
In today’s technology-driven world, the intricacies of mobile devices play a crucial role in their performance and functionality. A thorough comprehension of the various elements within these advanced gadgets can significantly enhance one’s ability to troubleshoot issues or upgrade specific features. This exploration into the internal structure of a contemporary device provides insights into how each component interacts to deliver a seamless user experience.
The modern smartphone is a complex amalgamation of cutting-edge technology and innovative design. Each individual component, from the processing unit to the display interface, is engineered to work in perfect harmony with the others. Understanding how these elements are organized and function together not only demystifies the device but also empowers users to make informed decisions regarding repairs and enhancements.
As we delve deeper into this subject, the focus will shift to specific components, outlining their roles and interconnections. This knowledge is invaluable for anyone looking to grasp the fundamentals of smartphone architecture, whether for academic purposes, repair endeavors, or simply out of curiosity.
Iphone 14 Pro Parts Overview
This section delves into the intricate components that constitute a cutting-edge mobile device. Understanding these elements is essential for appreciating the technology behind modern smartphones. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring optimal performance and user experience, from the display to the internal circuitry.
Key Components
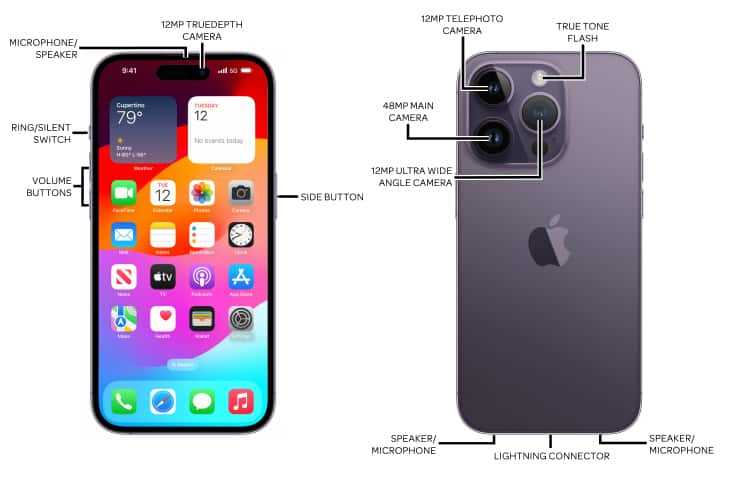
The primary elements of a high-end mobile gadget can be categorized into several groups. Each group has specific functionalities that contribute to the overall efficiency and usability of the device.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Display Assembly | The visual interface that allows users to interact with the device. |
| Mainboard | The central hub where all electronic connections converge. |
| Battery | The power source that keeps the device operational. |
| Camera Modules | Components responsible for capturing images and videos. |
| Audio Components | Parts that manage sound output and input functionalities. |
Conclusion
In summary, each component plays a significant role in the device’s functionality. A comprehensive understanding of these elements enhances the appreciation of modern mobile technology.
External Components and Their Functions
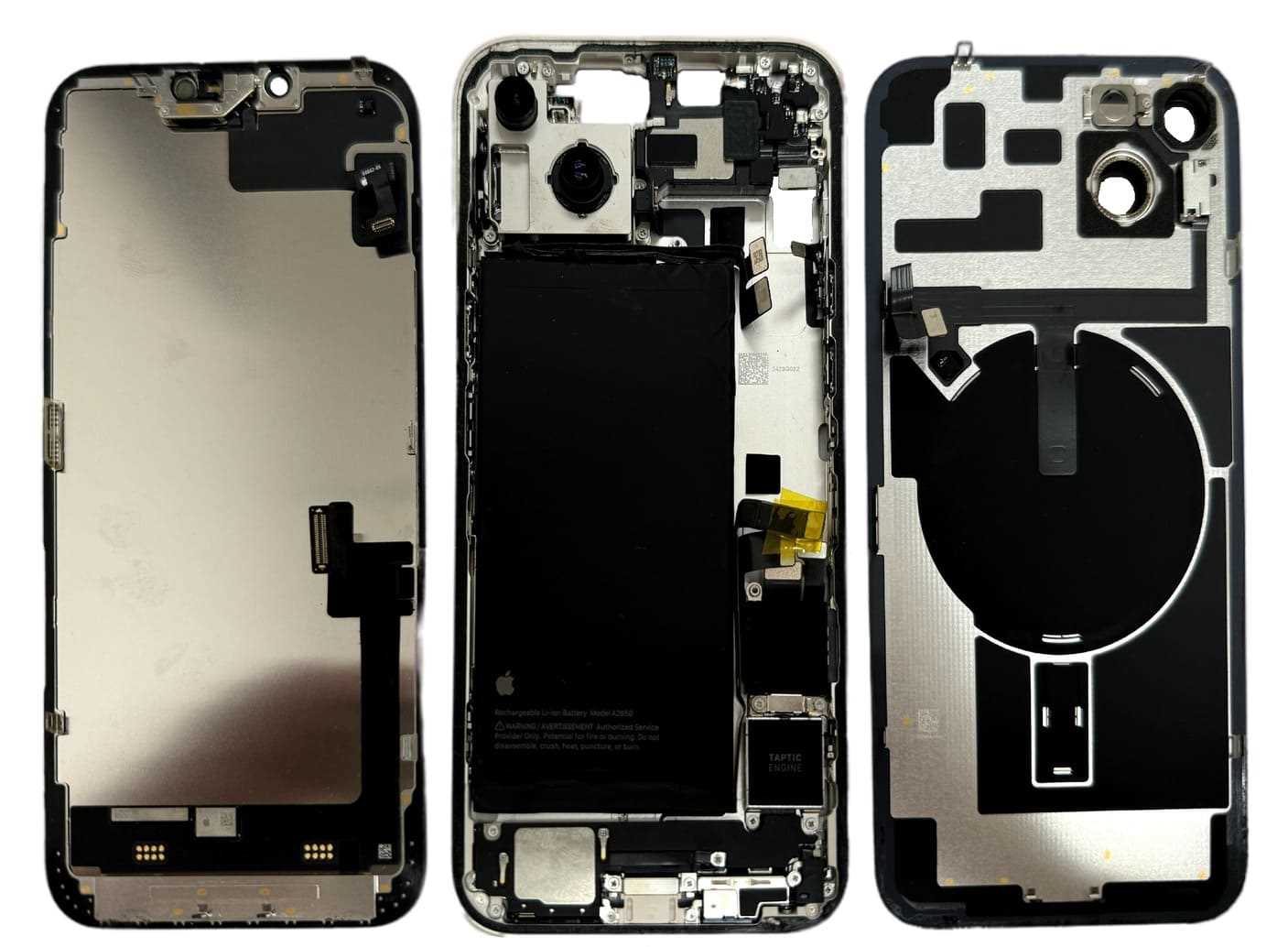

The exterior elements of a modern smartphone play a crucial role in its overall functionality and user experience. Each component is meticulously designed to enhance performance, protect internal mechanisms, and provide a seamless interaction between the device and its user.
Among the most vital features are the display, which serves as the primary interface for interaction, and the camera systems, which enable high-quality photography and videography. Additionally, the housing provides structural integrity while also shielding sensitive internal components from damage. Other significant elements include buttons for navigation and control, speakers for audio output, and ports for connectivity and charging.
Each of these external features not only contributes to the device’s aesthetics but also serves specific purposes that enhance usability and functionality. Understanding the roles of these components helps users appreciate the engineering behind their devices.
Internal Hardware Layout Explained
In this section, we delve into the intricate arrangement of internal components that constitute the operational core of the device. Understanding the internal architecture involves dissecting the intricate assembly of electronic parts and their cohesive integration. The internal framework encompasses a sophisticated network of interconnected modules, each contributing uniquely to the device’s functionality. Components are strategically positioned within the framework to optimize spatial efficiency and functional synergy, ensuring seamless operation across varied tasks and environmental conditions.
- The central processing unit (CPU), serving as the computational hub, orchestrates data processing and task execution.
- Memory modules, comprising RAM and storage units, store and retrieve data swiftly, supporting multitasking capabilities.
- Communication interfaces, such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth modules, facilitate seamless connectivity for data transfer and communication.
- Power management units regulate energy distribution to ensure efficient utilization and longevity of the device’s battery life.
- Sensors and detectors, including gyroscopes and accelerometers, provide real-time environmental data for enhanced user interaction and device orientation.
This holistic breakdown offers a comprehensive insight into the internal hardware landscape, underscoring the meticulous design philosophy aimed at optimizing performance, reliability, and user experience.
Display Assembly and Features
The section focuses on exploring the intricate construction and notable attributes of the display unit. It delves into the structural components that constitute the screen’s framework, highlighting its inner workings and distinctive characteristics. Key elements of the screen’s design and functionality are discussed, emphasizing its essential role in delivering visual content and interactive experiences.
Structural Composition
The display’s architecture comprises various elements meticulously integrated to ensure optimal performance and durability. Components such as the substrate, encapsulation materials, and interface layers contribute to its robust build, facilitating vibrant visuals and responsive touch capabilities.
Enhanced Visual Capabilities
Advanced technologies embedded within the display enhance its visual prowess, offering vivid color reproduction and sharp clarity. Features like adaptive brightness, high refresh rates, and pixel-dense configurations elevate the viewing experience, catering to diverse user preferences and environmental conditions.
Battery Specifications and Positioning
The power source is a crucial component that determines the overall functionality and efficiency of modern mobile devices. Understanding its specifications and optimal placement within the device enhances performance and longevity.
Specifications of the power supply unit generally include voltage, capacity, and type. The typical voltage for most units is around 3.7V, with capacities varying significantly, often measured in milliampere-hours (mAh). Higher capacity translates to longer usage times between charges, making it a vital aspect for users.
Positioning plays an equally important role in the design and functionality of the device. The battery is usually strategically placed to ensure even weight distribution and protection from physical damage. Proper alignment with other components is necessary to avoid overheating and to maintain optimal thermal management.
Camera Module Configuration Details
The camera module is a crucial component of modern smartphones, significantly contributing to the overall imaging capabilities. Understanding its configuration helps users appreciate the intricate design and functionality that enable high-quality photography and videography.
Typically, the camera assembly consists of several key elements: the lens, image sensor, and various supporting electronics. The lens focuses light onto the sensor, while the image sensor converts the incoming light into electrical signals, allowing for the capture of images. Additionally, optical image stabilization mechanisms are often integrated to reduce blurriness caused by hand movement during shots.
In many devices, the rear camera may feature multiple lenses for different focal lengths, enhancing versatility in capturing various scenes. The configuration often includes a primary wide-angle lens, a telephoto lens for zoom capabilities, and an ultra-wide lens for expansive shots. This arrangement allows users to switch seamlessly between modes, catering to diverse photography needs.
Furthermore, advanced software algorithms work in tandem with the hardware to optimize image quality, adjust settings automatically, and enable features such as portrait mode and night mode. These enhancements demonstrate the synergy between hardware and software, resulting in a remarkable user experience.
Audio Jack and Speaker Integration
The harmonious integration of audio connectivity and sound output components is essential for delivering an immersive auditory experience in modern handheld devices. This section explores the relationship between the audio input port and the internal speaker system, emphasizing their combined role in ensuring clear and rich sound quality.
At the core of this integration lies the audio jack, which facilitates the connection of external sound devices. This component is designed to accommodate various headphone types while providing a seamless user experience. Coupled with the speaker system, it enables users to switch effortlessly between personal listening and shared audio playback.
Additionally, sound quality is significantly influenced by the positioning and engineering of these components within the device. The internal speaker’s placement is optimized to enhance sound projection and minimize distortion, ensuring that audio playback remains crisp and clear, regardless of the source. By carefully coordinating the design and functionality of both the audio jack and the speaker, manufacturers create a cohesive audio experience that meets user expectations.
Processor and Memory Arrangement

The intricate architecture of mobile devices is pivotal in ensuring efficient performance and responsiveness. This section delves into the layout and integration of central processing units (CPUs) and memory modules, emphasizing their roles in overall functionality.
Central Processing Unit (CPU) Placement

The CPU is strategically positioned within the device to optimize heat dissipation and power consumption. Its location facilitates seamless communication with other components, enabling rapid data processing and task execution.
Memory Configuration
The arrangement of memory chips complements the processing unit’s capabilities. By employing a combination of volatile and non-volatile memory, the device achieves a balance between speed and data retention, enhancing user experience and application performance.
Wireless Antenna Locations
In modern mobile devices, effective communication relies on the strategic placement of antennas. These components are essential for ensuring optimal signal reception and transmission across various networks, including cellular, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth. Understanding their locations within the device is crucial for troubleshooting connectivity issues and for any repair or modification tasks.
- Main Cellular Antenna: Located at the top section of the device, this antenna is primarily responsible for connecting to cellular networks.
- Wi-Fi Antenna: Positioned along the edges of the device, this antenna facilitates connections to wireless networks, enhancing internet browsing and streaming experiences.
- Bluetooth Antenna: Generally found near the lower section, this antenna supports Bluetooth connectivity for various accessories and peripherals.
- GPS Antenna: Typically situated near the rear of the device, this antenna ensures accurate location tracking and navigation services.
Each antenna is carefully placed to minimize interference and maximize performance, making their understanding essential for users and technicians alike.
Cooling System Design Elements
The efficiency of any advanced electronic device significantly depends on its thermal management system. Properly designed cooling mechanisms play a crucial role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures, thereby enhancing performance and prolonging the lifespan of the components. This section will explore the essential elements that contribute to an effective cooling system in modern devices.
Key Components
- Heat Sinks: These are typically made of materials with high thermal conductivity and are strategically placed to dissipate heat generated by the internal components.
- Thermal Paste: This compound is applied between heat-generating components and heat sinks to improve thermal conductivity and reduce air gaps.
- Ventilation Channels: Designed to facilitate airflow, these channels help in the circulation of air, allowing hot air to escape while drawing in cooler air.
- Fans: Active cooling solutions that actively move air across heat-generating components to enhance heat dissipation.
Design Considerations
- Material Selection: Choosing the right materials for heat sinks and other components is crucial for optimizing thermal management.
- Layout Optimization: The arrangement of internal components can significantly impact airflow and heat dissipation efficiency.
- Noise Levels: Incorporating quieter fan designs or passive cooling methods can enhance user experience by reducing operational noise.
In summary, a well-thought-out thermal management strategy is essential for ensuring the reliable performance of sophisticated electronic devices. By focusing on the key components and carefully considering design aspects, engineers can create systems that effectively manage heat and enhance overall device functionality.
Connections for Charging Port
The charging interface is a critical component in modern mobile devices, facilitating power transfer and data exchange. Understanding the various connections involved in this assembly is essential for diagnosing issues or performing repairs.
Typically, the charging port consists of several key connectors. These include power lines responsible for transferring voltage, ground connections that complete the circuit, and data lines that enable communication between the device and the power source. Each of these connections plays a vital role in ensuring efficient charging and functionality.
In many designs, the power connections are usually linked to the device’s battery management system, which regulates charging levels and prevents overheating. Data connections, on the other hand, allow for the synchronization of data between the device and external sources, such as computers or power banks.
Moreover, the physical layout of these connections can impact the overall performance of the charging mechanism. Proper alignment and secure attachment are crucial for optimal power transfer and reliable data communication.
By comprehending the intricacies of these connections, technicians can effectively troubleshoot and resolve issues related to charging and data transfer, ensuring devices operate smoothly and efficiently.
SIM Card Tray Placement
The placement of the SIM card tray is a critical aspect of mobile device design, influencing both functionality and user experience. This component allows users to insert or remove their SIM cards with ease, facilitating network connectivity and access to mobile services. Understanding its location can help in troubleshooting connectivity issues or during repairs.
Location and Accessibility
The SIM card tray is strategically positioned on the device to ensure quick access while maintaining the overall aesthetic. Typically, it is located on one of the edges, allowing for straightforward insertion and removal without requiring extensive disassembly. This design choice enhances user convenience and contributes to the sleekness of the device.
Technical Specifications
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Nano SIM |
| Material | Metal/Plastic |
| Orientation | Vertical/Horizontally Aligned |
| Retention Mechanism | Spring Loaded |