
The intricate mechanisms behind document destruction tools are vital for ensuring security and efficiency. These devices are designed to transform sensitive information into unreadable fragments, preventing unauthorized access. A thorough comprehension of their internal structure can enhance maintenance and troubleshooting processes.
In this section, we will delve into the various elements that comprise these essential machines. Each component plays a specific role in the operation, contributing to the overall functionality and reliability. By familiarizing yourself with these elements, you can make informed decisions regarding usage and care.
Furthermore, recognizing how these components interact can empower users to optimize their devices for peak performance. Whether for personal or professional use, understanding these fundamentals is key to maximizing the lifespan and efficiency of your document destruction solution.
Understanding Paper Shredder Components
This section delves into the essential elements that constitute a device designed for the secure disposal of sensitive documents. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient operation, durability, and safety. By familiarizing oneself with these components, users can better understand functionality and maintenance requirements.
Main Elements
- Cutting Mechanism: This is the core of the device, responsible for slicing through materials. Various designs determine the level of security and the size of the resulting particles.
- Motor: The power source that drives the cutting mechanism. Motor strength can influence the speed and efficiency of the shredding process.
- Feed Slot: The entry point for documents. Its size can affect the volume of material that can be processed at once.
- Control Panel: The interface for users, providing options for operation and settings adjustments.
- Safety Features: These may include automatic shut-off and jam prevention systems, enhancing user protection and machine longevity.
Additional Components

- Bin: The receptacle for collected particles, varying in capacity and design.
- Housing: The outer casing that protects internal components and ensures durability.
- Cooling System: A mechanism to prevent overheating during prolonged use, critical for maintaining performance.
Understanding these elements not only aids in proper use but also enhances the longevity and effectiveness of the device, making informed decisions about maintenance and troubleshooting more accessible.
Types of Paper Shredders Available
There are various devices designed to handle the disposal of confidential documents efficiently. These machines differ in structure, cutting mechanisms, and intended use, catering to personal, office, and industrial needs.
- Strip-Cut Models: These machines create long, narrow strips, offering a basic level of security suitable for non-sensitive materials.
- Cross-Cut Devices: With blades that produce smaller pieces, these units provide enhanced security by making reconstruction difficult.
- Micro-Cut Variants: Ideal for handling highly sensitive data, these machines shred materials into tiny particles, ensuring the highest level of confidentiality.
- Auto-Feed Systems: Designed for convenience, these units can process large stacks of documents automatically, minimizing user interaction.
- Continuous-Duty Machines: Built for industrial applications, these heavy-duty models operate without interruption, perfect for large-scale usage.
Key Parts of a Shredder Explained
A cutting machine is composed of multiple components working together to ensure smooth operation and efficiency. Each element plays a unique role in breaking down material into smaller fragments, contributing to security and proper disposal. Understanding these elements can help with maintenance and troubleshooting.
Cutting Mechanism
The core function relies on rotating blades or cutting cylinders that slice material into strips or particles. These blades are strategically aligned to ensure precise fragmentation. Regular sharpening or replacement may be necessary to maintain performance.
Feeding and Collection System
Materials are guided into the machine through a feed entry, which often includes safety sensors to prevent accidents. The processed fragments are collected in a receptacle bin, designed to hold varying capacities based on usage. Proper bin alignment is essential to prevent jamming and ensure smooth operation.
How Blades Function in Shredders
Rotating knives play a key role in transforming large sheets into smaller fragments. Their operation depends on sharp edges and precise alignment to ensure smooth and efficient processing. Understanding the mechanics behind these components reveals the importance of both material quality and engineering precision.
- Interlocking Design: Blades are arranged in a pattern that allows them to overlap, increasing the cutting surface for more effective results.
- Rotation Speed: The speed at which the knives rotate directly influences how fast and finely the material is cut.
- Cutting Angles: Adjusting the angle of the blades impacts the type of fragments produced, whether strips or confetti-like pieces.
- Maintenance Requirements: Regular sharpening or replacement ensures continuous high performance and prevents mechanical failures.
- Material enters the device and meets the rotating knives.
- The blades grip and slice the input into smaller bits.
- Fragments are deposited into a collection area for disposal or recycling.
Proper blade operation is crucial to avoid jams and maintain durability. Ensuring correct alignment and rotation speed helps extend the life of the device, improving overall efficiency in the long run.
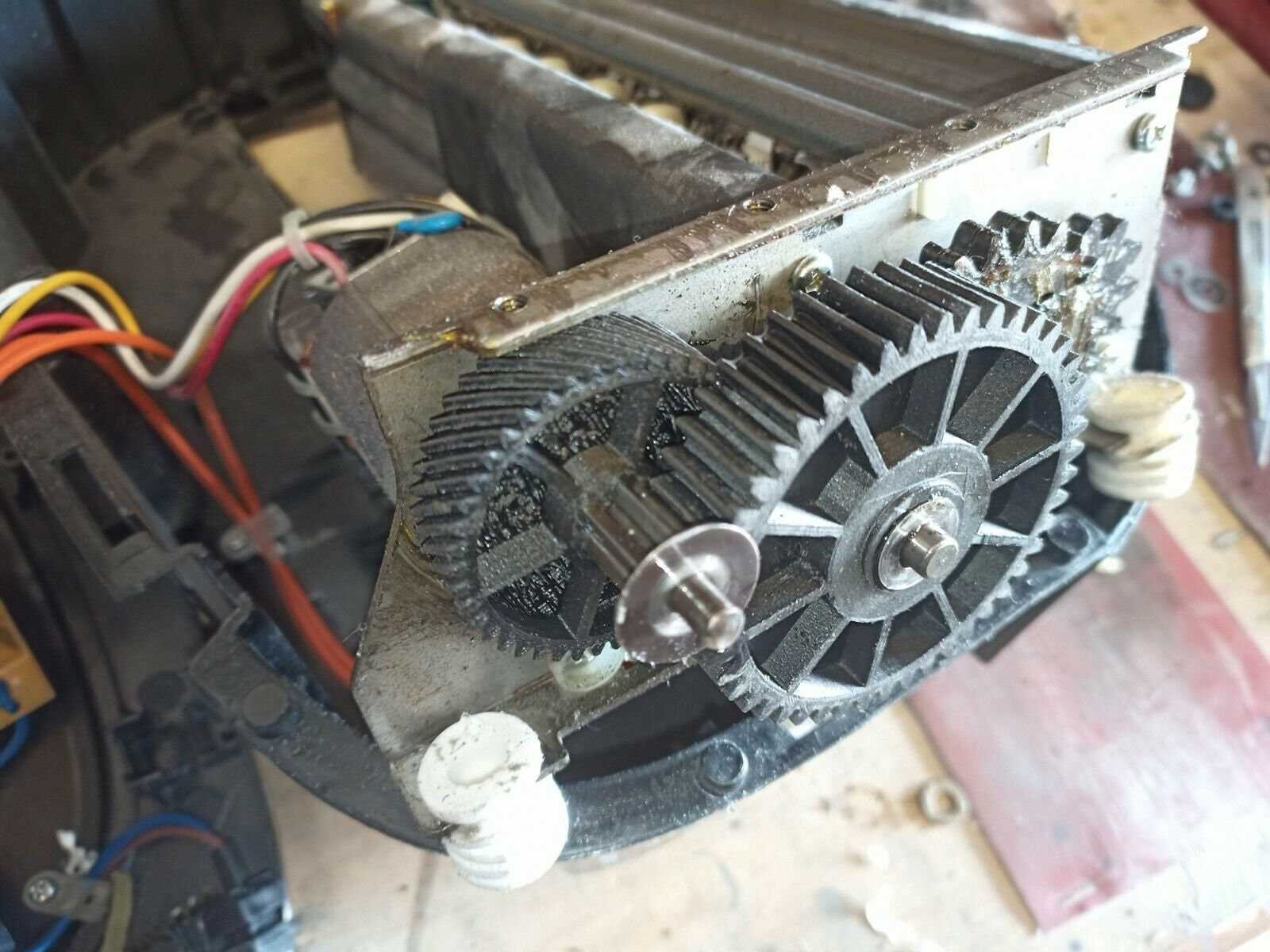
The Role of the Motor Assembly
The motor assembly serves as the core driving mechanism, converting electrical energy into rotational force. Its function is essential for ensuring consistent movement and enabling the smooth operation of the entire system.
The primary function of the motor is to generate torque, which is transmitted through gears or belts to various internal components. This power transfer ensures that the entire unit operates efficiently, handling varying loads without interruptions.
A well-maintained motor improves overall performance and longevity. Regular inspection and lubrication of moving parts help prevent overheating, wear, and mechanical failures, ensuring the mechanism remains functional under continuous use.
Common Issues with Shredder Parts
Mechanical devices that handle frequent material processing can encounter various operational challenges. Over time, individual components may wear down or become misaligned, leading to decreased performance and potential malfunctions. Identifying common faults early helps maintain smooth operation and prevent costly repairs.
Blade Dulling and Misalignment: One of the primary issues is the gradual dulling of cutting edges, which reduces efficiency. Additionally, misaligned blades can jam the mechanism, requiring manual realignment or replacement.
Motor Overheating: Continuous heavy use may cause motors to overheat, triggering automatic shutdown systems. Proper maintenance, such as regular cooling intervals, can prevent this issue.
Clogging and Jammed Materials: Accumulation of material inside the device can cause blockages. Regular cleaning of internal sections and proper loading techniques help mitigate this problem.
Roller Wear and Gear Damage: Prolonged use can lead to worn-out rollers or broken gears, causing uneven movement or complete failure of the feed system. Replacing these elements promptly ensures smooth operation.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Proper upkeep ensures smooth operation and prevents early wear, extending the life of your equipment. By following a few simple routines, you can reduce mechanical strain and keep everything running efficiently for years to come.
Regular Cleaning
- Remove accumulated dust and debris from internal mechanisms to avoid clogs.
- Use a soft brush or compressed air for delicate areas that may be hard to reach.
- Wipe external surfaces with a dry or slightly damp cloth to maintain cleanliness.
Lubrication and Inspection
- Apply oil to moving components regularly to prevent friction and overheating.
- Check for loose screws or worn-out parts and replace them promptly to avoid malfunction.
- Inspect electrical connections to ensure they remain secure and free from corrosion.
Following these maintenance practices will help minimize downtime, improve reliability, and ensure the long-term functionality of your equipment.
Safety Features in Shredding Machines
Modern cutting devices are equipped with various protective mechanisms to ensure secure and efficient operation. These features are designed to minimize risks to both the user and the equipment during use, offering enhanced reliability in different work environments.
Overload Protection: This system prevents motor damage by automatically stopping the device when it detects excessive input or prolonged usage beyond the recommended capacity.
Auto Shut-off: Many machines include sensors that halt operations when the lid is opened or if hands come too close to the cutting area, reducing the chance of accidents.
Reverse Functionality: In the event of jamming, this feature allows the motor to run in the opposite direction, ensuring safe removal of stuck materials without requiring manual intervention.
Thermal Overload Sensors: To prevent overheating, these sensors monitor internal temperature and temporarily disable the device if critical thresholds are reached.
Such safety systems make these machines practical and reliable for both personal and professional use, emphasizing not just performance but also user well-being.
Choosing the Right Shredder Model
Selecting the most suitable cutting device ensures smooth operation and long-term performance. The ideal model balances functionality, capacity, and efficiency, aligning with both personal and professional needs.
Capacity and Usage Frequency

Understanding capacity helps determine how many sheets or materials can be processed at once without straining the device. Regular use requires a machine with higher durability, while occasional tasks might need a simpler solution.
Additional Features and Noise Level
Advanced models offer extra features such as safety mechanisms, auto-reverse options, and low-noise operation. Consider where the device will be used to ensure it meets environmental demands, including sound sensitivity and energy efficiency.
How to Assemble a Shredder
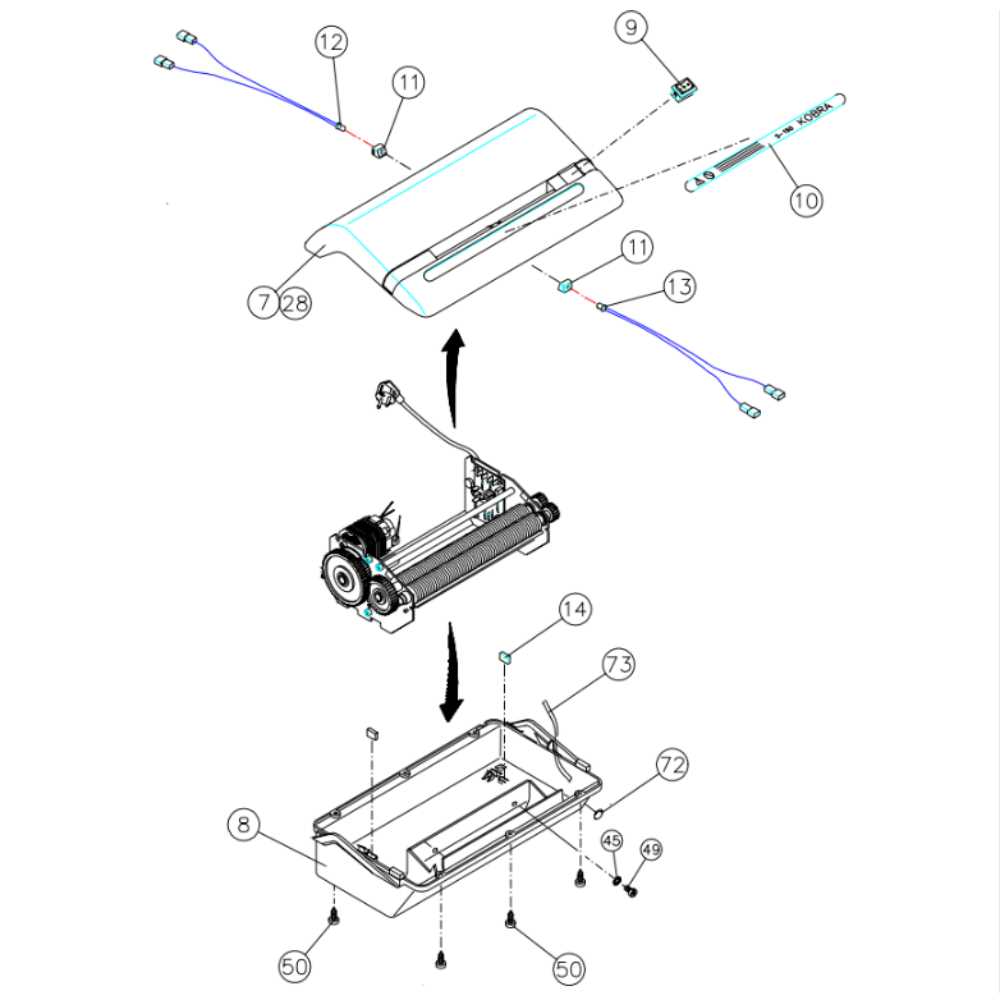
Putting together a cutting device requires attention to detail to ensure smooth operation. With proper alignment of the components, you can guarantee both functionality and safety. Each element has its place in the overall structure, and following the correct sequence is essential to avoid any issues during use.
Step 1: Preparing the Main Unit
Start by placing the base unit on a stable surface. Make sure all moving components are free from obstructions. Attach the motor section carefully, ensuring it clicks or locks into position. Secure it tightly to prevent any vibrations that could affect performance.
Step 2: Installing the Blades
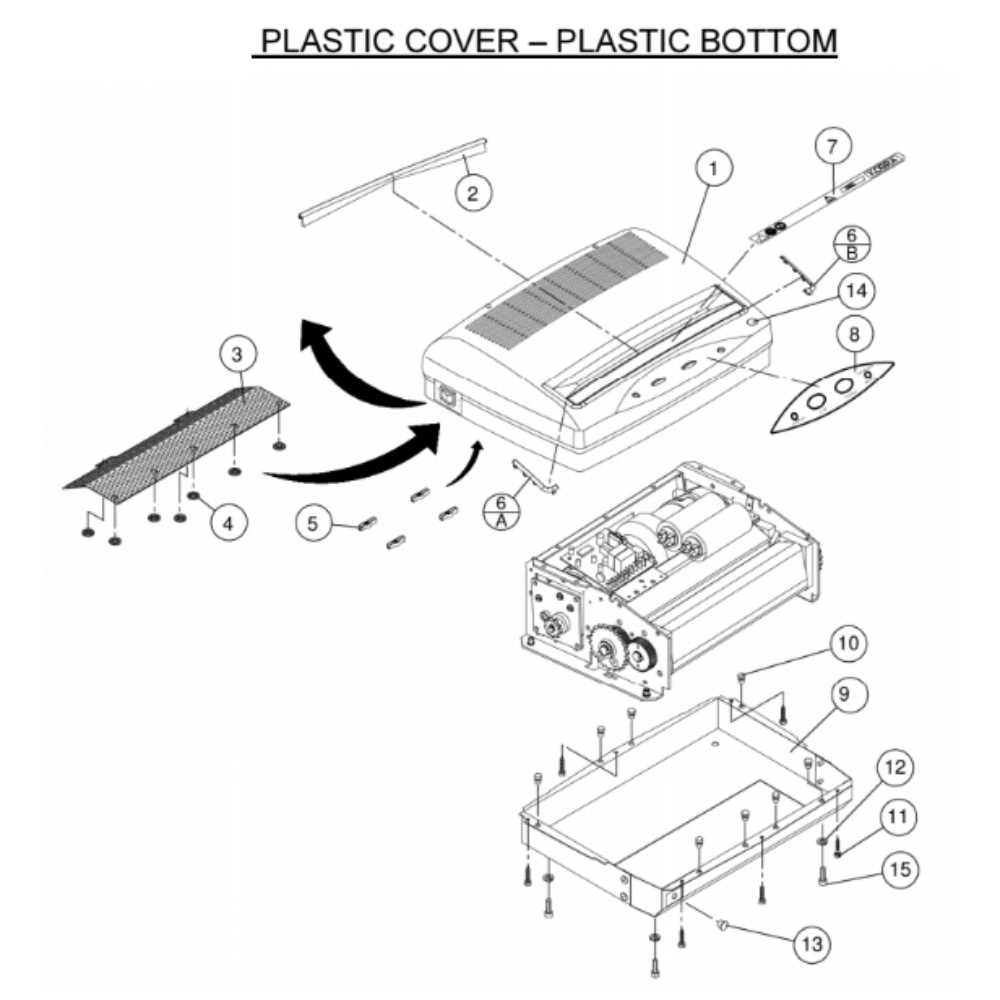
Insert the cutting cylinders into the designated slots. Align them precisely, as even a slight misplacement could interfere with the rotation. It is advisable to lubricate them slightly if recommended in the instructions. Once in place, rotate them manually to ensure smooth movement.
Final Touches: Once the assembly is complete, connect the power
Understanding Shredder Performance Ratings
Performance ratings help users evaluate how effectively a device handles material reduction tasks. These ratings reflect the equipment’s capacity, efficiency, and suitability for various operational demands, ensuring it meets user expectations for both occasional and intensive use.
The evaluation metrics typically include the amount of material processed in one cycle, speed of operation, and durability under continuous use. Each factor contributes to determining the ideal use case, whether for light home tasks or demanding industrial applications.
| Rating Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Processing Capacity | The volume of material the device can handle per session, often measured in sheets or weight units. |
| Operational Speed | The time required to process a given amount of material, influencing overall task efficiency. |
| Continuous Run Time | How long the equipment can function without overheating or requiring a cooldown period. |
| Noise Level | The amount of sound generated during use, important for offices or shared spaces. |
| Security Rating | Indicates the level of data protection provided by the cutting style, |