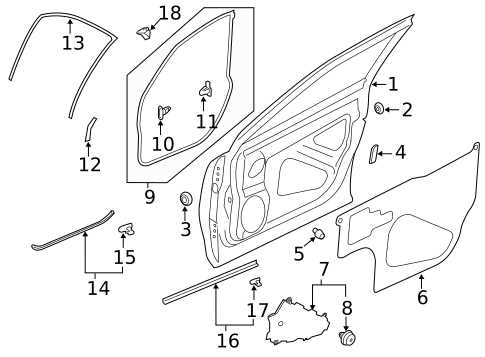
The intricate network of a vehicle’s assembly is crucial for its overall performance and longevity. Understanding the arrangement of various elements is essential for both enthusiasts and professionals engaged in maintenance or modification tasks. This section delves into the essential components that contribute to the functionality of a particular model, offering insights into their positions and relationships within the system.
By examining the structural configuration, individuals can gain a comprehensive view of how each element interacts with others. This knowledge not only aids in troubleshooting issues but also enhances the ability to make informed decisions during repairs or upgrades. Familiarity with the layout fosters a deeper appreciation for the engineering that underpins modern automotive design.
Whether you are a DIY enthusiast seeking to enhance your mechanical skills or a technician aiming to streamline your workflow, having access to a clear overview of component locations proves invaluable. This resource serves as a guide to navigating the complexities of the assembly, empowering users to tackle projects with confidence.
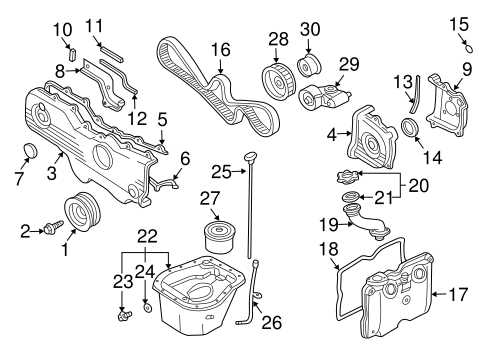
The suspension system of a vehicle plays a crucial role in providing a smooth ride while ensuring stability and handling. This system comprises various components that work together to absorb shocks and maintain contact between the tires and the road surface. Understanding these elements is essential for anyone interested in automotive mechanics or maintenance.
Key components of the suspension system include:
- Shock Absorbers: These devices dampen the impact of bumps and irregularities on the road, enhancing ride comfort and vehicle control.
- Struts: Struts combine the functions of a shock absorber and a structural element, providing support for the vehicle’s weight and absorbing road shocks.
- Springs: Springs store energy and absorb energy from road conditions. They are vital for maintaining vehicle height and handling.
- Control Arms: These components connect the chassis to the wheels, allowing for controlled movement and alignment of the wheels as the vehicle travels over uneven surfaces.
- Stabilizer Bars: Also known as sway bars, these bars reduce body roll during cornering, improving stability and handling.
Proper maintenance and understanding of these components can significantly enhance vehicle performance and safety. Regular checks and replacements, when necessary, ensure optimal functionality and comfort during travel.
Braking System Components Overview
The braking system plays a crucial role in vehicle safety, allowing for effective deceleration and control. Understanding the various elements that comprise this system is essential for maintenance and repair. Each component works in harmony to ensure optimal performance and responsiveness when bringing the vehicle to a stop.
Key components of the braking assembly include the master cylinder, brake lines, calipers, rotors, and pads. Each part serves a distinct function, contributing to the overall efficiency and reliability of the braking process.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Master Cylinder | Generates hydraulic pressure to activate the braking mechanism. |
| Brake Lines | Transport hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the brake components. |
| Calipers | Clamp the brake pads against the rotors to create friction. |
| Rotors | Provide a surface for the brake pads to press against, facilitating stopping. |
| Brake Pads | Friction material that engages with the rotors to slow down the vehicle. |
Electrical System Layout
The configuration of the electrical network in a vehicle plays a crucial role in its overall functionality. This network encompasses various components, including wiring harnesses, sensors, and control units, all working together to ensure optimal performance and safety. Understanding this arrangement is essential for diagnosing issues and implementing repairs effectively.
At the core of the electrical system lies the power distribution module, which manages the flow of electricity to different areas of the vehicle. This unit connects the battery to various electrical components, allowing them to operate efficiently. Additionally, fuse boxes serve as protective barriers, safeguarding the system from overloads and shorts.
Within this framework, numerous electronic control units (ECUs) monitor and regulate functions such as engine management, climate control, and infotainment systems. Each ECU communicates with others through a network, facilitating seamless operation and enhancing user experience. Understanding the layout of these components aids technicians in troubleshooting and maintaining the vehicle’s electrical integrity.
Cooling System Insights
The efficiency of a vehicle’s cooling apparatus is crucial for maintaining optimal engine performance and longevity. This system plays a vital role in regulating temperature, preventing overheating, and ensuring the smooth operation of various components. Understanding its functionality can help in diagnosing potential issues and implementing effective maintenance practices.
A comprehensive examination of the cooling apparatus includes its main constituents, each contributing to the system’s overall efficacy. Proper maintenance of these elements is essential for ensuring the vehicle operates efficiently under various conditions.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Radiator | Dissipates heat from the coolant, allowing it to cool before circulating back to the engine. |
| Water Pump | Circulates coolant throughout the engine and radiator, maintaining fluid flow. |
| Thermostat | Regulates coolant temperature by controlling flow to the radiator based on engine heat. |
| Cooling Fan | Assists in air circulation through the radiator, enhancing heat dissipation, especially at low speeds. |
| Hoses | Transport coolant between the engine, radiator, and other components, ensuring a closed system. |
Regular inspections and timely replacements of these components can prevent overheating and ensure the vehicle remains in peak condition. Understanding the cooling apparatus enhances overall vehicle reliability and performance.
Fuel System Configuration
The arrangement of the fuel delivery system plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and efficiency of any vehicle. This configuration consists of various components that work together to manage the flow of fuel from the tank to the engine, facilitating proper combustion and enhancing overall functionality.
Key elements of this assembly include:
- Fuel Tank: The storage unit that holds the fuel until needed.
- Fuel Pump: Responsible for drawing fuel from the tank and pushing it through the system.
- Fuel Filter: Ensures that any contaminants are removed from the fuel before it reaches the engine.
- Fuel Lines: Tubes that transport fuel from the tank to the engine, maintaining pressure and flow.
- Fuel Injectors: Devices that atomize the fuel and deliver it into the combustion chamber at the right moment.
- Pressure Regulator: Maintains consistent fuel pressure within the system, ensuring efficient operation.
Understanding the arrangement and function of these components is essential for diagnosing issues related to fuel delivery, ensuring that the engine receives the necessary amount of fuel for optimal performance.
Steering Mechanism Explanation
The steering system plays a crucial role in vehicle maneuverability, allowing the driver to guide the automobile effectively. This intricate assembly transforms the rotational movement of the steering wheel into directional control of the wheels, ensuring a smooth and responsive driving experience.
Key components of the steering assembly include:
- Steering Wheel: The primary interface for the driver, enabling input for direction changes.
- Steering Column: Connects the steering wheel to the rest of the system and often houses essential electrical components.
- Gearbox: Converts the circular motion of the steering wheel into linear motion, facilitating wheel movement.
- Linkage: Transfers motion from the gearbox to the wheels, often consisting of rods and joints.
- Wheel Assembly: The final point of control, where the directional adjustments are executed.
In modern vehicles, power assistance is often integrated, enhancing the driver’s ability to steer effortlessly, especially at low speeds. This system can be hydraulic or electronic, offering varying levels of support based on driving conditions.
Regular maintenance of the steering assembly is vital for safety and performance. Common issues that may arise include:
- Worn-out components leading to looseness in the steering.
- Fluid leaks in hydraulic systems causing diminished power assistance.
- Electrical failures in electronic systems impacting responsiveness.
Understanding the functionality of the steering system is essential for diagnosing problems and ensuring optimal performance during operation.
Exhaust System Components
The exhaust system is a crucial part of any vehicle, designed to manage and direct harmful gases produced during the combustion process. Its primary function is to expel exhaust gases away from the engine while minimizing noise and emissions, thereby contributing to overall performance and environmental standards.
Key elements of the exhaust assembly include the manifold, which collects gases from the engine cylinders; the catalytic converter, responsible for converting harmful substances into less harmful emissions; and the muffler, which reduces noise generated by the escaping gases. Additionally, pipes connect these components, allowing for efficient gas flow.
Maintaining these components is essential for ensuring optimal engine performance and compliance with regulatory requirements. Regular inspections and timely replacements can prevent potential issues that may arise from wear and tear, ultimately enhancing the longevity of the vehicle’s systems.
Body Structure and Design
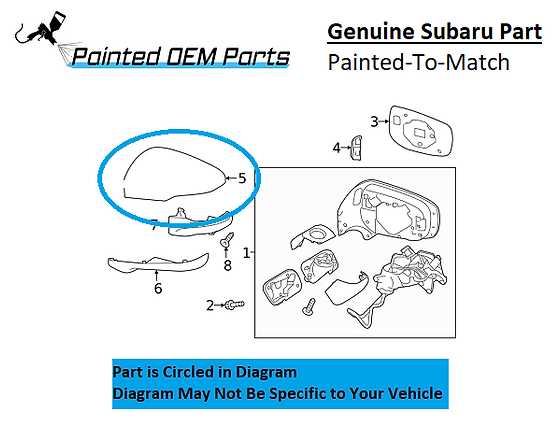
The framework and aesthetics of a vehicle play a crucial role in its performance, safety, and overall appeal. A well-engineered structure enhances stability and durability while contributing to the vehicle’s distinctive appearance. This section explores the essential aspects of a vehicle’s outer framework and design elements, focusing on how they interrelate to create a harmonious and functional unit.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Chassis | The main support structure that houses various components, providing rigidity and strength. |
| Exterior Panels | These elements not only protect the internal parts but also define the aesthetic character of the vehicle. |
| Safety Reinforcements | Strategically placed features designed to absorb impact energy and enhance occupant protection during collisions. |
| Weight Distribution | Careful balance of mass across the structure to optimize handling and stability. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Materials and coatings used to protect the structure from environmental damage and extend longevity. |
Understanding these characteristics can help in recognizing the importance of a vehicle’s outer structure, contributing not only to its functionality but also to the visual identity that resonates with consumers.
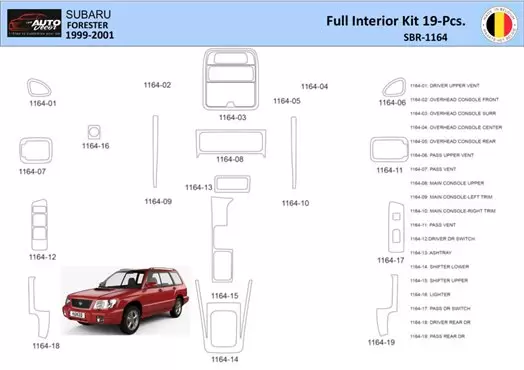
Interior Components Overview
This section provides a comprehensive look at the various elements found within the cabin of a vehicle, highlighting their functions and importance in enhancing the driving experience. Each component plays a vital role in comfort, accessibility, and overall usability.
The interior of a vehicle consists of numerous features designed to improve the user’s experience. Here are some key elements:
- Dashboard: Central hub for instruments and controls.
- Seating: Arrangements designed for comfort and support during travel.
- Infotainment System: Provides entertainment and connectivity options.
- Climate Control: Regulates temperature for passenger comfort.
- Storage Compartments: Offers space for personal items and travel necessities.
Understanding these components allows for better maintenance and upgrades, ensuring optimal functionality and comfort. Each feature is meticulously designed to cater to the needs of the driver and passengers alike.
Aftermarket Parts Considerations
When enhancing a vehicle’s performance or aesthetics, opting for alternatives can provide significant benefits. Many enthusiasts explore options beyond original components to achieve desired specifications or savings. However, careful evaluation is essential to ensure compatibility and longevity.
Quality Assurance: It is crucial to select alternatives from reputable manufacturers. Cheaper options may save money initially but can lead to increased wear and potential failures, compromising the overall experience.
Compatibility: Ensuring that chosen components fit seamlessly with existing systems is vital. Mismatched specifications can result in inefficiencies, increased maintenance, or even safety hazards.
Performance Impact: Alternatives often promise enhanced performance. It is important to understand how modifications might affect the vehicle’s operation, including handling, fuel efficiency, and overall reliability.
Warranty Considerations: Utilizing non-original components can void existing warranties. Understanding the implications of modifications on manufacturer guarantees is necessary to avoid unexpected expenses.
Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to local regulations concerning modifications is essential. Non-compliant parts can lead to legal issues, including fines or restrictions on vehicle use.
In conclusion, while exploring alternatives can be beneficial, a thorough understanding of the implications ensures a rewarding and trouble-free enhancement experience.