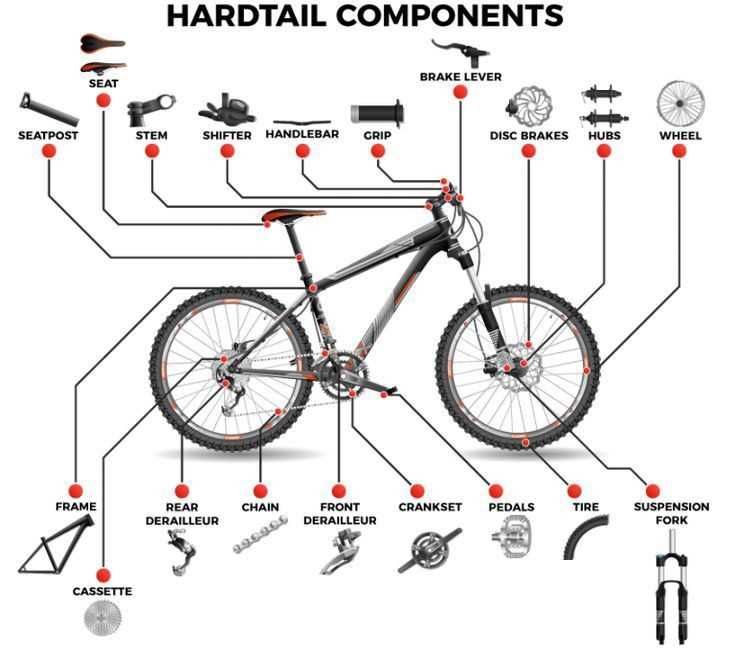
The efficiency of any two-wheeled vehicle relies heavily on its ability to slow down or come to a complete stop when necessary. In this section, we will explore the intricacies of the mechanisms involved in this essential function, shedding light on how various elements interact to ensure safety and control.
By breaking down the essential components, we can delve into their specific roles and understand the ultimate purpose they serve. Each element, from the activation levers to the friction surfaces, plays a critical part in the overall performance of the system, contributing to a seamless riding experience.
Through careful examination of these components, riders can gain insight into maintenance practices, potential upgrades, and troubleshooting techniques. This knowledge not only enhances performance but also empowers enthusiasts to make informed decisions regarding their equipment.
Understanding Disc Brake Components
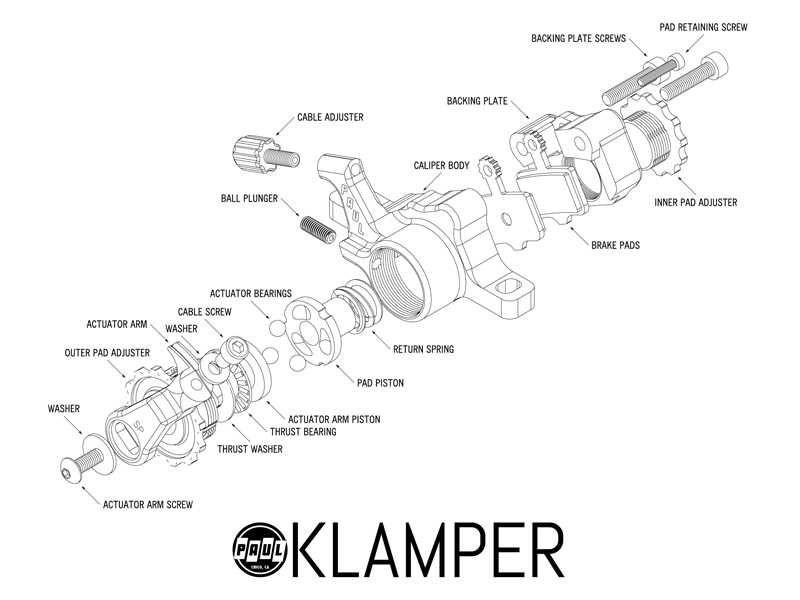
Effective stopping mechanisms are crucial for any high-performance riding experience. Grasping the essential elements involved in these systems can enhance performance and maintenance skills.
- Caliper: The mechanism that houses the friction material and applies pressure.
- Pads: The materials that create friction against the rotating element to slow down.
- Rotors: The circular metal components that the pads grip to facilitate slowing.
- Lever: The control used by the rider to initiate the stopping process.
- Hydraulic Lines: Tubes that transfer fluid to activate the caliper.
Understanding these components will ultimately help in troubleshooting and optimizing the system’s performance.
Types of Mountain Bike Disc Brakes
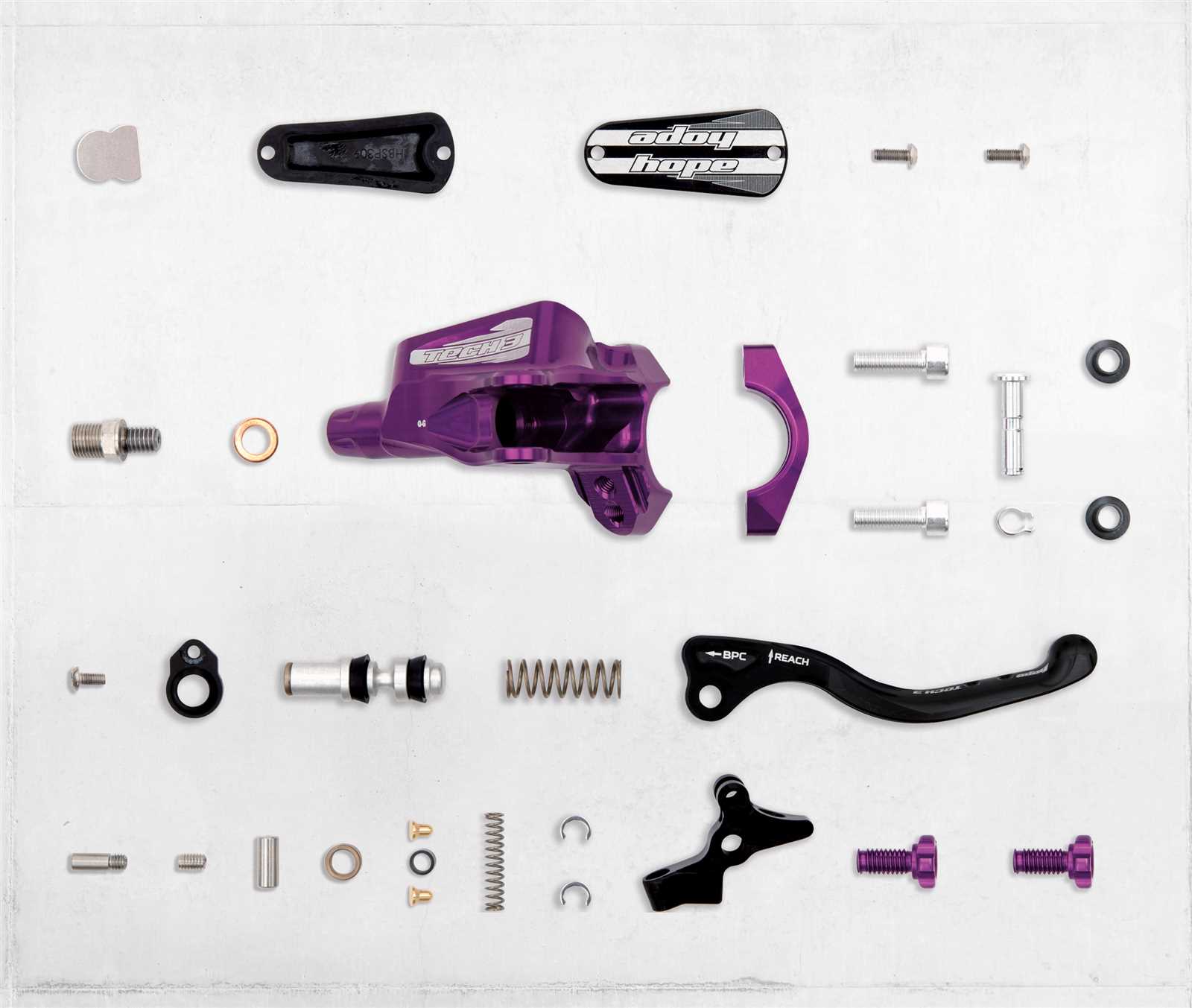
Understanding the various systems for stopping mechanisms is essential for riders looking to enhance their experience and performance. Each variant offers distinct features and benefits, catering to different preferences and riding styles. Below are the main classifications based on design and functionality.
- Mechanical Systems:
These utilize cables to engage the stopping mechanism. They are often favored for their simplicity and ease of maintenance.
- Hydraulic Systems:
This type employs fluid to transmit force, resulting in a more responsive and powerful action. Ideal for those seeking enhanced control and performance.
Each classification can further be divided based on specific features:
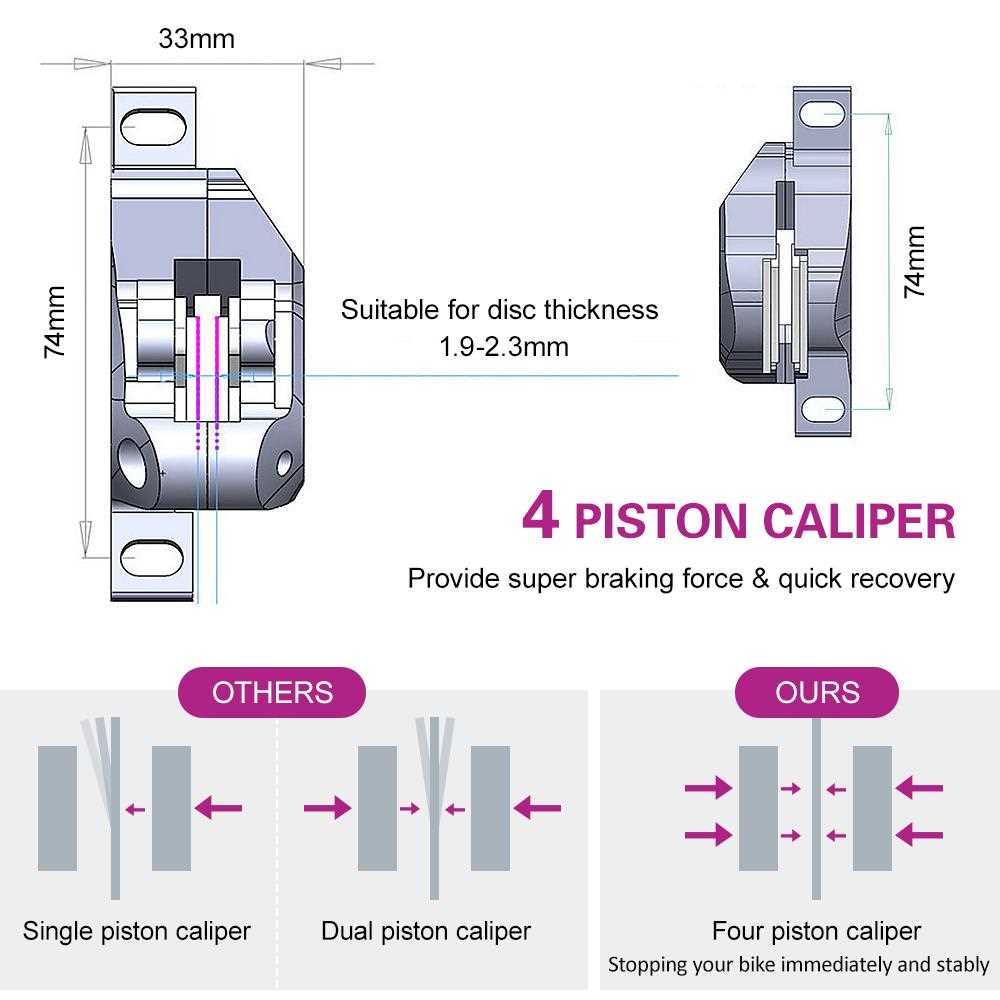
- Two-Piston Models:
These offer balanced force distribution and are suitable for various terrains.
- Four-Piston Models:
Designed for aggressive riding, these provide superior stopping power and modulation.
- Single-Piston Models:
Generally lighter and less expensive, these are often chosen for casual or recreational use.
Choosing the right system can significantly impact overall performance, making it crucial for enthusiasts to consider their specific needs and riding conditions.
Key Parts of Brake System
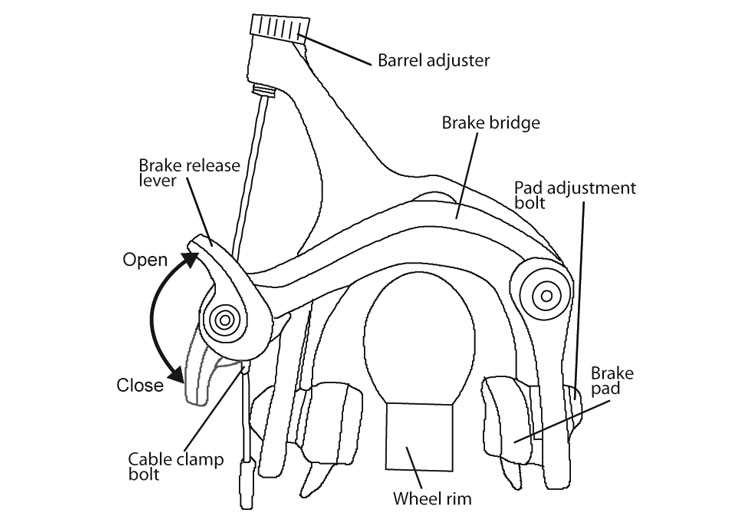
The effectiveness of a stopping mechanism relies on several crucial components that work in harmony to ensure safety and control. Understanding these elements is essential for maintenance and optimal performance.
Caliper: This unit houses the squeezing mechanism that grips the rotor, generating the necessary friction to slow down the motion.
Rotor: A circular metal disc that interacts with the caliper, transforming kinetic energy into thermal energy through friction.
Pads: These are the materials that press against the rotor, playing a vital role in the deceleration process by providing the necessary grip.
Lever: This component allows the user to apply force, initiating the stopping action through a mechanical or hydraulic system.
Hydraulic System: In systems utilizing fluid, this mechanism amplifies the force applied at the lever, ensuring effective pressure on the caliper.
Each of these elements contributes to the ultimate function of the stopping mechanism, highlighting the importance of regular inspections and timely replacements to maintain performance.
Function of Brake Calipers Explained

Calipers play a crucial role in the stopping mechanism of wheeled vehicles, converting hydraulic pressure into mechanical force. This component ensures that when the driver applies pressure, the necessary force is exerted on the rotating surfaces to slow down or halt motion efficiently.
The operation of calipers involves several key elements working in harmony. When the lever is engaged, hydraulic fluid is pushed through the system, causing the calipers to clamp down on the rotor. This interaction generates the friction needed to achieve deceleration. Understanding the components and their functions helps in recognizing the importance of this mechanism in maintaining safety and performance.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Caliper Body | Houses the pistons and provides a structure for the system. |
| Pistons | Convert hydraulic pressure into a mechanical force to squeeze the pads against the rotor. |
| Brake Pads | Provide the friction material that contacts the rotor, enabling effective slowing. |
| Hydraulic System | Transmits force from the lever to the calipers, ensuring precise control. |
Regular maintenance of calipers is essential for optimal function. Worn components can lead to diminished performance, resulting in increased stopping distances and potential safety hazards. Awareness of their role and condition can greatly enhance overall vehicle handling and reliability.
Role of Brake Rotors in Performance

The components responsible for slowing down a vehicle play a crucial role in ensuring optimal functionality and safety. Their design and material significantly influence responsiveness and heat management, ultimately impacting overall effectiveness during use.
Key Functions
- Heat Dissipation: Helps manage temperatures during intense usage.
- Modulation: Provides feedback to the user for better control over stopping power.
- Durability: Ensures longevity under various conditions.
Impact on Performance

- Enhanced Stopping Power: Quality components lead to more reliable deceleration.
- Improved Handling: Better modulation allows for smoother transitions in control.
- Consistency: High-performance materials maintain effectiveness across diverse terrains.
Importance of Brake Pads Selection

Choosing the right components for halting mechanisms is crucial for both performance and safety. The selection process significantly influences the overall functionality, longevity, and responsiveness of the entire system. Making informed decisions can enhance user experience and ensure reliability during rides.
Several factors must be considered when selecting these essential elements:
- Material Composition: Different materials offer varying levels of friction and wear resistance. Understanding the benefits of organic, metallic, and semi-metallic options is vital.
- Climate Adaptability: Some formulations perform better under specific weather conditions, affecting performance in wet or dry environments.
- Performance Needs: Depending on the riding style–be it casual, competitive, or downhill–specific features may be required for optimal results.
- Compatibility: Ensuring that the chosen items match with other system elements is essential for seamless operation.
Neglecting these considerations can lead to compromised safety and inefficient performance. Thus, careful evaluation and selection of these components are paramount for achieving the desired riding experience.
Hydraulic vs. Mechanical Brakes

When it comes to stopping power and control, two distinct systems offer varying advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these differences can help enthusiasts make informed decisions based on their riding style and terrain.
Hydraulic systems utilize fluid to transfer force, providing smooth and consistent performance. They often require less effort to engage, making them ideal for steep descents and challenging environments. The design allows for finer modulation, which enhances overall handling and responsiveness.
On the other hand, mechanical systems rely on cables to function, making them simpler and easier to maintain. While they may not deliver the same level of performance under extreme conditions, their straightforward mechanics often appeal to those who prioritize reliability and ease of adjustment.
Ultimately, the choice between these two types depends on personal preference, riding conditions, and the desired balance between performance and maintenance. Delving deeper into each system reveals unique characteristics that can significantly impact the overall experience.
How to Read Brake Diagrams
Understanding visual representations of complex systems can significantly enhance your ability to maintain and repair them. These illustrations often provide a clear overview of the components involved, their relationships, and how they function together. Familiarity with the symbols and layout is crucial for effective interpretation.
Begin by identifying the key elements depicted in the illustration. Look for labels that indicate specific components, and familiarize yourself with common symbols used in technical drawings. Each element typically represents a different part of the system, and recognizing these can help you follow the flow of mechanics more easily.
Next, pay attention to the connections between elements. Arrows or lines may indicate the movement or interaction between parts. Understanding these connections will allow you to grasp how forces are transmitted through the assembly, which is essential for troubleshooting and performance enhancement.
Finally, consult accompanying documentation if available. Manuals or guides often provide detailed explanations of the illustration, including notes on assembly, maintenance, or common issues. This supplementary information can clarify any uncertainties and enhance your comprehension of the system as a whole.
Maintenance Tips for Disc Brakes
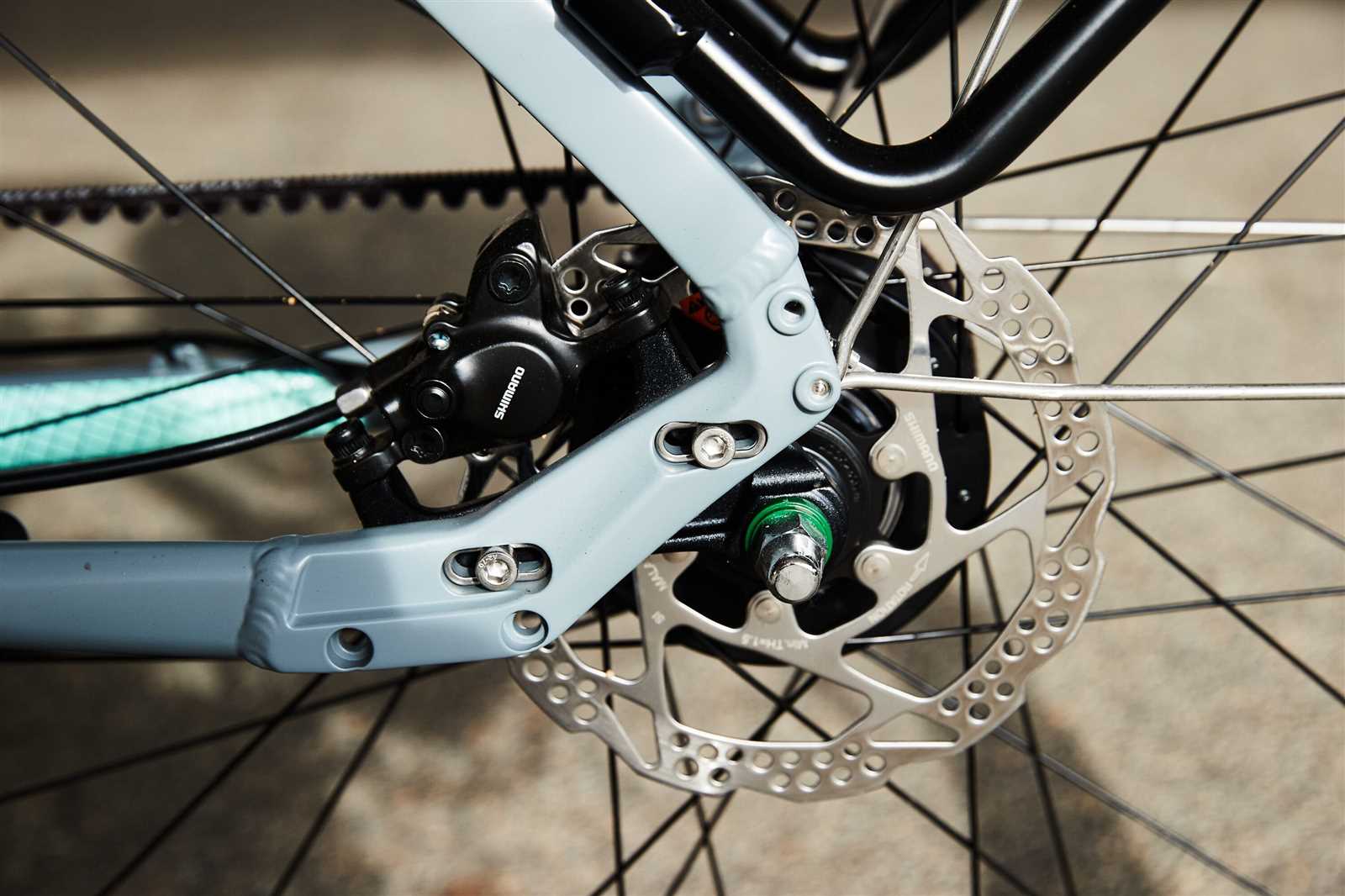

Regular upkeep of your stopping system is essential for optimal performance and longevity. By following a few straightforward guidelines, you can ensure that your equipment remains in top condition, providing safety and reliability on your rides.
- Inspect Regularly: Check for wear and tear on components. Look for any signs of damage or corrosion that may affect functionality.
- Clean Components: Use a suitable cleaner to remove dirt and debris. This prevents buildup that can compromise performance.
- Adjust Tension: Ensure that the system is properly calibrated for effective stopping power. Misalignment can lead to uneven wear.
- Check Fluid Levels: Maintain appropriate hydraulic fluid levels if applicable. Low levels can impact the system’s responsiveness.
- Monitor Performance: Pay attention to how the system responds during use. Unusual sounds or decreased stopping power may indicate a need for further inspection.
By adhering to these practices, you can enhance the efficiency and durability of your stopping mechanism, ensuring a safer and more enjoyable experience on the trails.
Common Issues with Brake Systems
When it comes to stopping mechanisms in cycling, several challenges can arise that may impact performance and safety. Understanding these common problems is essential for maintaining optimal functionality and ensuring a smooth riding experience.
1. Insufficient Stopping Power: One of the most prevalent issues is inadequate force when attempting to halt motion. This may stem from worn components or improper adjustments, leading to a less effective stopping response.
2. Noise and Vibration: Unwanted sounds during operation, such as squeaking or grinding, can indicate underlying issues. These noises often result from debris accumulation or misalignment, which can further compromise effectiveness.
3. Fluid Leaks: For systems that utilize hydraulic fluid, leaks can significantly diminish performance. Noticing a decrease in responsiveness may signal the need for an inspection and potential fluid replacement.
4. Overheating: Excessive heat build-up during prolonged use can lead to a reduction in effectiveness. This issue typically arises from intense riding conditions or inadequate ventilation, necessitating careful monitoring.
5. Contamination: The presence of dirt or oil on surfaces can hinder the operation of the mechanism. Regular cleaning and maintenance are crucial to prevent contaminants from affecting performance.
Addressing these common challenges promptly can lead to enhanced safety and longevity of the stopping system, ensuring a reliable experience on every ride.
Upgrading Your Brake Components
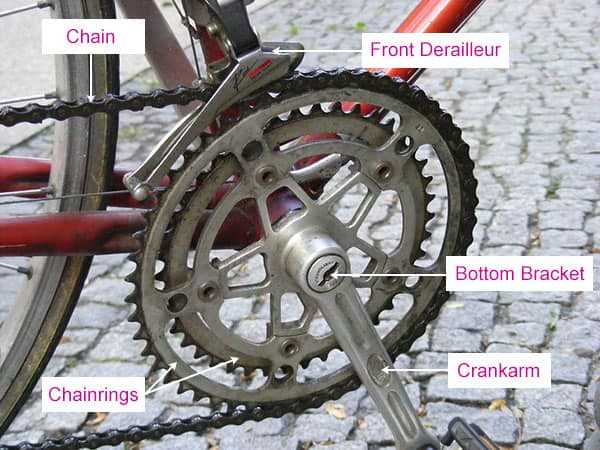
Enhancing the performance of your stopping system can significantly improve your overall riding experience. By investing in superior elements, you can achieve greater responsiveness and control, ensuring safety and efficiency on varied terrains.
| Component | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Calipers | Improved modulation and stopping power |
| Pads | Better heat dissipation and longevity |
| Rotors | Enhanced cooling and consistent performance |
| Levers | Increased comfort and precision in operation |
Ultimately, selecting the right components tailored to your needs can transform your ride, allowing you to delve into new challenges with confidence.
Choosing the Right Brake Tools

Selecting appropriate tools for your stopping system is crucial for effective maintenance and performance. The right instruments ensure that every component functions optimally, providing both safety and reliability during rides. Understanding which tools to utilize can simplify the servicing process and enhance your overall experience.
Compatibility is a key factor when choosing your tools. Different setups may require specific instruments, so it’s essential to check the requirements of your system before making a purchase. Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines to ensure a proper fit.
Additionally, consider quality over quantity. Investing in durable, well-designed tools can save time and effort in the long run. High-quality instruments often provide better precision and ease of use, making routine maintenance less of a chore.
Lastly, don’t overlook the importance of ergonomics. Tools that feel comfortable in your hands can make tasks more manageable, especially during prolonged usage. A thoughtful approach to tool selection can lead to a more enjoyable and efficient experience.
Impact of Weight on Brake Efficiency
The relationship between mass and stopping power is a critical factor in performance dynamics. Heavier assemblies require more force to decelerate effectively, influencing the overall functionality of the stopping system. Understanding this correlation helps in optimizing design for better response and safety.
Factors Influenced by Weight

- Force Required: Increased mass results in a higher force needed for effective halting.
- Heat Generation: Greater weight can lead to enhanced friction and, consequently, more heat buildup during operation.
- Durability: Heavier components may experience different wear patterns, affecting longevity.
Optimizing Design for Weight
- Material Selection: Utilizing lighter yet durable materials can significantly enhance efficiency.
- Component Configuration: Analyzing the layout can lead to a balanced distribution of mass, improving performance.
- Testing and Feedback: Regular evaluation of systems under varied weights can yield insights for future innovations.
In conclusion, the weight of components plays a crucial role in their operational efficiency, and thoughtful design choices can mitigate negative impacts, enhancing performance and safety.