Understanding the layout and structure of key elements in high-performance vehicles is crucial for both enthusiasts and professionals. The comprehensive overview of these interconnected systems can offer insights into how each element contributes to overall functionality. Whether you’re interested in maintenance or upgrades, having a clear view of the internal structure is beneficial.
In this section, we will take a closer look at the various mechanical and electronic systems that play a pivotal role in performance optimization. By exploring how these elements are organized, you’ll gain a better understanding of their individual purposes and how they interact as a whole to ensure smooth operation.
Through detailed examination, you will uncover the importance of each component and how they collectively form a well-balanced system. This knowledge not only aids in troubleshooting but also provides valuable information
S1000RR Parts Diagram: Comprehensive Overview
The structure and key elements of the high-performance motorcycle are designed with precision, ensuring optimal performance. Understanding the intricate layout is essential for both maintenance and upgrades, allowing riders to maximize efficiency and longevity.
Main Components Breakdown
The machine consists of various interconnected systems, each playing a critical role in overall functionality. The framework supports the main body, while the engine and exhaust work in harmony to deliver peak power. Electrical elements provide control and monitoring, enabling a smooth and responsive ride.
Critical Mechanical Systems
Focusing on the mechanical elements, the suspension system is responsible for maintaining balance and comfort, while the braking system ensures safety in high-speed conditions. These features, combined with cutting-edge technology, define the bike’s superior handling and
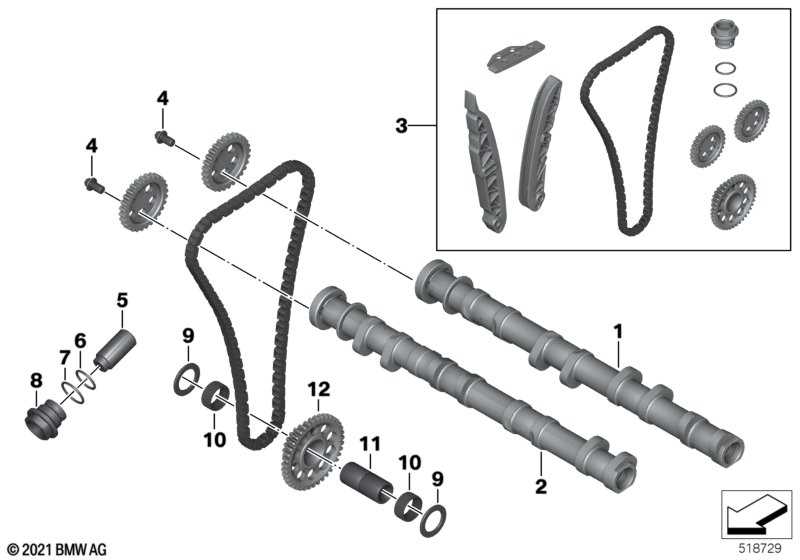
Engine Components and Their Functions
The internal structure of a motorcycle’s engine consists of multiple elements working together to deliver power and efficiency. Each component plays a critical role in the overall functionality, ensuring smooth operation and optimal performance. Below is an overview of key components and how they contribute to the engine’s operation.
- Cylinder: This is the chamber where fuel combustion occurs, powering the engine.
- Piston: Positioned inside the cylinder, it moves up and down, converting fuel combustion into mechanical energy.
- Crankshaft: The crankshaft translates the piston’s linear motion into rotational energy, driving the vehicle forward.
- Camshaft:
Frame Structure and Key Elements

The framework is the core component that provides stability and balance, ensuring optimal performance and control. Each part within this structure plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity and functionality of the overall system. Understanding how these elements interact is essential for maintaining smooth operation and safety.
Main Frame Components
- Chassis: The backbone that supports the entire structure and connects various systems for seamless coordination.
- Subframe: A lighter, detachable section providing support for the rear end and additional attachments.
- Engine Mounts: Crucial connectors that secure the engine within the frame, reducing vibration and improving balance.
Key Structural Attachments
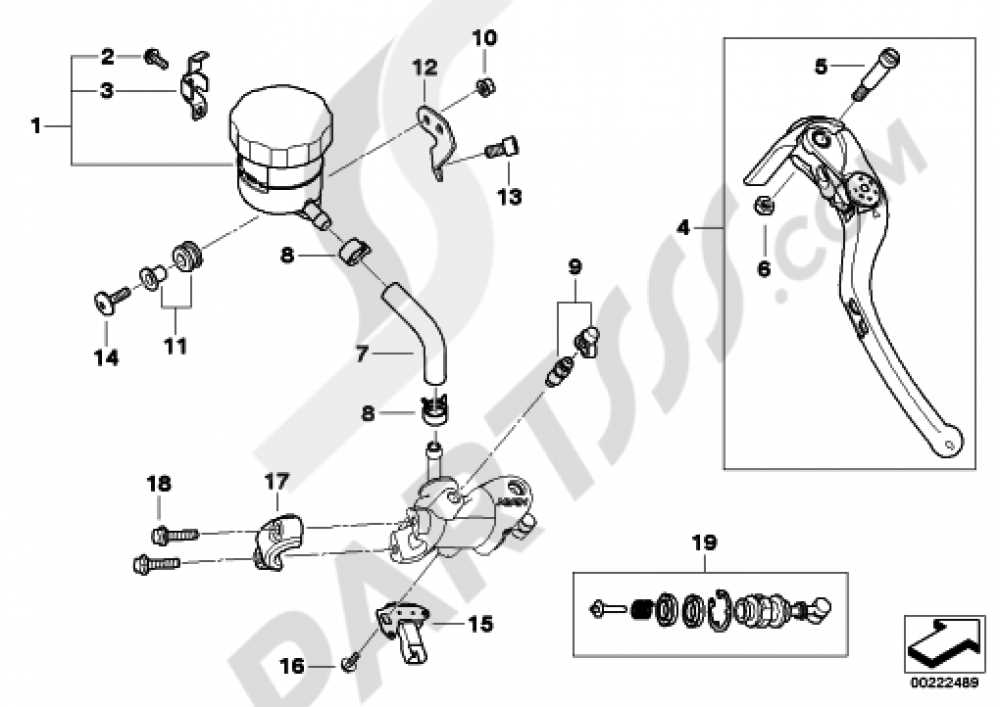
Suspension System Layout and Design
The suspension system plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal handling and comfort during dynamic riding conditions. Its configuration is meticulously engineered to provide stability, absorb road irregularities, and maintain precise control under various loads and speeds. This section delves into the structural arrangement and core components that contribute to a balanced and responsive setup.
Front Suspension is designed to enhance steering responsiveness and ensure a smooth ride over uneven surfaces. It typically incorporates mechanisms that allow adjustments to match the rider’s preferences and the type of terrain.
Rear Suspension works in harmony with the front to deliver overall stability, particularly during acceleration and cornering. Its construction often involves multiple elements that can be fine-tuned to achieve the desired performance and comfort levels.
Both preload settings and damping mechanisms are essential for adapting the suspension to various riding styles and conditions, ensuring optimal balance
Braking Mechanism Parts and Operation
The braking system is an essential component for ensuring vehicle safety and control during movement. Its role is to slow down or stop the motorcycle efficiently, transforming kinetic energy into heat through friction. Understanding the individual elements involved in this process is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and reliability.
The primary elements responsible for the braking process include the caliper, which houses the pistons, and the brake pads that create the necessary friction. The brake disc, attached to the wheel, rotates in conjunction with the motion of the motorcycle. When the brake lever is applied, hydraulic pressure forces the pistons to press the pads against the disc, slowing down the wheel’s rotation.
Additionally, the master cylinder regulates the fluid pressure throughout the system, ensuring the appropriate amount of force is applied to achieve the desired braking effect. Regular maintenance of these components is essential for ensuring consistent performance and avoiding potential issues that may arise
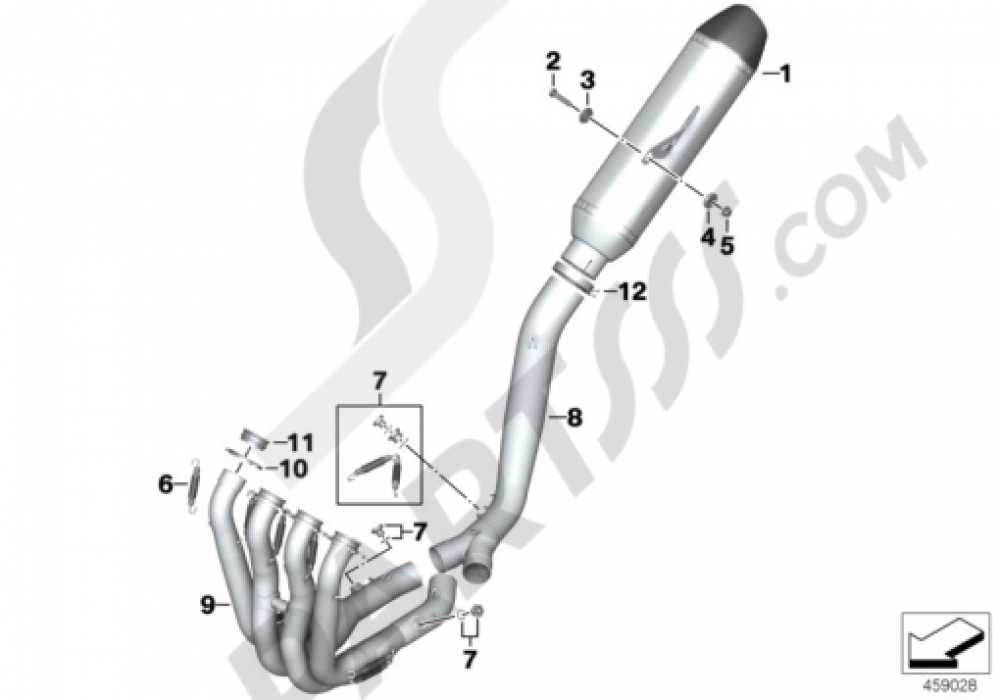
Exhaust System Breakdown and Explanation
The exhaust system is a critical component of any high-performance motorcycle, playing a vital role in both efficiency and sound. Understanding its structure and function can enhance maintenance and performance tuning. This section provides an in-depth look at the various elements that constitute the exhaust assembly and their specific roles.
Components of the Exhaust System: The exhaust setup typically includes several key parts, such as headers, catalytic converters, mufflers, and tailpipes. Each of these elements serves a distinct purpose, from channeling exhaust gases away from the engine to reducing noise and harmful emissions.
Headers are the first section of the exhaust system, directly connected to the engine. Their primary function is to collect exhaust gases from the engine’s cylinders and direct them towards the next component. The design of headers can significantly influence performance, with options available that enhance flow and efficiency.
Following the headers, the catalytic converter is responsible for reducing harmful emissions. It utilizes chemical reactions to convert toxic gases into less harmful substances before they exit the system. This component is essential for meeting environmental regulations and ensuring cleaner air.
The muffler is another crucial element, designed to minimize noise produced by the engine’s exhaust gases. Mufflers come in various designs, each affecting sound levels and performance differently. Selecting the right muffler can enhance the riding experience while maintaining compliance with noise regulations.
Finally, the tailpipe is the visible section that directs exhaust gases out of the motorcycle. The design of the tailpipe can impact the overall aesthetic and sound of the vehicle, as well as its performance characteristics.
Understanding these components and their interactions allows riders to make informed choices regarding modifications and maintenance, ultimately enhancing the overall riding experience.
Electrical System Wiring and Components
The electrical system of a motorcycle plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and safety. It encompasses various wiring and components that work together to deliver power to essential functions, including lighting, ignition, and instrumentation. Understanding these elements is vital for maintenance and troubleshooting.
At the core of the electrical system are the wiring harnesses, which facilitate the distribution of electricity throughout the vehicle. These harnesses connect various parts, allowing for seamless communication between components. Connectors are equally important, providing secure links that prevent disruptions in the electrical flow.
Another key aspect is the battery, which serves as the primary power source. Its health directly influences the performance of the entire electrical system. Regular checks and maintenance of the battery ensure reliability during operation. Additionally, components such as fuses and relays protect the system from overloads and help manage electrical circuits efficiently.
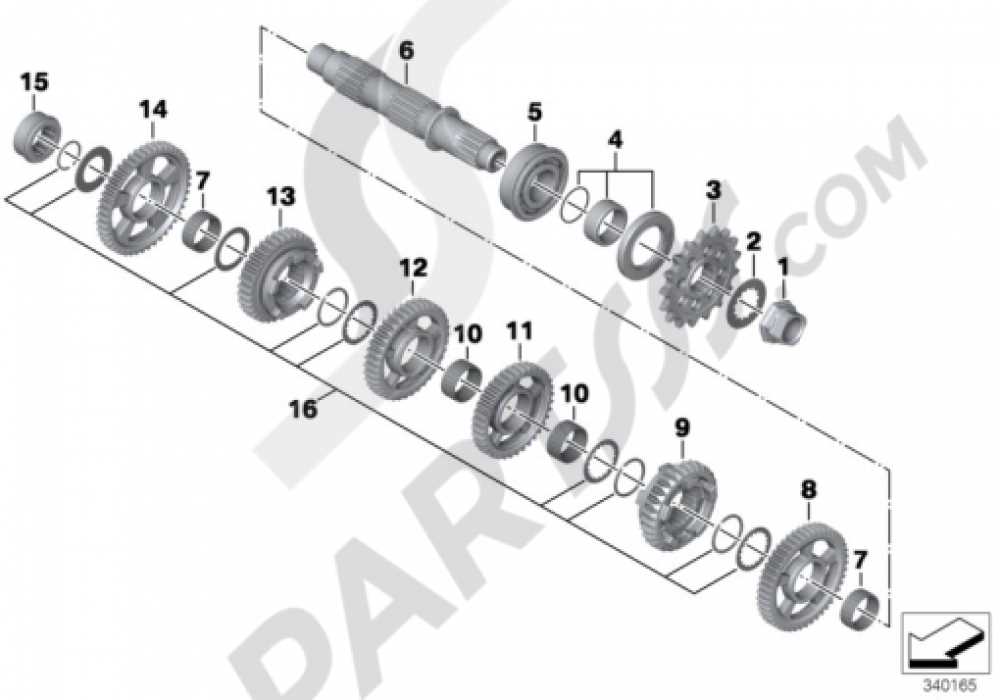
Transmission and Gearbox Parts Overview
The transmission system plays a crucial role in converting the engine’s power into motion, ensuring a smooth and efficient ride. This section delves into the key components involved in this vital mechanism, highlighting their functions and significance in maintaining optimal performance.
Key Components of the Transmission System
The primary elements of the transmission assembly include the gearbox, clutch, and various linkages. Each component works in harmony to facilitate seamless gear shifts, allowing for effective torque management. The gearbox, often referred to as the heart of the transmission, is responsible for altering the speed and torque delivered to the wheels, while the clutch enables smooth engagement and disengagement of power.
Functionality and Importance
Understanding the functionality of these components is essential for any motorbike enthusiast. A well-maintained transmission system ensures not only better performance but also enhanced durability. Regular inspections and timely replacements of worn-out components can significantly improve the riding experience and extend the life of the motorcycle.
Fuel System Components and Layout
The fuel system is a critical element in the operation of any high-performance motorcycle, as it ensures the optimal delivery of fuel to the engine for efficient combustion. Understanding the various components and their arrangement can greatly enhance maintenance and performance tuning.
- Fuel Tank: The primary reservoir for storing fuel before it is fed to the engine.
- Fuel Pump: This component is responsible for transporting fuel from the tank to the engine at the required pressure.
- Fuel Filter: Essential for removing impurities from the fuel to protect the engine’s internal components.
- Fuel Injector: Delivers the precise amount of fuel into the combustion chamber at the right moment.
- Fuel Pressure Regulator: Maintains consistent fuel pressure in the system, adjusting the flow as needed.
- Fuel Lines: These hoses connect the various components, ensuring the safe and efficient transfer of fuel.
The layout of these elements is designed to maximize efficiency and minimize potential issues. Proper understanding of the system helps in troubleshooting and optimizing performance.
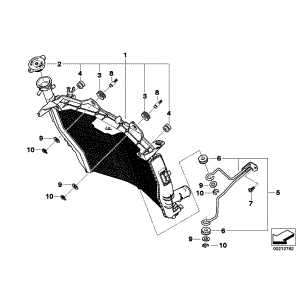
Cooling System Parts and Flow Diagram
The cooling system is vital for maintaining optimal engine temperatures, ensuring performance and longevity. This section delves into the essential components of the cooling mechanism, illustrating how each element contributes to the overall efficiency.
- Radiator: This component dissipates heat from the coolant, allowing it to return to a lower temperature.
- Water Pump: It circulates the coolant through the system, ensuring consistent flow.
- Thermostat: This device regulates the temperature by controlling coolant flow to the radiator.
- Coolant Hoses: These flexible tubes transport the coolant between the engine, radiator, and other components.
- Expansion Tank: It accommodates changes in coolant volume due to temperature variations.
Understanding the flow of the cooling fluid is crucial for troubleshooting and enhancing system efficiency. The typical flow pattern begins with the water pump drawing coolant from the expansion tank, circulating it through the engine block, where it absorbs heat. The heated coolant then moves to the radiator, where it releases heat into the atmosphere before returning to the water pump, thus completing the cycle.
Handlebars, Controls, and Interface Parts
The handlebars and associated controls are vital components that significantly influence the riding experience. They provide not only steering capabilities but also house various interfaces that facilitate communication between the rider and the motorcycle. Understanding these elements is essential for effective handling and overall performance.
These components are designed for ergonomic use, ensuring that the rider can maintain comfort and control during their journey. The layout of controls is strategically organized to allow for intuitive operation, making it easier to access essential functions without diverting attention from the road.
Component Description Handlebars The primary steering mechanism that allows for directional control. Throttle Control Regulates engine power and acceleration through twist or push mechanisms. Brake Levers Used to engage the front and rear brakes for slowing down or stopping. Clutch Lever Disconnects the engine from the transmission to facilitate gear changes. Instrument Cluster Displays critical information such as speed, RPM, fuel level, and warning indicators. Switches Controls various functions like lights, turn signals, and horn. Body Panels and Aesthetic Components
The exterior design of a motorcycle plays a crucial role in its overall appeal and performance. Various elements contribute to the aesthetic quality, as well as to the functionality of the vehicle. Understanding these components is essential for both enthusiasts and owners looking to customize their rides.
- Fairings: These panels not only enhance the visual aspect but also improve aerodynamics, reducing wind resistance while riding.
- Tank Covers: Serving both protective and aesthetic purposes, tank covers can add a personalized touch and are available in various finishes.
- Fenders: Positioned at the front and rear, fenders shield the bike from debris while contributing to its sleek profile.
- Side Panels: These components provide access to internal parts while maintaining a cohesive look and can often be customized for a unique appearance.
- Windshields: Not only do they protect the rider from wind and debris, but they also contribute to the bike’s style, available in different heights and tints.
Understanding these components allows for better customization choices, enhancing both the aesthetic and functional aspects of the motorcycle.