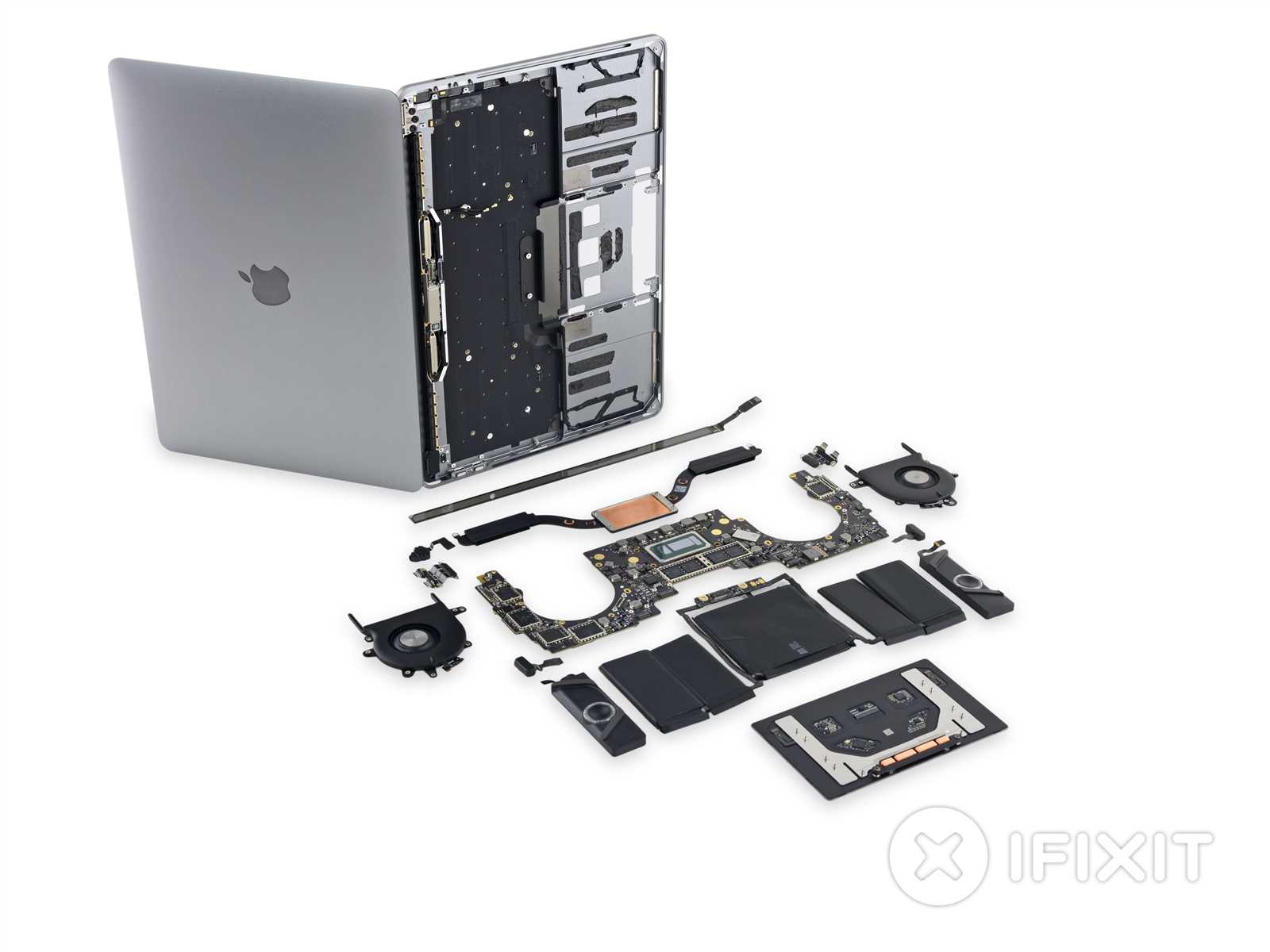

The intricate architecture of a high-performance portable computer is a marvel of modern engineering, combining functionality and design. Understanding the various elements that constitute this sophisticated device can enhance user experience and facilitate troubleshooting. Each section plays a vital role in ensuring optimal performance, from power management to data processing.
In this examination, we will delve into the various components, highlighting their functions and significance. By gaining insight into the arrangement and interconnections of these elements, users can better appreciate the complexity involved in creating a seamless computing experience. This knowledge is not only valuable for tech enthusiasts but also essential for those seeking to maintain or upgrade their devices effectively.
Whether you’re an avid user or a professional technician, familiarizing yourself with the internal structure will empower you to make informed decisions regarding repairs and enhancements. Join us as we uncover the various sections that contribute to the efficiency and longevity of a top-tier laptop.

This section aims to explore the essential elements that constitute a high-performance laptop. By breaking down the various components, readers can gain a comprehensive understanding of how these elements work together to enhance functionality and user experience. Each part plays a crucial role in the overall performance, and recognizing their functions can be beneficial for troubleshooting and maintenance.
Key Components of a High-Performance Laptop
- Processor: The brain of the machine, responsible for executing commands and processing data.
- Memory: Also known as RAM, this component temporarily stores data for quick access, enhancing multitasking capabilities.
- Storage: This is where all data, applications, and the operating system are permanently housed, with options varying from traditional hard drives to solid-state drives.
- Display: The screen quality and resolution significantly impact the visual experience, making it a vital aspect of any laptop.
- Battery: A crucial component that provides the necessary power for portability, influencing how long the device can operate without being plugged in.
Additional Elements to Consider
- Cooling System: This includes fans and heat sinks that help dissipate heat generated by various components, maintaining optimal operating temperatures.
- Input Devices: These encompass the keyboard and trackpad, facilitating user interaction with the device.
- Connectivity Ports: Essential for connecting external devices, such as USB ports, HDMI, and audio jacks.
- Enclosure: The outer shell that protects the internal components, contributing to the device’s durability and aesthetics.
Understanding these components and their roles provides insights into the functionality and performance of a sophisticated laptop. By familiarizing oneself with each element, users can make informed decisions regarding upgrades, repairs, and overall device management.
Overview of MacBook Pro Models
The lineup of high-performance laptops from Apple has evolved significantly over the years, showcasing innovative features and advancements in technology. Each iteration brings enhancements in design, functionality, and efficiency, catering to a diverse range of users from professionals to everyday consumers.
Initially introduced in the early 2000s, this series quickly gained popularity due to its sleek aesthetics and robust performance. Over the years, various editions have emerged, incorporating improved processors, high-resolution displays, and advanced connectivity options, making them suitable for demanding tasks such as graphic design, video editing, and software development.
Subsequent models have embraced the latest advancements in hardware, often including proprietary components that enhance user experience. Notable changes include the transition to solid-state drives for faster data access, the introduction of Retina displays for sharper visuals, and the integration of specialized chips for enhanced security and performance.
Moreover, the shift towards a more compact and lightweight design has made these devices increasingly portable, appealing to professionals who require power on the go. As technology continues to evolve, each new generation reflects Apple’s commitment to innovation, pushing the boundaries of what portable computing can achieve.
Key Internal Parts Explained
Understanding the essential components of a laptop is crucial for both maintenance and enhancement. Each element plays a vital role in ensuring the device operates efficiently, contributing to its overall performance and longevity. In this section, we will explore the primary internal components that make up this sleek computing machine, shedding light on their functions and importance.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The CPU is often referred to as the brain of the device, executing instructions and managing operations within the system. This critical component processes data and performs calculations, impacting everything from application performance to multitasking capabilities. The efficiency of the CPU directly correlates to the device’s speed and responsiveness.
Random Access Memory (RAM)

RAM is essential for temporary data storage, allowing for quick access to information needed by the system during operation. The amount of RAM influences how many applications can run simultaneously without slowing down the device. More RAM typically leads to smoother performance, especially when handling resource-intensive tasks.
External Features of MacBook Pro
The exterior design of this popular laptop combines elegance and functionality, making it a preferred choice for many users. Its sleek lines and premium materials not only enhance aesthetic appeal but also contribute to durability and portability. This section explores the distinct characteristics that define the exterior layout of the device.
Chassis is constructed from a solid aluminum unibody, providing both strength and lightweight properties. This material choice ensures resistance to wear and tear, while also maintaining a sophisticated appearance.
The keyboard features a comfortable layout with well-spaced keys, allowing for efficient typing. Backlighting enhances usability in low-light conditions, providing visibility without straining the eyes. The touchpad is large and responsive, enabling smooth navigation and gestures for improved productivity.
Ports play a crucial role in connectivity, with a variety of options available. The inclusion of USB-C and Thunderbolt ports facilitates rapid data transfer and compatibility with a range of peripherals. Additionally, a headphone jack is integrated, catering to audio needs.
On the display front, the screen boasts vibrant colors and sharp resolution, making it ideal for multimedia consumption and creative tasks. The thin bezels maximize the viewing area, enhancing the overall immersive experience.
Finally, the vents are strategically placed to optimize airflow, ensuring efficient cooling during intense usage. This thoughtful design aspect helps maintain performance while keeping the device silent and unobtrusive.
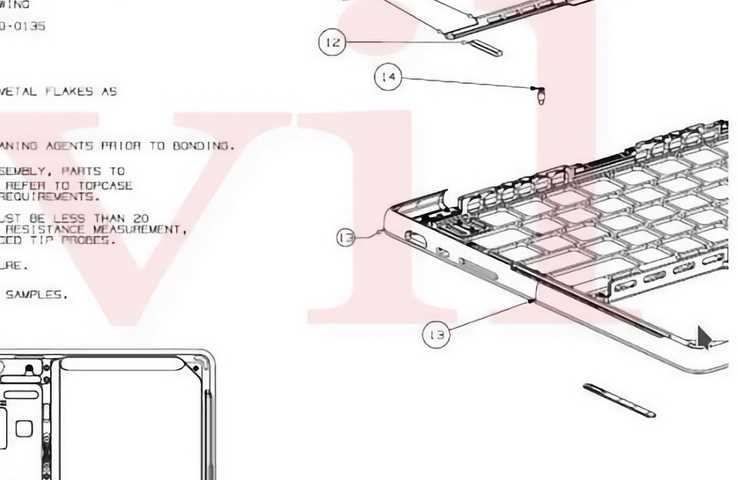
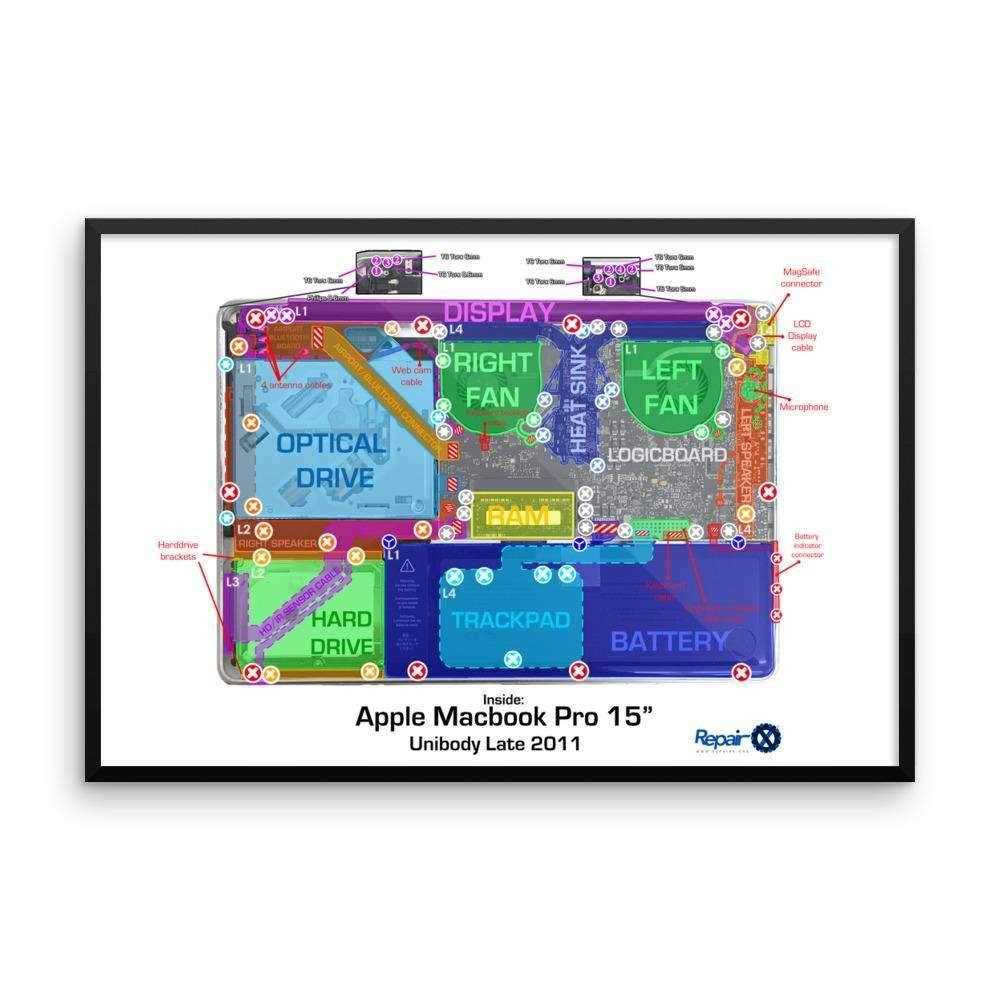
Identifying the Logic Board

The logic board serves as the central hub of a device, integrating essential components and facilitating communication between them. Understanding its layout and features is crucial for effective troubleshooting and repairs.
When locating the logic board, consider the following aspects:
- Placement: Typically situated towards the bottom of the casing, the board connects to various internal elements.
- Appearance: Look for a large rectangular circuit board with intricate pathways and multiple connection points.
- Components: Common elements found on the board include the CPU, RAM slots, and power connectors.
For identification, follow these steps:
- Remove the outer casing carefully, ensuring not to damage any clips or screws.
- Identify the main circuit board, noting its size and the arrangement of components.
- Look for labels or markings that indicate the manufacturer or model number, aiding in further identification.
By understanding these characteristics, you can accurately identify the logic board and navigate repairs or upgrades with confidence.
Battery Types and Specifications

Understanding the various energy storage options available for modern laptops is essential for optimizing performance and ensuring longevity. Different configurations serve distinct needs, and knowing the specifications can aid in selecting the right unit for your device.
Common Battery Types
- Lithium-Ion (Li-ion): This type is widely used due to its high energy density, low self-discharge rate, and lightweight design.
- Lithium Polymer (LiPo): Similar to Li-ion, LiPo batteries offer flexible shapes and sizes, making them suitable for thin devices.
- Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd): While less common today, NiCd batteries are known for their durability and ability to perform well in extreme temperatures.
- Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH): These batteries are an improvement over NiCd, offering higher capacity and less memory effect, but are still less popular than lithium-based alternatives.
Key Specifications
- Voltage: Typically measured in volts (V), this indicates the potential difference and affects the performance of the device.
- Capacity: Measured in milliampere-hours (mAh), this specification determines how long a battery can power a device before requiring a recharge.
- Cycle Life: This refers to the number of charge and discharge cycles a battery can undergo before its capacity significantly diminishes.
- Temperature Range: Each battery type operates optimally within a specific temperature range, impacting both performance and lifespan.
Cooling System Components Detailed

The efficiency of electronic devices heavily relies on their ability to manage heat effectively. A well-designed thermal management system is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. This section delves into the various elements that constitute a robust cooling mechanism, emphasizing their functions and interrelationships.
| Component | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Sink | A metallic structure designed to dissipate heat away from critical components. | Enhances heat dissipation through conduction and convection, maintaining optimal operating temperatures. |
| Fan | An electromechanical device that circulates air to cool components. | Increases airflow, promoting heat removal and preventing overheating. |
| Thermal Paste | A thermally conductive compound applied between surfaces for better heat transfer. | Improves thermal conductivity between components, enhancing overall heat dissipation. |
| Vents | Openings that allow air to enter and exit the system. | Facilitate airflow, crucial for cooling by providing a pathway for heat to escape. |
| Heat Pipes | Closed-loop systems that transfer heat via phase changes. | Efficiently transport heat away from critical areas, distributing it across larger surfaces. |
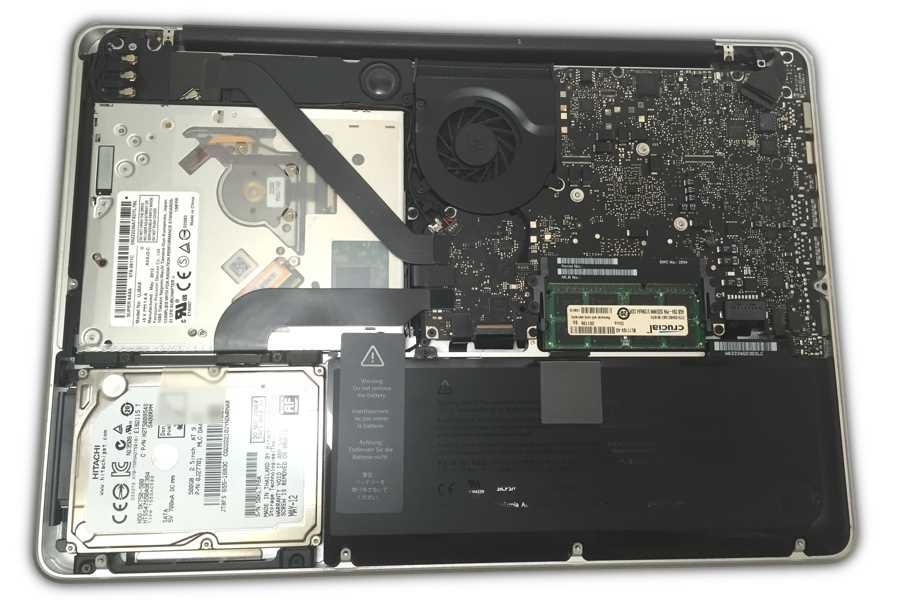
Storage Options in MacBook Pro
When considering the various choices for data retention in high-performance laptops, it’s essential to evaluate the available formats and configurations. The flexibility and efficiency of these solutions play a crucial role in enhancing overall system functionality and user experience. Various methods exist to store information, each offering distinct advantages and characteristics tailored to different needs.
Solid State Drives (SSDs)
Solid state drives are the most prevalent choice in modern systems, known for their speed and reliability. Unlike traditional storage devices, SSDs utilize flash memory, resulting in quicker boot times and faster data access. This technology not only improves performance but also minimizes power consumption, making it an ideal option for portable devices.
External Storage Solutions

For users requiring additional capacity beyond the built-in options, external storage devices offer an excellent solution. These can include portable hard drives or cloud-based services, providing the ability to expand storage seamlessly. Utilizing external options allows for easy backups and increased flexibility, catering to varying storage needs without compromising on performance.
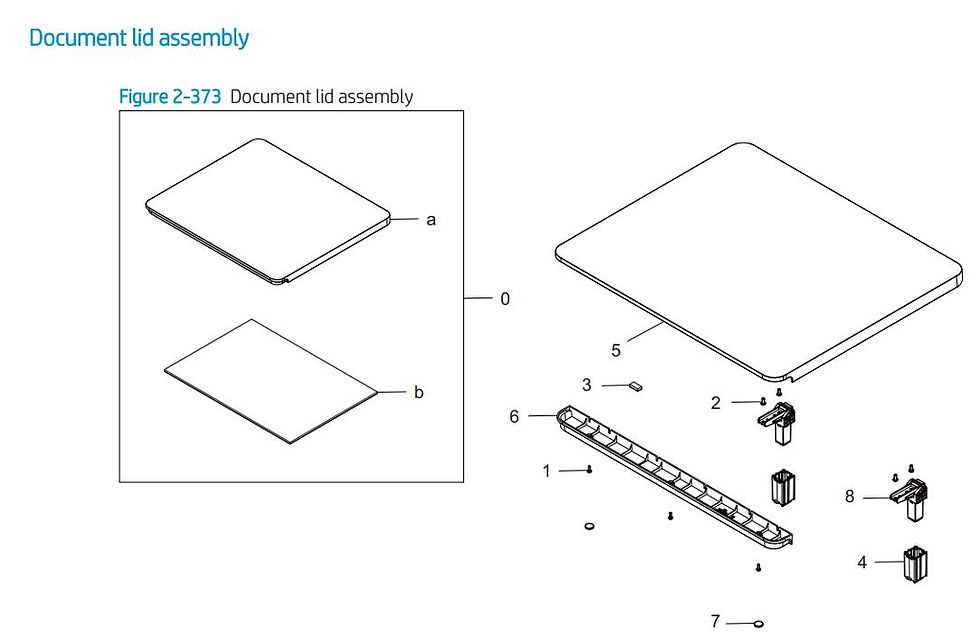
Display Assembly Breakdown
The display assembly serves as a crucial component in the functionality of portable computing devices. This section delves into the intricacies of this assembly, highlighting its essential elements and their interrelations.
Understanding the construction of the display assembly requires an exploration of its main components:
- Screen Panel: The primary visual interface that presents content to the user. It is designed for optimal clarity and responsiveness.
- Backlight: This element provides illumination to the screen panel, ensuring visibility in various lighting conditions.
- Display Cable: A vital connection that transmits video signals from the device’s motherboard to the screen.
- Hinges: These components allow the screen to pivot and securely attach to the body of the device, facilitating movement and stability.
- Front Glass: This protective layer safeguards the screen from physical damage while enhancing touch sensitivity.
- LCD Controller Board: A critical interface that manages the interaction between the display and the rest of the device, processing signals and adjustments.
Each of these components plays a significant role in ensuring that the display assembly functions efficiently and meets the demands of modern computing.
In summary, a thorough comprehension of the display assembly’s structure allows for better maintenance and potential upgrades, enhancing the overall user experience.
Keyboard and Trackpad Mechanisms
The input devices of a laptop play a crucial role in enhancing user experience and interaction. Understanding the underlying mechanisms that facilitate their operation reveals how design and functionality converge to provide seamless input capabilities.
The keyboard mechanism is composed of various components that work in harmony to ensure accurate keystrokes. Key elements include:
- Switches: These are responsible for registering key presses, with different types offering varying tactile feedback.
- Keycaps: The top part of each key that users interact with, which comes in diverse shapes and sizes for improved ergonomics.
- Backlighting: This feature enhances visibility in low-light conditions, providing a more versatile typing experience.
The trackpad, another essential input device, employs distinct technologies to deliver precise control. Key aspects include:
- Touch Sensitivity: This allows for detection of finger movement and gestures, enabling intuitive navigation.
- Multi-Touch Support: Facilitates gestures such as pinch-to-zoom and swipe, enhancing usability and functionality.
- Haptic Feedback: This feature provides tactile responses during interactions, simulating a physical click.
Both the keyboard and trackpad mechanisms are engineered for durability and efficiency, significantly impacting productivity and user satisfaction. Continuous advancements in technology ensure that these input devices evolve, offering enhanced performance and reliability.
Ports and Connectivity Elements
This section explores the various interfaces and connectivity options available on the device, highlighting how these features facilitate seamless communication with external peripherals and networks. Understanding these components is essential for users seeking to optimize their workflow and enhance their overall experience.
Among the key connectivity elements are the USB interfaces, which allow for quick data transfer and charging capabilities. These connections support a range of accessories, including external storage devices, printers, and other gadgets. Additionally, the presence of Thunderbolt ports offers high-speed data transfer, enabling users to connect multiple high-performance devices simultaneously.
Networking features also play a vital role, with integrated Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities providing wireless access to the internet and connection to various devices. This ensures that users can stay connected and productive without the hassle of cumbersome cables.
Furthermore, audio and video outputs enhance multimedia experiences. The inclusion of headphone jacks and display ports enables users to connect external monitors and audio systems, making it easier to engage in presentations or enjoy high-quality entertainment.
Overall, the combination of these elements creates a versatile ecosystem that caters to diverse user needs, ensuring that the device remains a valuable tool for both personal and professional tasks.
Audio System Components Overview
The audio system within a laptop is a critical element that enhances the overall user experience, providing immersive sound quality for various applications. This section will explore the essential elements that contribute to sound output, detailing their functions and interactions within the system.
Key Elements of the Audio System
At the core of the audio system are the speakers, which transform electrical signals into audible sound waves. These components are designed to deliver clear and balanced audio, catering to both casual listeners and audio professionals. Complementing the speakers are the audio processing units, which manage the conversion of digital signals and optimize sound quality through various enhancements.
Connectivity and Control Features
Effective audio performance relies on connectivity options, allowing users to link external devices such as headphones and speakers. The control interfaces, including volume knobs and software controls, provide users with intuitive management over audio settings, ensuring a tailored listening experience. Together, these elements create a cohesive audio system that significantly contributes to the functionality and enjoyment of the device.
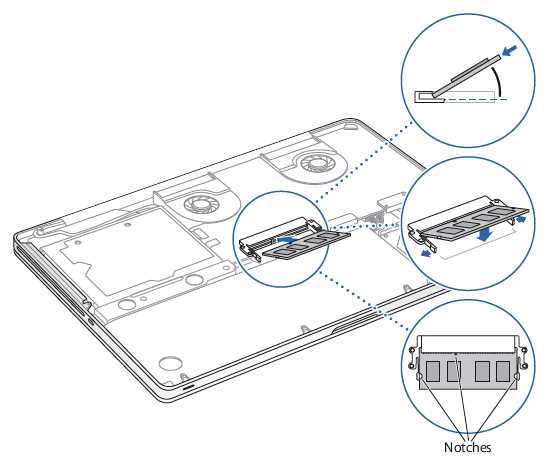
Upgrading and Replacing Parts

Enhancing and substituting components in your device can significantly improve its performance and extend its lifespan. Whether you’re looking to boost speed, increase storage capacity, or fix a malfunctioning element, understanding the options available is crucial for successful modifications. This section will guide you through the essentials of upgrading and replacing components effectively.
Before you begin, consider the following:
- Identify the specific component that requires attention.
- Research compatible replacements to ensure optimal functionality.
- Gather the necessary tools to facilitate the upgrade or replacement process.
When planning your upgrade or replacement, follow these key steps:
- Assess Compatibility: Ensure that the new component is compatible with your existing hardware.
- Backup Important Data: Always create backups of your essential files before making any changes.
- Follow Instructions Carefully: Refer to manuals or online guides for step-by-step instructions on disassembly and installation.
- Test the New Component: After installation, verify that the new component functions as expected.
By taking a methodical approach, you can successfully enhance your device’s capabilities, ensuring it meets your evolving needs.