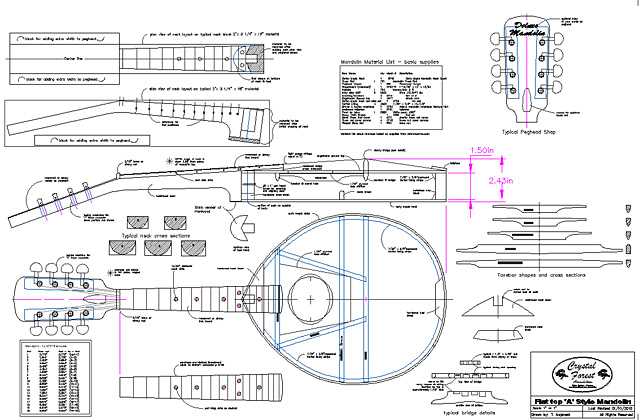
In the world of stringed musical instruments, a comprehensive knowledge of their structure is essential for both players and enthusiasts. Recognizing how various elements work together can enhance performance, facilitate maintenance, and inspire creativity. Each component plays a crucial role in the overall sound production and playability, making an understanding of these elements invaluable.
Every stringed creation features distinct sections that contribute to its unique tone and resonance. From the resonant body to the intricate tuning mechanisms, each segment is designed to fulfill a specific purpose. By familiarizing oneself with these characteristics, musicians can tailor their approach to playing and even modify their instrument for improved sound quality.
Additionally, delving into the construction of these musical tools allows for a deeper appreciation of craftsmanship. Knowledge of the individual components not only enriches one’s playing experience but also encourages a more profound connection with the art of music-making. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced player, understanding the assembly can lead to greater insights and artistic expression.
Understanding the Mandolin Structure
The design of this string instrument is a fascinating blend of craftsmanship and acoustics, comprising various elements that work together to create its unique sound. Each component contributes to the overall tone and playability, making it essential to comprehend how these features interact.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Body | The hollow section that amplifies sound and influences tonal quality. |
| Neck | The elongated part where the frets are placed, allowing for note variation. |
| Headstock | The area where tuning pegs are located, crucial for pitch control. |
| Bridge | Transfers string vibrations to the body, impacting resonance. |
| Strings | Thin wires that produce sound when plucked or strummed. |
Key Components of a Mandolin
Understanding the essential elements of this stringed instrument is crucial for musicians and enthusiasts alike. Each component plays a vital role in shaping the sound, playability, and overall aesthetic. Below is a breakdown of the significant features that contribute to its unique characteristics.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Body | The hollow structure that amplifies sound, usually crafted from various types of wood. |
| Neck | The elongated part where the fingerboard is located, allowing players to press the strings. |
| Strings | Metallic lines that produce sound when plucked or strummed, typically made of steel or other alloys. |
| Bridge | A small piece that supports the strings and transmits vibrations to the body. |
| Fingerboard | The flat surface on the neck where notes are played, featuring frets for accurate pitch. |
| Headstock | The end of the neck that houses the tuning pegs, crucial for adjusting string tension. |
| Tuning Pegs | Mechanical devices used to tune the strings by altering their tension. |
| Soundhole | A circular opening on the body that enhances resonance and projection of sound. |
How the Body Affects Sound
The structure and material of a musical instrument’s body play a crucial role in shaping its tonal characteristics. The interaction between the vibrations produced by the strings and the resonating cavity defines the overall sound quality and projection. Understanding this relationship helps in appreciating the nuances of acoustic design.
| Factor | Impact on Sound |
|---|---|
| Material | Different woods and composites affect warmth, brightness, and clarity. |
| Shape | Curvature and size influence volume and resonance patterns. |
| Thickness | Variations in thickness affect sustain and overall tonal balance. |
| Construction | Joinery and internal bracing determine durability and sound projection. |
Neck Design and Its Importance
The configuration of the elongated component of a string instrument plays a crucial role in its overall playability and sound production. This section explores the significance of thoughtful design in this area, focusing on how various aspects influence the musician’s experience and the instrument’s performance.
Ergonomics and Comfort
A well-designed neck contributes significantly to the comfort of the player. The shape, width, and profile affect how easily a musician can navigate the fingerboard. An ergonomic design reduces strain on the hands and promotes fluid motion, enabling longer practice sessions without discomfort. This aspect is essential not just for professional players but also for beginners, as it can greatly influence their learning curve.
Impact on Sound Quality
The construction materials and dimensions of the elongated section also have a profound effect on the instrument’s tonal characteristics. Different woods and shapes resonate uniquely, impacting the volume and quality of sound produced. A thoughtful approach to these elements ensures that the instrument not only feels right in the hands but also delivers the desired auditory experience.
Types of Mandolin Bridges Explained
Bridges play a crucial role in stringed instruments, influencing sound quality, playability, and overall performance. Various designs serve different purposes, catering to the preferences of musicians and the unique characteristics of each instrument. Understanding these variations can greatly enhance the playing experience and tonal richness.
The traditional design, often crafted from wood, provides a warm and resonant sound. Its simple construction allows for easy adjustments, making it a favorite among players seeking a classic feel. On the other hand, adjustable models offer versatility, enabling musicians to fine-tune string height and action for optimal comfort and playability.
Another option is the compensated bridge, designed to improve intonation by accounting for differences in string length and tension. This innovation helps ensure that notes played along the fretboard remain in tune, particularly in higher registers. Each of these designs serves a unique purpose, allowing players to select the one that best fits their style and needs.
Lastly, there are modern alternatives made from composite materials, which can enhance durability and maintain consistent performance over time. These innovative designs often combine traditional aesthetics with contemporary functionality, appealing to both seasoned artists and newcomers alike.
The Role of the Fingerboard

The fingerboard serves as a crucial component in string instruments, influencing playability and sound production. It provides a surface for musicians to press the strings, enabling them to create various pitches and tones.
Key functions of the fingerboard include:
- Pitch Control: Allows players to alter the pitch by pressing strings at different points.
- Articulation: Facilitates techniques such as slides, bends, and vibrato.
- Comfort: Designed for ergonomic play, enhancing the player’s experience.
Different materials and construction techniques can also affect the instrument’s overall sound and feel, making the fingerboard an essential aspect of performance.
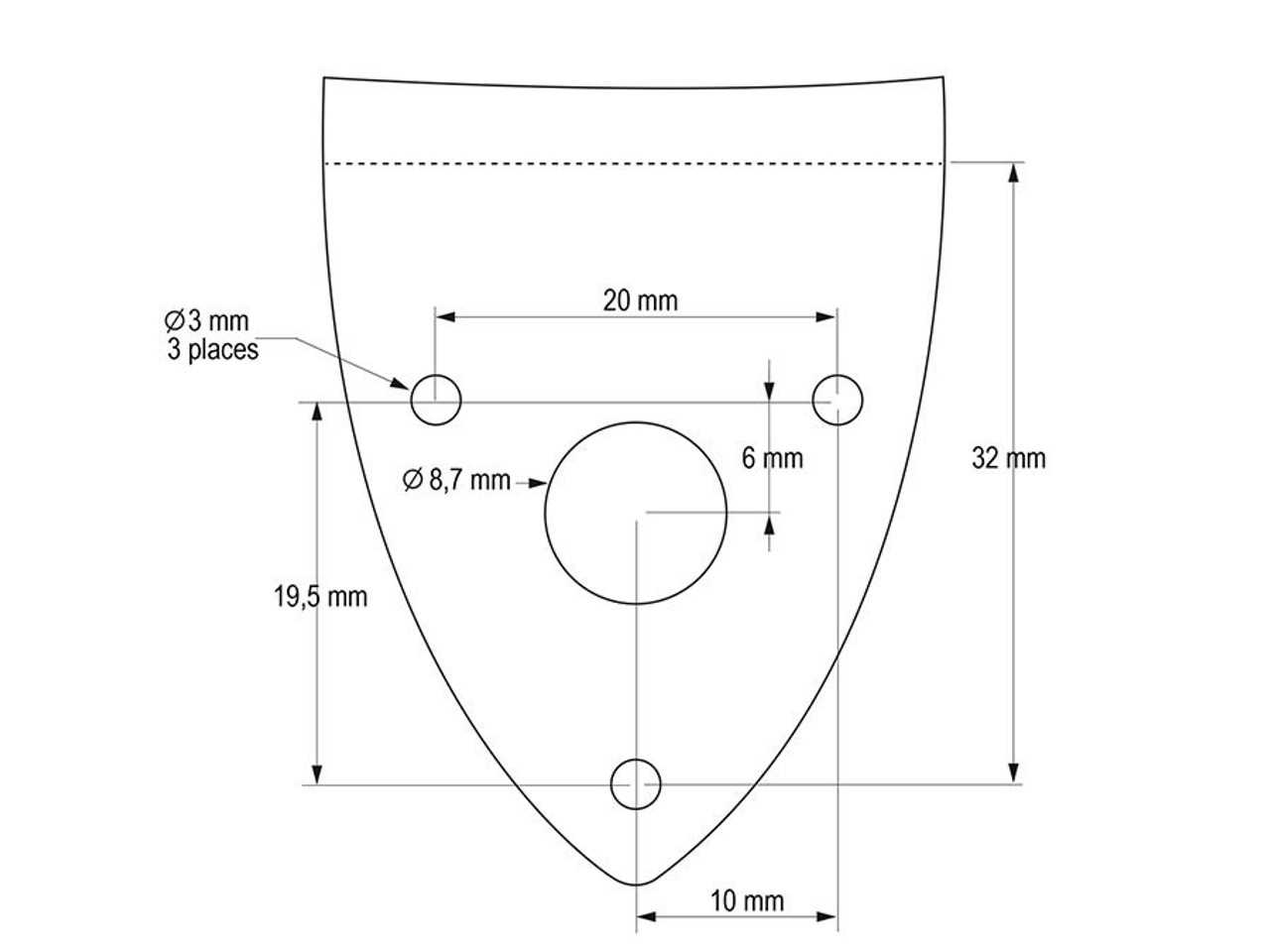
Understanding the Tailpiece Functionality
The tailpiece is a crucial component that plays a significant role in the overall performance and sound quality of stringed instruments. Its primary function is to anchor the strings securely, ensuring proper tension and vibration transfer. This element not only affects the instrument’s resonance but also contributes to the playability and stability of tuning.
One of the main purposes of this fixture is to maintain consistent string tension, which is vital for producing a clear and balanced tone. By holding the strings in place, it helps in transferring the vibrations effectively to the body, enhancing the instrument’s acoustic properties.
Additionally, the design and material of the tailpiece can influence the tonal characteristics. Different shapes and finishes can either amplify or dampen specific frequencies, allowing musicians to tailor their sound. Understanding these nuances can lead to a more informed choice when selecting or modifying an instrument.
In summary, the functionality of the tailpiece goes beyond mere string attachment; it is integral to the instrument’s sound production and overall performance. A well-designed tailpiece can greatly enhance the player’s experience, making it a key consideration for any serious musician.
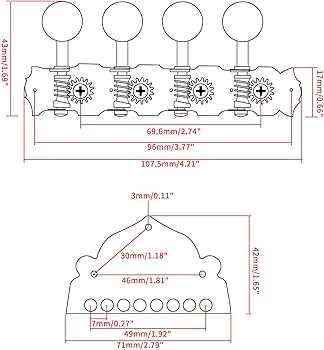
Different Types of Mandolin Tuners
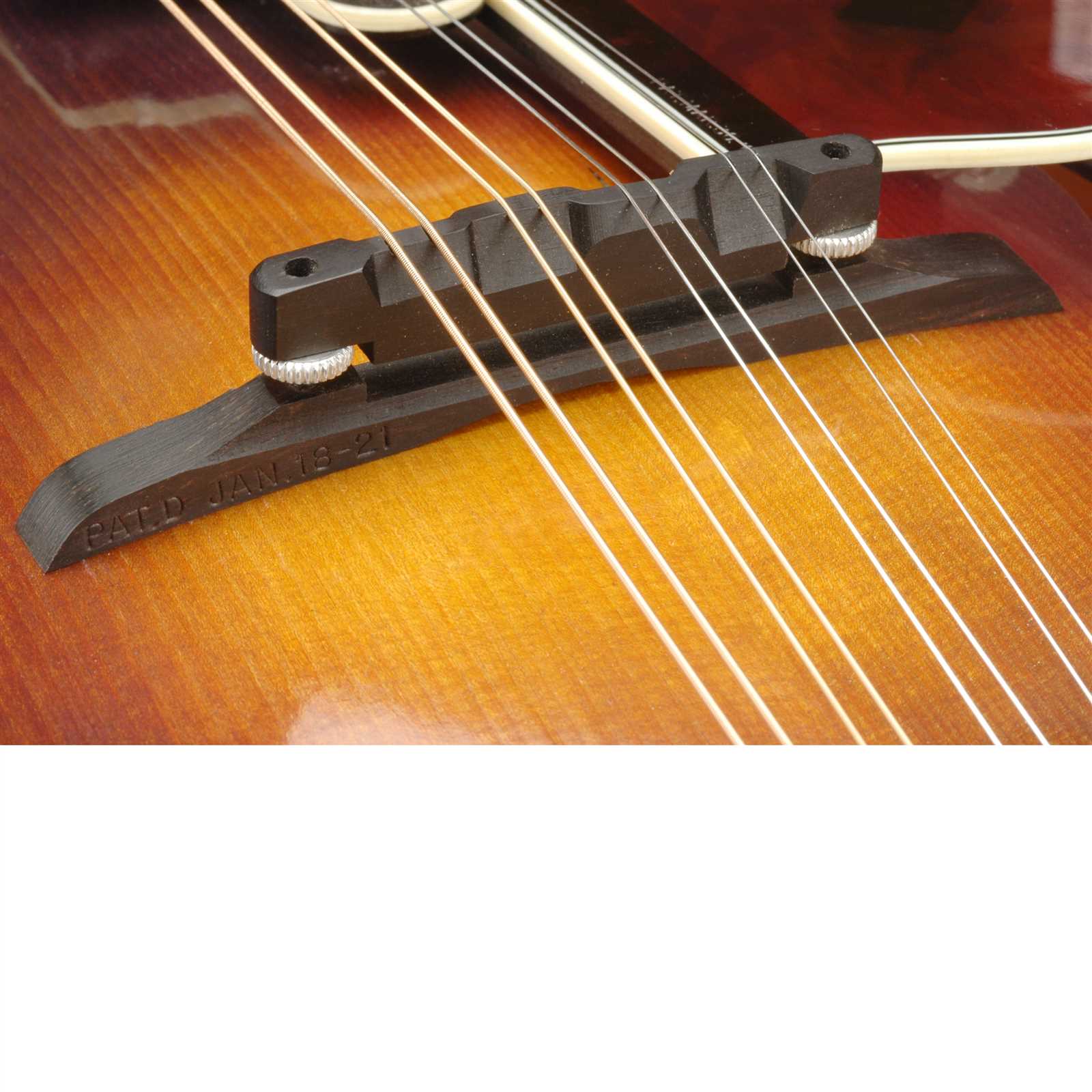

Tuning mechanisms are essential for maintaining pitch accuracy and enhancing the overall playing experience. Various designs cater to different preferences and playing styles.
- Open-Gear Tuners: These feature exposed gears, providing a classic aesthetic and lightweight design.
- Closed-Gear Tuners: Offering a more streamlined look, these are protected from dust and debris, ensuring longevity.
- Planetary Tuners: Known for their compact size, they provide precise adjustments and smooth operation.
Choosing the right tuning mechanism can greatly impact sound quality and ease of use, making it a crucial aspect for musicians.
Exploring the Fretboard Layout
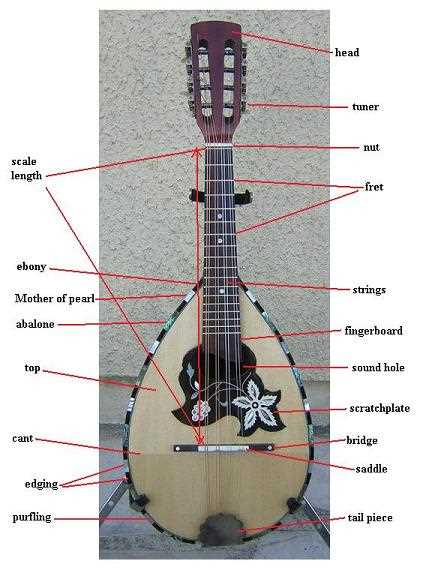
Understanding the arrangement of the playing surface is essential for any musician looking to master their instrument. This layout not only influences the way notes are produced but also affects the overall musical expression and creativity. By familiarizing oneself with the various positions and their relationships, players can unlock a world of possibilities.
The layout consists of several horizontal sections, each representing a specific pitch. As one moves along these sections, the notes change, creating a linear progression that is foundational for performance. Visualizing this structure can greatly enhance a player’s ability to navigate and improvise with confidence.
Moreover, understanding intervals between notes on the layout can assist in developing a deeper comprehension of scales and chords. Each fret serves as a stepping stone, connecting different sounds and allowing for seamless transitions. By exploring these connections, musicians can enhance their overall proficiency.
Ultimately, a thorough grasp of this arrangement paves the way for more advanced techniques and expressive playing, making it a critical aspect of musical mastery.
The Impact of Wood Choice
The selection of timber plays a crucial role in shaping the overall quality and character of string instruments. Different types of wood contribute unique tonal properties, influencing both the sound produced and the instrument’s aesthetic appeal. Each variety brings its own set of characteristics, affecting resonance, sustain, and projection.
Maple, for instance, is often favored for its bright, clear sound and excellent projection. Its dense structure enhances sustain, making it a popular choice for the back and sides of many instruments. In contrast, spruce is renowned for its dynamic range and responsiveness, providing warmth and richness to the sound. This combination of timbers can result in a harmonious balance that elevates the overall musical experience.
Additionally, the age and treatment of the wood significantly influence its performance. Well-seasoned materials often deliver superior tonal qualities, as they have had time to stabilize and develop their unique characteristics. Ultimately, the choice of wood is a fundamental consideration for luthiers, as it impacts not only the instrument’s sound but also its longevity and playability.
Comparing Acoustic and Electric Mandolins

This section explores the distinctions between traditional and modern string instruments, focusing on their construction, sound production, and suitability for various musical styles.
When considering these two types, it’s important to examine several key factors:
- Sound Quality: Traditional instruments offer a warm, resonant tone, while modern versions provide versatility and sharper sounds.
- Construction: Classic designs typically use wood, whereas contemporary models often incorporate electronic components.
- Playing Style: The choice may depend on genres; folk music often leans towards acoustic, while rock and jazz favor electric.
- Portability: Electric models can be more convenient for travel and performances due to their lightweight nature.
Ultimately, the decision hinges on personal preference and the specific musical context in which the instrument will be used.
Maintenance Tips for Mandolin Parts
Keeping your string instrument in optimal condition requires regular care and attention. Proper maintenance enhances performance and extends the lifespan of its components. By following some essential guidelines, you can ensure your instrument remains in excellent shape, delivering rich sound and playability.
Regular Cleaning

Dust and grime can accumulate on the surface, affecting both aesthetics and sound quality. Use a soft cloth to wipe down the body after each session, paying special attention to the fingerboard and bridge. For deeper cleaning, consider using a specialized cleaner suitable for your instrument’s material, ensuring it remains free from harmful residues.
String Care and Replacement
Strings are vital for sound production and should be regularly checked for wear and tear. Replace them when you notice a loss of tone or fraying. When installing new strings, ensure they are properly stretched and tuned to maintain stability. Additionally, consider cleaning them with a cloth after playing to prolong their lifespan and keep your instrument sounding its best.