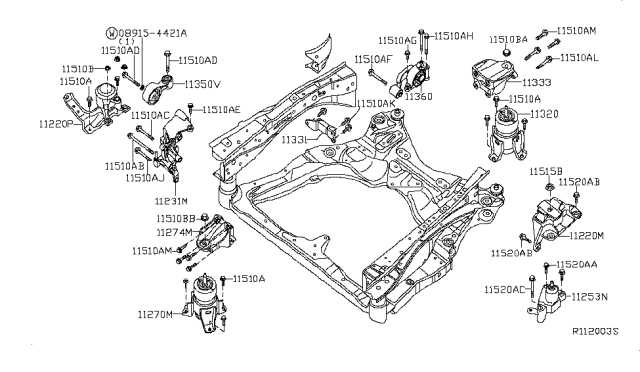
In the world of automotive maintenance and repair, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of how various elements of a vehicle are interconnected. Each mechanical and electrical system plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of a car. Whether you’re a seasoned technician or a car enthusiast, visualizing the layout and arrangement of these elements can significantly ease the process of maintenance.
Exploring the structure of different assemblies allows you to not only comprehend the internal workings but also identify potential issues that may arise over time. From the powertrain to the electrical connections, understanding how these elements are organized provides valuable insight into troubleshooting and replacement. A well-organized overview is key to enhancing efficiency and ensuring optimal performance in any repair or upgrade.
Being equipped with detailed visuals and comprehensive descriptions is crucial for both professionals and hobbyists. Whether addressing mechanical failures or performing routine checks, knowing how various systems interact
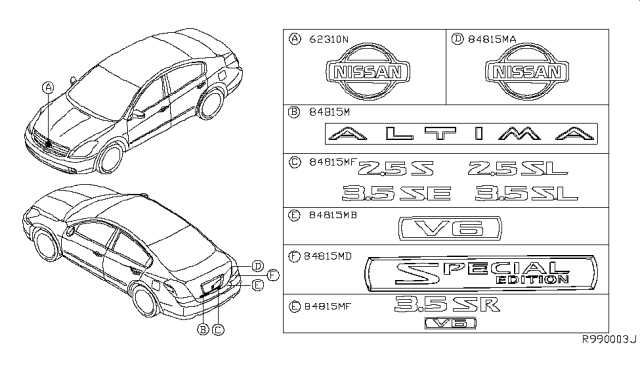
Exploring Essential Components of the 2012 Nissan Altima
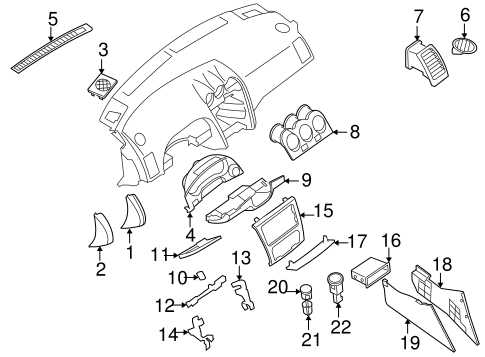
This section provides an overview of critical elements that make up the functionality and performance of a popular mid-sized sedan. By examining key mechanical and structural parts, we can gain insight into how each component contributes to the vehicle’s overall efficiency and reliability.
Key Engine Elements
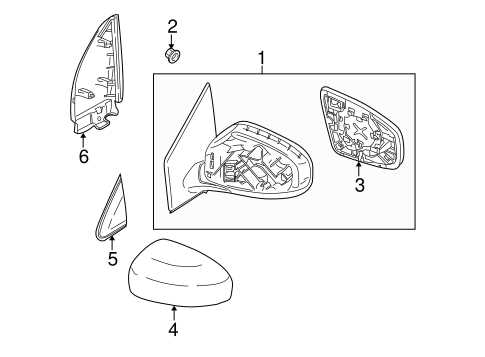
The engine is the heart of any automobile. Here, we explore the main components that ensure smooth operation, fuel efficiency, and optimal performance.
- Cylinder block
- Camshaft and crankshaft
- Fuel injectors
- Ignition system
Transmission and Drivetrain
The transmission system works in harmony with the engine, converting power into motion. Let’s take a closer look at some of the integral elements within this system:
- Automatic
Understanding the Engine Layout
The configuration of the engine is fundamental for the overall operation and efficiency of any vehicle. By analyzing the key components and how they interconnect, it becomes easier to grasp how various systems work together to power the car. This section will provide a detailed overview of the engine structure, focusing on its core elements and their roles in vehicle performance.
Main Components of the Engine
In an internal combustion engine, several essential parts ensure smooth functionality. These include the cylinder block, which forms the engine’s foundation, the pistons that move inside the cylinders, and the crankshaft that converts the pistons’ motion into rotational energy. Each of these parts plays a critical role in generating power.
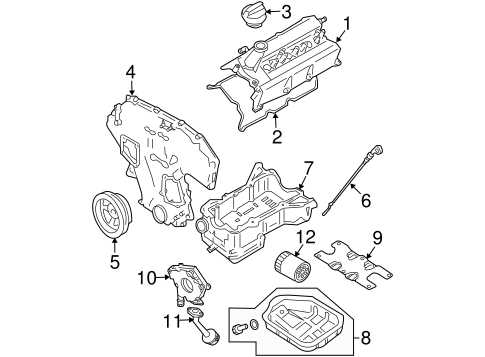
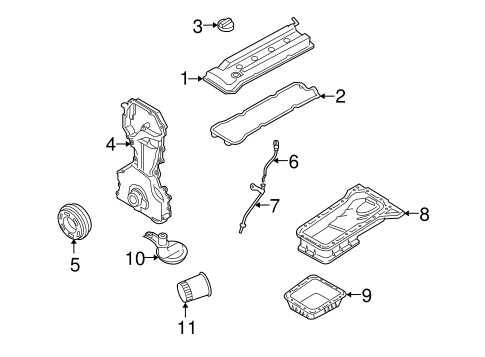
Cooling and Fuel Systems Integration
The engine’s cooling and fuel delivery systems are vital to maintaining optimal performance. The cooling system prevents overheating by circulating coolant through various channels, while the fuel system delivers the appropriate fuel mixture to the combustion chamber. Both systems must work in unison to maintain engine temperature and efficiency.
Component Transmission System Overview
The transmission system plays a crucial role in managing the power generated by the engine, ensuring smooth operation and optimal performance. It is responsible for transferring energy to the drive mechanism, allowing for efficient control of speed and torque. This section will cover the core components and how they interact to provide seamless power delivery during vehicle operation.
Key Components and Their Functions
A transmission system typically consists of several integral parts, each contributing to the overall function. These include the gearset, which allows for changes in vehicle speed, and the clutch or torque converter, which modulates the connection between the engine and drivetrain. Additionally, the system relies on hydraulic or electronic control units to facilitate precise gear shifting, enhancing both performance and fuel efficiency.
Manual vs. Automatic Systems
While manual systems require the driver to manually engage the gears, automatic systems use a series of sensors and actuators to perform this task. Both types have their advantages; manual setups offer more direct control, while automatic versions provide greater convenience. Regardless of the configuration, each
Brake System Components
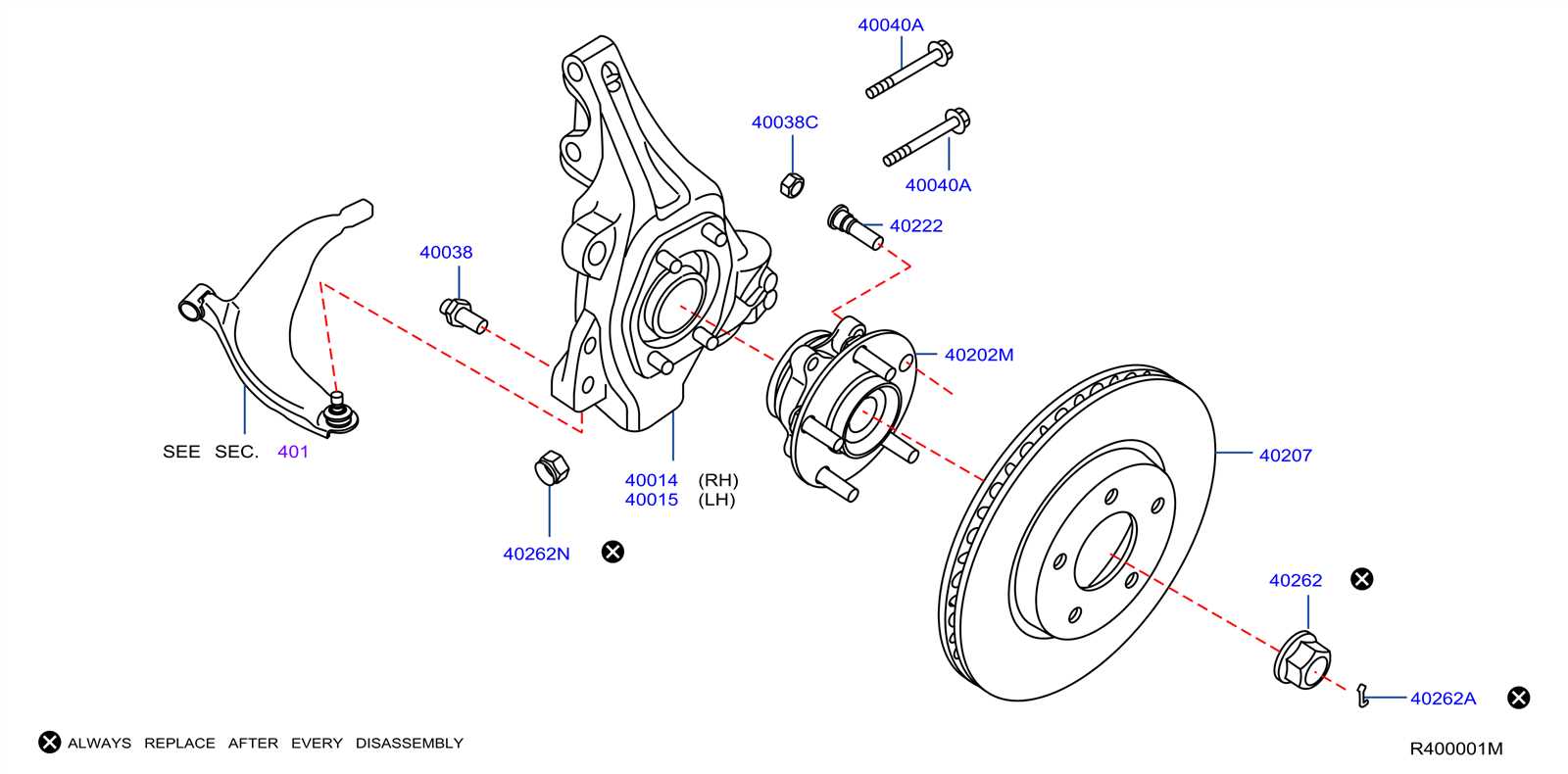
The braking system is an essential safety feature, designed to provide reliable stopping power in various driving conditions. Understanding the individual elements that work together to ensure effective braking can help in maintaining the system and identifying potential issues.
- Brake Calipers: These components house the brake pads and use hydraulic pressure to squeeze them against the rotors, creating the friction necessary to slow the vehicle.
- Brake Rotors: Rotating discs connected to the wheels, which the pads press against to generate the friction that stops the vehicle.
- Brake Pads: The friction material that contacts the rotors when the brakes are applied, playing a crucial role in slowing the vehicle.
- Brake Lines:
Suspension and Steering Mechanism
The suspension and steering system is a key component that ensures stability, control, and comfort while driving. It plays a critical role in maintaining a smooth ride by absorbing shocks and allowing the vehicle to respond effectively to driver input when turning or navigating uneven terrain.
Suspension System: The main function of the suspension is to support the weight of the vehicle while ensuring a comfortable ride. It minimizes the impact of road irregularities, helping to improve handling and braking performance. Key elements include springs, dampers, and stabilizers, all working together to maintain proper tire alignment and balance.
Steering Mechanism: The steering system allows precise control over the direction of the vehicle. Its components, including the steering rack, tie rods, and linkages, ensure that turning forces are transmitted efficiently from the steering wheel to the wheels. This system is designed to provide both
Interior Electrical Wiring and Connections
The electrical system within a vehicle plays a crucial role in ensuring the proper functionality of various components. This section delves into the intricate network of wiring and connections found throughout the cabin, highlighting their significance in maintaining electrical integrity and performance.
Understanding the layout and purpose of these electrical pathways is essential for troubleshooting issues and ensuring seamless operation of features such as lighting, infotainment systems, and climate control. Here are some key aspects to consider:
- Wiring Harness: A collection of wires bundled together, this harness facilitates the transmission of power and signals to various components.
- Connectors: Junctions that link different wiring segments, ensuring reliable electrical connections. Proper inspection of connectors is vital for preventing faults.
- Fuses: Protective devices that prevent overloads and short circuits, safeguarding the electrical system from damage.
- Ground Points: Essential for completing electrical circuits, ensuring that components function correctly by providing a return path for current.
Regular maintenance and inspection of the electrical connections and wiring within the vehicle can prevent potential issues and enhance overall performance. Familiarity with the wiring layout will aid in identifying and resolving problems more effectively.
Exhaust System and Its Function
The exhaust system is a critical component of any vehicle, designed to direct harmful gases produced during combustion away from the engine and passenger compartment. This system not only enhances performance but also ensures a safer and more efficient driving experience by reducing emissions and controlling noise levels.
Components of the Exhaust System
Understanding the various elements that comprise the exhaust system can help in appreciating its role. Key components include:
Component Description Exhaust Manifold Collects gases from the engine cylinders and directs them to the exhaust pipe. Catalytic Converter Converts harmful gases into less toxic substances before they exit the system. Muffler Reduces noise produced by the engine’s exhaust gases. Exhaust Pipe Channels the exhaust gases from the manifold to the rear of the vehicle. Functionality and Importance
The functionality of the exhaust system is paramount for optimal vehicle performance. It helps maintain engine efficiency, enhances fuel economy, and minimizes environmental impact by controlling emissions. Regular maintenance and inspection of the exhaust system can prevent potential issues, ensuring a smooth and safe operation.
Cooling and Heating System Components
The efficient functioning of a vehicle’s climate control system is vital for ensuring optimal comfort for passengers. This system consists of various elements that work together to manage the temperature within the cabin. Understanding these components can assist in diagnosing issues and planning maintenance effectively.
Component Description Radiator A device that dissipates heat from the engine coolant, allowing it to cool before returning to the engine. Compressor A mechanical pump that circulates refrigerant through the air conditioning system, compressing it to raise its temperature and pressure. Condenser A heat exchanger that cools the refrigerant from the compressor, transforming it from gas to liquid form. Evaporator A component that absorbs heat from the cabin air, causing the refrigerant to evaporate and cool the air that is circulated inside. Thermostat A valve that regulates the flow of coolant to maintain the desired engine temperature. Heater Core A small radiator located within the dashboard that provides heat to the cabin by transferring heat from the engine coolant. Blower Motor A fan that circulates air through the heating and cooling system, ensuring even distribution of air inside the vehicle. Fuel Delivery Mechanism Breakdown
The fuel delivery system is a critical component in ensuring efficient engine performance. It plays a vital role in transporting fuel from the tank to the engine, where it is mixed with air for combustion. Understanding the various elements of this system can help diagnose issues and enhance overall vehicle operation.
Key Components of the Fuel Delivery System

At the heart of the fuel delivery mechanism are several essential components. These include the fuel pump, which is responsible for moving fuel from the tank; the fuel filter, which ensures that impurities are removed; and the fuel injectors, which atomize the fuel for optimal mixing with air. Each of these parts must function correctly to maintain engine efficiency and responsiveness.
Common Issues and Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance is crucial for the longevity of the fuel delivery system. Common problems may arise from clogged filters or failing pumps, leading to poor engine performance or stalling. It is advisable to check fuel lines for leaks and replace filters at recommended intervals. Furthermore, using high-quality fuel can help minimize deposits and enhance the overall efficiency of the system.
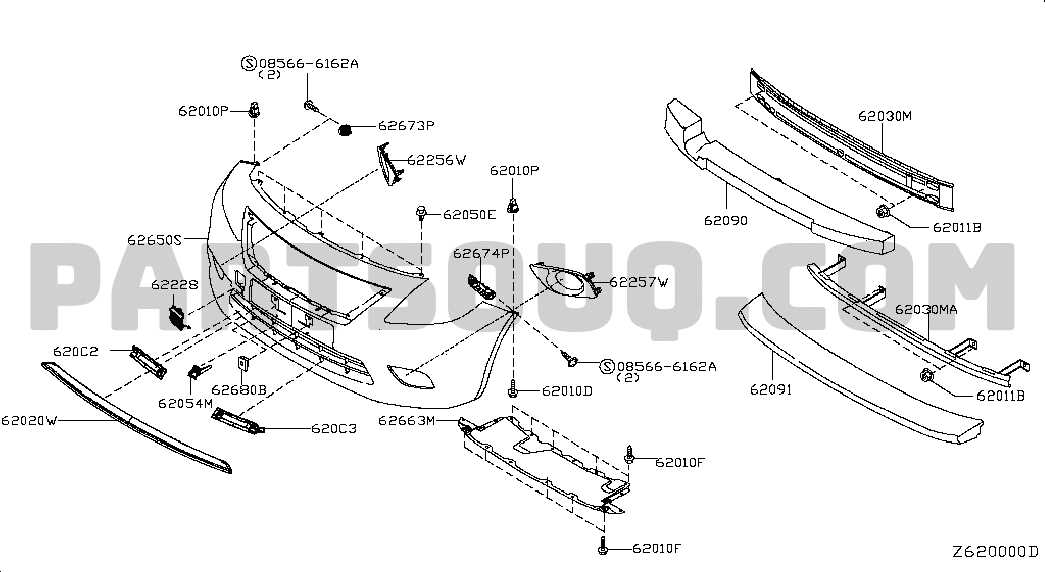
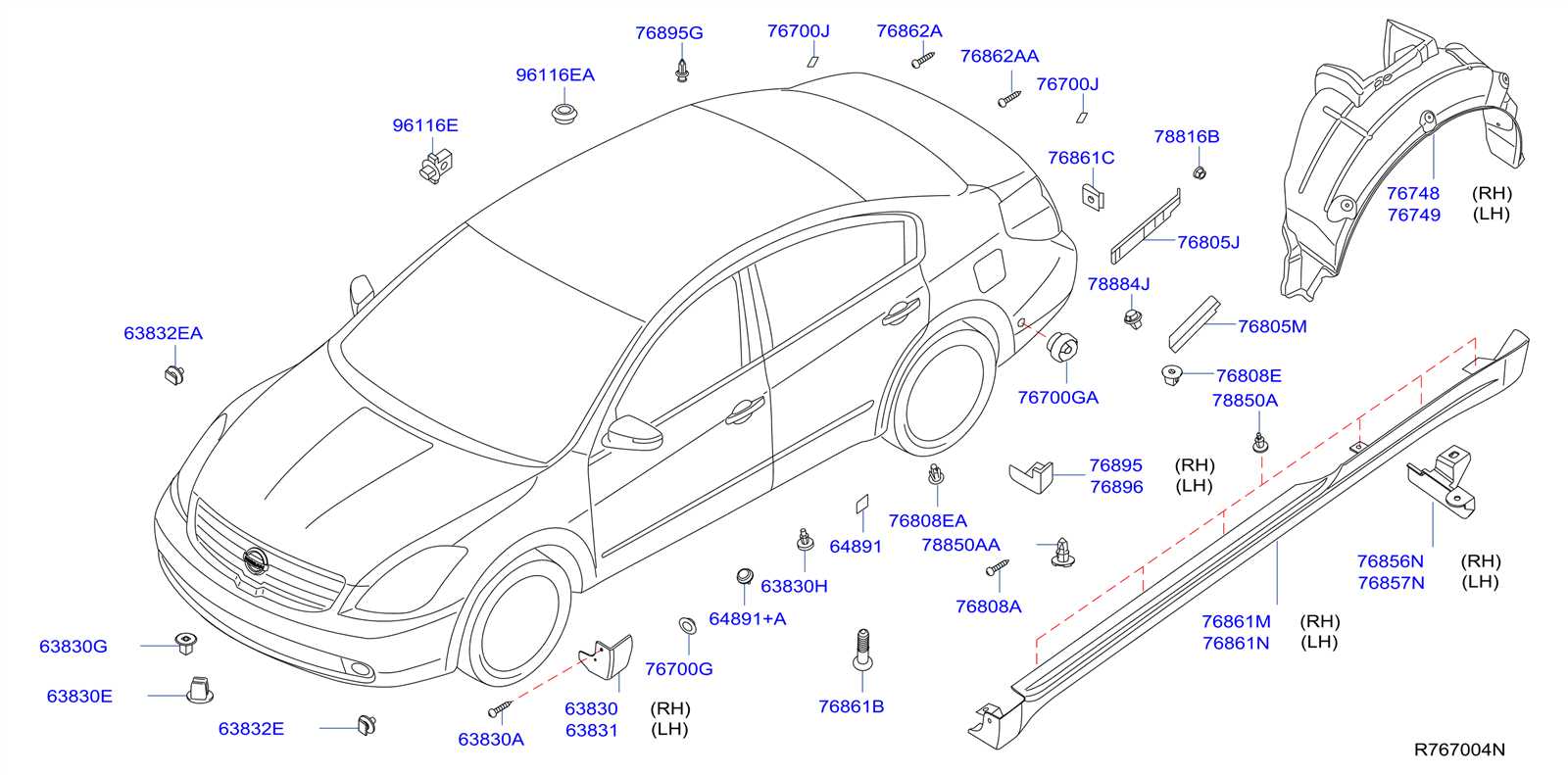
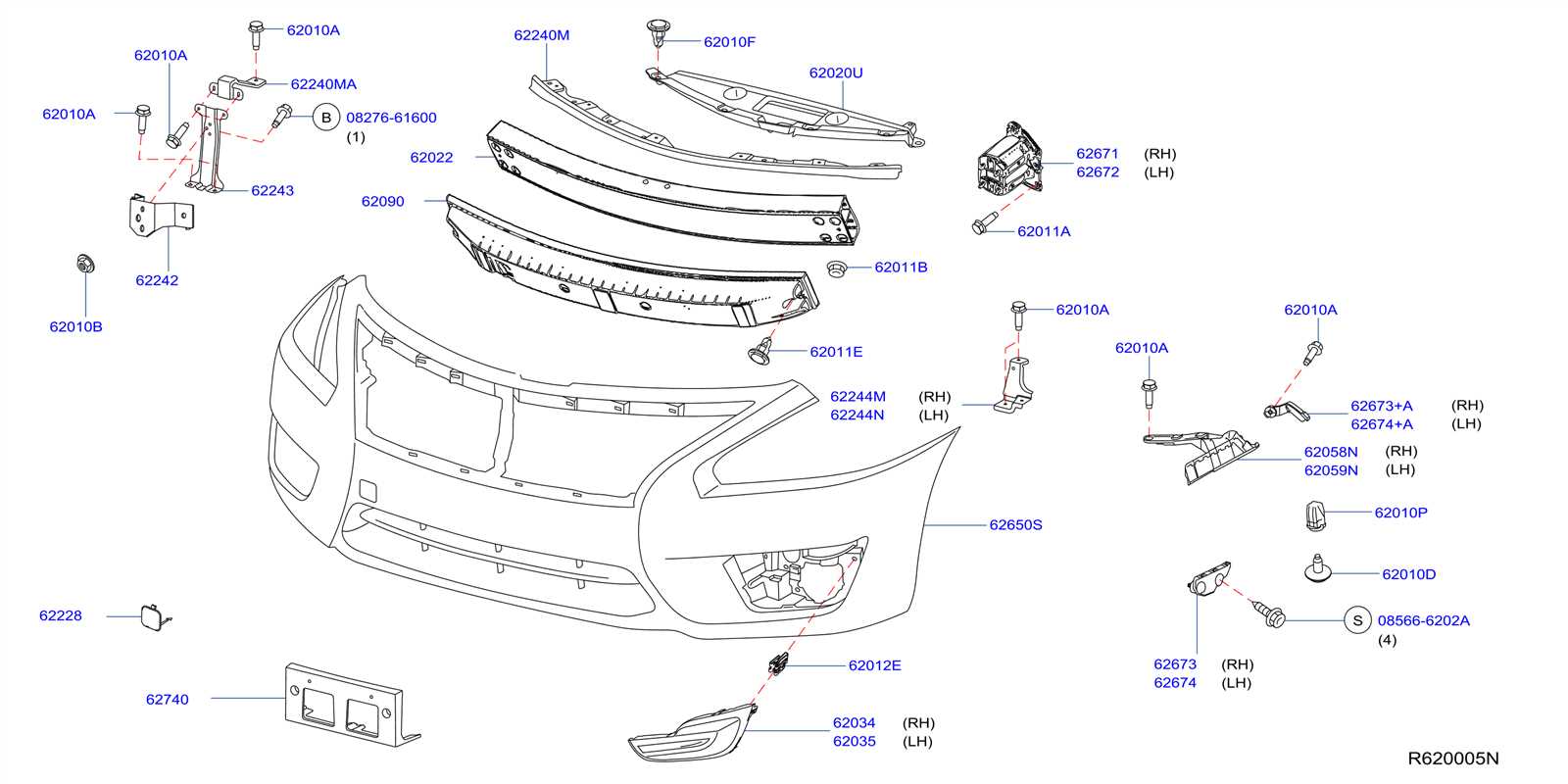
Exterior Body Panels and Frame
The exterior structure of a vehicle plays a crucial role in both aesthetics and functionality. These components not only define the visual appeal but also provide necessary support and protection to the internal systems. Understanding the configuration and materials of these elements is essential for maintenance and repair, ensuring longevity and performance.
Body panels are integral to the overall design, contributing to the vehicle’s aerodynamics and safety features. Each panel serves a specific purpose, from the front fascia that houses the grille and headlights to the side skirts that enhance airflow. The materials used, such as steel or aluminum, affect weight distribution and impact resistance.
The frame acts as the backbone of the vehicle, providing structural integrity and stability. It supports various components, including the engine and suspension systems, while also absorbing shocks during impacts. Proper alignment and maintenance of the frame are vital for optimal handling and safety.
Regular inspection of these exterior elements can prevent costly repairs and enhance the vehicle’s performance. By ensuring that body panels are free from dents and rust, and that the frame is intact, owners can significantly extend the lifespan of their vehicle.
Lighting and Signal Units
Effective illumination and signaling systems are crucial components for enhancing safety and visibility in any vehicle. These systems are designed to provide clear communication with other road users, ensuring that intentions are conveyed in various driving conditions. From headlights to turn signals, each unit serves a specific function that contributes to overall driving safety.
Headlights play a vital role in illuminating the road ahead, especially during nighttime or adverse weather conditions. Modern vehicles often feature advanced technologies such as LED or HID headlights, which offer brighter and more efficient lighting compared to traditional bulbs.
Additionally, turn signals are essential for indicating lane changes and turns, helping to prevent accidents. These indicators are typically located at the front and rear of the vehicle and are activated by the driver to communicate with other motorists.
Furthermore, tail lights and brake lights enhance safety by alerting drivers behind when the vehicle is slowing down or stopping. The integration of these systems is designed to function seamlessly, ensuring that all lighting and signaling units work harmoniously to promote safe driving practices.
Wheel and Tire Assembly Details
The assembly of wheels and tires plays a crucial role in the overall performance and safety of a vehicle. Understanding the components involved in this system is essential for maintaining optimal handling, ride quality, and stability. This section delves into the various elements that constitute the wheel and tire assembly, highlighting their functions and significance in automotive engineering.
Components of the Assembly

The primary components of the wheel and tire assembly include the rim, tire, valve stem, and hub. The rim serves as the outer edge of the wheel, providing structural support for the tire. Tires, available in various sizes and tread patterns, are mounted onto the rim, influencing traction and performance. The valve stem allows for inflation and deflation, maintaining the correct pressure within the tire, while the hub connects the wheel assembly to the axle, enabling smooth rotation.
Maintenance Considerations
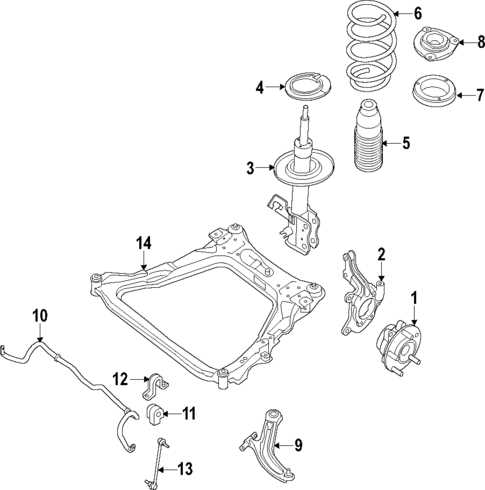
Regular inspection and maintenance of the wheel and tire assembly are vital for ensuring longevity and safety. It is essential to monitor tire pressure, tread wear, and alignment to prevent uneven wear and potential blowouts. Additionally, periodic rotation of the tires can promote even wear, extending their lifespan and enhancing performance. Keeping the assembly clean and free from debris will also contribute to optimal functionality.