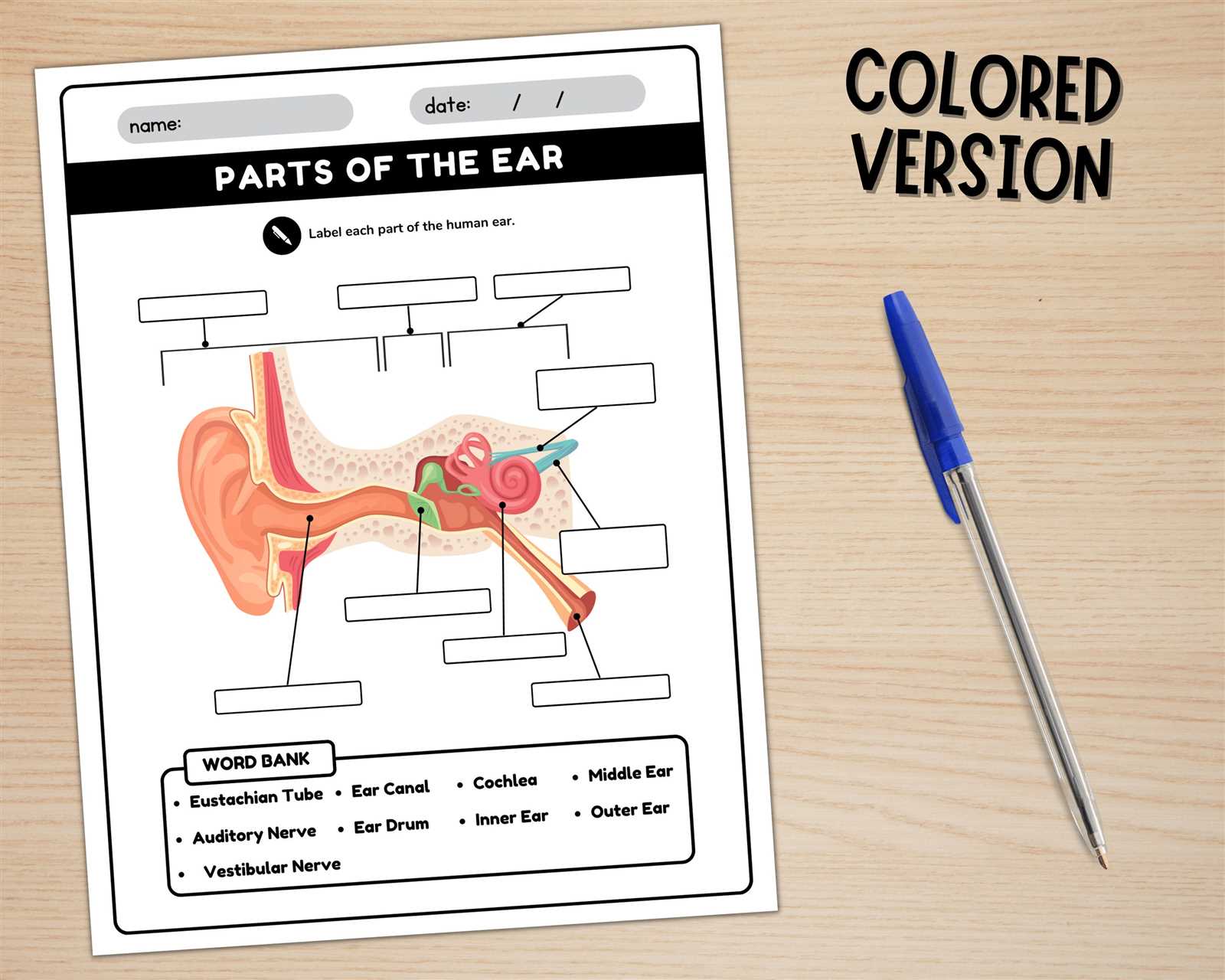
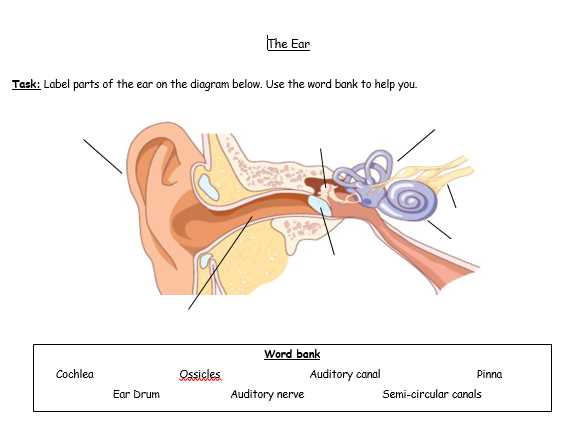
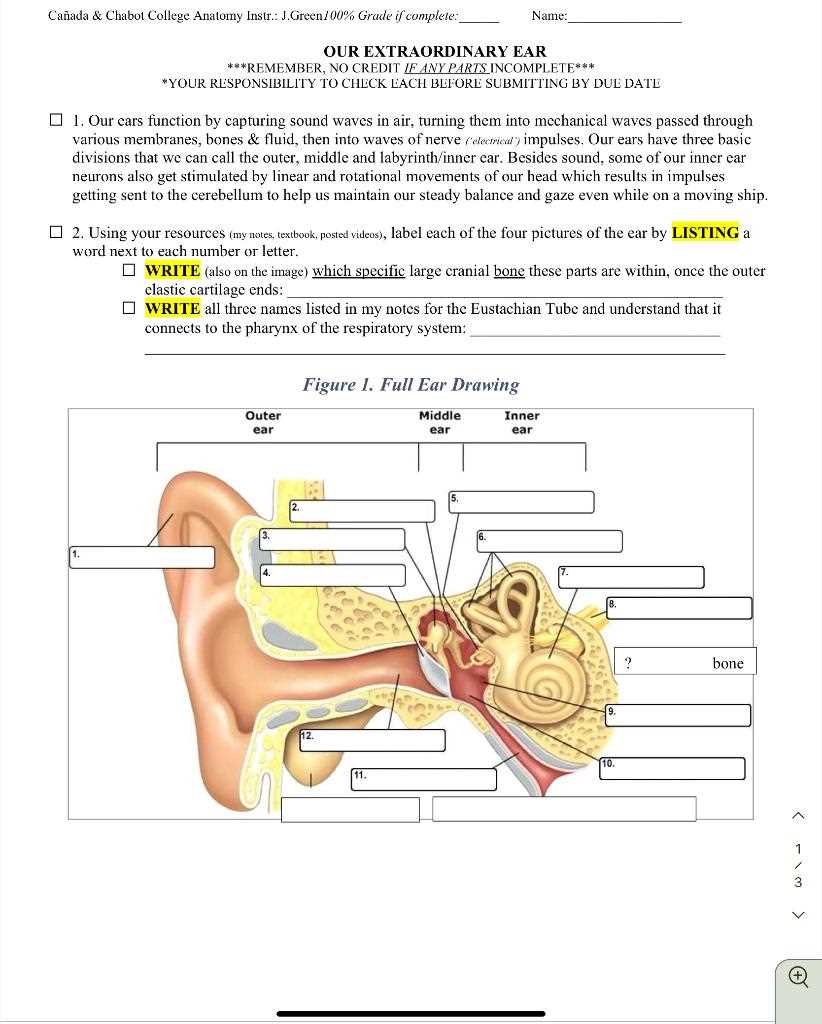
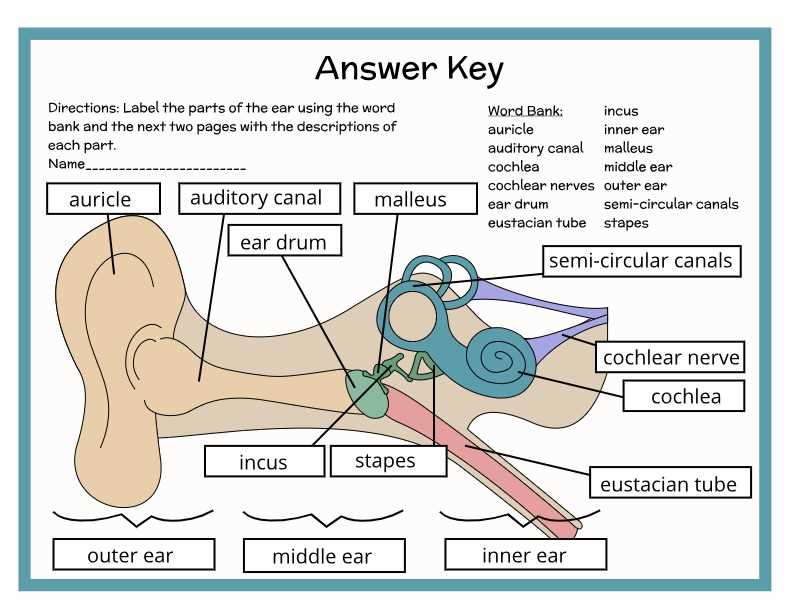
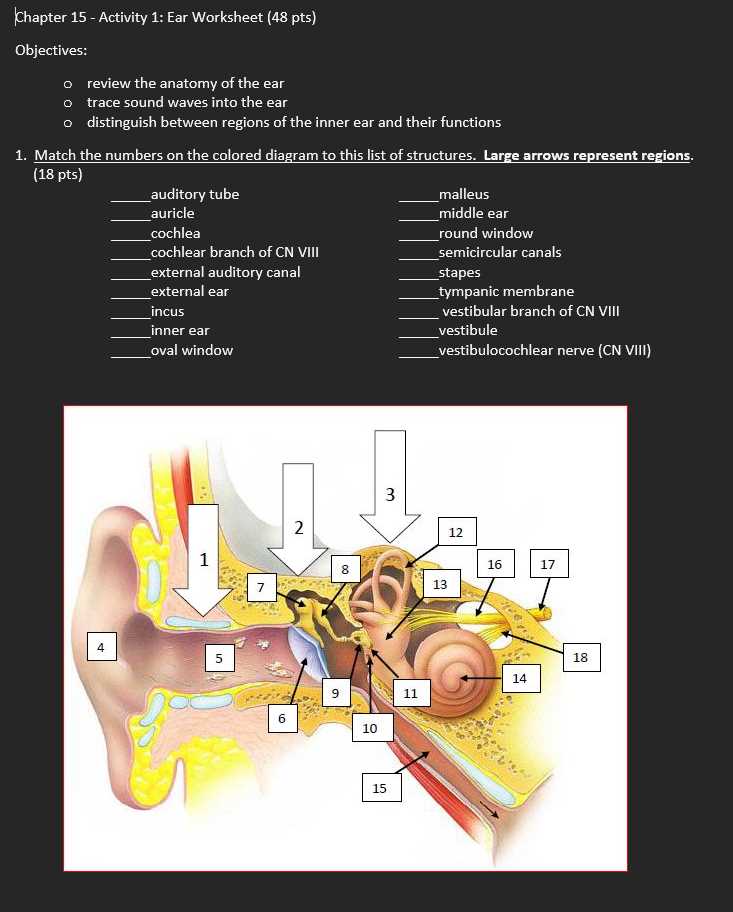
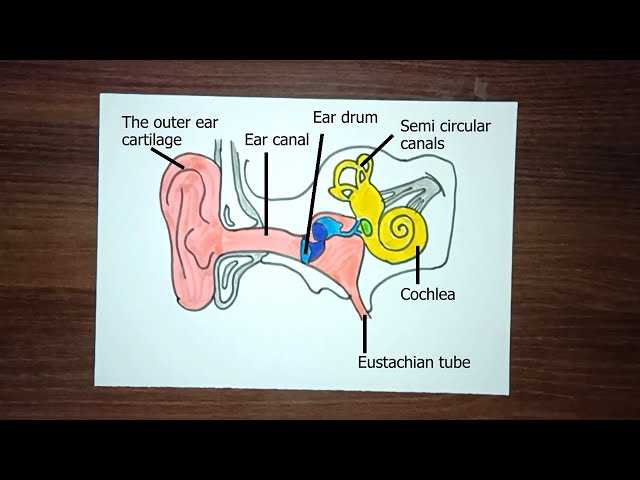
Anatomy of hearing organ is complex and fascinating, comprising various components that work together to facilitate sound perception. Each section plays a crucial role in the auditory process, contributing to our ability to perceive and interpret sounds from the environment.
Visual representations serve as valuable tools for comprehending these intricate structures. By studying these illustrations, individuals can gain insights into the functional relationships among different elements, enhancing their understanding of how we hear.
Engaging with this material can be particularly beneficial for students and anyone interested in biology or health sciences. It fosters a deeper appreciation for the remarkable capabilities of our sensory systems and emphasizes the importance of auditory health.
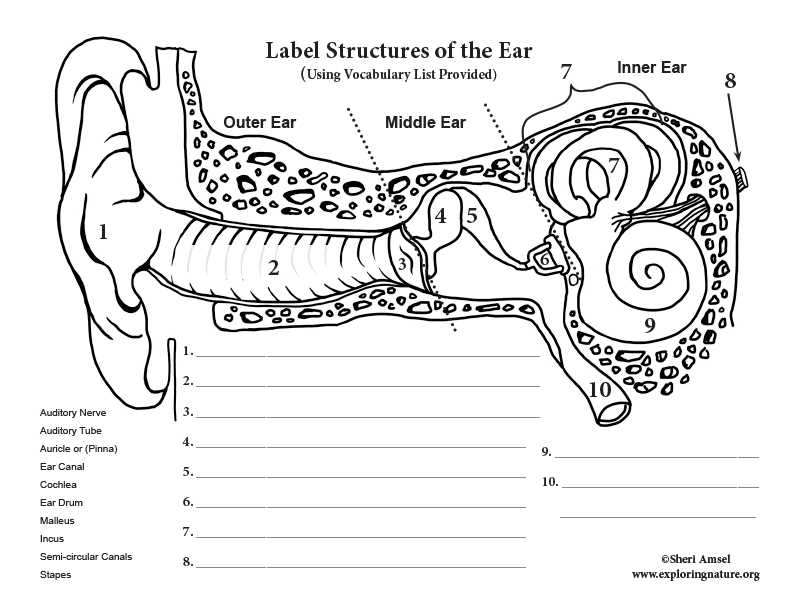
This section provides an overview of essential structures involved in auditory perception and balance. Understanding these components is crucial for comprehending how sound waves are processed and how our body maintains equilibrium. Each structure plays a distinct role, contributing to the overall functionality of hearing and balance.
Key Structures
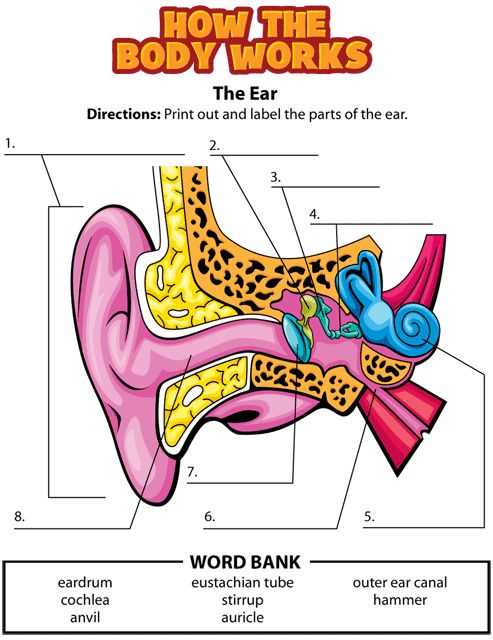
In this overview, we will explore various crucial elements that work together to facilitate the hearing process and maintain stability. Recognizing these components can enhance one’s knowledge about auditory systems and their operations.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Outer Section | Captures sound waves and directs them inward. |
| Middle Chamber | Amplifies and transmits vibrations to the inner area. |
| Inner Area | Converts sound vibrations into neural signals. |
| Balance Organs | Regulate spatial orientation and equilibrium. |
Conclusion
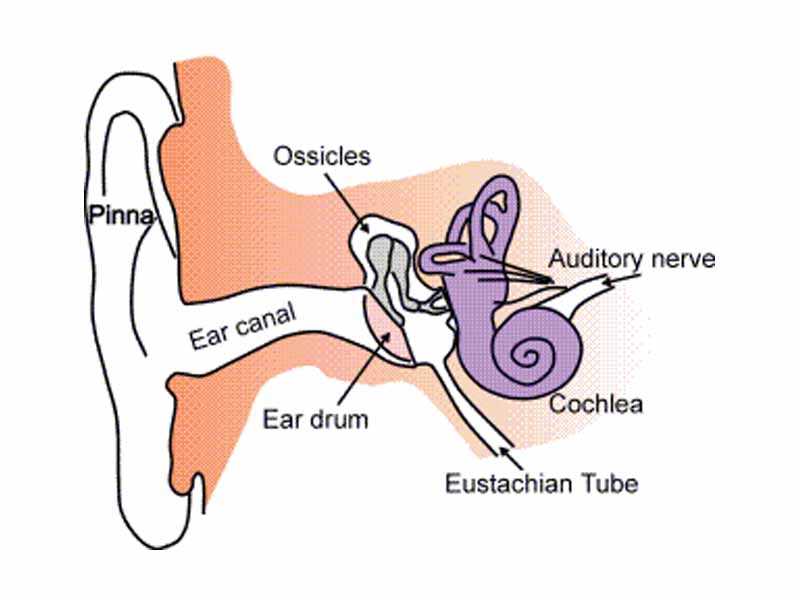
Grasping the roles of these vital elements offers insights into how our auditory system operates. This knowledge is fundamental for anyone interested in the mechanics of sound perception and balance maintenance.
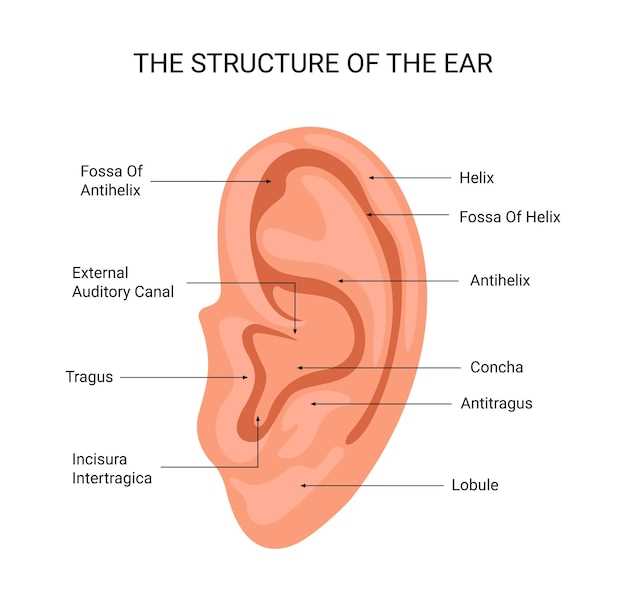
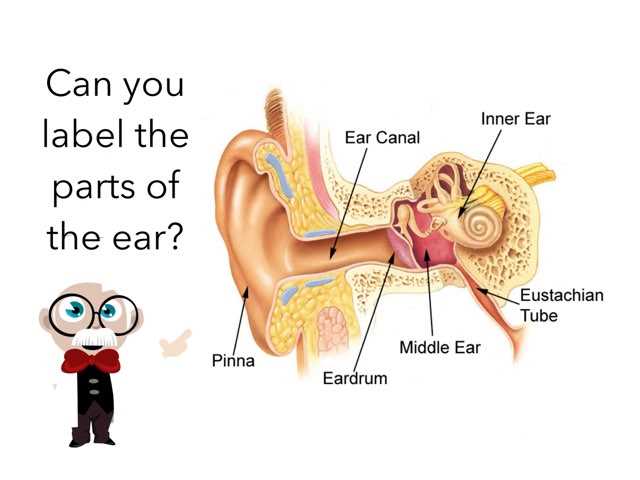
External Ear Components Explained
This section delves into crucial structures involved in sound collection and amplification. Understanding these components enhances comprehension of how we perceive auditory stimuli and interact with our environment.
Key Structures
Pinna serves as the visible portion, capturing sound waves from various directions. Its unique shape aids in locating sound sources, contributing to spatial awareness.
Auditory Canal
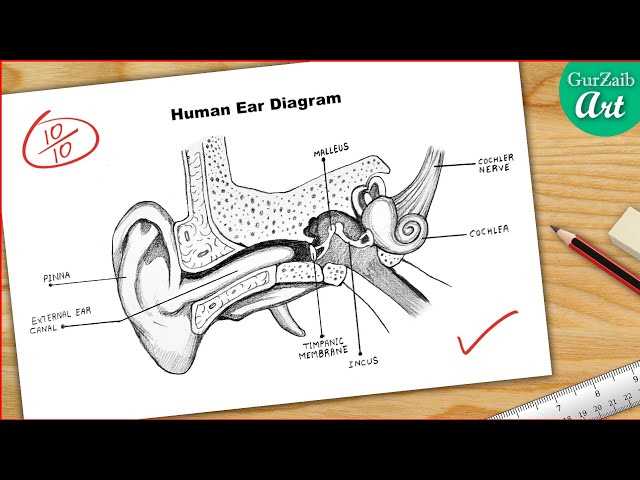
The auditory canal, a tubular pathway, channels sound waves towards deeper regions. It plays a vital role in protecting delicate components by filtering out foreign particles, ensuring optimal functionality.
Understanding the Middle Ear Structure
The middle section of our auditory system plays a crucial role in transmitting sound waves from the outer environment to the inner components responsible for processing auditory information. This area acts as a bridge, facilitating the efficient transfer of vibrations that ultimately lead to our ability to hear and interpret sounds.
Anatomical Features
Within this central region, several key elements contribute to its function. A series of small bones work in unison to amplify and convey sound vibrations from the external surroundings to the internal structures. Additionally, a cavity filled with air is essential for maintaining pressure balance, ensuring optimal performance in hearing tasks.
Functionality and Importance
This section of the auditory system not only aids in sound transmission but also plays a protective role. It helps prevent potential damage to more delicate inner components by regulating pressure and filtering out harmful frequencies. Understanding its structure and functions can enhance our appreciation of the complexities involved in hearing.
Inner Ear Anatomy Details
The intricate structure located within the skull plays a crucial role in hearing and balance. This fascinating system consists of various components that work harmoniously to process sound waves and maintain equilibrium. Understanding this complex arrangement is essential for grasping how auditory and vestibular functions operate seamlessly.
Key Components
Among the primary elements are the cochlea, responsible for transforming sound vibrations into neural signals, and the vestibular system, which helps regulate balance and spatial orientation. The cochlea resembles a spiral staircase, filled with fluid that moves in response to sound waves. Additionally, the semicircular canals play a vital role in detecting rotational movements.
Functional Importance
Each component within this inner structure contributes to an overall function. Efficient communication between these elements is vital for interpreting sound and maintaining stability. Any disruption within this system can lead to hearing impairments or balance disorders, highlighting the importance of its integrity.
Function of the Ear Canal
The auditory passage serves a vital role in hearing, acting as a conduit for sound waves. Its structure is specifically designed to enhance auditory experiences, ensuring that sounds are effectively channeled toward the inner workings of hearing.
One of the primary functions is to protect delicate components within, filtering out dust and foreign particles. Additionally, this channel aids in maintaining balance and pressure within the auditory system, contributing to overall auditory health.
Moreover, the auditory passage helps amplify certain frequencies, allowing for a clearer perception of sounds. This amplification process is essential for distinguishing between different pitches and tones, which is crucial for effective communication and environmental awareness.
In summary, the auditory passage not only facilitates the transmission of sound but also plays a protective and amplifying role, significantly influencing auditory perception and overall ear functionality.
The Role of the Eardrum
An essential component of auditory perception, this structure serves as a boundary between outer and inner chambers, facilitating sound transmission. Vibrations produced by external stimuli are transformed into mechanical waves, allowing for effective communication of auditory information.
Functionality in Sound Processing
Upon encountering sound waves, this membrane vibrates in response, initiating a chain reaction that leads to the conversion of acoustic signals into neural impulses. The efficiency of this process is vital for clarity and precision in hearing.
Protection and Pressure Regulation
Beyond its role in sound detection, this membrane also acts as a protective barrier, preventing foreign particles from entering deeper structures. Additionally, it helps maintain equilibrium by regulating pressure within the auditory system, contributing to overall auditory health.
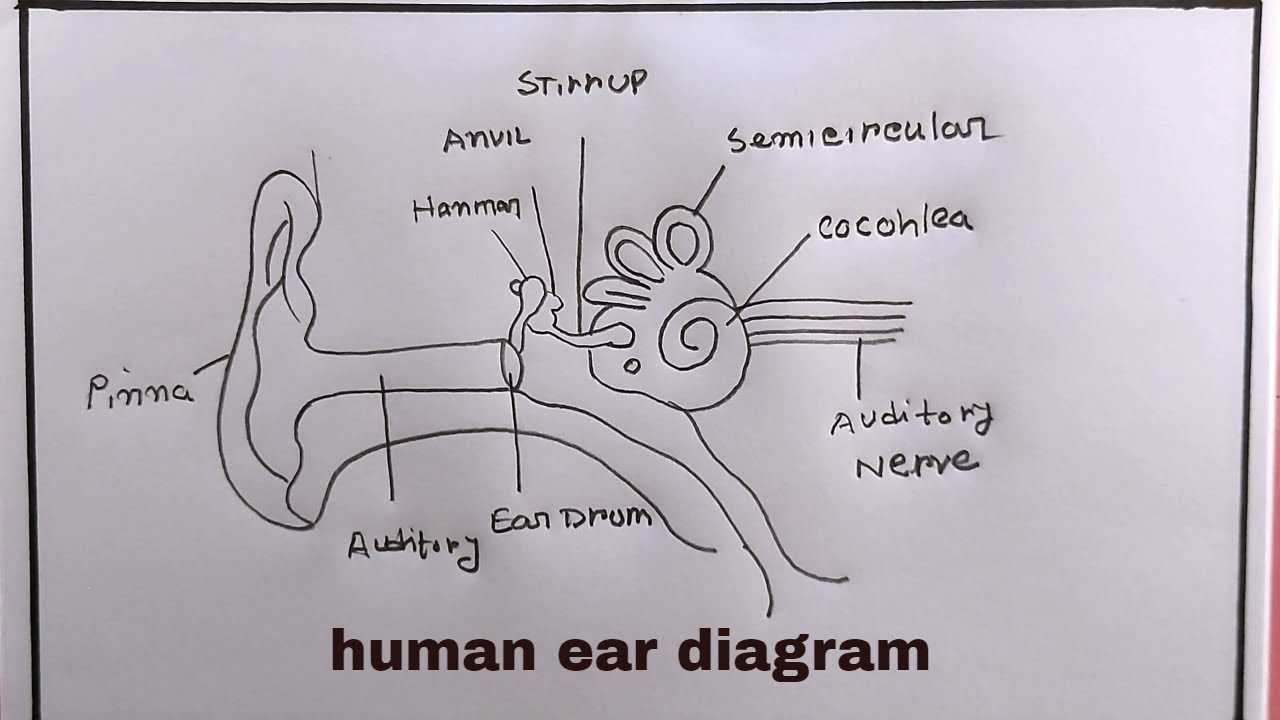
Identifying the Ossicles
Within the intricate structure responsible for auditory perception, three small bones play a crucial role in sound transmission. These delicate components are essential for converting vibrations from the outer realm into signals that can be interpreted by the brain.
These bones, known for their unique shapes and functions, work in harmony to enhance hearing. Below are the key characteristics of each:
- Malleus – Also called the hammer, this bone connects to the eardrum and is the first in the chain of transmission.
- Incus – Commonly referred to as the anvil, it serves as the bridge between the malleus and the stapes.
- Stapes – Known as the stirrup, this bone is the smallest in the body and interfaces with the inner structure, facilitating sound entry.
Understanding these essential components is vital for grasping how sound travels through the auditory system, ultimately leading to the experience of hearing.
The Cochlea and Its Importance
The cochlea is a spiral-shaped structure crucial for auditory perception. This unique formation plays a vital role in transforming sound waves into electrical signals that the brain interprets as sound. Understanding this mechanism is essential for grasping how hearing functions and the significance of maintaining auditory health.
Structure and Function
Inside the cochlea, fluid-filled chambers contain specialized hair cells that respond to sound vibrations. When sound waves enter, they create pressure changes that move the fluid. This movement stimulates the hair cells, converting mechanical energy into neural impulses, allowing for sound recognition.
Significance in Hearing
The cochlea not only facilitates sound perception but also enables the discrimination of different frequencies. Its intricate design allows for the detection of a wide range of pitches, making it essential for understanding speech and enjoying music. Damage to this structure can lead to hearing loss, emphasizing the importance of protecting auditory health.
Understanding the Semicircular Canals
These intricate structures play a vital role in maintaining balance and spatial orientation. They are part of a complex system that helps the body detect movement and changes in position, providing essential information to the brain.
Located within a bony chamber, these components are oriented in three different planes. Each canal is filled with fluid that moves in response to head movements. This fluid motion stimulates sensory cells, which send signals to the brain regarding the body’s orientation.
Understanding how these components function can enhance knowledge about balance disorders and related conditions. Their sensitivity to rotational movements makes them crucial for activities such as walking, running, and any action requiring coordination.
In summary, these structures are essential for processing information about motion and equilibrium, allowing individuals to navigate their surroundings with confidence.
The Vestibular System Functionality
This intricate network plays a crucial role in maintaining balance and spatial orientation. By processing various sensory inputs, it enables individuals to navigate their environment effectively.
Key functions of this system include:
- Detecting head movements and position changes
- Regulating balance during physical activities
- Facilitating coordination between visual and sensory information
- Contributing to postural stability
Furthermore, disruptions in its functionality can lead to various challenges, including dizziness and disorientation. Understanding how this system operates is essential for diagnosing and managing related conditions.
Connections to the Auditory Nerve
The auditory pathway plays a crucial role in the perception of sound. It encompasses various structures that transmit signals from sensory receptors to the brain, enabling the interpretation of auditory information.
Components of the Auditory Pathway
Key elements involved in this pathway include:
- Cochlea
- Hair cells
- Spiral ganglion neurons
- Auditory nerve fibers
Function of Connections
Connections facilitate communication between sensory receptors and the central nervous system. When sound waves enter the cochlea, they stimulate hair cells, which convert mechanical vibrations into electrical signals. These signals are then transmitted through the spiral ganglion neurons to the auditory nerve fibers, leading to the auditory cortex in the brain.
Importance of Ear Labelling for Education
Understanding auditory anatomy is crucial for students and professionals in various fields, including medicine, audiology, and music. By familiarizing oneself with these components, individuals can enhance their comprehension of auditory functions and disorders. This knowledge serves as a foundation for further studies and practical applications in diverse disciplines.
Accurate identification of these structures not only aids in educational settings but also fosters effective communication among specialists. Furthermore, it empowers learners to engage with complex topics such as hearing health and sound production. Developing a clear mental image of these elements is vital for anyone aspiring to excel in related areas.
| Concept | Importance |
|---|---|
| Identification | Facilitates understanding of auditory functions |
| Communication | Enhances dialogue among professionals |
| Application | Supports practical skills in related fields |
| Foundation | Builds a base for advanced studies |