
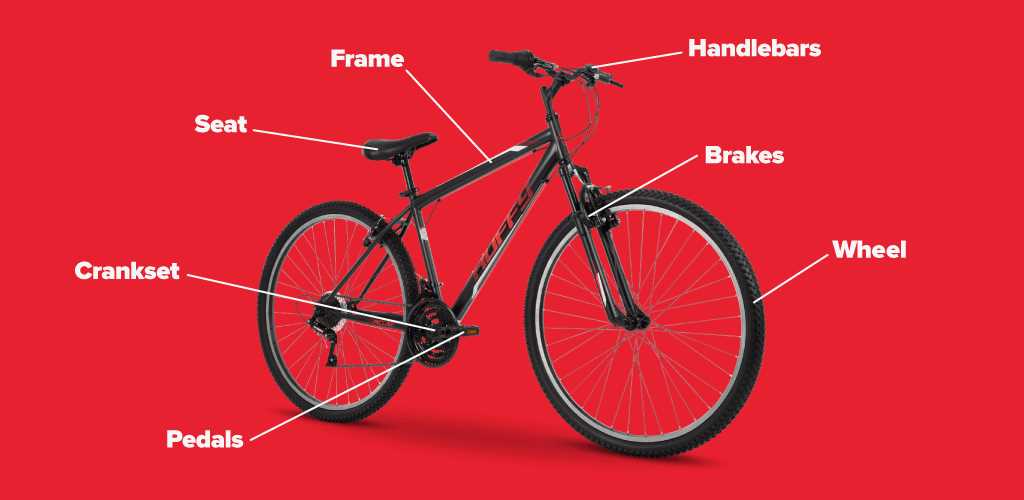
For anyone looking to enhance their knowledge of mechanical systems in two-wheeled transport, it is essential to grasp how each segment interacts to drive motion. The central piece of this mechanism is often overlooked, but it plays a crucial role in transferring power from the rider to the wheels.
The structure consists of multiple interconnected elements that work together to ensure smooth and efficient movement. These components must function in harmony to deliver optimal performance, whether you’re commuting or tackling challenging terrain.
This article will explore the specific elements involved in this process, detailing how they contribute to overall efficiency and power transfer. A better understanding of these mechanics can help in both maintenance and upgrading, ensuring a more enjoyable and efficient ride.
Overview of Bike Crank Components

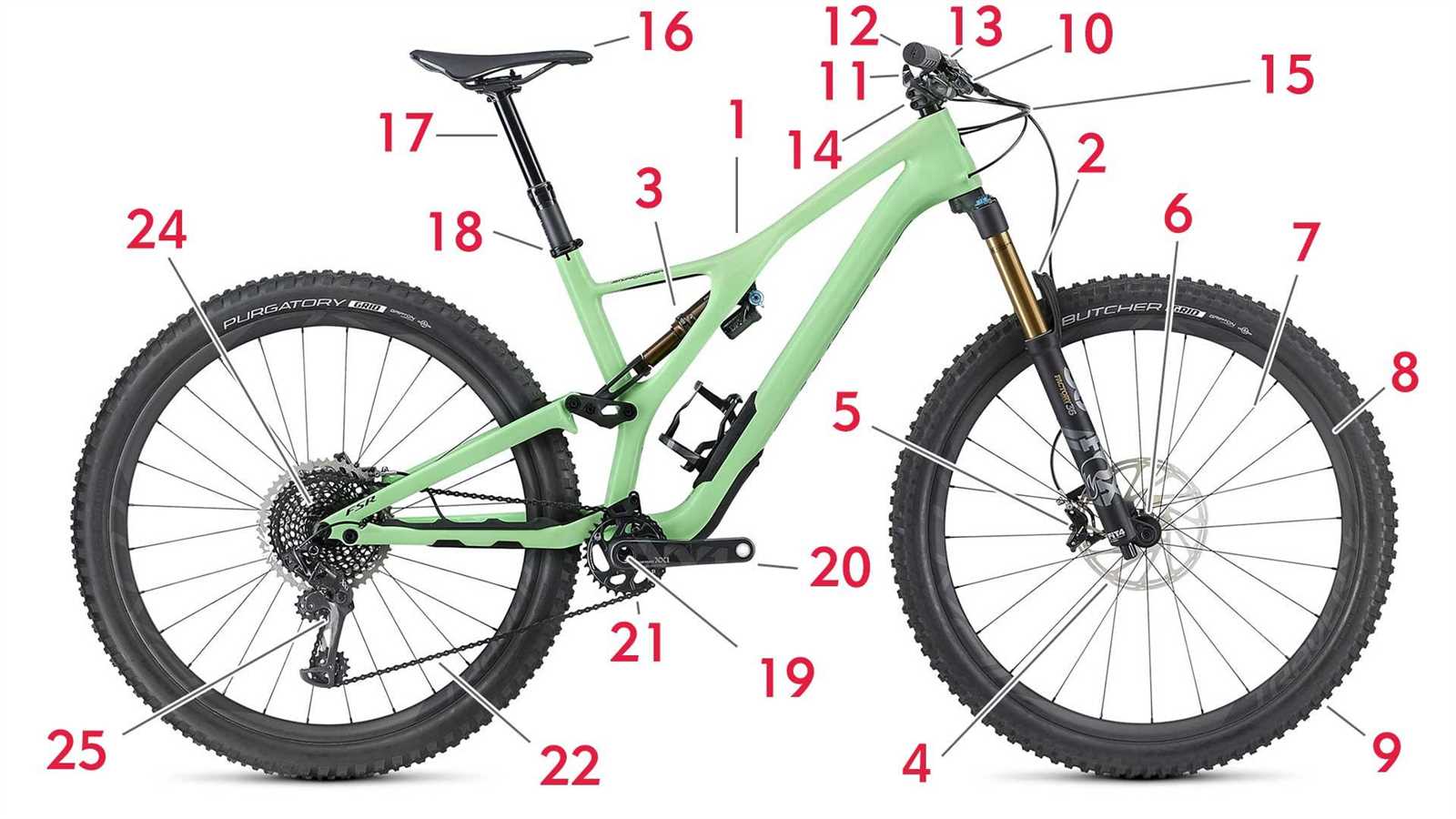
The mechanical structure that transfers motion to the vehicle’s drivetrain is made up of several essential elements. Each component plays a critical role in ensuring smooth rotation, efficient power delivery, and overall performance of the system. Understanding these elements can help with both maintenance and upgrades, improving the efficiency of the ride.
Main Elements
- Axle Mechanism: Connects the rotating system to the frame, allowing smooth circular movement.
- Pedal Arms: Long levers where foot pressure is applied, transmitting force to the connecting parts.
- Rotational Bearings: Minimize friction between moving sections, ensuring fluid motion.
Additional Components

- Gear Rings: The toothed segments that interact with the chain to regulate speed and force.
- Understanding the Role of the Crankset
The crankset is a crucial component in transforming human energy into motion. It functions as a key part of the system responsible for transferring power from the rider’s legs to the drivetrain, which then propels the vehicle forward. Proper understanding of its mechanism can improve both performance and maintenance.
Main Functions of the Crankset

- Energy Transfer: The crankset channels the force applied by the legs into the rotating chain, creating momentum.
- Pedaling Efficiency: A well-functioning crankset helps maintain a smooth and consistent pedal stroke, ensuring effective power delivery.
- Support for Chainrings: It provides a stable platform for the chainrings, which interact with the chain to maintain forward motion.
Impact on Performance

The condition of the crankset directly affects the efficiency and responsiveness of the pedaling motion. Worn-out components may lead to energy loss, requiring more effort for the same output. Regular inspection and timely replacement of parts can enhance overall riding experience.
Key Differences Between Crank Arms
The design and structure of arm components can greatly influence performance, durability, and comfort during rides. These elements vary in terms of material, length, and compatibility with other elements of the drive system, making it essential to choose the right one for your needs.
- Material: Arm components are typically made from aluminum, carbon fiber, or steel. Aluminum offers a balance of weight and strength, while carbon fiber is lighter but more expensive. Steel is the heaviest but provides maximum durability.
- Length: The length can impact the rider’s leverage and efficiency. Longer arms offer better power transfer, while shorter ones are ideal for a faster cadence and improved agility.
- Compatibility: It’s crucial to ensure the arms are compatible with the rest of the drive system. Different models may require specific connections or sizes to work properly.
Understanding these key factors can help in selecting the most suitable arm components for a more optimized and efficient ride.
Functionality of Chainrings in a Crankset
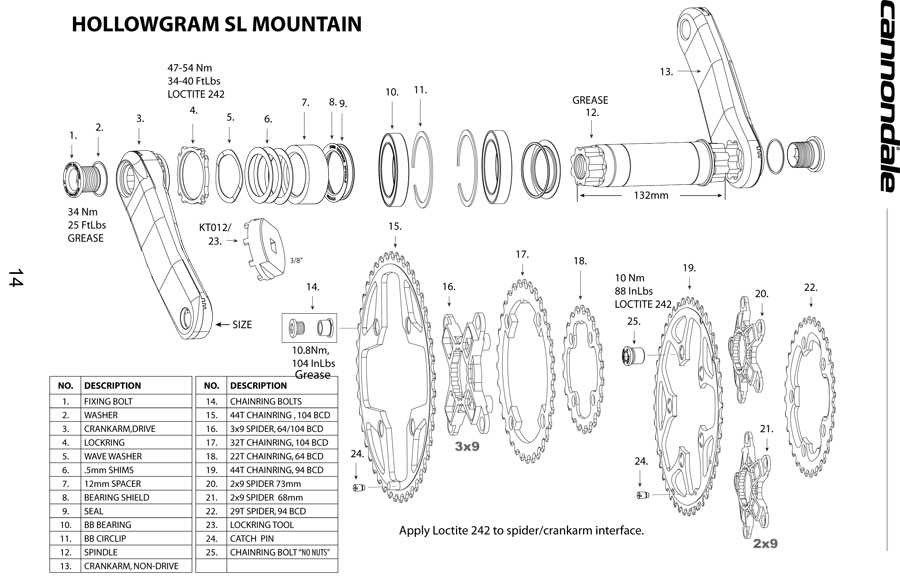
Chainrings are essential components that transfer the rider’s pedaling power to the drivetrain, allowing for efficient propulsion. They come in various sizes and configurations, impacting how smoothly the gears shift and how much torque is applied with each pedal stroke. By engaging with the chain, chainrings help manage speed and control over different terrains.
The positioning of these circular components in relation to the front mechanism ensures that energy is effectively distributed across the drivetrain. A well-matched set of chainrings allows riders to optimize their power output, ensuring both high-speed travel and ease in challenging conditions.
How the Bottom Bracket Supports the Crank
The bottom bracket plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth rotation of the pedals and transferring energy efficiently. It acts as a connection point between the rotating arms and the frame, allowing for stable and fluid movement while minimizing friction and wear.
Main Functions of the Bottom Bracket
- Stability: Provides a secure housing for the spindle, ensuring balanced motion during pedaling.
- Rotation: Allows the spindle to turn freely, reducing resistance for efficient energy transfer.
- Durability: Protects internal components from moisture and dirt, extending the lifespan of the entire mechanism.
Different Types of Bottom Brackets
Various models are available, each designed to fit specific frames and enhance performance. Some focus on lightweight construction, while others prioritize strength and durability.
- Threaded: A traditional design that screws into the frame, offering easy maintenance.
- Press-fit: A modern design that presses into the frame, reducing weight and simplifying the structure.
Types of Pedal Attachments
Understanding the various types of pedal attachments is crucial for optimizing performance and comfort while cycling. Different designs cater to specific riding styles and preferences, ensuring that every cyclist can find a suitable option for their needs.
There are several common types of pedal attachments, each offering unique features and benefits. Below is a summary of these options:
Attachment Type Description Advantages Platform Flat pedals that provide a stable surface for the foot. Easy to use with any footwear; great for casual riding. Clipless Pedals that securely attach to special shoes using cleats. Enhanced power transfer; improved stability and efficiency. Toe Clips Straps that hold the foot in place on traditional pedals. Better control and power transfer compared to flat pedals. Hybrid Pedals featuring both flat surfaces and clipless mechanisms. Versatile for various riding styles and shoe options. Choosing the right attachment type can significantly impact the overall cycling experience, enhancing both comfort and efficiency on the road or trail.
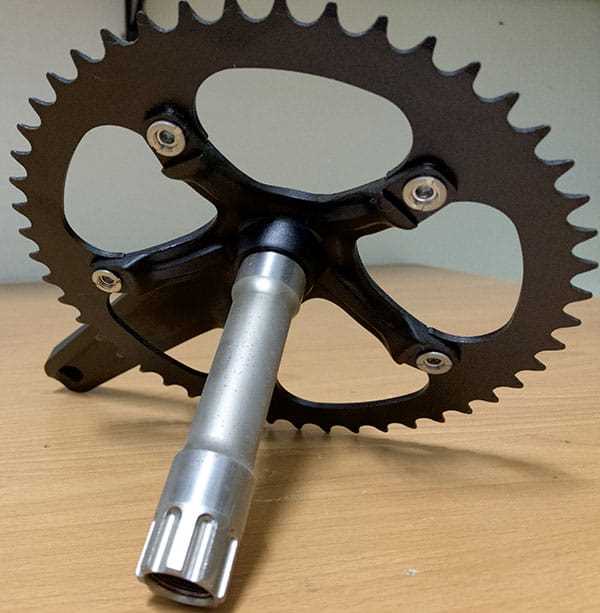
Exploring the Spider in a Crank Assembly

The spider is a crucial component of the assembly, playing a significant role in the overall functionality. This element serves as the connection point between the main body and the pedals, facilitating power transfer with precision. Understanding its design and operation is essential for enthusiasts and mechanics alike, as it impacts both performance and efficiency.
Functionality and Design

The design of the spider influences how torque is distributed across the assembly. By optimizing the shape and material, manufacturers enhance the strength and reduce weight, which ultimately improves the efficiency of energy transfer. Different configurations may cater to specific riding styles, highlighting the importance of selecting the right spider for individual needs.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular inspection of the spider is vital for maintaining optimal performance. Signs of wear or damage can lead to inefficiencies and even component failure. Proper maintenance, including cleaning and lubrication, can prolong the lifespan of this critical element, ensuring a smoother experience. Familiarity with common issues will aid in troubleshooting, allowing for timely interventions.
Importance of Crank Arm Length

The length of the arm connected to the pedal is a crucial factor that influences the efficiency and comfort of pedaling. This dimension affects the leverage applied to the pedals, which directly impacts the rider’s performance and energy expenditure. Selecting the appropriate arm length is essential for optimizing the overall cycling experience.
A well-matched arm length allows for smoother pedaling and improved power transfer. When the length is tailored to an individual’s leg size and riding style, it can enhance biomechanics, reduce the risk of injury, and improve overall cycling efficiency. Additionally, riders may notice better control and stability, leading to a more enjoyable journey.
In competitive scenarios, the correct arm length can make a significant difference in performance outcomes. By maximizing leverage and optimizing pedal stroke, cyclists can achieve higher speeds and greater endurance. Therefore, understanding and considering the importance of arm length is vital for anyone looking to improve their cycling experience.
Material Choices for Crank Components
When it comes to constructing the essential elements of a pedaling system, the selection of materials plays a crucial role in determining performance, durability, and overall functionality. Various materials offer unique advantages, influencing weight, strength, and resistance to wear and tear. Understanding these options is vital for achieving optimal efficiency and enhancing the riding experience.
Aluminum is a popular choice due to its lightweight nature and good strength-to-weight ratio. It is often used in mid-range and high-end models, providing excellent performance while keeping the overall weight low.
Steel, on the other hand, is renowned for its durability and resistance to bending. It is commonly found in entry-level designs, offering robustness that can withstand heavy use, albeit at a higher weight compared to aluminum.
Carbon fiber represents a premium option, prized for its exceptional strength and minimal weight. This composite material allows for intricate designs and enhanced stiffness, making it a favored choice among competitive enthusiasts seeking peak performance.
Additionally, titanium has gained recognition for its unique properties, combining lightweight with incredible strength and corrosion resistance. Though often more expensive, it appeals to those prioritizing longevity and performance in demanding conditions.
Ultimately, the choice of material significantly influences the characteristics of these components, shaping the riding experience and overall satisfaction.
Common Crankset Designs and Standards
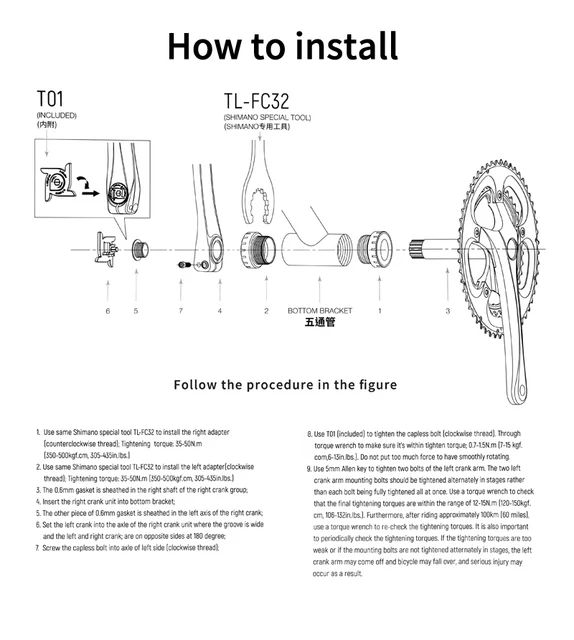
Understanding the various configurations and specifications of drivetrain systems is essential for optimizing performance and compatibility. Different models exhibit unique characteristics that cater to specific riding styles and preferences. This section delves into the prevalent designs and benchmarks within this vital component of cycling.
Design Type Description Common Standards Standard This classic format features a traditional configuration, typically suitable for a wide range of riding scenarios. ISO, JIS Compact Designed for enhanced versatility, this style offers a lower gear ratio, making it ideal for climbing. Shimano, Campagnolo Single Speed Streamlined for simplicity, this setup focuses on minimalism and ease of maintenance. Track, BMX Double Features two chainrings for improved gear range, suitable for various terrains. Shimano, SRAM Triple Incorporating three chainrings, this design maximizes gearing options, ideal for touring and off-road adventures. Shimano, Campagnolo Crank Maintenance Tips for Cyclists

Proper upkeep of your cycling mechanism is essential for ensuring a smooth and efficient ride. Regular attention to specific components can prevent wear and tear, enhancing overall performance. Here are some valuable suggestions to help you maintain these crucial elements of your cycling equipment.
- Regular Cleaning: Keep the area free from dirt and debris. Use a soft brush and mild soap to clean any grime that accumulates.
- Lubrication: Apply appropriate lubricant to the moving parts. Ensure that excess oil is wiped off to prevent attracting dust.
- Check for Wear: Frequently inspect for signs of damage or excessive wear. Replace any components that show significant signs of deterioration.
- Tighten Fasteners: Periodically check and tighten any screws or bolts to ensure everything remains securely in place.
- Storage: Store your equipment in a dry, cool place to avoid rust and corrosion. Consider using a cover if storing for long periods.
By following these simple maintenance tips, you can significantly extend the life of your cycling equipment and enjoy a more reliable and enjoyable riding experience.
Choosing the Right Crank for Your Bike

Selecting the appropriate component for your cycling setup is crucial for achieving optimal performance and comfort. Various options are available, each designed for specific riding styles, terrains, and personal preferences. Understanding the differences can help you make an informed choice that enhances your overall experience on the road or trail.
Types of Components
Different designs cater to diverse riding techniques, such as endurance, mountain, or urban cycling. Each variety features unique attributes that affect power transfer, weight, and overall efficiency. Assessing your typical riding conditions will guide you toward the most suitable selection.
Material Considerations
The composition of the selected component significantly impacts durability and performance. Materials range from aluminum to carbon fiber, each offering distinct advantages. For instance, carbon fiber is lightweight and stiff, ideal for racing, while aluminum provides strength and reliability for everyday use.