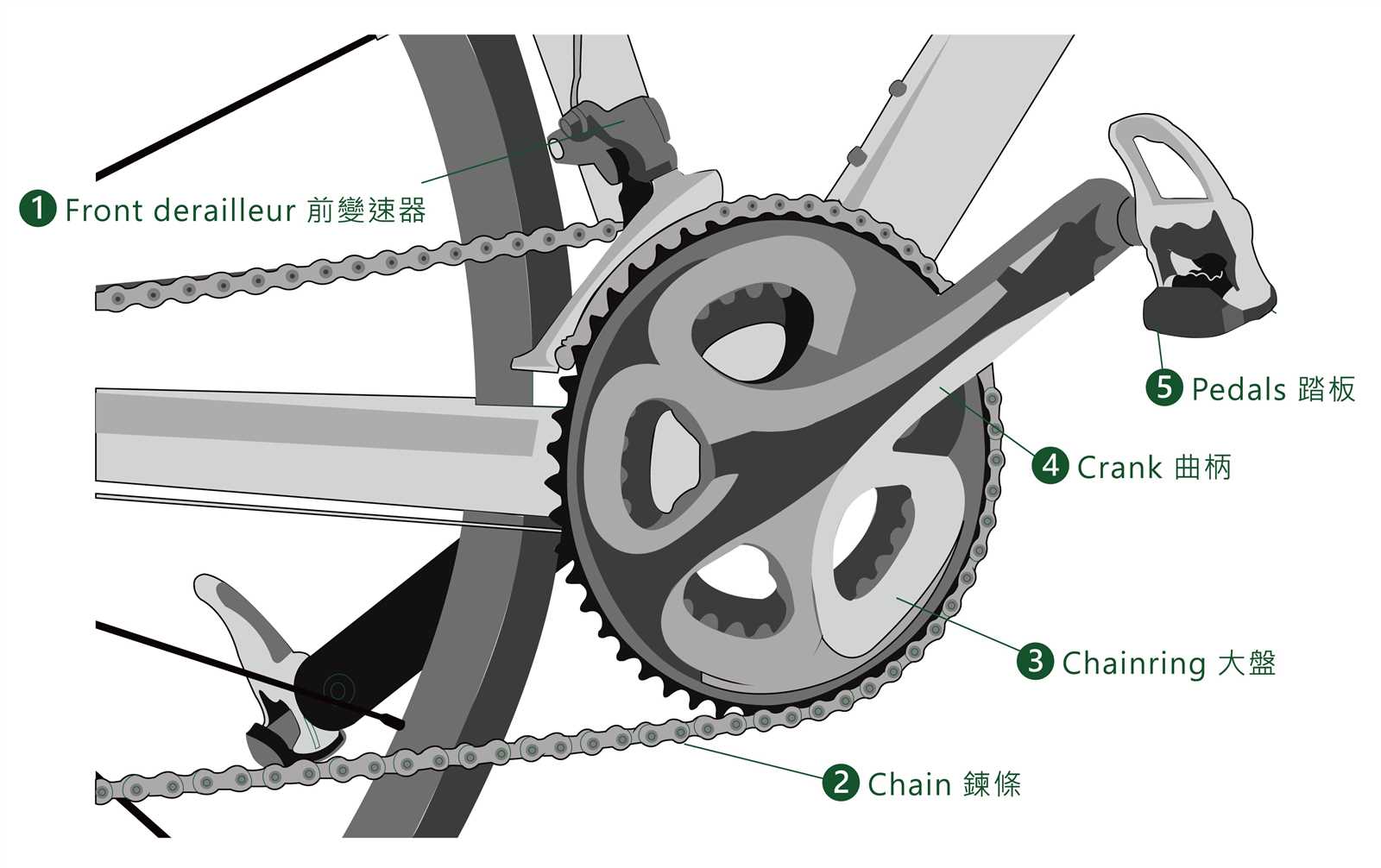
The intricacies of a two-wheeled transport system involve a variety of mechanisms that work together to ensure smooth operation and optimal performance. These essential elements play a crucial role in the overall functionality, enabling riders to navigate various terrains with ease and efficiency.
In this section, we will explore the fundamental components that contribute to the movement and control of the vehicle. Each element serves a specific purpose, facilitating seamless transitions and enhancing the overall riding experience. By gaining insight into these crucial mechanisms, enthusiasts can better appreciate the engineering behind their preferred mode of transportation.
Whether you’re a seasoned rider or a novice, understanding these mechanical features can empower you to make informed decisions regarding maintenance, upgrades, and modifications. This knowledge not only enhances your appreciation for the craft but also allows for a more enjoyable journey.
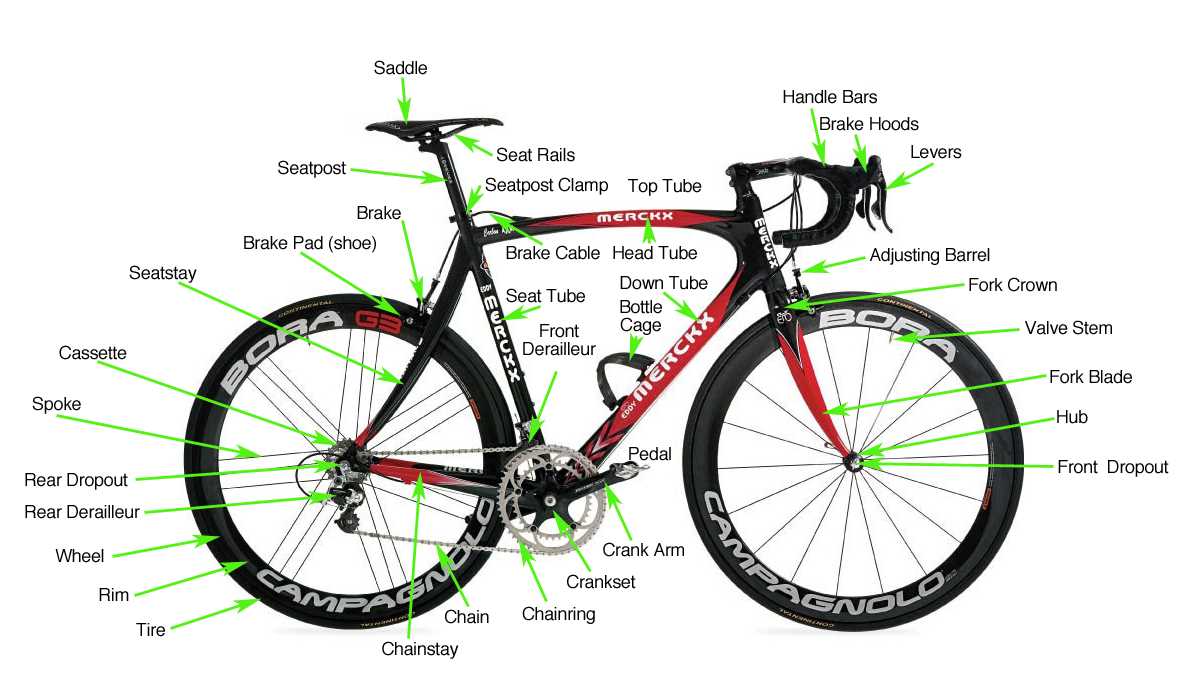
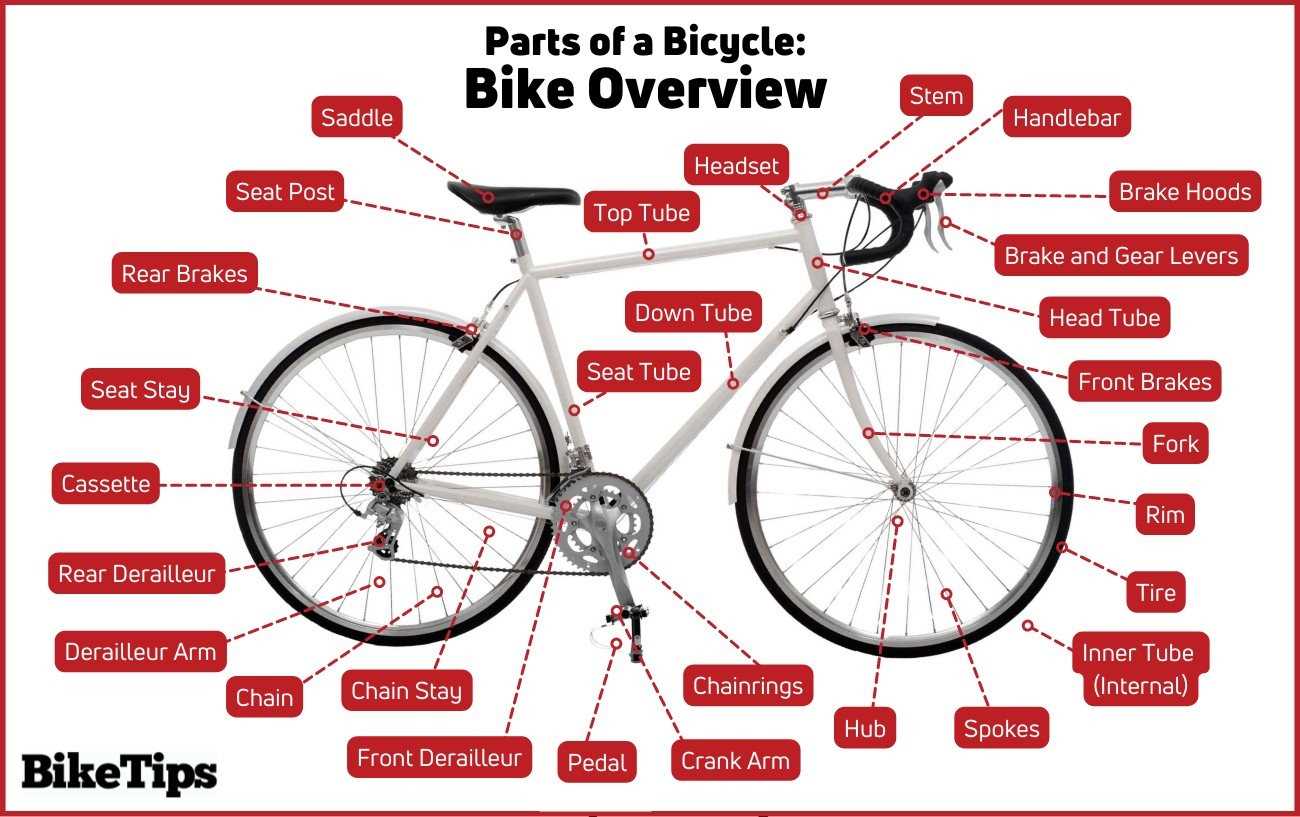
Recognizing components of a transmission system is essential for maintenance and performance enhancement. By understanding the various elements, one can effectively troubleshoot issues and make informed decisions during repairs or upgrades.
Common Components and Their Functions
Different elements within the transmission play distinct roles. Below is a table highlighting several key components along with their primary functions:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Chain | Transfers power from the crankset to the rear wheel. |
| Shifters | Controls the movement of the chain across various cogs. |
| Derailleur | Adjusts the position of the chain on the sprockets for changing speeds. |
| Sprockets | Engages with the chain to provide different speed ratios. |
Tips for Identification
When attempting to identify the elements of a transmission system, consider the following tips:
- Examine the arrangement and size of the components, as this can indicate their specific roles.
- Familiarize yourself with the common types and brands to differentiate between various models.
- Refer to technical manuals or online resources for detailed illustrations and descriptions.
Maintenance Tips for Gear Systems
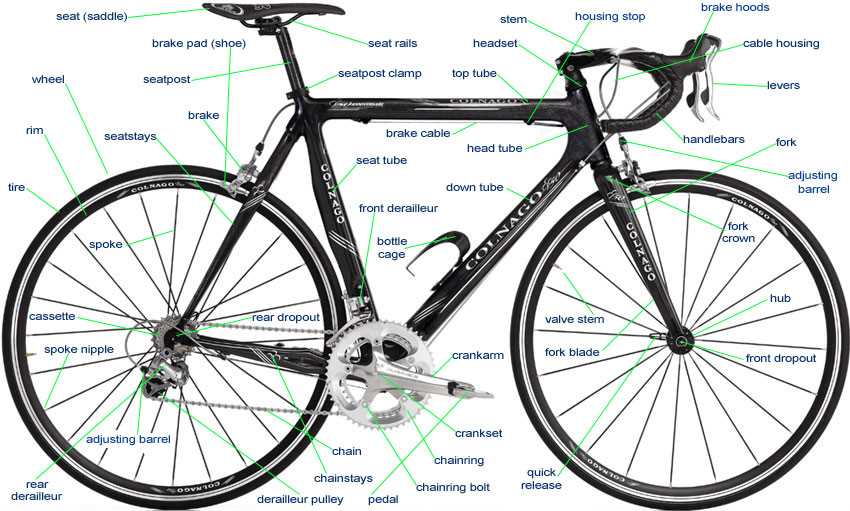
Proper upkeep of your transmission components is essential for optimal performance and longevity. Regular attention can help prevent wear and ensure smooth operation. Below are some key recommendations to maintain these systems effectively.
- Regular Cleaning: Keep the components clean by removing dirt and debris. Use a soft brush or cloth to avoid damaging sensitive areas.
- Lubrication: Apply appropriate lubricant to moving elements to reduce friction and prevent rust. Make sure to choose a product designed for your specific application.
- Inspect Components: Routinely check for signs of wear, such as fraying or unusual noise. Look for any cracks or damage that might require replacement.
- Adjustments: Make necessary adjustments to ensure proper alignment and function. This includes tuning tension and ensuring all connections are secure.
- Periodic Servicing: Schedule regular professional inspections. A technician can identify potential issues that may not be visible to the untrained eye.
By following these maintenance tips, you can enhance the reliability and efficiency of your transmission system, ensuring it performs at its best for years to come.
Common Issues with Bicycle Gears
When it comes to cycling, there are several challenges that riders may encounter related to their transmission system. Understanding these problems can help ensure a smooth and enjoyable ride.
- Skipping or Jumping: This occurs when the chain fails to engage properly with the sprockets, leading to a sudden loss of power during pedaling.
- Difficulty Shifting: A common issue where the mechanism does not transition smoothly between settings, often due to misalignment or wear.
- Unusual Noises: Unwanted sounds can indicate underlying issues, such as a loose chain or components that require lubrication.
- Chain Wear: Over time, the chain may stretch or degrade, which affects its performance and can lead to further complications if not addressed.
- Rust and Corrosion: Exposure to moisture can lead to deterioration, affecting functionality and lifespan.
By being aware of these common problems, cyclists can take proactive measures to maintain their equipment and enhance their riding experience.
Upgrading Your Bicycle Gear Setup

Enhancing the performance of your ride can significantly improve your overall experience. Whether you’re looking to increase speed, efficiency, or comfort, making informed upgrades is crucial. From selecting the right components to ensuring compatibility, there are several key considerations to keep in mind.
Assessing Your Current Configuration
Before making any changes, evaluate your existing setup. Take note of what functions well and what could be improved. Consider factors such as weight, durability, and responsiveness. Identifying the strengths and weaknesses of your current arrangement will guide your decisions in selecting new components.
Selecting Upgrades Wisely
When choosing enhancements, prioritize components that align with your riding style and objectives. Upgrading to higher-quality materials or advanced technology can yield noticeable benefits. For instance, lighter materials can enhance acceleration, while precision-engineered elements can improve shifting performance. Always ensure that any new addition integrates seamlessly with your existing system for optimal results.
Importance of Proper Gear Alignment
Ensuring accurate alignment within the transmission system of a cycling machine is crucial for optimal performance. When components are properly positioned, it leads to smoother operation, enhances efficiency, and extends the lifespan of various mechanisms. Misalignment can result in premature wear, increased friction, and potentially costly repairs.
Benefits of Accurate Alignment
- Smoother Operation: Correct positioning minimizes resistance, allowing for seamless transitions between different settings.
- Improved Efficiency: A well-aligned system optimizes energy transfer, enabling the rider to conserve strength and maintain speed.
- Longer Lifespan: Preventing undue stress on components reduces wear and tear, leading to fewer replacements.
Consequences of Misalignment
- Increased Friction: Poorly aligned elements generate extra resistance, making it harder to operate.
- Premature Wear: Continuous strain on misaligned components can lead to quicker degradation.
- Potential Failures: Severe misalignment may result in catastrophic breakdowns, necessitating costly repairs.
Tools Needed for Gear Repairs
Having the right tools is essential for maintaining and fixing various components of your two-wheeled vehicle. Proper equipment ensures that repairs are efficient and effective, helping to extend the lifespan of your ride. Below is a list of necessary instruments to have on hand for successful maintenance.
- Wrenches: A set of adjustable and fixed wrenches will help you tackle various bolt sizes.
- Screwdrivers: Both flathead and Phillips screwdrivers are essential for tightening or loosening screws.
- Allen Keys: These are crucial for adjusting components that require hex screws.
- Pliers: Useful for gripping and bending wires or small parts during repairs.
- Tire Levers: These are needed to help remove tires from rims when necessary.
- Chain Tool: A specialized tool to remove and install links in the chain.
- Lubricants: Keeping parts well-lubricated helps reduce wear and tear.
- Cleaning Supplies: Brushes and cloths are important for keeping components clean.
Equipping yourself with these tools will simplify the repair process and contribute to better performance. Regular maintenance using the correct instruments ensures a smooth and enjoyable experience on the road.
Differences Between Gear Types
The variety of mechanical systems available can significantly influence performance and usability. Each design offers unique characteristics, making them suitable for different conditions and preferences. Understanding these distinctions allows individuals to select the most appropriate option for their needs.
Types of Mechanical Systems
When examining various designs, two primary categories emerge: those focused on speed and those emphasizing torque. Speed-oriented systems enable higher velocities, while torque-centric designs provide better acceleration and climbing capabilities.
Comparison Table
| Type | Characteristics | Best Use |
|---|---|---|
| Speed-Focused | Lightweight, streamlined, optimized for high speeds | Flat terrains, racing, and time trials |
| Torque-Centric | Robust, designed for enhanced power transfer | Steep climbs, rugged trails, and off-road conditions |
Visual Guide to Gear Diagrams
This section provides an insightful overview of the various mechanisms involved in the transmission of motion within two-wheeled vehicles. Understanding the intricate arrangements and functions of these systems is essential for both enthusiasts and those looking to enhance their riding experience.
Understanding the Mechanisms
Exploring the components that facilitate smooth transitions between different speeds allows riders to optimize their performance. Each element plays a critical role in ensuring efficient operation, enabling users to tackle diverse terrains with ease.
Importance of Maintenance
Regular upkeep of these systems is crucial for longevity and optimal functionality. Familiarizing oneself with the layout and function of each component can greatly assist in timely repairs and adjustments, ultimately leading to a more enjoyable journey.