Maintaining peak performance in any high-performance vehicle requires a thorough understanding of its mechanical systems. Each element is meticulously designed to ensure functionality, durability, and precision. For riders and technicians alike, exploring the internal setup of a two-wheeled machine can reveal how various components interact to deliver exceptional performance and reliability.
Focusing on essential mechanisms, it is crucial to delve into the layout of the engine, chassis, and electrical systems. These areas form the foundation of any well-engineered vehicle, supporting both speed and control. Understanding these intricate systems helps with troubleshooting, repairs, and enhancing the vehicle’s overall efficiency.
Detailed visual representations
Overview of Key Components in 2006 GSX-R 1000
In this section, we will take a closer look at the essential elements that form the backbone of this high-performance machine. These parts work in harmony to deliver both power and control, ensuring optimal performance on the road and track. Understanding these core components is crucial for maintaining the vehicle and maximizing its potential. We will explore the main systems responsible for propulsion, handling, and safety.
One of the most important systems is the engine, which provides the necessary force to propel the vehicle forward. Complementing the engine is the transmission, responsible for efficiently delivering power to the wheels. Alongside these, the suspension and braking systems ensure
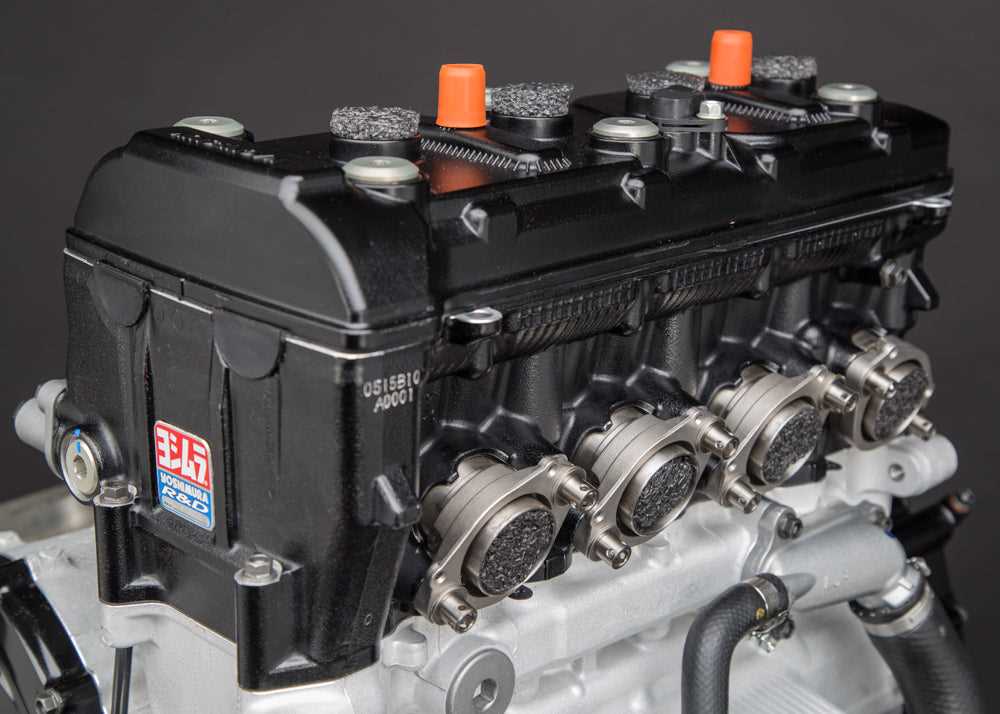
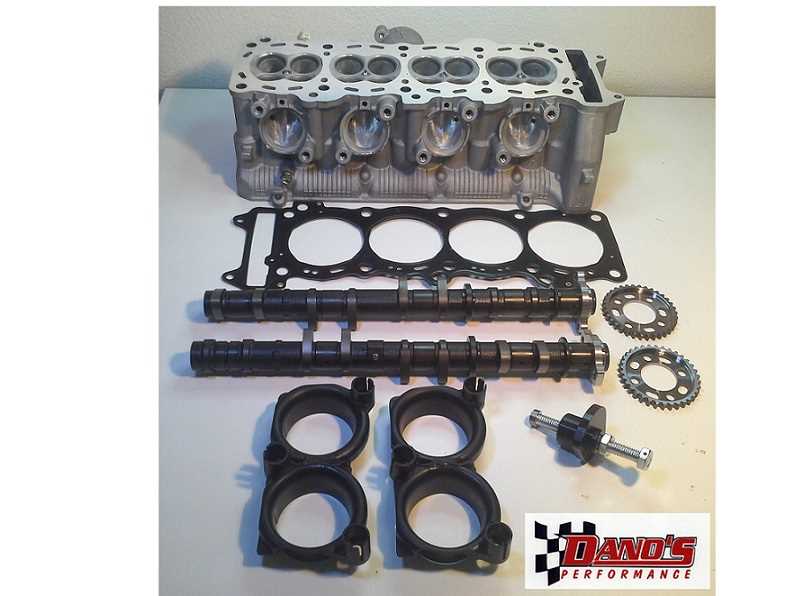
Engine Layout and Main Parts
The core of the engine structure is designed to combine several key systems that work in unison to deliver optimal performance. This section outlines the essential components, explaining how they interact to ensure smooth operation and efficiency. Each element contributes to the overall balance and functionality of the machine.
- Cylinder Block: The foundation that houses the combustion chambers and pistons, ensuring a stable and controlled environment for the engine’s operation.
- Pistons and Crankshaft: Working together, these parts convert the energy from fuel combustion into mechanical power, which drives the machine forward.
- Camshaft and Valves: Regulating the intake and exhaust cycles, these components control the flow of air and fuel, ensuring efficient combustion and optimal power output.
- Cooling System: A vital network designed to prevent overheating by circulating coolant through the engine, maintaining a
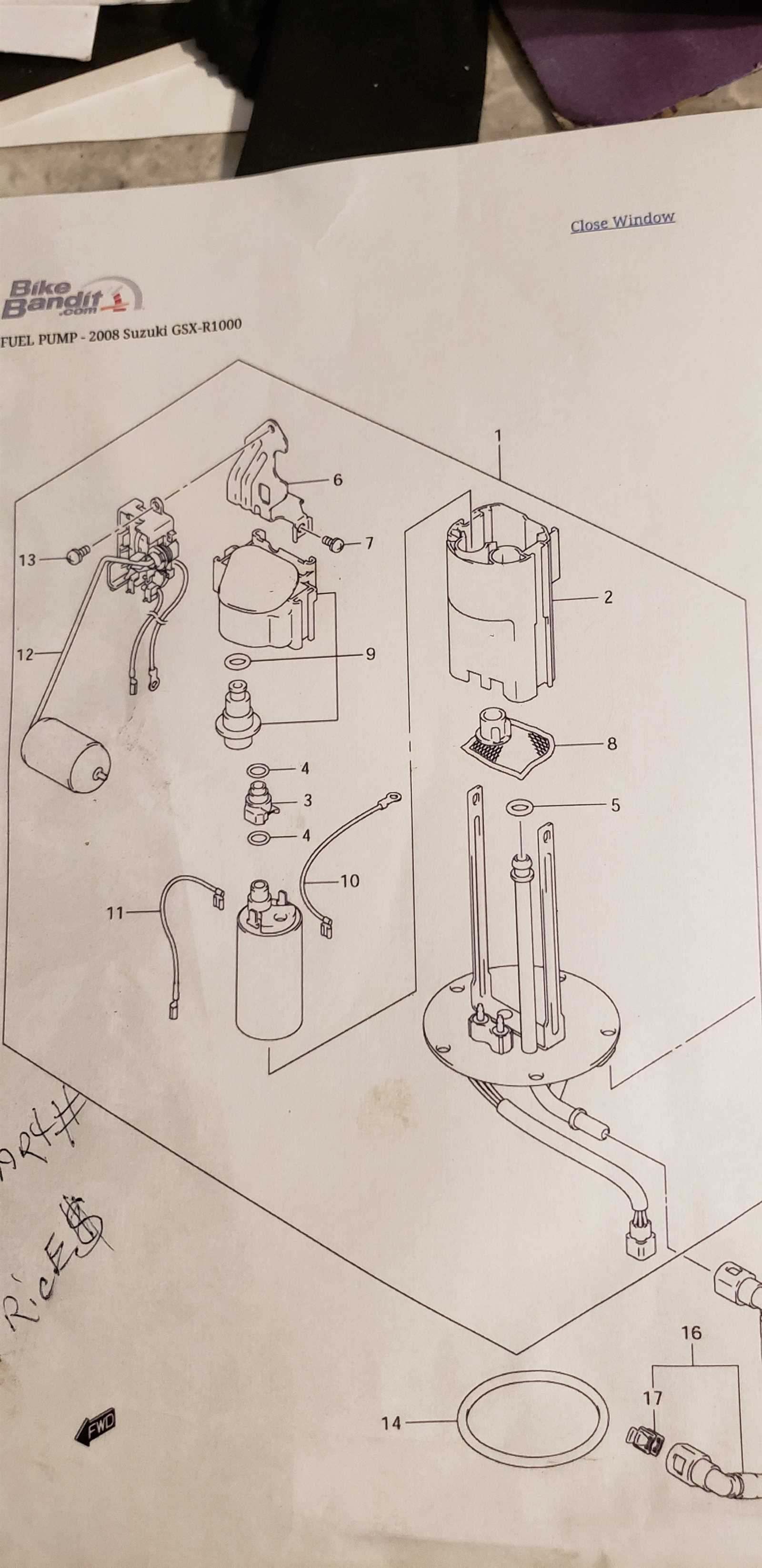
Fuel System Structure and Elements

The fuel system is a crucial component in any motorized vehicle, responsible for delivering fuel to the engine in the proper ratio and at the right time. It ensures the efficient combustion process that powers the engine, allowing for smooth and responsive performance. The system incorporates various elements that work together to regulate the fuel flow, maintain pressure, and monitor overall efficiency.
Main Components
The primary elements of this system include components that store, transport, and manage fuel distribution. These parts work in harmony to ensure a continuous and controlled flow of fuel to the engine, ensuring optimal performance
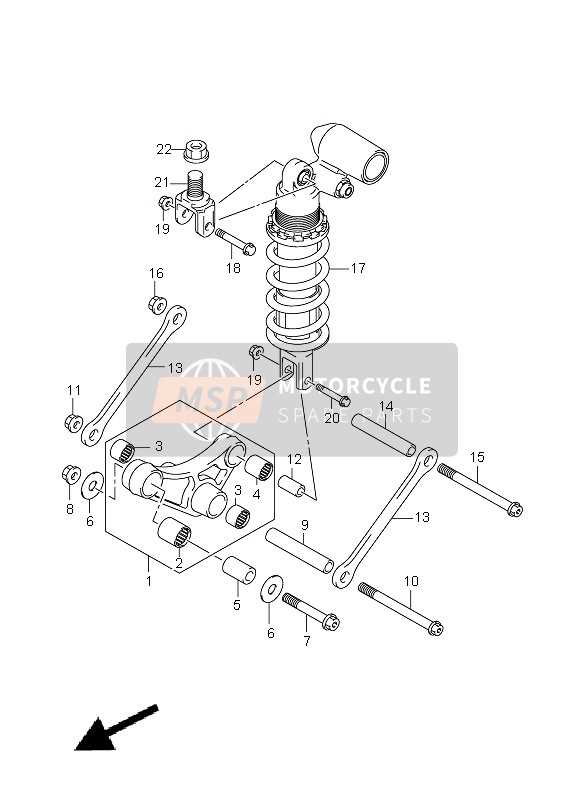
Suspension System Breakdown
The suspension plays a critical role in ensuring smooth handling and stability. It is responsible for absorbing shocks and maintaining tire contact with the road, allowing for better control and comfort during rides. This section explores the various components that work together to provide optimal performance.
Forks and Shocks: The front forks and rear shocks are the primary elements that manage the bike’s balance and damping. These elements compress and rebound, adjusting to different
Cooling System Components
The cooling system plays a critical role in ensuring optimal engine performance by maintaining a stable operating temperature. It comprises various interconnected elements that work together to dissipate heat efficiently. Understanding the main elements of this system is key to ensuring proper functioning and preventing overheating, which can lead to significant mechanical issues.
Main Components
The core components of this system include a fluid reservoir, channels that circulate the coolant, and a mechanism that aids in heat exchange. Each part has a specific function in managing and regulating the engine’s thermal levels.
Component Overview Table
Electrical Wiring and Key Connectors
Understanding the structure and arrangement of electrical components is essential for ensuring the optimal performance of any vehicle. The system of wiring and the connections between different electrical parts form the backbone of the entire electrical circuit. Proper handling of these connections ensures both safety and functionality, making it vital to grasp their role and configuration.
Key connectors within the system play a critical role in linking essential components, allowing for efficient transmission of power and data. These connectors are often designed to handle specific functions, from lighting to ignition, and must be carefully maintained to avoid malfunction.
Additionally, harnesses that group wires together help
Brake System Parts Explained
The braking mechanism of a motorcycle is a vital component responsible for ensuring safe and effective stopping. Understanding its individual elements is crucial for proper maintenance and performance. In this section, we will explore the various components involved in the system and their functions without delving into unnecessary specifics or complex terminology.
Key Components of the Braking Mechanism

The primary element of the system is the caliper, which houses the brake pads and applies pressure to the rotor to slow the vehicle down. This pressure is created when the rider activates the lever or pedal, sending hydraulic fluid through the brake lines. The rotor, connected to the wheel, is essential for converting kinetic energy into heat, facilitating
Transmission Assembly Overview
The transmission system is a crucial component in any high-performance machine, enabling seamless power transfer from the engine to the wheels. This section focuses on the key elements of this assembly, highlighting the importance of precision in gear shifting and smooth operation under various conditions. Understanding its structure and function can provide insights into maintaining optimal performance.
Gearbox plays a pivotal role in regulating speed and torque, ensuring that the power output is efficiently managed. Each gear is meticulously designed to synchronize with the engine’s revolutions, enabling smooth transitions.
Clutch operation is essential for engaging and disengaging the engine’s connection to the
Exhaust System Configuration
The exhaust system plays a critical role in both the performance and efficiency of the motorcycle, ensuring proper expulsion of gases while contributing to overall engine output. Understanding its layout and key components is essential for maintaining an optimal flow, reducing emissions, and enhancing riding experience.
Main Components Overview
This system includes several vital sections that work in unison to manage the exhaust process. These components typically include headers, a catalytic converter, a muffler, and exhaust pipes, each with a distinct function. Their alignment ensures efficient removal of gases and improves engine power.
Performance and Maintenance Tips
Regular inspection of the exhaust assembly can prevent potential issues like leaks or
Frame and Chassis Components
The frame and chassis form the backbone of any motorcycle, playing a crucial role in both structural integrity and handling. These components are designed to support the engine, suspension, and other critical systems, ensuring a balance between strength and flexibility for optimal performance. In this section, we’ll explore the key elements that make up this essential foundation.
- Main Frame: The central structure that holds together the major systems, providing a solid yet lightweight platform.
- Subframe: A supporting section that connects to the main frame, often responsible for holding the seat and rear bodywork.
- Forks
Handlebar and Controls Arrangement

The design and layout of the handlebar and control system play a critical role in ensuring both rider comfort and control. These components are intricately positioned to provide a seamless riding experience, allowing for easy maneuverability and quick access to essential functions.
Key elements such as the throttle, brake levers, and clutch are strategically placed for optimal performance, enhancing the rider’s ability to navigate different terrains with precision. The arrangement is designed to minimize fatigue, ensuring that all controls are within reach, promoting a more intuitive interaction between the rider and the machine.
Attention to ergonomics ensures that the setup not only supports high performance but also enhances safety. Each control
Wheel Assembly and Bearings
The structural integrity of the wheel system is essential for ensuring stability and smooth operation during rides. The components of the wheel assembly work together to provide support, while the bearings allow for frictionless rotation, reducing wear and tear over time. Proper maintenance of these elements is key to ensuring optimal performance.
Components Overview
- Rim
- Spokes
- Hub
- Axle
- Bearings
Each part plays a vital role in the overall function of the wheel. The rim and spokes give the wheel its form, while the hub holds the axle in place, allowing for free movement. Bearings, placed within the hub, are designed to minimize resistance and allow for smooth rotation.
Maintaining Bearings for Longevity
Lighting
Efficient illumination plays a critical role in ensuring visibility and safety while riding. Properly functioning lights enhance the rider’s ability to see the road ahead, as well as make the vehicle more noticeable to others. This section explores the key elements involved in maintaining and upgrading the lighting system for a smooth and secure ride.
Types of Lights
The lighting system is composed of various components that serve specific purposes. The headlamp ensures forward visibility, while the rear lights signal braking and indicate position. Additionally, signal indicators and auxiliary lights add extra layers of functionality, helping to communicate intentions to other road users.