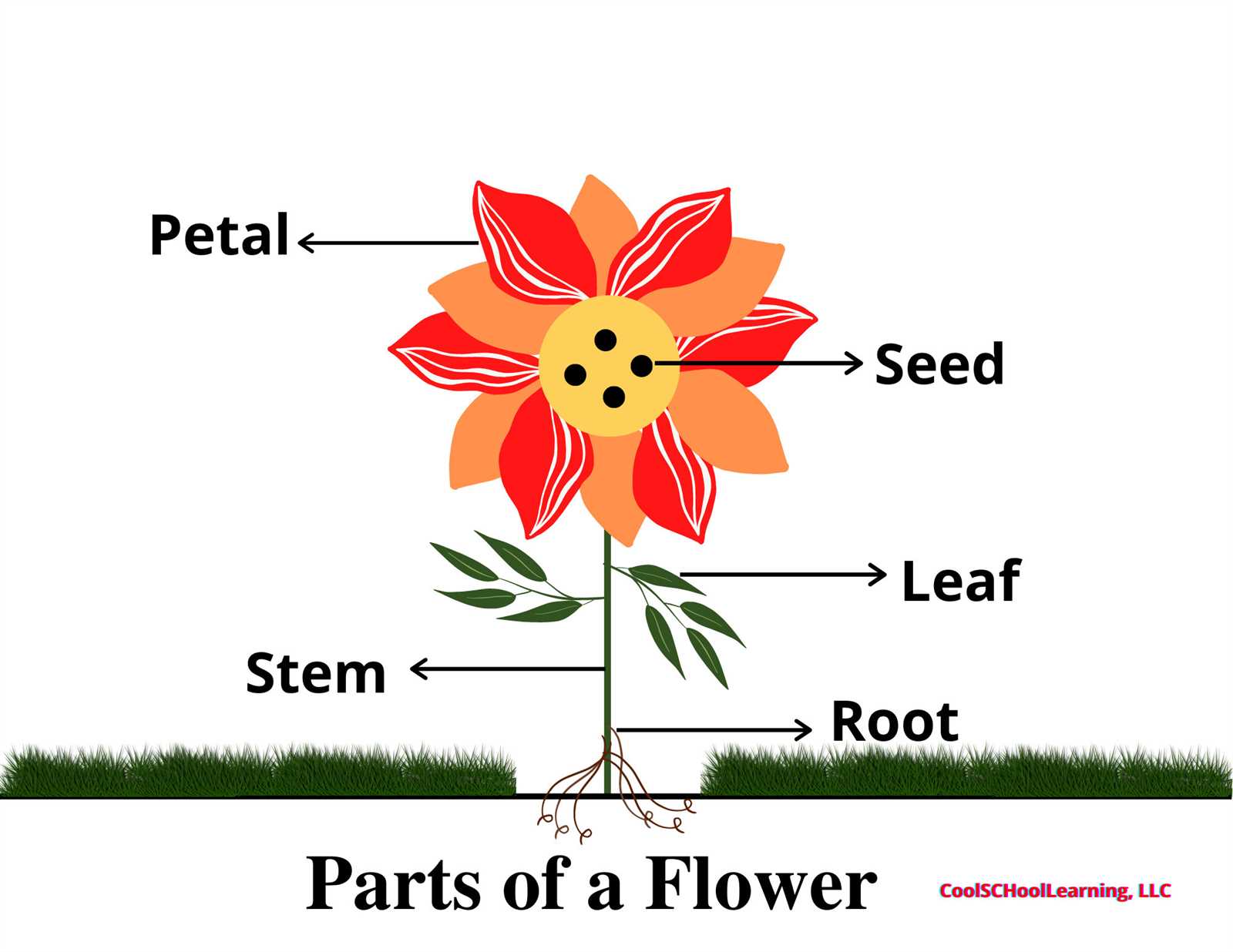
In nature, many living organisms rely on complex systems to sustain and propagate life. One of the most intricate structures is found in plants, specifically in the reproductive segment. These components work together harmoniously, playing a key role in the process of reproduction.
The different sections of this vital structure serve distinct functions. Some are responsible for attracting essential pollinators, while others ensure successful fertilization. Each element is crucial to the life cycle, contributing to the continuation of plant species across ecosystems.
By examining these components closely, we can appreciate the balance and efficiency of plant reproduction. This exploration highlights the beauty and sophistication inherent in even the smallest details of nature’s designs.
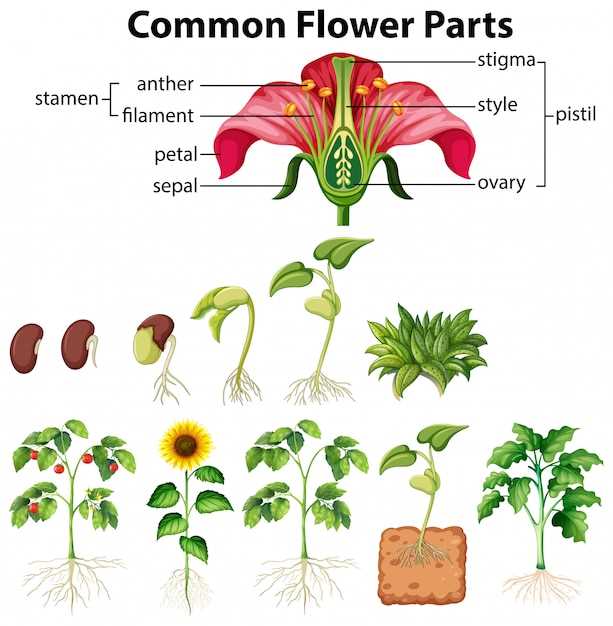
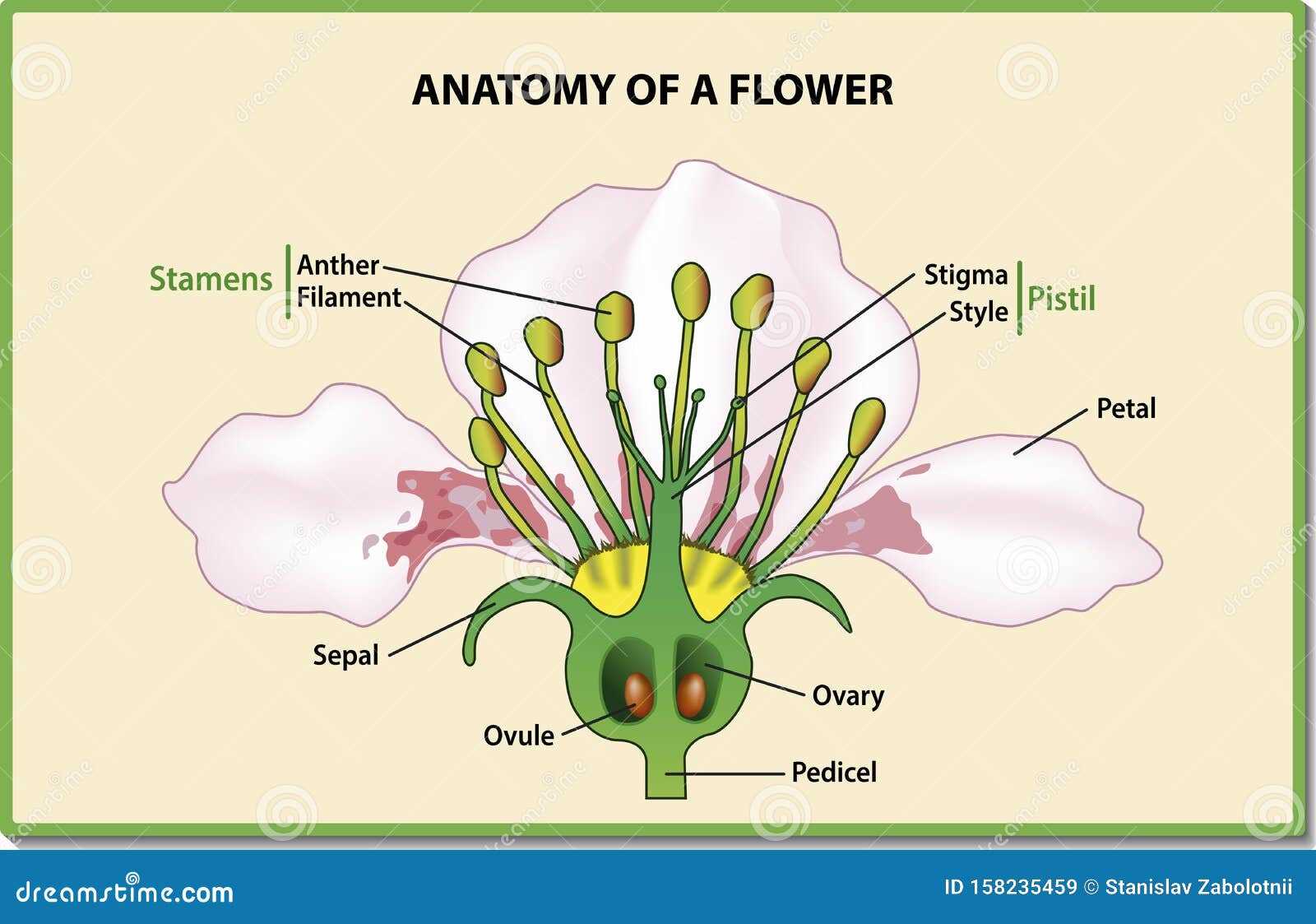
Diagram Showing Parts of a Flower
The structure of a typical plant’s reproductive unit contains multiple essential elements, each serving a unique function for its development and reproduction. By examining these components, we can better understand how the plant produces seeds and perpetuates its lifecycle. The arrangement and roles of these elements are fundamental for the process of pollination and fertilization.
Main Elements Overview
The primary features include specialized areas responsible for reproduction and support. These components work together to ensure the successful production of seeds, allowing the plant to thrive in its environment.
Key Functional Zones
The reproductive unit of the plant is composed of various zones, each contributing to its overall operation. Below is a simple representation of the key sections:
| Component | Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper Section | Involved in the creation of pollen and seed development. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| Stamen | Produces pollen grains containing male gametes. |
| Pistil | Receives pollen and houses the ovary, where fertilization occurs. |
| Ovary | Contains ovules which develop into seeds post-fertilization. |
| Style | Connects the stigma and ovary, providing a pathway for pollen tubes. |
| Stigma | Serves as the receptive surface for pollen grains. |
How Nectar Guides Attract Pollinators
Nectar guides are essential features that play a significant role in drawing in various pollinators. These unique markings and patterns provide visual cues that direct these creatures toward the reward of nectar. By facilitating the foraging process, nectar guides enhance the efficiency of pollination.
The vibrant colors and intricate designs of these guides are strategically placed to be easily noticed by pollinators, such as bees and butterflies. The contrast between the guide patterns and the surrounding petals creates a visual pathway, leading pollinators straight to the nectar source. This not only aids pollinators in locating food but also promotes cross-pollination, which is vital for the reproductive success of many plants.
Moreover, the presence of nectar guides can influence the behavior of pollinators, encouraging them to visit more flowers. This repetitive movement from one bloom to another increases the likelihood of successful pollen transfer, ensuring that both the plants and the pollinators benefit from this mutual relationship.
Exploring the Function of Filament
The filament plays a crucial role in the reproductive process of angiosperms. It acts as a supportive structure that connects the anther to the main stem, facilitating the transfer of nutrients and moisture essential for pollen development. Understanding its function offers insight into the complex mechanisms that ensure successful reproduction in these organisms.
Structure and Composition
The filament is typically slender and elongated, composed of vascular tissues that allow for the efficient transport of vital resources. This structural design not only supports the anther but also contributes to the overall stability of the reproductive system.
Role in Reproduction
During the flowering stage, the filament elevates the anther, enhancing its exposure to pollinators. This elevation increases the likelihood of successful pollination, which is fundamental for seed formation and genetic diversity. The filament’s adaptability to various environmental conditions further aids in the reproductive success of the species.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Support | Holds the anther in position for optimal pollen dispersal. |
| Nutrient Transport | Transports essential nutrients from the plant to the anther. |
| Pollination Aid | Elevates the anther to attract pollinators more effectively. |
Formation and Purpose of Pollen
Pollen is a crucial biological substance produced by certain reproductive structures in plants. This fine powder plays an essential role in the reproductive cycle, enabling the transfer of genetic material. Understanding the formation of this substance and its functions reveals the intricacies of plant reproduction.
The process of pollen development begins within specialized areas of the reproductive structures. These locations undergo various stages, ultimately leading to the creation of grains. Each grain contains male gametes, which are vital for fertilization. The formation process can be influenced by numerous factors, including environmental conditions and genetic makeup.
| Stage of Formation | Description |
|---|---|
| Microsporogenesis | The initial stage where microspores are formed from the sporogenous tissue. |
| Microgametogenesis | The process where microspores develop into pollen grains. |
| Pollen Maturation | The final stage in which pollen grains are fully developed and ready for dispersal. |
The primary function of pollen is to facilitate fertilization by transferring male gametes to female reproductive structures. This process often involves various pollinators, such as insects, birds, or wind, which assist in moving pollen from one plant to another. By achieving this transfer, plants can ensure genetic diversity and the continuation of their species.
Floral Diagrams for Educational Use
Visual representations play a crucial role in understanding botanical structures and their functions. These illustrative materials serve as valuable tools for students and educators alike, enabling a clearer grasp of complex biological concepts. By utilizing these graphics, learners can enhance their comprehension and retention of information.
There are various benefits to employing these educational resources:
- Enhanced Learning: Visual aids facilitate quicker understanding and allow students to make connections between different elements.
- Engagement: Interactive visuals can captivate students’ attention, making the learning process more enjoyable.
- Simplification: Complex information becomes more accessible when represented visually, reducing cognitive load.
In educational settings, these graphics can be utilized in multiple ways:
- Classroom Activities: Integrating these visuals into lessons can encourage discussions and collaborative learning.
- Study Aids: Students can use these resources for revision, aiding memory recall during examinations.
- Project Work: Assignments that involve creating or interpreting these graphics can foster creativity and critical thinking.
Ultimately, employing visual representations in botanical education fosters a deeper understanding of biological concepts while making the learning experience more interactive and engaging.
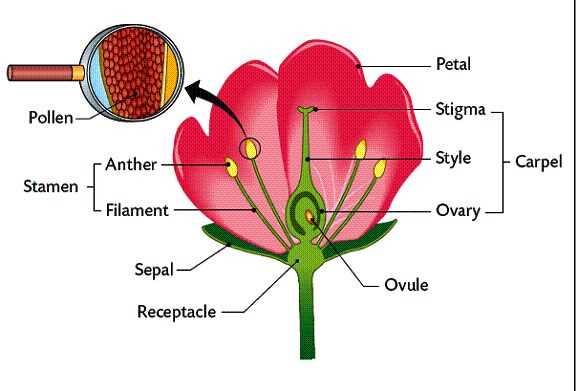
Cross-Section View of a Flower

The internal structure of a bloom reveals intricate details that contribute to its function and beauty. Analyzing this view allows us to appreciate the complexity involved in reproduction and support within the plant kingdom. Each component plays a crucial role, working harmoniously to ensure the success of the reproductive cycle.
Understanding the Internal Arrangement
When examining the inner composition, various elements can be identified, each serving distinct purposes. The central reproductive organs are surrounded by supportive structures, which help in the processes of pollination and fertilization. The arrangement of these features can vary significantly among different species, highlighting the diversity of botanical forms.
Functional Importance of Each Component
Each section within this structure contributes uniquely to the overall vitality of the plant. The reproductive components facilitate genetic exchange, while other structures provide protection and nourishment. This intricate interplay underscores the significance of understanding the inner workings of these natural wonders.
Comparison of Monocot and Dicot Flowers
Understanding the distinctions between two major groups of plants provides insight into their unique characteristics and evolutionary adaptations. These two classifications exhibit variations in structure, growth patterns, and reproductive features, which play significant roles in their respective ecological niches.
| Feature | Monocots | Dicots |
|---|---|---|
| Leaf Venation | Parallel | Reticulate |
| Number of Cotyledons | One | Two |
| Root System | Fibrous | Taproot |
| Floral Parts | In multiples of three | In multiples of four or five |
| Pollen Structure | Single aperture | Three apertures |