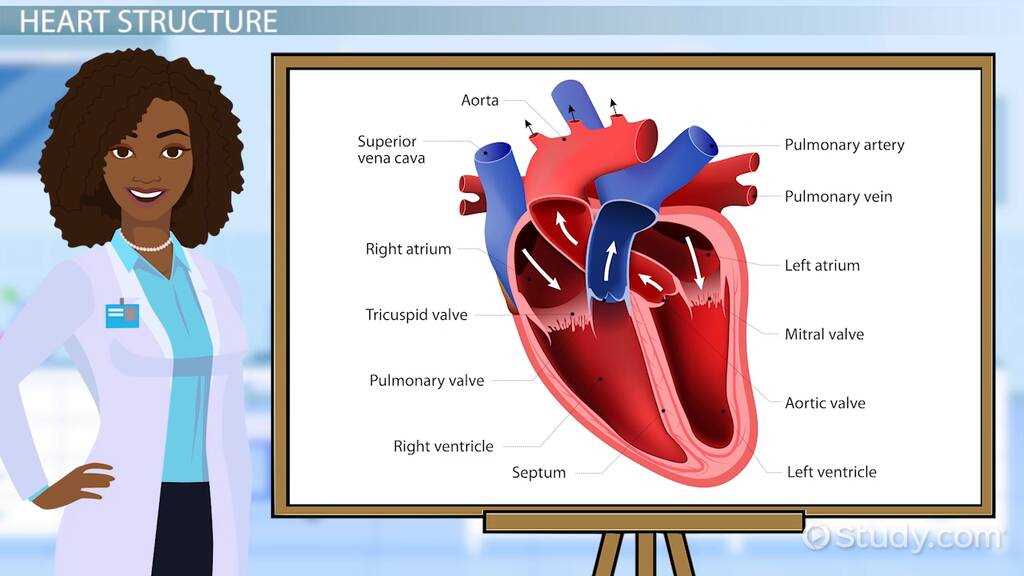
Understanding the intricate workings of a vital organ can greatly enhance one’s knowledge of human biology. This section delves into the essential elements that contribute to its function, showcasing how each segment plays a unique role in overall performance.
By exploring the various sections of this crucial organ, one can appreciate the complexity and harmony inherent in its design. Each area collaborates seamlessly with others, ensuring that blood circulates effectively throughout the body.
Visual representations can significantly aid in comprehending these intricate connections. A clear illustration can provide a quick reference, making it easier to grasp how these individual elements interact and contribute to the organ’s essential tasks.
This section provides an essential understanding of the structure and organization of a vital organ responsible for circulating blood throughout the body. By exploring its various components, readers can gain insight into how each section plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health.
The following table summarizes the key structures and their functions within this remarkable organ:
This section focuses on the essential components that contribute to the overall functionality of the circulatory mechanism. Understanding these vital elements provides insight into how blood circulates throughout the body, ensuring that tissues receive necessary nutrients and oxygen.
By comprehending these core structures, one can appreciate the intricate design that enables efficient circulation, ultimately sustaining life.
The cardiovascular system relies on several distinct elements, each playing a vital role in circulating life-sustaining fluids throughout the body. Understanding how these individual components work in unison helps explain the essential processes that keep us alive.
| Component |
Function |
| Chamber A |
Receives fluid from external vessels, serving as the initial point for circulation. |
| Chamber B |
Pumps the fluid into the main circulation pathways, ensuring it reaches all parts of the body. |
| Valve X |
Regulates the flow, preventing backflow and maintaining a one-way direction through the system. |
| Muscle Layer |
Contracts rhythmically to propel the fluid with necessary force, sustaining the movement. |
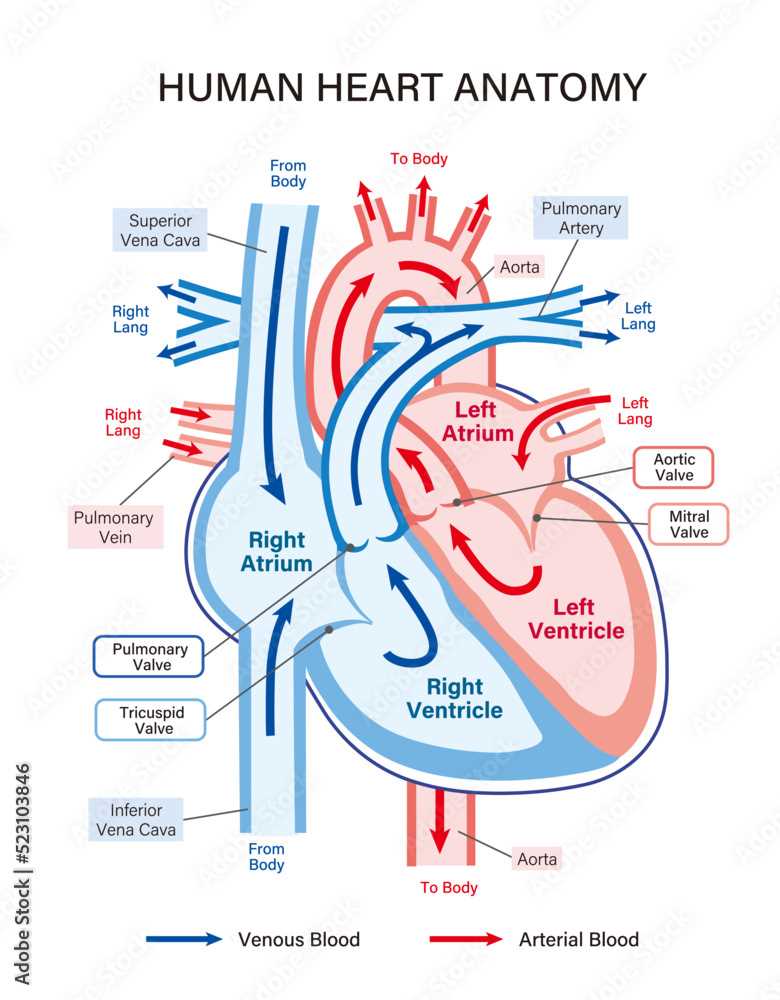
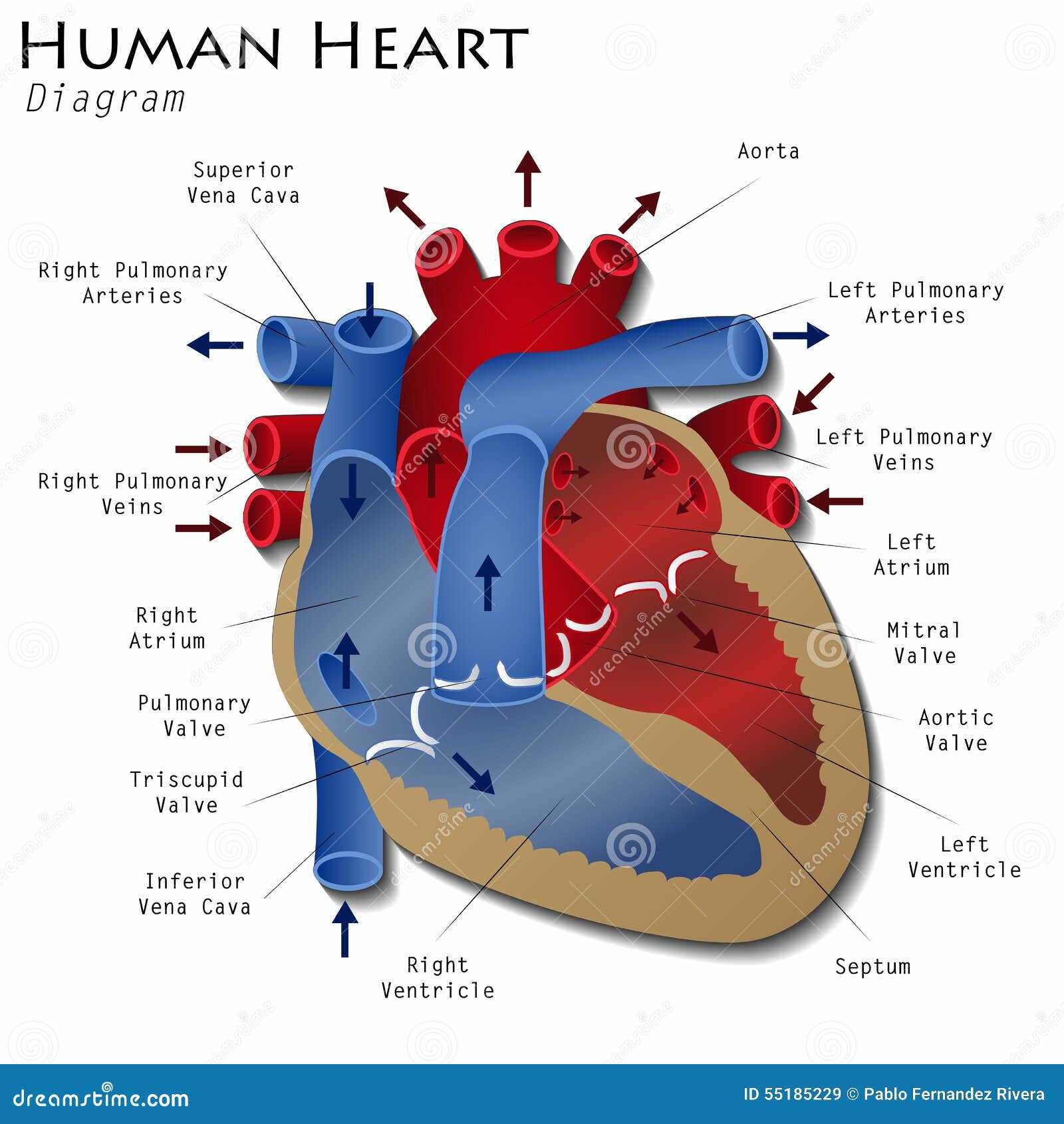
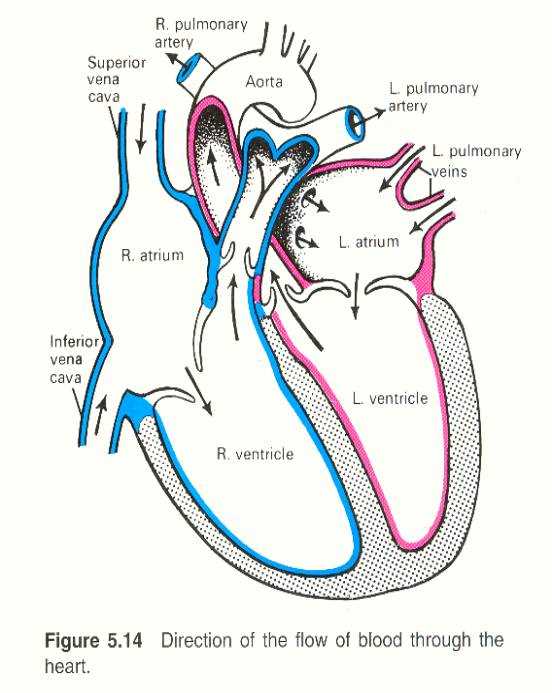
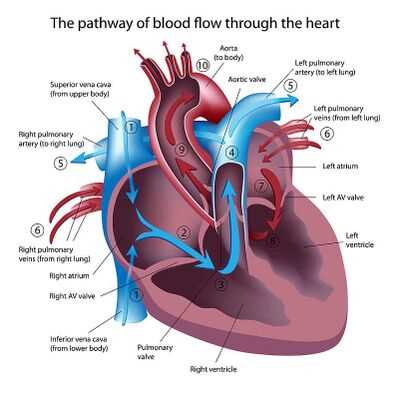
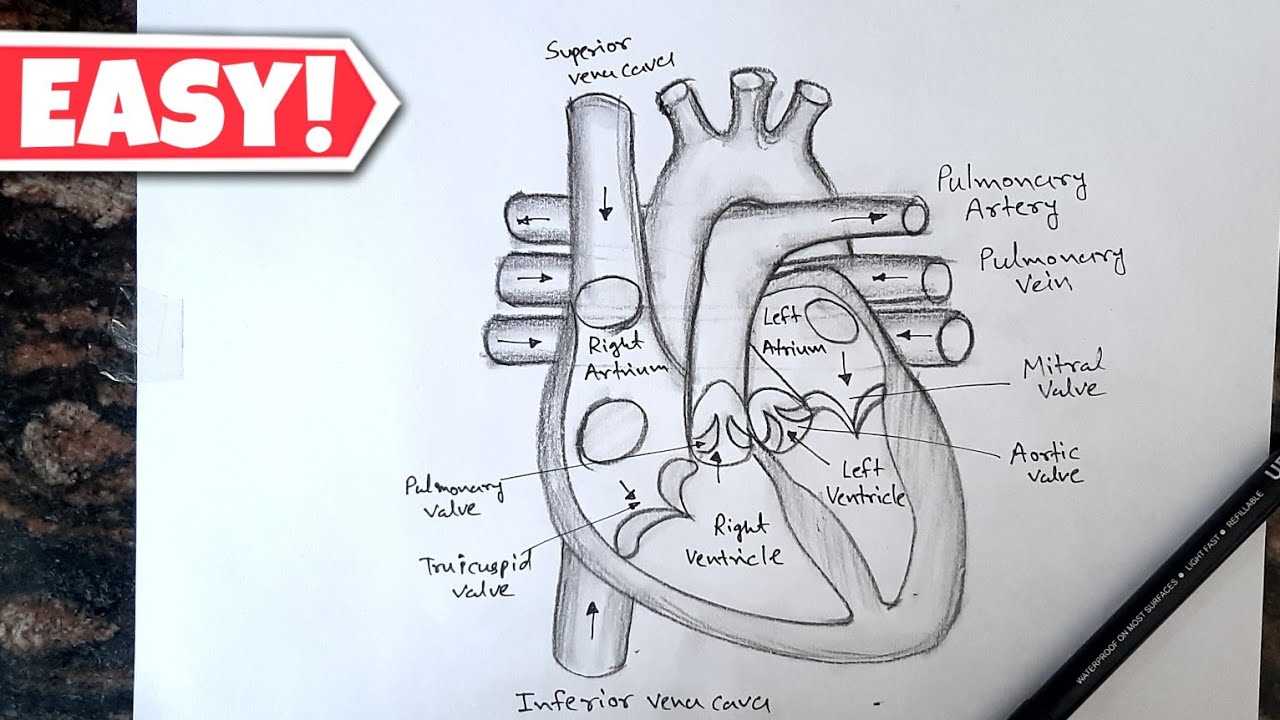
Blood Flow Pathway Explained
The movement of oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor fluids through the circulatory system is a crucial process in sustaining life. This system ensures that tissues receive vital oxygen while removing waste products such as carbon dioxide.
The process follows a specific route, moving through key vessels and regions in a continuous loop. Understanding this journey helps in grasping how nourishment and waste management are maintained in the body.
- Oxygen-depleted fluid enters the initial phase of circulation, where it is directed toward purification.
- Upon cleansing, it moves to areas responsible for replenishing its oxygen content.
- Oxygen-enriched fluid is then sent through major vessels, reaching various organs and tissues.
- After delivering oxygen, the fluid picks up waste products, returning to the starting point for filtration.
This cycle repeats continuously, ensuring the body’s cells function optimally.
Valves and Their Importance
Valves serve a crucial role in maintaining proper circulation within the circulatory system. These structures act as gatekeepers, ensuring that blood flows in the correct direction and preventing any backflow. Their functionality is vital for overall health, as they help regulate the pressure and volume of blood as it moves throughout various chambers.
Functions of Valves
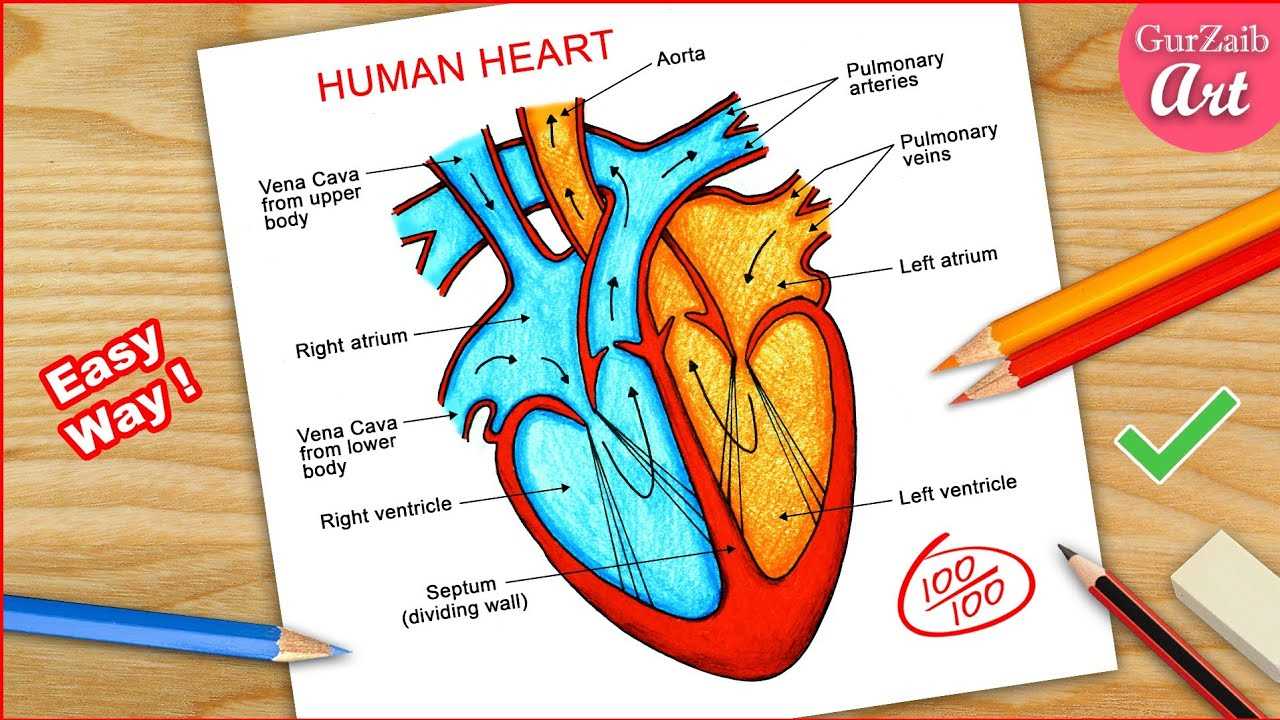
Each valve performs a specific function that contributes to efficient blood flow. By opening and closing at the appropriate times, they facilitate the movement of blood between different regions, allowing for optimal oxygen delivery and nutrient distribution. This precise coordination ensures that all tissues receive the essential substances they need to function effectively.
Impact on Circulatory Health
Any dysfunction or damage to these structures can lead to significant health issues. Conditions such as regurgitation or stenosis can hinder blood flow, resulting in fatigue and other serious complications. Therefore, understanding the role of valves is essential for recognizing potential risks and maintaining cardiovascular well-being.
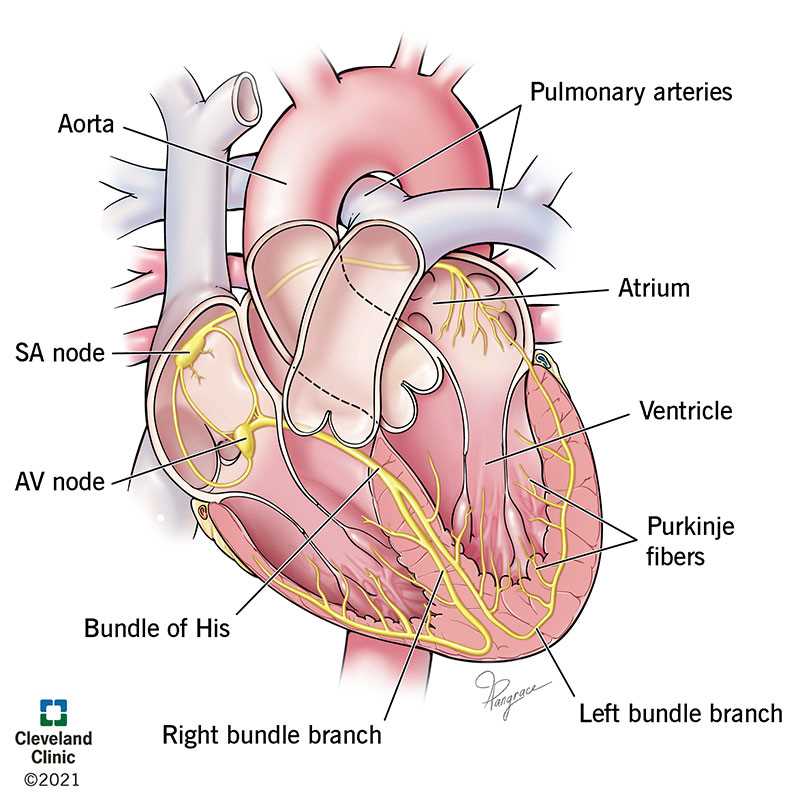
Electrical System of the Heart
The intricate network responsible for coordinating contractions is vital for maintaining efficient circulation. This system ensures that signals are transmitted smoothly, allowing for synchronized beating and optimal blood flow throughout the body.
Components of the Electrical Network
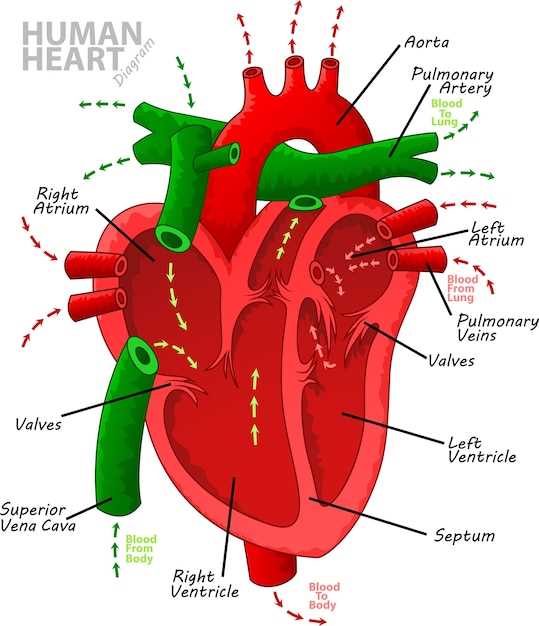
At the core of this framework lies a specialized group of cells that generate electrical impulses. These impulses travel through distinct pathways, influencing muscle contractions. The primary elements include nodes and fibers that play crucial roles in timing and rhythm.
Functionality and Regulation
The electrical activity is tightly regulated to meet varying demands. During physical exertion, the system adapts by increasing heart rate, ensuring that tissues receive sufficient oxygen and nutrients. Disruptions in this delicate balance can lead to various health issues, underscoring the importance of maintaining a well-functioning network.
Common Heart Disorders
Various conditions affecting the organ responsible for pumping blood can lead to significant health issues. Understanding these disorders is crucial for prevention and effective management. Each condition may present distinct symptoms and complications that require attention from healthcare professionals.
Coronary Artery Disease
This condition occurs when the blood vessels supplying the organ become narrowed or blocked, usually due to plaque buildup. It can lead to chest pain, heart attacks, or other serious complications if not addressed promptly.
Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation is a type of irregular heartbeat that can increase the risk of stroke and other heart-related complications. It often results in palpitations, fatigue, and shortness of breath, necessitating medical evaluation and treatment.
Heart Health Maintenance Tips
Maintaining optimal well-being of this vital organ is essential for overall health. Incorporating healthy habits into daily routines can significantly contribute to longevity and vitality. Below are some practical recommendations to support wellness and function.
Nutritional Choices
- Incorporate plenty of fruits and vegetables into meals.
- Opt for whole grains instead of refined options.
- Choose lean protein sources, such as fish and legumes.
- Limit saturated fats, sugar, and sodium intake.
Physical Activity
- Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise each week.
- Include strength training exercises at least twice weekly.
- Stay active throughout the day; consider walking or cycling instead of driving.
By adopting these practices, individuals can significantly improve their organ’s efficiency and reduce risks associated with various conditions.
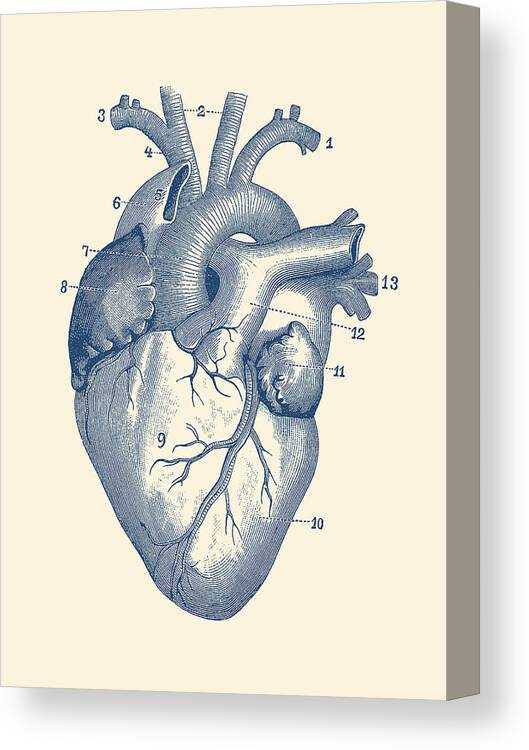
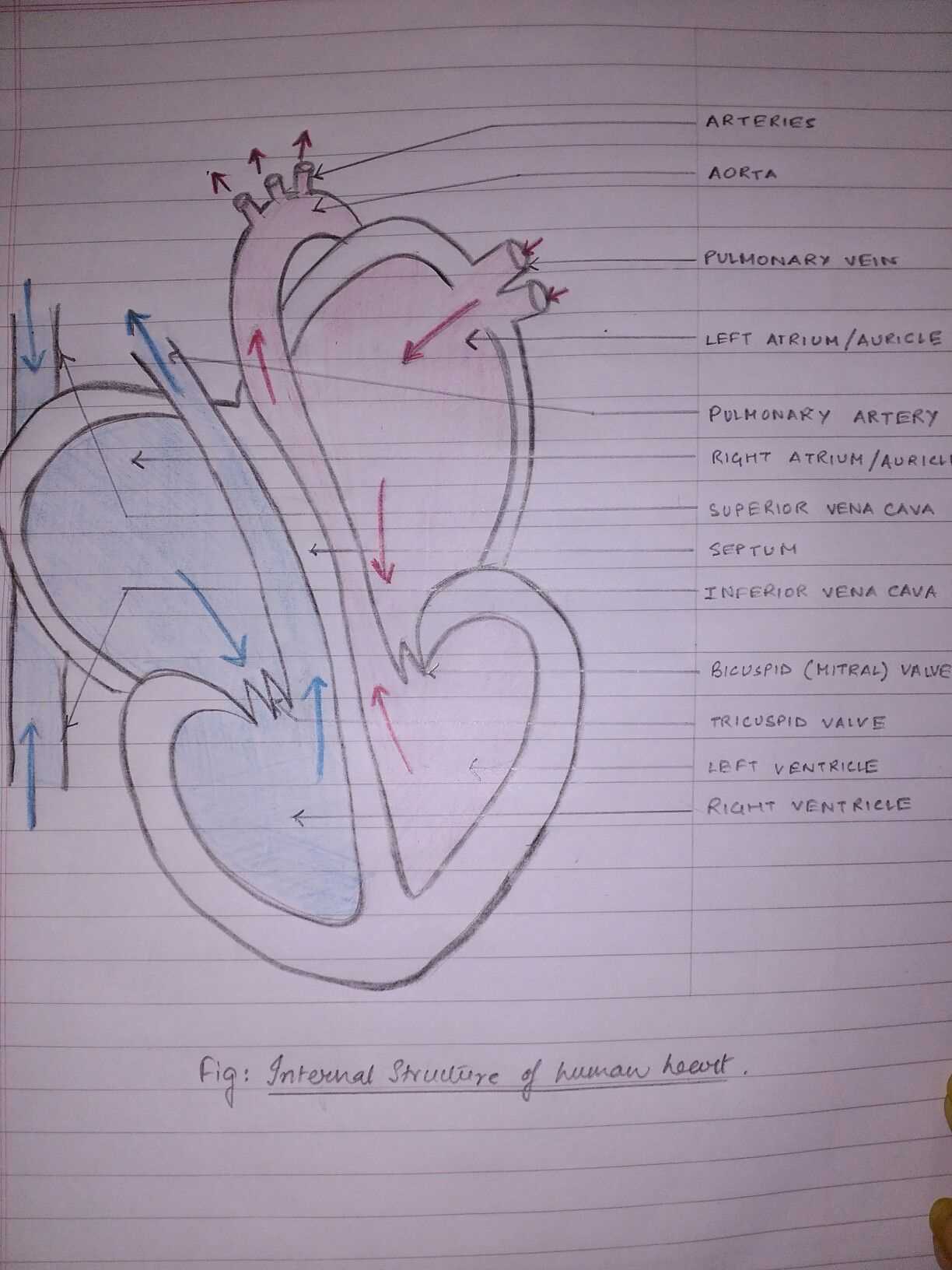
Visual Representation of Heart Parts
This section aims to illustrate the various components of a vital organ responsible for circulating blood throughout the body. A clear depiction aids in understanding the intricate structure and function of this essential organ.
Key Components Overview
- Aorta: The main artery delivering oxygen-rich blood from the organ to the body.
- Ventricles: Lower chambers that pump blood away from the organ.
- Atria: Upper chambers that receive blood returning to the organ.
- Valves: Structures that ensure unidirectional blood flow.
- Septum: A wall dividing the left and right sides of the organ.
Illustrative Details
- Each component plays a crucial role in maintaining efficient circulation.
- Understanding these elements contributes to grasping how blood flows through the body.
- Visual aids can enhance comprehension of spatial relationships and functionality.
Understanding Heart Size Variations
Size differences in this vital organ can significantly influence its functionality and overall health. Various factors contribute to these variations, including genetics, age, and lifestyle choices. Understanding how and why these dimensions can change is crucial for comprehending individual health profiles.
Genetic predisposition plays a pivotal role in determining dimensions. Some individuals may naturally possess larger or smaller structures due to hereditary traits. Additionally, as people age, their bodies undergo changes that can impact size. For instance, muscle mass may decrease, potentially leading to a reduction in volume.
Lifestyle factors, such as diet and exercise, also have a profound effect. Engaging in regular physical activity can lead to hypertrophy, where muscle tissue increases in size to meet heightened demands. Conversely, sedentary habits can contribute to atrophy, resulting in reduced dimensions over time.
Comprehending these variations is essential for medical professionals when diagnosing conditions and creating tailored treatment plans. Recognizing that each individual’s anatomy may differ helps ensure more effective healthcare interventions.
Heart’s Role in Circulatory System
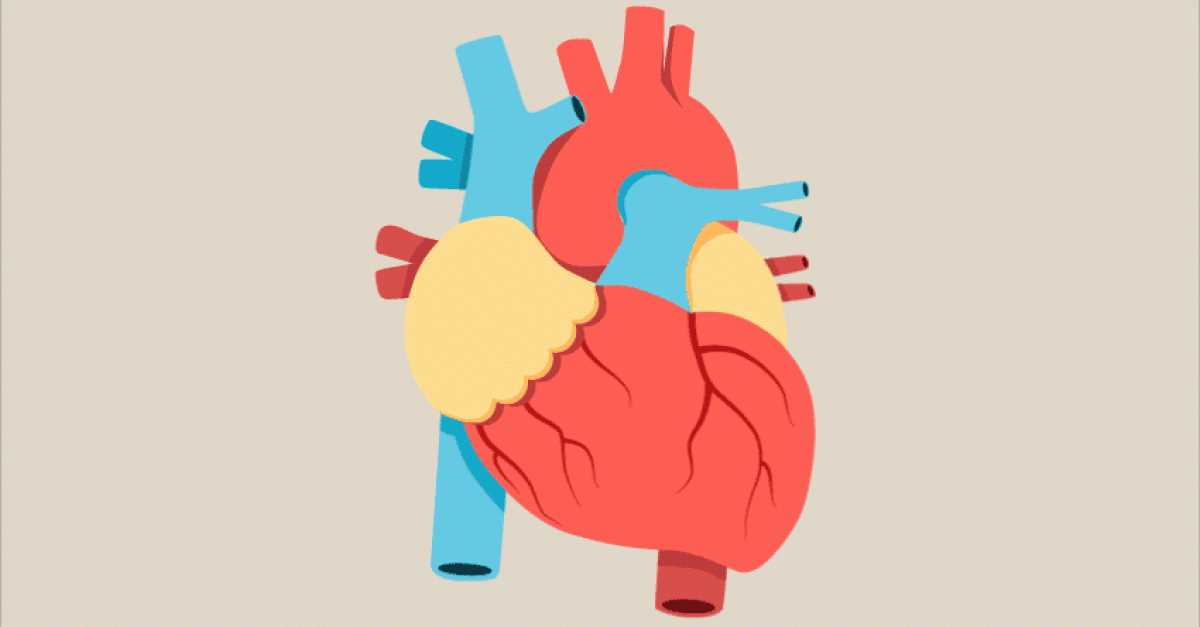
This vital organ functions as a pump, facilitating the movement of blood throughout the body. Its rhythmic contractions ensure that oxygen-rich fluid reaches every cell, while also helping to remove waste products efficiently. By maintaining this continuous flow, it plays an essential part in sustaining life and supporting various bodily functions.
Functionality and Mechanism
The rhythmic beats of this organ are regulated by an intricate electrical system. As it contracts and relaxes, blood is propelled into vessels, creating a dynamic network that delivers nutrients and oxygen. The coordination of these actions is critical, allowing for the adaptation to varying physical demands, such as exercise or rest.
Importance of Circulation
Effective circulation is fundamental to overall health. When this organ functions optimally, it contributes to maintaining stable body temperature, balancing fluids, and distributing hormones. Any disruption in its operations can lead to significant health issues, highlighting its importance within the larger context of bodily systems.
| Function |
Importance |
| Pumping blood |
Delivers oxygen and nutrients |
| Regulating flow |
Maintains stable body temperature |
| Removing waste |
Prevents toxicity in the body |
| Supporting immune function |
Distributes immune cells |
Interesting Facts About the Heart
Numerous intriguing aspects surround this vital organ, showcasing its remarkable capabilities and fascinating characteristics. It plays a crucial role in sustaining life, continuously pumping essential fluids throughout the body. Understanding these unique features can enhance appreciation for its function.
1. Size Variation: This organ can vary significantly in size among individuals, typically being about the size of a fist. Its dimensions can be influenced by factors such as age, sex, and overall health.
2. Exceptional Endurance: It beats approximately 100,000 times a day, tirelessly working to circulate blood and provide oxygen to every cell. Over a lifetime, it can beat more than 2.5 billion times without needing rest.
3. Electrical System: An internal electrical system controls its rhythm, enabling it to maintain a steady beat. This natural pacemaker adjusts heart rate based on physical demands, ensuring efficient operation during various activities.
4. Unique Patterns: Each individual has a distinct rhythm, akin to a fingerprint. This uniqueness can be measured and monitored, aiding in the detection of potential health issues.
5. Emotional Connection: The organ is often associated with emotions, symbolizing love and compassion in various cultures. Research suggests that emotional well-being can directly impact cardiovascular health, illustrating a profound connection between feelings and physiological function.