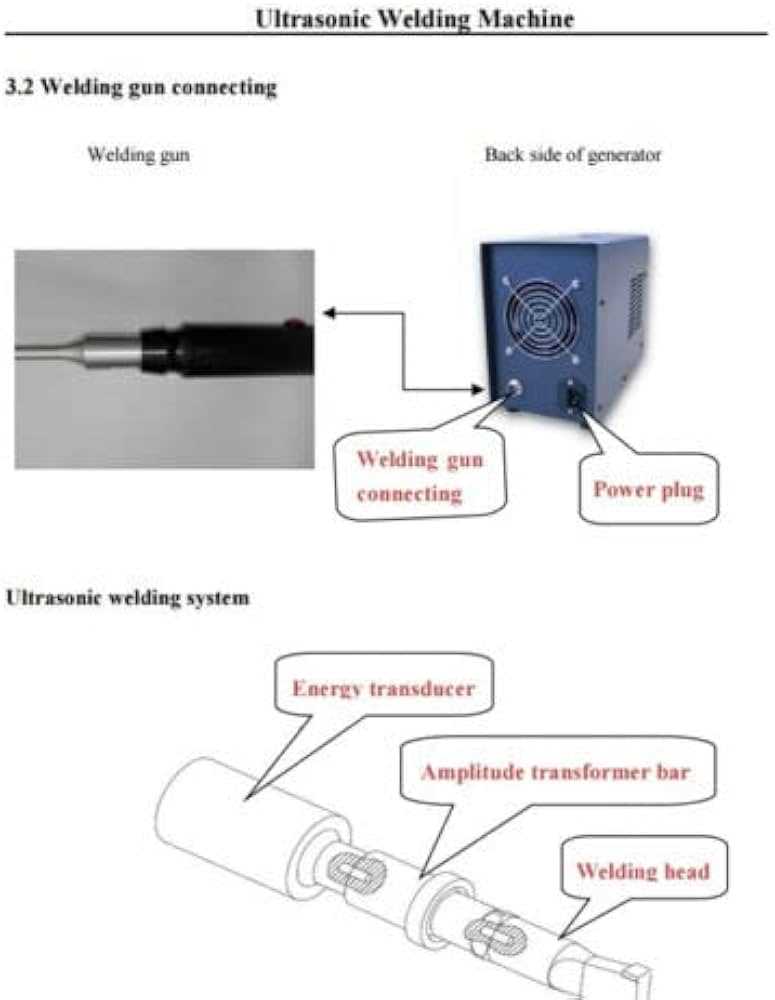
The intricate world of fabrication equipment is pivotal in various industries, encompassing an array of tools designed to join materials seamlessly. This section delves into the essential elements that contribute to the functionality and efficiency of these innovative devices, highlighting their unique roles in the assembly process. By exploring the individual components, we can gain a deeper appreciation for how they work together to achieve precise results.
Each component serves a specific purpose, ensuring optimal performance and reliability during use. Understanding the interplay between these vital elements not only enhances one’s technical knowledge but also aids in troubleshooting and maintenance. With this insight, users can effectively harness the capabilities of their equipment, leading to improved productivity and superior outcomes in their projects.
As we break down the various features, the significance of each element will become apparent. From the core functionality to the intricate details, this examination will provide a comprehensive overview of how these sophisticated tools operate. Equipped with this knowledge, individuals can navigate the complexities of their tasks with confidence and expertise.
Overview of Welding Machines
This section explores the essential concepts and components that contribute to the functionality of joining metals through heat and pressure. These devices are crucial in various industries, enabling the creation of durable and robust structures.
Types of Equipment
Various types of devices serve specific purposes in metal joining tasks. Understanding these variations helps users select the right tool for their needs.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Arc Tool | Utilizes an electric arc to generate heat for melting metal pieces together. |
| Resistance Tool | Employs electrical resistance to produce heat, fusing materials at their contact points. |
| Laser Device | Uses concentrated light to precisely melt and join metals, ideal for intricate applications. |
| TIG Gear | Involves a non-consumable tungsten electrode to create the arc and often requires a filler material. |
| MIG Gear | Feeds a continuous wire electrode that melts to form a bond between metal pieces. |
Importance in Industries
The role of these devices spans numerous sectors, from automotive to construction. Their ability to create strong, permanent connections ensures the integrity and longevity of products and structures.
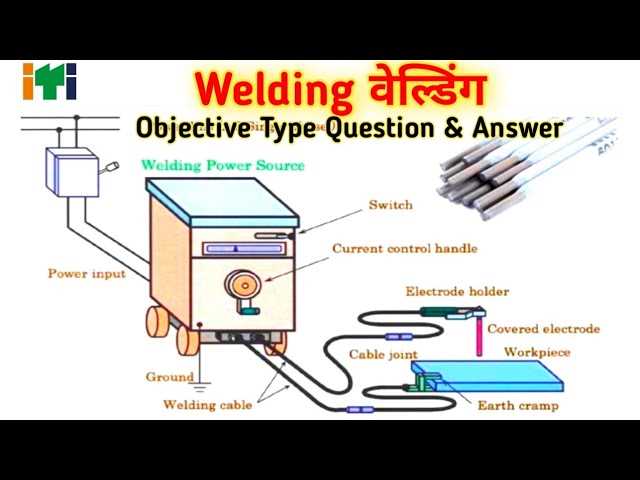
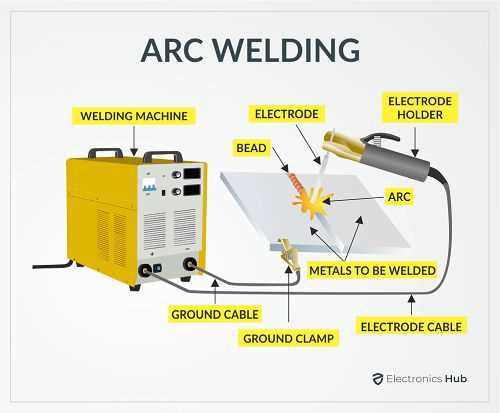
Essential Components of Welding Equipment
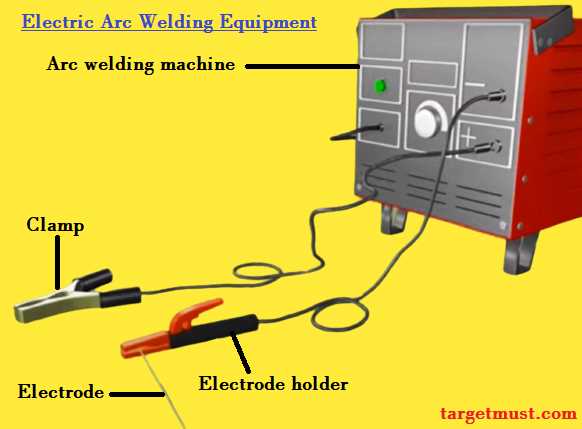
Understanding the key elements of fabrication tools is crucial for both novices and experienced operators. These components work together to create the necessary conditions for effective bonding of materials through high heat and pressure. Familiarity with these essential items ensures safety, efficiency, and the quality of the final product.
Power Source: The heart of the setup, the power source provides the necessary electrical energy to generate heat. Different types, such as alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC), cater to specific applications, influencing the outcome of the process.
Electrode: Acting as a conduit for electrical current, the electrode also serves as a filler material in some processes. The choice of electrode significantly impacts the strength and appearance of the joint.
Workpiece Holder: This element securely positions the materials being joined. A stable holder is vital for maintaining alignment and ensuring the integrity of the connection throughout the procedure.
Protective Gear: Safety equipment, including helmets, gloves, and clothing, shields the operator from harmful radiation, sparks, and heat. Proper protective gear is essential to prevent injuries during operation.
Cooling System: Many setups include a cooling mechanism to dissipate heat and protect components from overheating. This is particularly important in prolonged operations to maintain performance and longevity.
In summary, these fundamental components are integral to the functionality and effectiveness of joining techniques. Knowledge of each element enhances operational proficiency and contributes to successful outcomes in fabrication tasks.
Types of Welding Processes Explained
The art of joining materials through various techniques has evolved significantly, offering multiple approaches tailored to specific applications. Understanding these distinct methods is crucial for selecting the appropriate technique based on factors like material type, thickness, and desired strength of the bond.
Arc Techniques
One of the most prevalent approaches involves using an electric arc to generate intense heat, melting the base materials. This category includes several variations, each with its unique features. For instance, in shielded metal arc processes, a consumable electrode provides the filler material while protecting the molten pool from contaminants. Conversely, gas tungsten approaches utilize a non-consumable electrode, delivering exceptional precision.
Fusion Processes
Fusion methods rely on melting the base materials themselves, creating a strong bond as they cool and solidify. Techniques such as oxy-fuel utilize a flame generated from a mixture of oxygen and fuel gas to achieve the necessary temperature. These methods are favored for their simplicity and effectiveness in a variety of scenarios.
In summary, each technique presents unique advantages and considerations, enabling operators to choose the most effective method for their specific requirements.
Understanding Power Supply Systems
Power supply systems are essential components that ensure the efficient and reliable operation of various equipment. They convert electrical energy from one form to another, delivering the required voltage and current to the devices that depend on them. Understanding the intricacies of these systems is vital for optimizing performance and maintaining functionality.
Key elements of power supply systems include:
- Transformers: Devices that change the voltage levels in the electrical supply.
- Rectifiers: Components that convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC).
- Regulators: Systems that maintain a constant output voltage despite fluctuations in input voltage.
- Filters: Circuits that smooth out the output to remove noise and voltage spikes.
When selecting or designing a power supply system, consider the following:
- Voltage Requirements: Ensure the output matches the needs of the equipment.
- Current Capacity: Assess the maximum current draw to prevent overloads.
- Efficiency: Opt for systems that minimize energy loss during conversion.
- Safety Features: Implement protective measures against surges and faults.
By grasping the fundamental aspects of power supply systems, one can enhance the reliability and longevity of electrical devices.
Importance of Cooling Systems
Effective temperature regulation is crucial in many industrial processes. Overheating can lead to equipment failure, reduced efficiency, and compromised safety. Implementing robust cooling solutions helps maintain optimal operating conditions, ensuring longevity and reliability.
Enhancing Performance
Cooling systems play a significant role in maximizing operational efficiency. By preventing excessive heat buildup, these systems ensure that components function smoothly, which translates into higher productivity and lower downtime. Consistent temperature control allows for more precise and reliable operations.
Safety Considerations
Proper thermal management is vital for ensuring the safety of personnel and equipment. Overheating can pose serious risks, including fire hazards and electrical failures. By utilizing effective cooling solutions, organizations can minimize these dangers and create a safer working environment.
Safety Features in Welding Machines
Ensuring the well-being of operators is paramount in any industrial setting, particularly in activities that involve intense heat and electrical currents. The incorporation of protective mechanisms is essential to mitigate risks associated with these high-energy tasks. By prioritizing user safety, modern devices are designed to include various features that minimize hazards and promote secure working conditions.
Among the critical safety attributes are automatic shut-off systems, which deactivate the device when not in use or when overheating occurs. This prevents potential accidents and equipment damage. Furthermore, insulation materials are employed to protect users from electrical shocks, while advanced ventilation systems help disperse harmful fumes, maintaining a healthier workspace.
Moreover, protective gear is often integrated into the setup, ensuring that users are shielded from sparks, UV radiation, and intense light generated during operations. These enhancements not only comply with industry standards but also foster a culture of safety and responsibility within workplaces. By incorporating these essential features, operators can work with greater confidence and focus on the task at hand.
Control Panels and Their Functions
Control panels play a crucial role in the operation of equipment by providing an interface for users to manage various functionalities. These panels are designed to enhance the overall efficiency and safety of the systems they govern, allowing operators to easily monitor and adjust settings as needed.
Key Components of Control Panels
- Power Switches: Essential for turning the system on and off.
- Indicator Lights: Provide visual feedback regarding the operational status of the equipment.
- Control Knobs: Allow users to adjust settings such as voltage and amperage.
- Digital Displays: Show real-time data, including current output and operational metrics.
Functions of Control Panels
- Monitoring: Users can observe various parameters to ensure optimal functioning.
- Adjustment: Enables precise modifications to settings to match specific requirements.
- Safety Features: Often include emergency stop buttons and alarms to prevent accidents.
- Diagnostics: Some panels provide error codes and troubleshooting information for maintenance.
Welding Machine Maintenance Tips
Regular upkeep is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of your equipment. Proper care not only enhances efficiency but also minimizes the risk of unexpected breakdowns. Following these guidelines can help you maintain your device in peak condition, ensuring reliability during operation.
Here are some essential tips for effective maintenance:
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Inspect cables and connections | Weekly | Look for signs of wear or damage. |
| Clean the exterior | Monthly | Remove dust and debris to prevent overheating. |
| Check coolant levels | Monthly | Ensure adequate levels to prevent overheating. |
| Replace worn tips | As needed | Use manufacturer-recommended replacements. |
| Test functionality | Before major projects | Verify all settings and features are operational. |
By adhering to these maintenance practices, you can extend the lifespan of your equipment and ensure consistent performance during tasks. Regular checks and timely interventions can save time and resources in the long run.
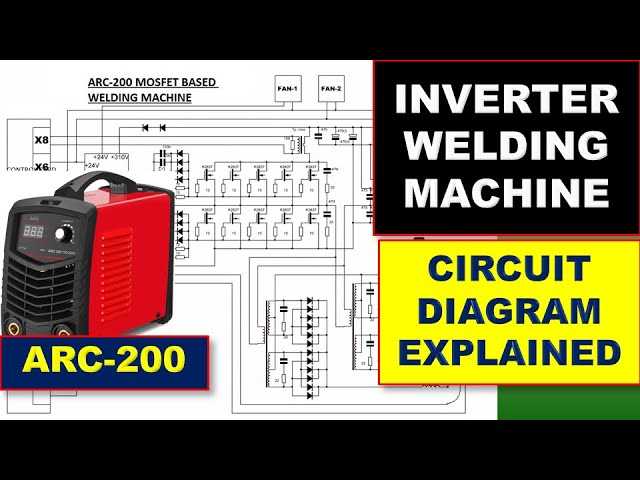
Wiring Diagrams for Welders
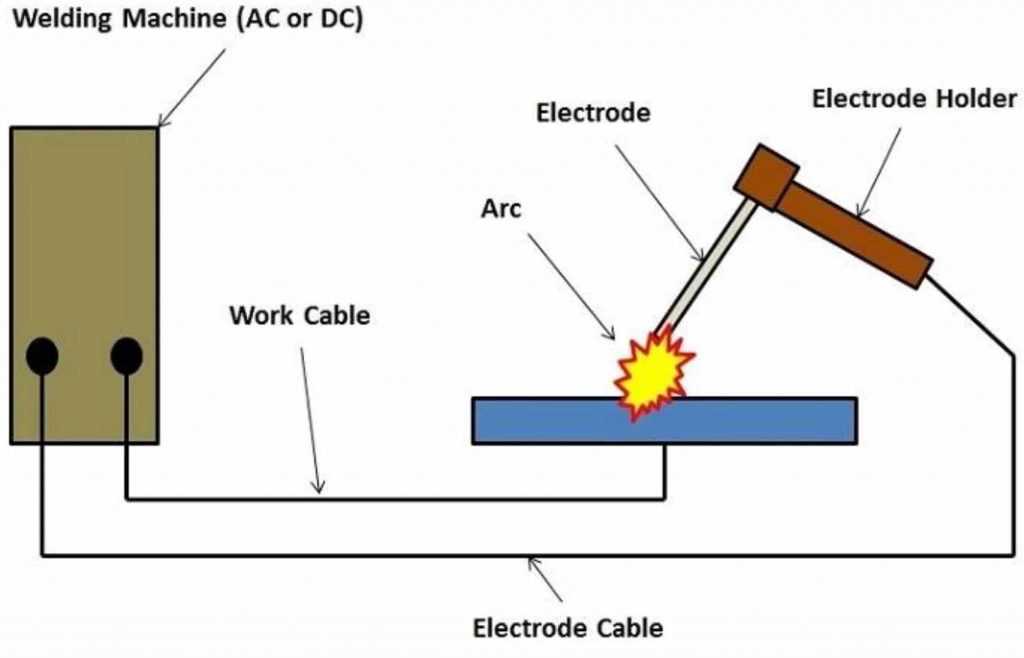
Understanding the connections within an apparatus is crucial for ensuring its optimal performance. These visual representations serve as essential guides, illustrating how various components are linked together to create a functional unit. Mastering these schematics enables technicians and enthusiasts alike to troubleshoot issues, perform maintenance, and enhance overall efficiency.
Typically, these representations highlight the flow of electricity through different sections, detailing how each element interacts with others. A thorough examination of these connections can reveal potential problems, such as incorrect wiring or insufficient power supply. Moreover, familiarity with these layouts aids in the safe assembly and disassembly of the equipment.
Key Elements: Familiarity with key components is vital when interpreting these visuals. Each element plays a significant role, and understanding their functions can simplify the process of diagnosing issues. Components such as transformers, contactors, and circuit breakers often feature prominently, each contributing to the overall operation.
In summary, mastering these connection layouts equips users with the knowledge necessary to ensure safety and functionality. With a solid grasp of how each component fits into the larger system, users can confidently tackle any challenges that arise.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
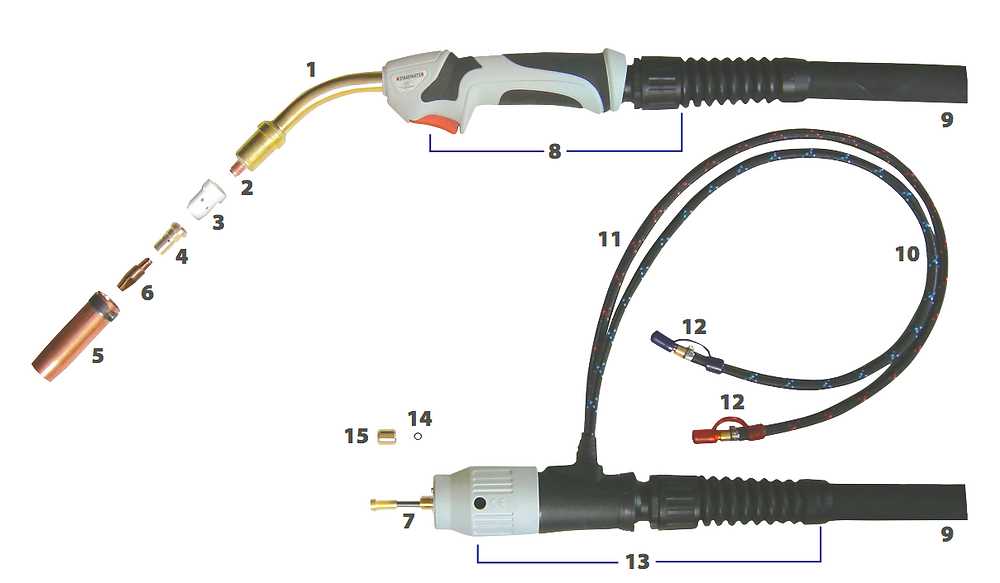
In the realm of industrial equipment operation, users often encounter various challenges that can hinder performance and efficiency. Identifying these issues early can prevent costly downtime and ensure optimal functionality. Below are some frequent problems and their corresponding solutions.
Frequent Challenges
- Poor electrical connections leading to inadequate power supply.
- Overheating due to insufficient ventilation or overload.
- Inconsistent performance resulting from wear and tear of components.
- Faulty controls affecting precision and reliability.
Troubleshooting Steps
- Inspect all electrical connections for signs of wear or corrosion.
- Ensure that cooling systems are functioning properly and not obstructed.
- Check components for damage and replace as necessary.
- Calibrate controls to ensure accuracy and responsiveness.
By adhering to these guidelines, users can effectively address common challenges and maintain the efficiency of their equipment. Regular maintenance and vigilance are key to preventing issues from escalating.