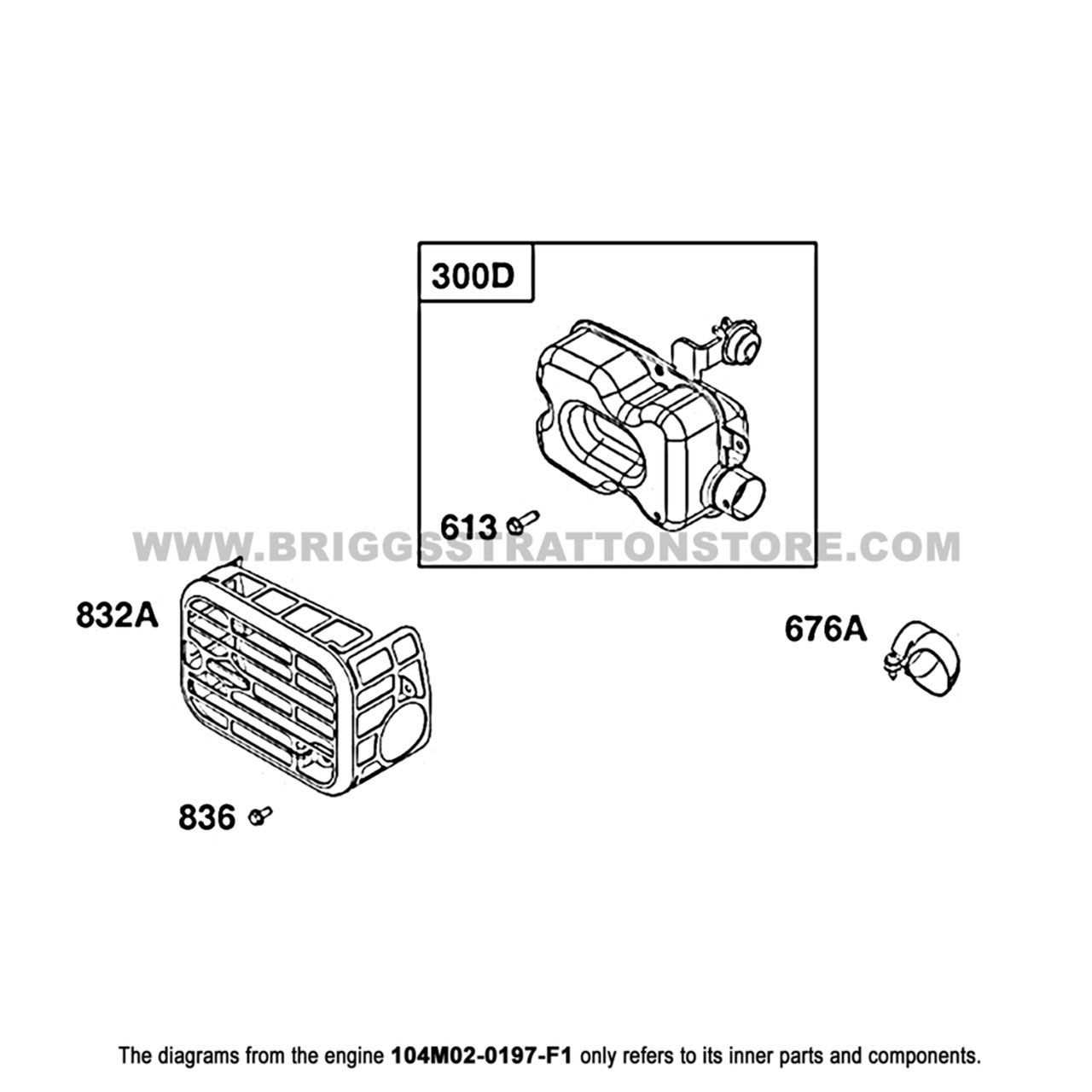
Understanding the layout and structure of various essential elements is crucial for anyone working with mechanical systems. Every system is built from carefully engineered pieces, each serving a distinct function. This guide aims to offer a clear and detailed explanation of how these individual elements are organized and how they work together to ensure optimal performance.
By examining the arrangement and relationship between these components, users can gain a deeper insight into the system’s overall functionality. Knowing how each section fits and operates is fundamental for maintenance, troubleshooting, or any modifications that may be required.
We will explore the different elements in a structured manner, focusing on their roles and connections within the assembly. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced technician, this overview will serve as a helpful reference for understanding the inner workings of this complex system.
Overview of the 104M02-0131-F1 Model
This section provides a comprehensive look at one of the most widely utilized mechanical systems in its category. Known for its efficiency and robust construction, this model has gained popularity for both its reliability and ease of integration into various machinery. It stands out for its optimal performance in demanding environments, ensuring smooth operation and longevity.
Core Features and Functionality
The model is built with precision to meet a range of functional requirements. Its components are designed to work seamlessly, providing consistent output while minimizing wear and tear. Enhanced durability is achieved through the use of high-quality materials, ensuring that the system can handle significant operational loads over time.
Applications and Versatility
This unit is versatile and finds use in various sectors, from industrial to commercial applications.
Key Components of the 104M02-0131-F1
The structure of this unit is built from a combination of essential elements, each playing a crucial role in its overall functionality. Understanding these elements provides insight into the unit’s operational efficiency and longevity. Below, we explore the main sections that contribute to its performance.
One of the primary elements is the core assembly, which serves as the central framework. This component ensures stable operation and is integral to the system’s design. Surrounding this are several interconnected modules, each dedicated to supporting specific tasks within the mechanism.
Another important segment is the fuel delivery system, responsible for providing the necessary power. This includes multiple channels that regulate flow, ensuring smooth and
Exploring the Mechanical Structure
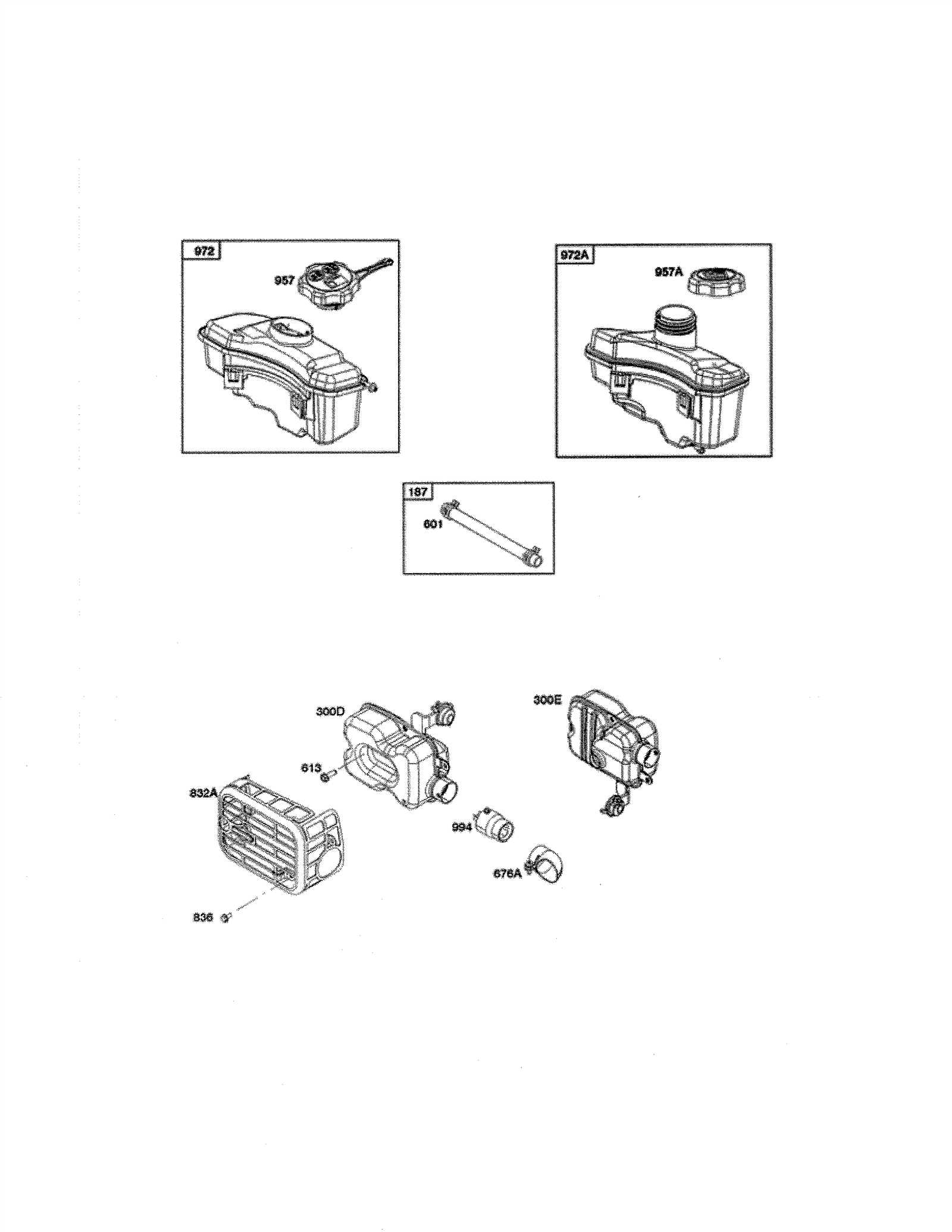
Understanding the inner workings of complex mechanical systems is essential for effective maintenance and repair. By analyzing the arrangement of various components, one can gain insight into how each element contributes to the overall functionality. This section delves into the physical configuration, focusing on key structural elements that define the operational efficiency.
Main Framework
The core framework supports the entire system, providing stability and alignment for moving parts. It is designed to withstand stress and ensure smooth operation by maintaining the necessary balance between strength and flexibility.
Key Connectors and Fasteners
Connectors and fasteners play a crucial role in holding the mechanical elements together. These components ensure that all parts remain securely in place, preventing any displacement
Electrical Connections and Wiring Layout

Understanding how components are interconnected and the overall layout of wiring is crucial for ensuring proper functionality. This section provides an overview of the necessary pathways and key connections involved in setting up a stable and efficient electrical system.
- Power Supply Routes: The proper distribution of power through designated channels is essential to avoid overloading. Each unit within the system requires a distinct connection to ensure uninterrupted current flow.
- Signal Transmission Paths: To facilitate effective communication between devices, dedicated lines for transmitting signals must be set up. Careful placement of these lines minimizes interference and enhances signal clarity.
- Grounding Techniques: Grounding plays a critical role in maintaining safety and preventing electrical faults. Establishing a solid grounding scheme helps to dissipate excess electrical charges
Functional Role of Each Part
Understanding the specific purpose of individual elements within a mechanical system is crucial for ensuring its smooth operation and maintenance. Each component plays a unique role, contributing to the overall efficiency and performance of the assembly. Let’s explore the functionality of key components and how they interact within the system.
- Engine Unit: This section is responsible for providing the core power, converting fuel into mechanical energy that drives the entire system.
- Transmission Mechanism: It ensures the proper distribution of energy from the power source to various functional areas, maintaining optimal performance under different conditions.
- Cooling System: Its role is to regulate the temperature, preventing overheating by dissipating excess heat generated during
Common Maintenance and Repair Guidelines
Regular upkeep and timely repairs are essential to ensure the longevity and efficiency of machinery. By following a structured approach to maintenance, operators can identify potential issues before they escalate, thereby reducing downtime and repair costs.
1. Regular Inspections: Conduct routine checks on all components to identify wear, damage, or misalignment. Look for signs of corrosion, leaks, or loose connections, which can indicate underlying problems that require immediate attention.
2. Lubrication: Ensure all moving parts are adequately lubricated to prevent friction and overheating. Use the recommended type of lubricant and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for frequency and application methods.
3. Cleaning: Keep the equipment free from dirt, dust, and debris. Accumulated contaminants can lead to mechanical failures and reduced efficiency. Use appropriate cleaning agents and techniques to avoid damaging sensitive components.
4. Component Replacement: When components show significant wear or damage, timely replacement is crucial. Always use high-quality replacement parts to maintain optimal performance and reliability.
5. Record Keeping: Maintain detailed records of all maintenance activities, including inspections, repairs, and part replacements. This documentation helps track the performance and history of the equipment, aiding in future maintenance planning.
By adhering to these guidelines, operators can effectively manage the health of their equipment, ensuring smooth operation and minimizing unexpected failures.
How to Identify Faulty Components
Recognizing defective elements in a device is crucial for effective troubleshooting and maintenance. Various symptoms can indicate a malfunction, including physical damage, unusual noises, or operational inconsistencies. By systematically assessing each part, one can determine which components require replacement or repair, ensuring optimal performance.
Common Signs of Malfunction
Understanding the typical indicators of failure is essential for efficient diagnostics. Here are some prevalent signs to look for:
Symptom Possible Cause Unresponsive behavior Power supply issues or circuit failure Overheating Faulty connections or short circuits Unusual noises Mechanical wear or damaged elements Fluctuating performance Intermittent faults or degraded components Steps to Diagnose Issues
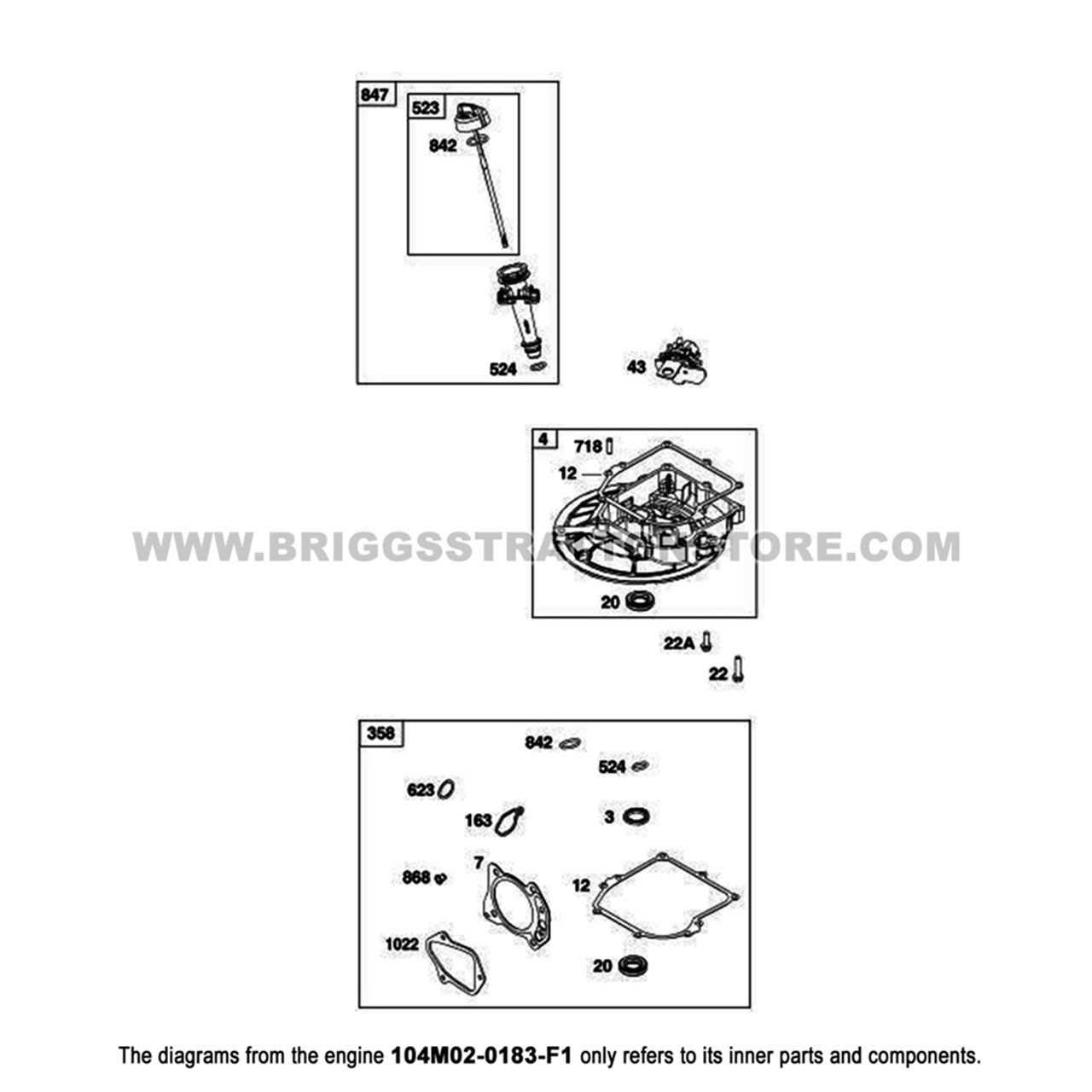
To effectively identify faulty components, follow these steps:
- Conduct a visual inspection for signs of damage.
- Test each element using appropriate diagnostic tools.
- Replace or repair components showing clear signs of malfunction.
Compatibility with Other Models
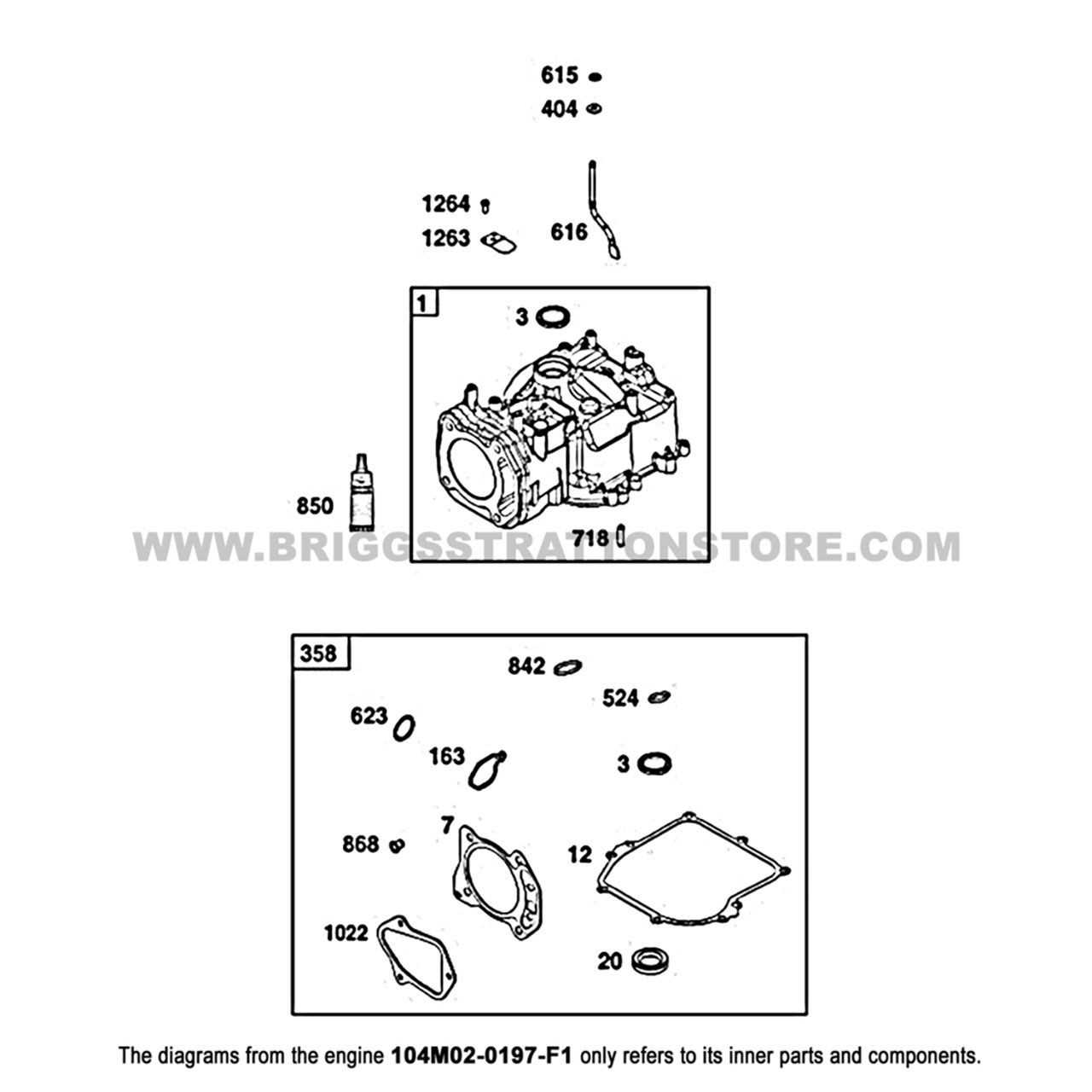
This section explores the interchangeability of components among various units within the same product line. Understanding how different models relate to each other can enhance maintenance and repair processes, allowing users to utilize compatible elements effectively. By examining the specifications and designs, users can identify which units share common features, facilitating smoother upgrades or replacements.
Similar Models in the Series
Several units within the same series offer a range of interchangeable components. These models may share similar design philosophies, making them suitable for upgrades or replacements. Users should consult specific technical manuals or compatibility charts to ensure seamless integration when substituting parts.
Cross-Compatibility with Other Lines
In addition to the internal compatibility within a series, some components may also work with other lines of products. Manufacturers often standardize certain features across different models, which can be advantageous for users seeking alternatives. It’s essential to verify compatibility by checking specifications before attempting to replace or upgrade components from different product lines.
Best Practices for Replacement Parts
When it comes to maintaining the longevity and efficiency of any equipment, understanding the best strategies for swapping out components is crucial. Utilizing high-quality substitutes not only enhances performance but also ensures safety and reliability in operation. Here are some essential guidelines to follow when considering replacements.
Quality over Cost
Choosing components based solely on price can lead to complications down the line. It’s essential to invest in quality replacements that meet or exceed the original specifications. This approach minimizes the risk of failures and costly repairs in the future.
Proper Installation Techniques
Even the best replacements can underperform if not installed correctly. Always refer to manufacturer guidelines and ensure that tools are suitable for the job. Proper alignment and secure fastening can make a significant difference in functionality.
Consideration Recommendation Material Quality Opt for OEM or reputable aftermarket options Installation Method Follow manufacturer’s installation instructions carefully Post-Installation Checks Conduct thorough testing to ensure proper operation Troubleshooting Tips for Smooth Operation
Ensuring optimal functionality of any complex system often requires attention to detail and proactive maintenance. Identifying common issues early can prevent minor setbacks from evolving into major failures, thereby enhancing the overall performance and longevity of the equipment.
Regular Maintenance Checks
Implementing a routine inspection schedule is essential. Look for signs of wear and tear, including loose connections or signs of corrosion. Regularly clean components to prevent dust buildup, which can hinder performance. Keep an eye on fluid levels and ensure that they meet the manufacturer’s specifications.
Effective Troubleshooting Techniques
When issues arise, systematic troubleshooting is key. Start by isolating the problem–this can often be achieved by observing the system during operation. If a malfunction is detected, consult the user manual for diagnostic guidance. Utilizing a process of elimination can help pinpoint faulty components, allowing for efficient repairs.
Frequently Asked Questions About Parts

This section addresses common inquiries related to components and their specifications. Understanding various aspects of these elements can help ensure effective maintenance and optimal performance. Below are some of the most frequently asked questions along with their detailed responses.
What Should I Consider When Selecting Components?
When choosing components, it’s crucial to assess factors such as compatibility, specifications, and quality. Compatibility ensures that the selected item will function correctly with existing systems. Additionally, reviewing specifications guarantees that the component meets performance requirements.
How Can I Identify a Malfunctioning Element?
Identifying a malfunctioning element often involves observing irregular behavior, such as unexpected noises or performance issues. Performing routine inspections can aid in early detection. Look for signs of wear or damage, and consult documentation for troubleshooting tips to address any issues.