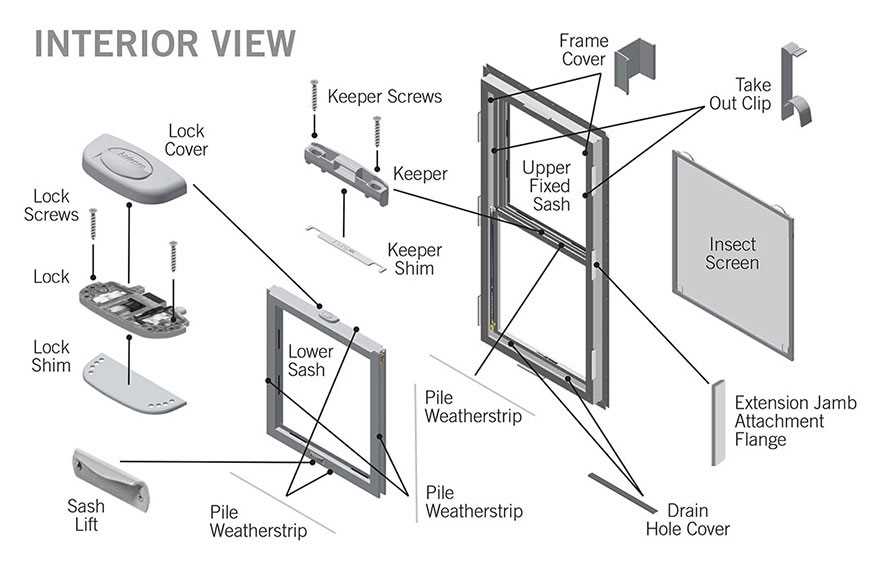
The intricate design of any architectural element encompasses various essential features that contribute to its functionality and aesthetics. These distinct elements play a crucial role in ensuring the integrity and appeal of the overall composition. By exploring these integral aspects, one can gain a deeper appreciation for the craftsmanship and engineering involved in creating such structures.
Each individual component serves a specific purpose, working harmoniously to enhance both performance and visual appeal. From frames to openings, these elements not only fulfill practical roles but also contribute to the unique character of the assembly. Recognizing the interplay between these features allows for a comprehensive understanding of how they collectively form a cohesive whole.
Moreover, the diversity of styles and materials available today presents numerous possibilities for customization. Homeowners and architects alike can select from a variety of options to best suit their needs and preferences. This exploration of the various components highlights the importance of thoughtful design in creating an inviting and functional space.
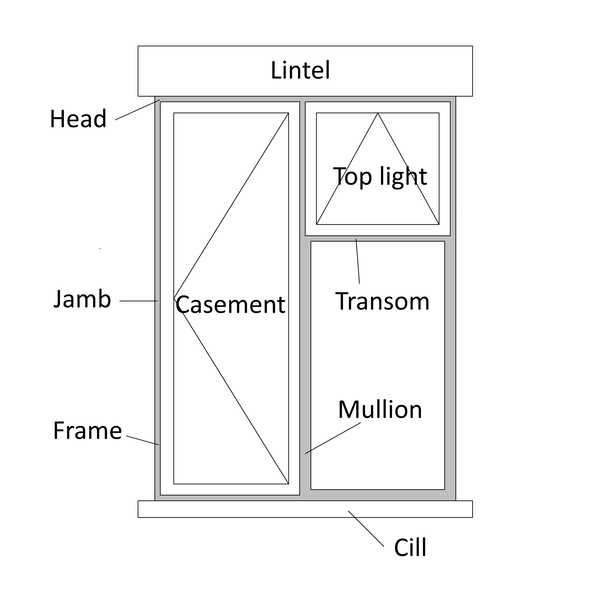
The design of an opening in a building is an intricate composition that serves both aesthetic and functional purposes. Understanding the various components involved is essential for grasping how they work together to provide light, ventilation, and insulation. Each element contributes to the overall performance and efficiency of the structure.
Key Components
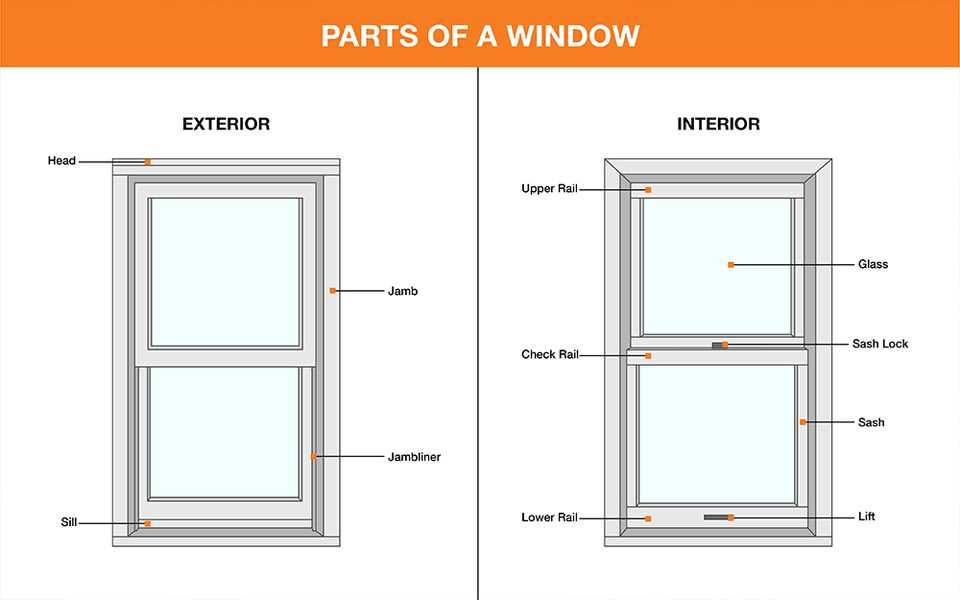
Several fundamental elements come together to form a cohesive unit. These components interact to ensure stability and functionality while enhancing the visual appeal of the entire setup.
Functional Attributes
Different characteristics play a critical role in determining how the assembly performs under various conditions. The arrangement and quality of materials can significantly influence energy efficiency and durability.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Frame | Provides structural support and defines the shape. |
| Sash | Holds the glazing in place and allows for movement. |
| Glazing | Allows natural light in and contributes to thermal insulation. |
| Seal | Prevents air and water infiltration, enhancing energy efficiency. |
| Hardware | Facilitates the operation of opening and closing mechanisms. |
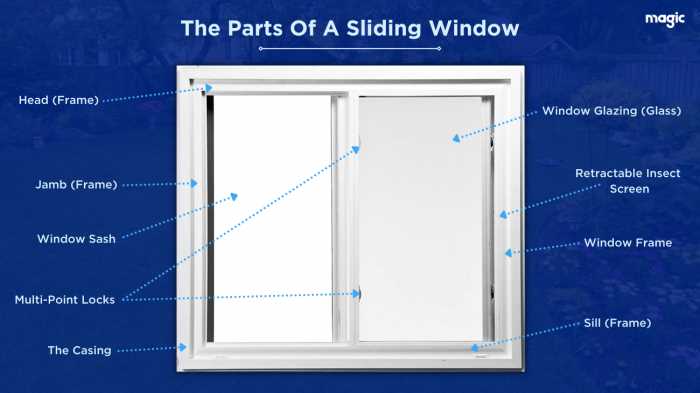
Main Elements of a Window
Understanding the fundamental components of an opening allows for a deeper appreciation of its functionality and design. Each element contributes to the overall aesthetic and operational efficiency, creating a harmonious blend of form and purpose. Recognizing these essential features is crucial for anyone looking to enhance their knowledge of architectural structures.
At the forefront is the frame, which provides support and defines the boundaries of the installation. It is typically constructed from durable materials, ensuring stability and resistance to environmental factors. The glazing is another critical aspect, serving as the transparent barrier that allows light to enter while offering protection from external elements. Various types of glazing can be utilized, each with its own benefits in terms of insulation and UV protection.
Additionally, the sash plays a vital role in holding the glazing in place and may facilitate movement for ventilation. This component can be designed in different styles, allowing for flexibility in operation and access to fresh air. The hardware, which includes locks and handles, ensures security and ease of use, adding to the overall functionality.
Lastly, the sill acts as the bottom support structure, directing water away from the interior and providing an additional layer of protection against moisture. Each of these features works together seamlessly, contributing to the overall effectiveness and appeal of the installation.
Functionality of Window Panes
The significance of transparent barriers in architectural design extends beyond mere aesthetics. They serve multiple purposes that enhance both comfort and utility within a space. Understanding their roles can illuminate their impact on everyday living and energy efficiency.
Light Transmission and Aesthetics
Transparent surfaces allow natural illumination to penetrate interiors, creating inviting environments. This feature not only reduces the need for artificial lighting but also contributes to the overall ambiance of a room. The visual appeal of these barriers can complement various architectural styles, enhancing the beauty of both residential and commercial structures.
Insulation and Energy Efficiency
Modern transparent barriers are designed with advanced materials that provide excellent thermal insulation. By minimizing heat transfer, they help maintain comfortable indoor temperatures while reducing energy consumption. This functionality is crucial for promoting sustainability and lowering utility costs, making them an essential element in contemporary construction.
Exploring the Window Frame
The framework that supports and surrounds the glass openings plays a crucial role in both aesthetics and functionality. This essential structure not only enhances the visual appeal of a building but also contributes to its energy efficiency and overall durability. Understanding the components that make up this framework can provide insight into its importance and maintenance.
Key Components of the Framework
Different elements work together to create a cohesive and efficient structure. These components are designed to withstand environmental factors while ensuring a secure and tight fit around the glazing. Here are some of the primary elements:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Sill | The horizontal ledge at the bottom that directs water away from the interior. |
| Head | The top horizontal part that provides structural integrity and support. |
| Jambs | The vertical sides that frame the opening and support the glass. |
| Mullion | A vertical divider between two openings, enhancing stability and support. |
Importance of Material Selection
The choice of materials for constructing this framework significantly influences its performance and longevity. Options range from traditional wood to modern composites and metals, each offering unique benefits. Selecting the right material can enhance insulation properties, reduce maintenance requirements, and improve aesthetic appeal.
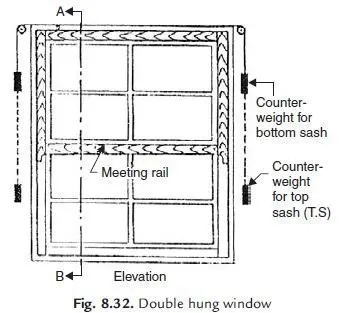
Role of Sashes in Windows
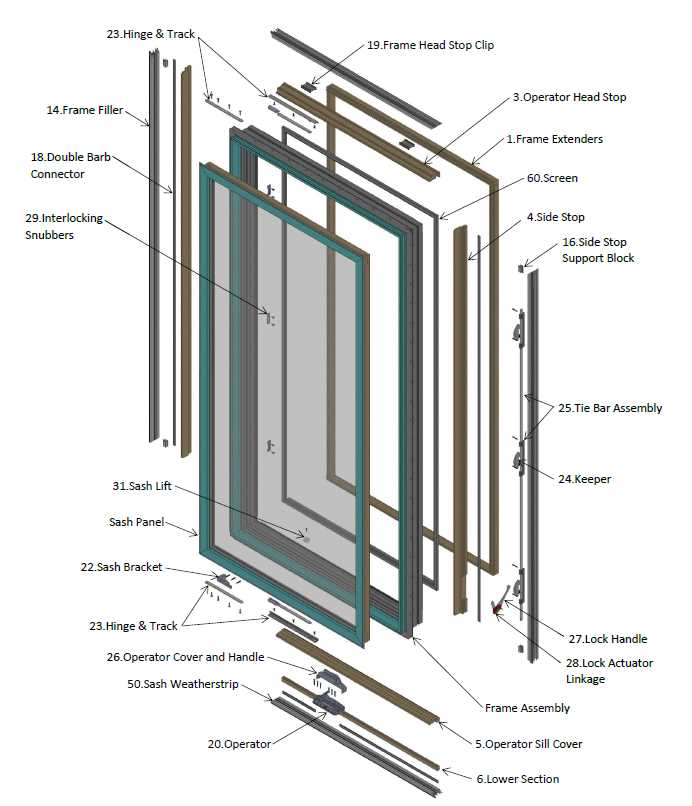
Sashes serve a crucial function in the overall structure of an opening, providing both aesthetic appeal and practical benefits. They are designed to hold glazing elements in place, contributing to the integrity and functionality of the entire setup.
One of the primary responsibilities of sashes is to facilitate movement. They enable the operation of different types of openings, allowing for ventilation and light control. The design of the sashes can vary, impacting how easily these features can be accessed and adjusted.
Additionally, sashes play a significant role in insulation. By effectively sealing the area around the glass, they help maintain internal temperatures and improve energy efficiency. This is particularly important in varying climates, where temperature fluctuations can significantly affect comfort levels.
Furthermore, the aesthetic aspects of sashes cannot be overlooked. They contribute to the style and character of the entire structure, enhancing its visual appeal. Various designs and materials allow for personalization, enabling individuals to select options that align with their preferences and overall architectural themes.
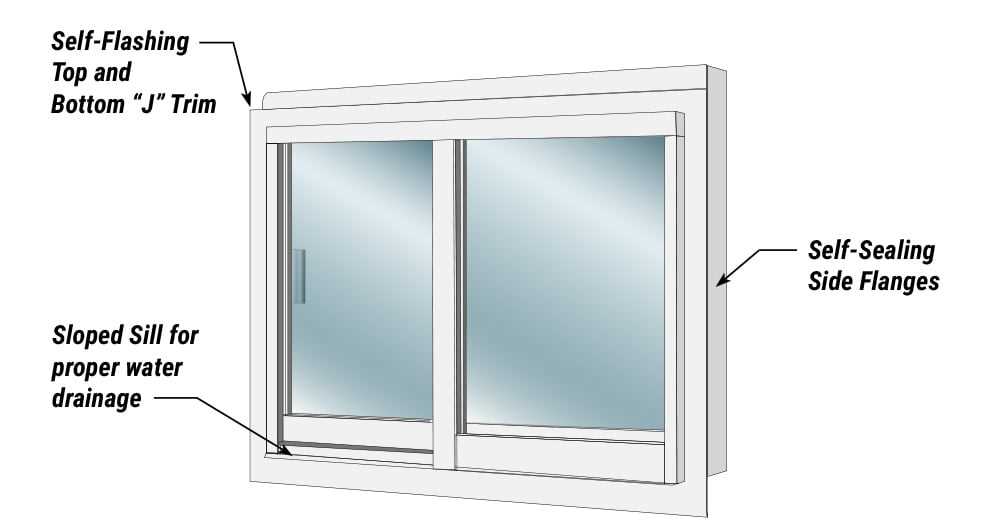
Significance of Window Casings
The framework surrounding an opening plays a crucial role in both aesthetic appeal and structural integrity. It serves as the boundary that enhances the overall look of the area while providing essential support to the surrounding architecture.
These enclosures not only protect against the elements but also contribute to energy efficiency by minimizing drafts and heat loss. Proper installation and maintenance of these structures are vital for ensuring durability and longevity.
Furthermore, the choice of materials and design can greatly influence the style and character of a space. Selecting the right casing can complement the interior decor and enhance the property’s value, making it an important consideration for homeowners and builders alike.
Types of Window Hardware Explained
Understanding the various components that facilitate the functionality of openings in a building is essential for both aesthetics and efficiency. These elements not only enhance the ease of operation but also contribute to the overall performance and security of the structure. This section delves into the different categories of mechanisms and fixtures commonly found in modern installations.
Operating Mechanisms
One of the primary classifications includes the operating mechanisms, which determine how the fixture functions. Sliding and crank systems are prevalent choices, each offering distinct advantages. Sliding mechanisms allow for smooth lateral movement, making them ideal for limited spaces, while crank systems provide greater control and are often utilized in openings that need to be elevated for ventilation.
Locks and Security Features
Another vital category encompasses locking mechanisms and security features. These are crucial for safeguarding against unauthorized access. Multi-point locks distribute force across several points, enhancing protection, whereas keyed locks offer traditional security. Understanding these options helps ensure that safety considerations are met without compromising design elegance.
Importance of Weatherstripping
Weatherstripping plays a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency and comfort of any space. By creating a barrier against external elements, it helps maintain a stable indoor environment while reducing energy costs.
Here are some key benefits of effective weather sealing:
- Energy Efficiency: Proper insulation minimizes heat loss in winter and keeps cool air inside during summer, leading to lower energy bills.
- Comfort: By preventing drafts, it ensures a consistent temperature throughout the area, enhancing overall comfort for occupants.
- Moisture Control: A well-sealed enclosure helps prevent water intrusion, reducing the risk of mold and mildew growth.
- Noise Reduction: Effective barriers can significantly decrease outside noise, contributing to a quieter and more peaceful environment.
- Longevity: By protecting against harsh weather conditions, it extends the lifespan of structural components, saving on costly repairs and replacements.
Incorporating quality sealing materials can significantly improve the overall performance of an enclosed space, leading to a more sustainable and enjoyable living or working environment.
Window Screens and Their Uses
Screening elements serve as a vital barrier, allowing fresh air to circulate while keeping unwanted elements at bay. They provide essential protection against insects and debris, enhancing indoor comfort and hygiene.
Benefits of Using Screens
- Insect Prevention: They effectively block pests, ensuring a more enjoyable indoor environment.
- Improved Airflow: These barriers facilitate ventilation, allowing natural breezes without compromising safety.
- Visibility: They provide a clear view of the outside world, maintaining the connection to nature.
Types of Screening Options
- Fiberglass: Lightweight and resistant to rust, making them a popular choice.
- Aluminum: Durable and long-lasting, offering excellent protection.
- Retractable: A flexible option that can be opened or closed as needed, providing convenience.
Common Window Accessories Overview
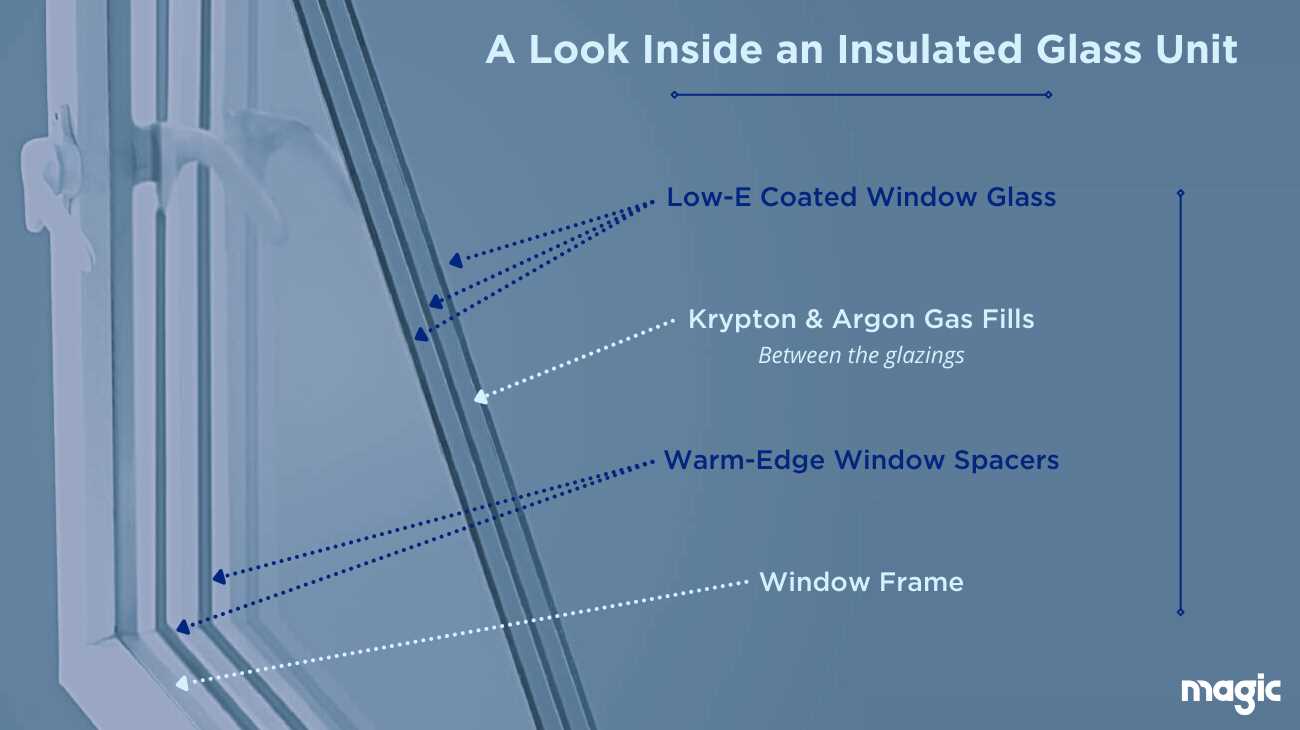
Understanding the various components that enhance functionality and aesthetics can greatly improve the overall experience of any opening in a structure. These additional elements serve multiple purposes, from providing comfort and security to adding style and efficiency.
Types of Accessories
- Shades: Available in numerous styles and materials, shades offer control over light and privacy.
- Blinds: Adjustable slats provide flexibility in light management and can complement various interior designs.
- Locks: Essential for safety, these mechanisms secure the frame against unauthorized access.
- Grilles: Often used for aesthetic purposes, these can enhance the visual appeal while allowing for ventilation.
- Seals: Vital for insulation, these help maintain energy efficiency by preventing drafts.
Functional Benefits
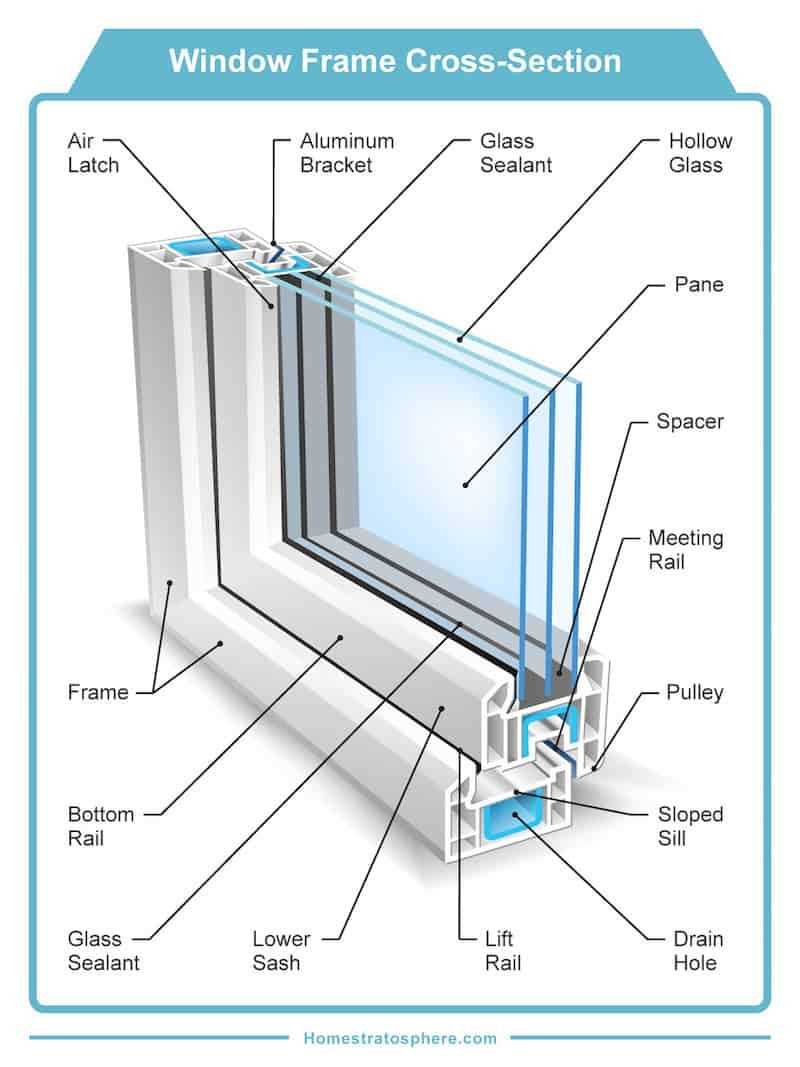
- Improved energy efficiency through insulation and light control.
- Enhanced security with durable locking systems.
- Personalized aesthetic options to suit individual tastes and home styles.
- Increased property value by adding attractive and functional elements.