
When it comes to keeping sewing machines in top working condition, having a clear understanding of how individual elements are organized is essential. Each element, from the tiniest screw to larger mechanical assemblies, plays a crucial role in the seamless operation of the device. This overview offers insights into how various elements fit together to create a cohesive and efficient system.
The intricate arrangement of different mechanisms ensures that each action, whether it’s a simple stitch or a more complex process, operates smoothly. By exploring the detailed organization of these elements, it becomes easier to troubleshoot issues and maintain performance. Knowing the structure is key to understanding how the machine functions as a whole.
Overview of Key Components
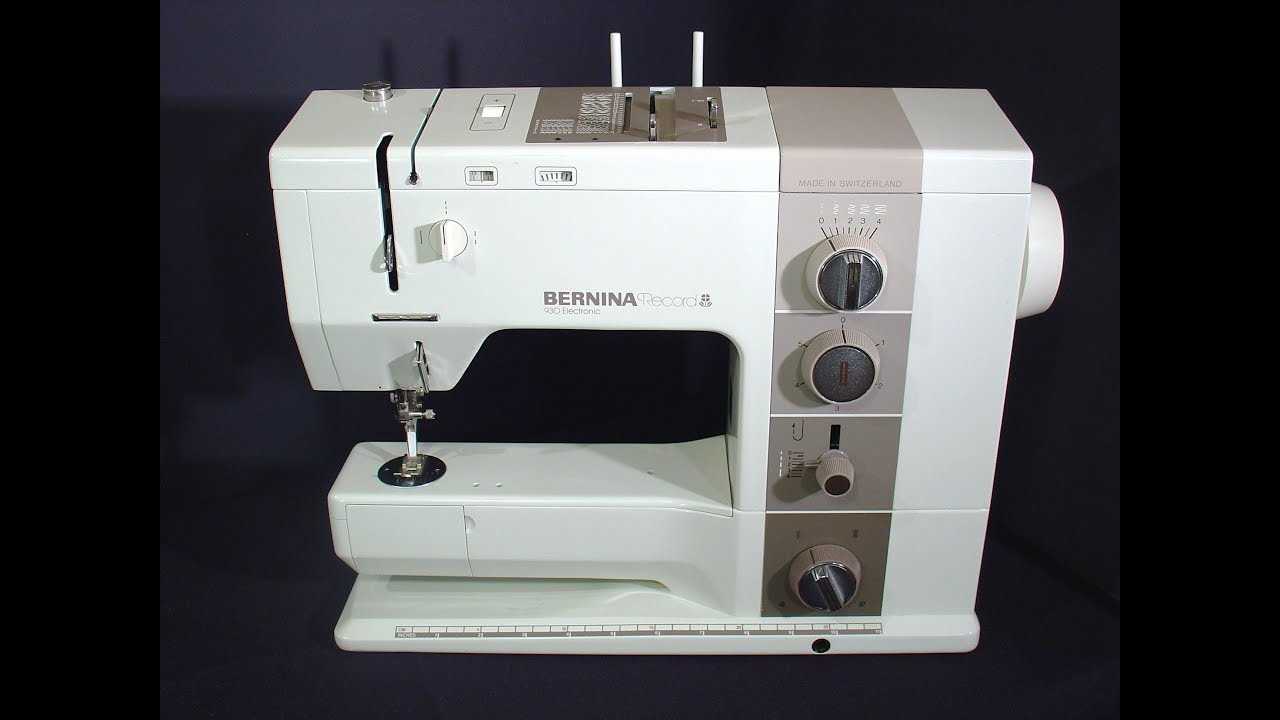

In this section, we will explore the main elements essential for the operation and functionality of the device. Each component plays a vital role, contributing to both performance and durability. Understanding these elements will provide insight into the device’s structure and how its mechanisms work in unison.
The mechanical system is designed to offer precision and control. This intricate arrangement of moving parts ensures smooth operation and reliable outcomes, making it a core feature of the overall setup.
Electronic controls enable users to adjust settings with ease. These intuitive systems are crucial for customizing functionality, offering flexibility for various tasks while maintaining consistent accuracy.
Another critical element is
Understanding the Internal Mechanism
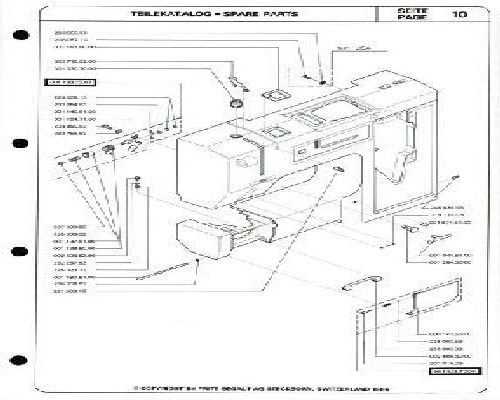
The inner workings of this precision device are the result of a well-coordinated assembly of components, designed to operate seamlessly together. Each element within the system has a specific role, contributing to the overall function of the machine, ensuring smooth operation and reliability.
Main Functional Components
- Drive System: A core element responsible for initiating motion and maintaining consistent operation during use.
- Stitch Formation Elements: These parts work together to create the necessary tension and movement required for precise stitching.
- Control Mechanism: Provides the user with the ability to adjust settings, ensuring adaptability for various tasks and fabric types.
Coordinated Movements

Exploring the Stitching Unit
The stitching mechanism plays a critical role in ensuring smooth and consistent operation during fabric handling. By examining its individual components, we gain a clearer understanding of how each element contributes to the precision and reliability of the entire system.
Needle Movement and Control – One of the essential aspects of this mechanism is the ability to adjust needle positioning. Whether for intricate designs or robust stitching, the flexibility offered by the adjustment system ensures that fabric of varying thickness and types can be handled with ease.
Thread Tension and Delivery – Maintaining consistent thread tension is vital for creating uniform stitches. This unit houses the tools required to manage the flow and tautness of the thread, providing stability for both delicate and dense fabrics.
Presser Foot and Fabric Feeding
Guide to Thread Tension Adjustments
Proper thread tension is a crucial factor in ensuring smooth stitching and high-quality results. Balancing this setting can be challenging, but it is necessary for maintaining uniform stitches, preventing fabric puckering, and avoiding thread breakage. Understanding how to fine-tune this adjustment allows for greater control over the sewing process and contributes to more professional finishes.
Recognizing Imbalances
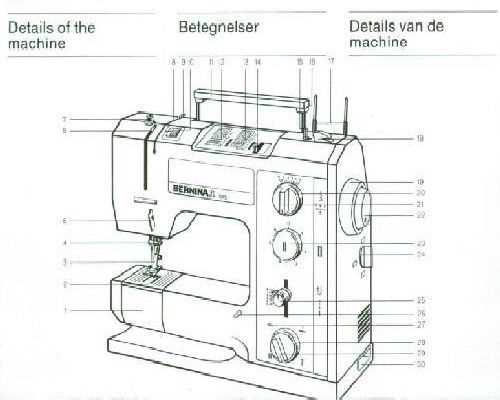
One of the first signs of incorrect tension is uneven stitching, with either the upper or lower thread appearing too tight or too loose. This often results in loops or bunching on one side of the fabric. To resolve this, adjustments can be made b
Essential Parts of the Needle Assembly

The precise structure of the sewing mechanism is crucial for achieving smooth and accurate stitching. Each component in this arrangement plays a distinct role, working in harmony to ensure consistent performance and durability. This section explores the vital elements that contribute to the effectiveness of the stitching process, highlighting their individual functions and how they interact.
Needle Shaft: The central piece that holds the needle securely in place. It is designed to maintain stability while guiding the needle through fabric layers.
Thread Guide: A small but significant element, ensuring that the thread moves smoothly through the stitching process. This component helps prevent tangling and maintains consistent tension.
Needle Clamp: This adjustable section ensures the needle is firmly attached to the machine, providing easy replacement and precise alignment.
Position Adjuster: An essential feature that allows the needle’s height
Breaking Down the Bobbin Winding System

The mechanism responsible for winding the thread onto the bobbin plays a crucial role in the overall functionality of a sewing machine. This intricate system ensures that the bobbin is filled efficiently, providing a steady supply of thread during the stitching process. Understanding how this assembly operates can greatly enhance one’s ability to maintain and troubleshoot sewing equipment.
Components of the Winding Mechanism
At the heart of the winding process are several key components. The bobbin case, where the bobbin resides, is designed to secure the thread in place while it is being wound. The thread guide directs the thread from the spool to the bobbin, ensuring a smooth transfer without tangling. Additionally, the winding tension disc regulates the amount of tension on the thread, crucial for achieving optimal results.
Operation Process
The winding operation begins with the user engaging the winding function, which typically involves a simple lever or switch. As the machine runs, the spool of thread feeds into the winding mechanism. The tension disc adjusts the thread’s tension, allowing for even distribution as it wraps around the bobbin. This process not only fills the bobbin but also ensures that the thread is wound tightly enough to prevent slippage during sewing.
Maintenance Tips
To ensure the longevity of the winding system, regular maintenance is essential. Users should periodically clean the tension disc and the bobbin area to remove any lint or debris that may interfere with the winding process. Additionally, checking the alignment of the components can prevent issues such as uneven winding or thread breakage. By maintaining this system, users can achieve consistent performance from their sewing machine.
Exploring the Presser Foot Structure

The presser foot is a vital component in sewing machines, designed to hold the fabric in place while stitches are being formed. Its construction plays a significant role in determining the quality of the stitches and the ease of use for various sewing tasks. Understanding its intricate design can greatly enhance one’s sewing experience.
Typically made of durable materials, the presser foot consists of several key elements, each contributing to its overall functionality. The foot plate serves as the primary surface that makes contact with the fabric, ensuring stability during operation. Additionally, the foot lift mechanism allows for easy adjustment of the foot’s height, accommodating different fabric thicknesses.
Moreover, various attachments can be utilized with the presser foot, such as those designed for quilting, hemming, or zipper insertion. These adaptations enhance the machine’s versatility, allowing users to tackle a wide range of sewing projects with precision. By exploring the structure of the presser foot, sewists can make informed decisions about their sewing machine capabilities and optimize their creative endeavors.
Motor and Electrical Assembly Details
This section provides an overview of the motor and electrical components that are integral to the operation of sewing machines. Understanding these elements is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and ensuring longevity in functionality.
The motor assembly plays a pivotal role in powering the entire mechanism. It is typically composed of a durable housing that encases the motor, along with wiring and connectors that facilitate electrical flow. The positioning of the motor is designed for efficient transmission of power to the moving parts of the machine.
Electrical assemblies include various components such as circuit boards, switches, and relays, which work in harmony to control the machine’s operations. The wiring layout is strategically arranged to minimize interference and ensure reliable connections, contributing to the overall safety and performance of the device.
Regular inspection and maintenance of these components can prevent malfunctions and enhance the user experience. Familiarity with the assembly details is beneficial for troubleshooting issues and performing repairs when necessary.
Foot Pedal and Speed Control System

The foot-operated device and its associated speed modulation mechanism play a crucial role in the functionality of sewing machines. This system enables users to adjust the machine’s operational pace according to their specific requirements, providing a more tailored experience for various sewing tasks.
Components of the Speed Control Mechanism

Key elements within this control system include the pedal, which serves as the primary input for speed adjustment, and the electronic circuit that translates the pedal’s position into speed variations. Together, these components ensure smooth operation and enhance user comfort.
Functionality Overview
The interaction between the foot pedal and the control system allows for precise adjustments. Pressing the pedal increases speed, while releasing it slows down or stops the machine entirely. This responsive design is essential for achieving intricate sewing patterns and maintaining consistent results.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Foot Pedal | Controls speed through pressure applied by the user’s foot |
| Electronic Control Circuit | Translates pedal position into operational speed |
| Speed Limiter | Prevents excessive speed, ensuring safety and precision |
Insights into the Machine Housing
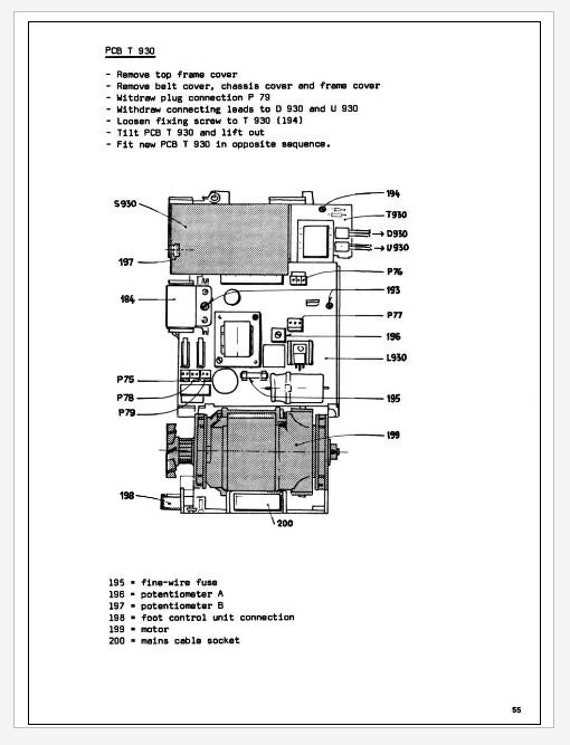
The outer casing of a sewing machine plays a crucial role in both functionality and aesthetics. It serves as the protective shell that houses essential components, ensuring durability and stability during operation. Understanding its structure and design can provide valuable insights into the overall performance and longevity of the device.
Material Composition

The construction of the machine’s exterior often involves a combination of high-quality materials designed to withstand wear and tear. Metallic elements offer strength and resilience, while plastic components contribute to a lightweight design. This careful selection of materials helps to balance robustness with ease of handling, enhancing user experience.
Design Considerations
Design elements are not merely aesthetic; they significantly impact usability. Features such as ergonomic shapes and strategically placed controls make the device more accessible and comfortable for users. Additionally, adequate ventilation in the housing ensures that internal components remain cool during extended use, preventing overheating and potential damage.
Maintenance of Moving Parts and Gears

Regular upkeep of mechanical components is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of sewing equipment. Proper care helps in preventing wear and tear, minimizing the risk of breakdowns, and maintaining smooth operation. This section outlines best practices for the maintenance of these crucial elements.
Lubrication: Keeping the moving mechanisms well-lubricated is vital. Use appropriate lubricants to reduce friction and protect against corrosion. Apply lubricant to gears, shafts, and any other moving parts, ensuring that excess is wiped away to avoid attracting dust and debris.
Cleaning: Regularly clean the machine to remove lint, dust, and fabric remnants that can accumulate in and around moving components. A soft brush or compressed air can be effective in reaching tight spots. Ensuring cleanliness not only improves functionality but also extends the lifespan of the internal mechanisms.
Inspection: Periodic inspection of mechanical elements is crucial. Look for signs of wear, such as unusual noises, misalignment, or sluggish movement. Addressing any irregularities promptly can prevent further damage and ensure that the equipment remains in peak condition.
Adjustment: As time progresses, certain components may require adjustments to maintain accurate operation. Check for proper tension on belts and gears, and adjust as necessary to ensure smooth functioning. Regular adjustments can help maintain the efficiency of the machine.
By following these maintenance guidelines, users can significantly enhance the durability and efficiency of their sewing equipment, ensuring reliable performance over time.
Troubleshooting Common Part Failures
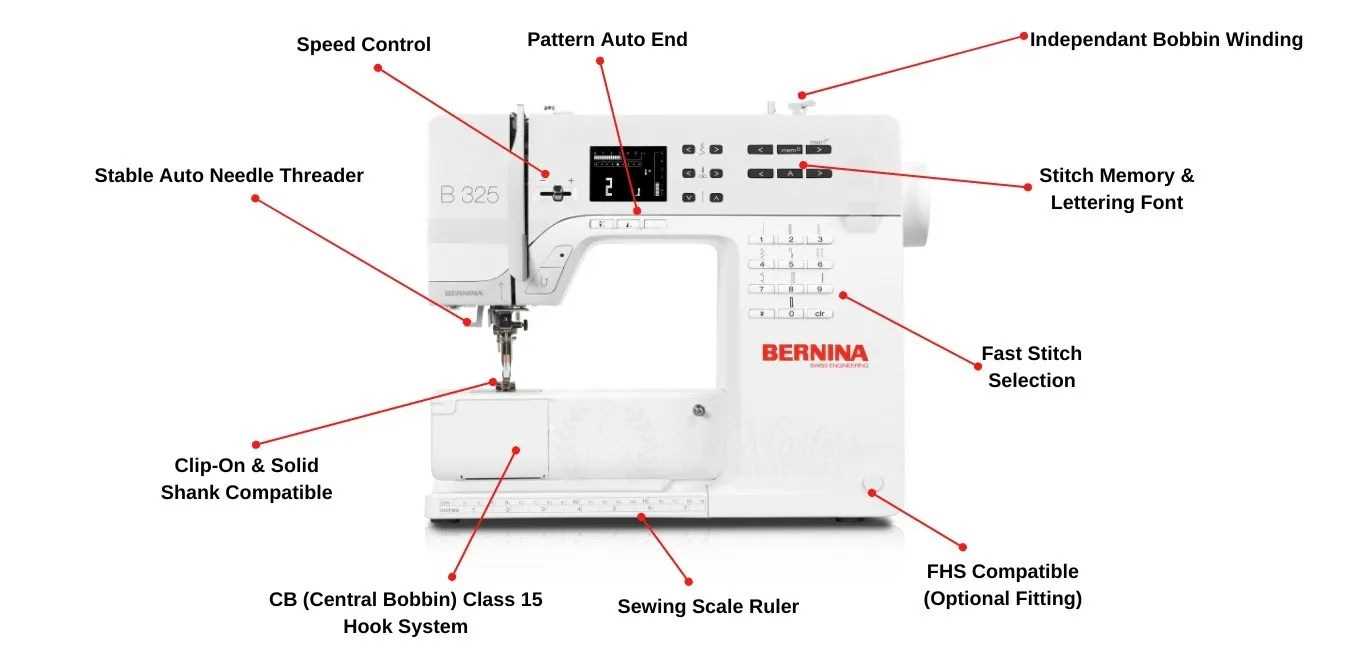
When operating any intricate device, it is not uncommon to encounter issues stemming from various components. Understanding these potential malfunctions can aid in efficient repairs and maintenance. This section aims to guide users through identifying and resolving frequent component failures, enhancing the overall performance and longevity of the machine.
Identifying Symptoms of Malfunction
The first step in addressing component issues is recognizing the symptoms. Unusual noises, inconsistent performance, or failure to function as expected are often indicators of underlying problems. By observing these signs, users can pinpoint which area may require attention, whether it’s related to the motor, tension mechanisms, or other critical elements.
Steps for Resolution
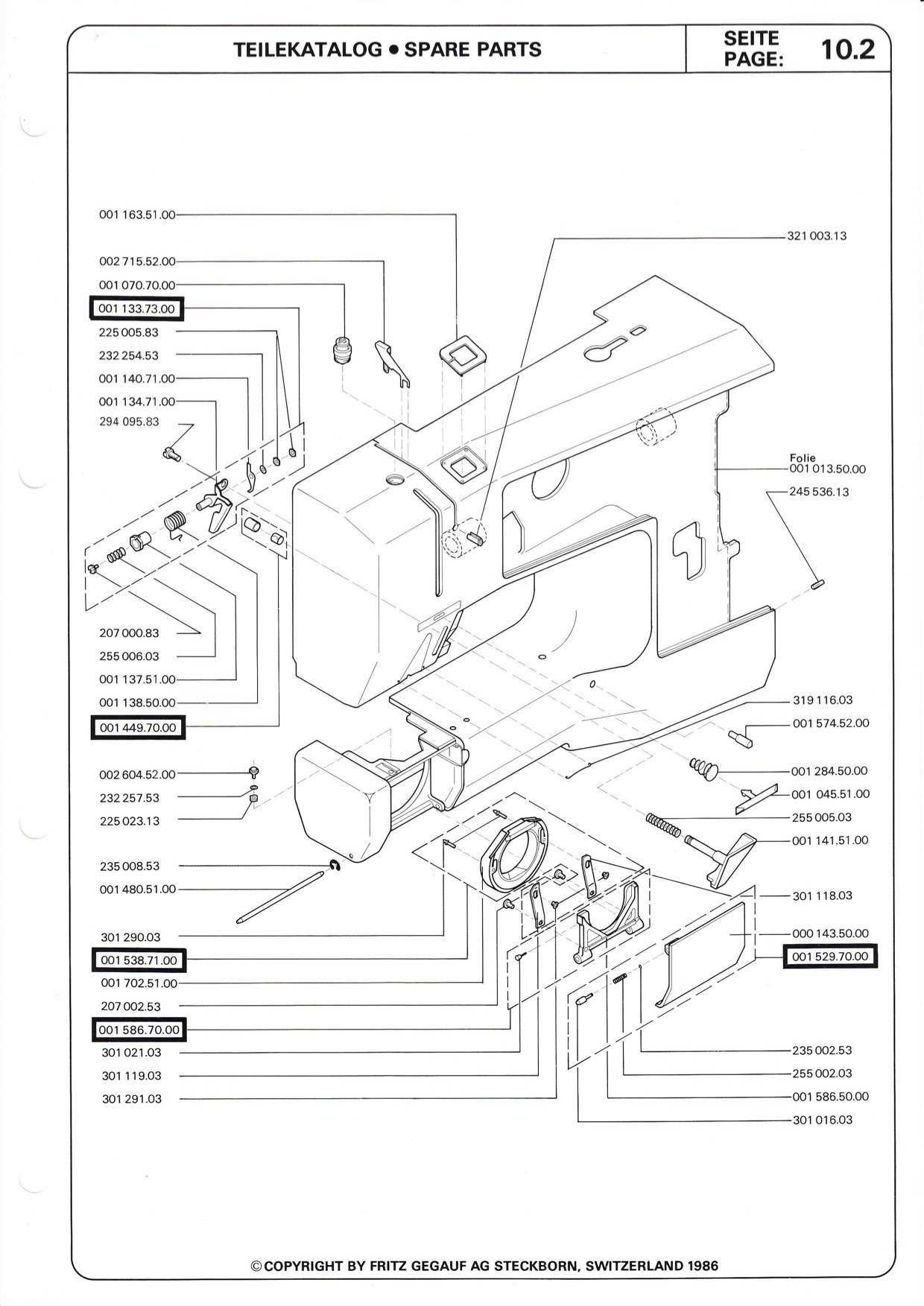
Once symptoms are identified, users can take proactive measures to resolve the issues. Regular maintenance checks, such as cleaning, lubricating moving parts, and ensuring all connections are secure, can significantly reduce the likelihood of failures. If specific components are identified as problematic, consulting the manual or seeking professional assistance can facilitate effective repairs.