Every vehicle is made up of countless interconnected elements that work in harmony to deliver performance, safety, and comfort. Exploring how these elements come together can help both mechanics and drivers gain valuable insights into the overall structure and functionality of their cars. Knowing where key elements are located and how they interact can make repairs and upgrades more efficient and less time-consuming.
When it comes to maintaining or enhancing a vehicle’s operation, having a clear visual representation of its components is essential. A detailed layout provides a roadmap to understanding how various mechanisms work together, helping to pinpoint any areas that may require attention. Whether you’re troubleshooting a malfunction or simply learning more about the intricate workings of your vehicle, this overview will guide you through the process.
By familiarizing yourself with the structure and placement of different mechanical sections, you can develop a more comprehensive understanding of your vehicle. This knowledge not only aids in practical tasks like maintenance and replacements but also deepens your appreciation for the engineering behind modern transportation.
Essential Components of the 2018 Altima
Understanding the key elements of a modern vehicle is crucial for anyone looking to maintain or repair their car effectively. Each section of the vehicle is designed to work in harmony, ensuring smooth operation and enhanced safety on the road. From the engine to the electrical system, every part has a specific role in delivering a balanced and reliable driving experience.
The powertrain is one of the most critical systems, transforming energy into the motion that propels the car forward. Alongside this, the transmission system efficiently manages how that power is distributed, allowing for seamless gear changes and optimized fuel usage. Meanwhile, the suspension system provides stability and comfort, ensuring the vehicle remains responsive even on uneven surfaces.
The braking system is another essential feature, offering both safety and control. High-performance disc brakes, paired with advanced sensors, help prevent skidding and ensure a reliable stopping distance. Lastly, the electrical system powers various components inside and outside the vehicle, from lighting to infotainment, keeping drivers connected and secure during their journey.
Front Suspension Parts Overview
The front suspension system plays a critical role in maintaining vehicle stability and ensuring a smooth ride. It absorbs shocks and vibrations from the road, improving overall comfort and safety during driving. Understanding the components involved helps in identifying areas that may require maintenance or upgrades for better handling and performance.
Key Components
- Control Arms – These connect the wheel hub to the frame, allowing for controlled movement while maintaining alignment.
- Ball Joints – Pivot points that enable the wheels to turn while supporting the vehicle’s weight.
- Struts – They combine a shock absorber and coil spring, ensuring the vehicle remains balanced over uneven surfaces.
- Stabilizer Bar – Helps reduce body roll during cornering, improving control and balance.
Maintenance Tips
- Inspect bushings for wear, as they can impact handling and ride quality if damaged.
- Regularly check for any signs of fluid leaks around the struts and shocks to ensure optimal performance.
- Ensure ball joints are lubricated properly to prevent premature wear and failure.
Engine Bay Layout and Components
The area under the hood is home to various mechanical systems, each playing a vital role in ensuring the vehicle operates smoothly. This section offers an overview of the essential components that are organized within this space, detailing how they interact to maintain efficiency and performance.
Main Structural Elements
- Engine Block – The core of the system, responsible for generating power.
- Transmission – Connected to the engine, it transfers energy to the wheels.
- Radiator – Keeps temperatures in check, preventing overheating.
- Battery – Supplies electrical power, especially during startup and idle moments.
Supporting Systems
- Air Intake – Ensures the engine receives adequate airflow for combustion.
- Alternator – Generates electricity to recharge the battery and power various electrical systems.
- Coolant Reservoir – Stores excess coolant, which circulates to prevent the engine from overheating.
- Power Steering Pump – Assists in steering by reducing the physical effort required to turn the wheel.
Brake System Configuration
The brake system is a critical component that ensures the safety of the vehicle by controlling its ability to slow down or come to a complete stop. It relies on a combination of mechanical, hydraulic, and electronic parts working together seamlessly to provide precise control over braking performance. Understanding how these elements interact helps in maintaining and optimizing the system for reliable operation.
Hydraulic Components
At the core of most modern braking setups are hydraulic mechanisms. The system uses brake fluid to transfer pressure from the brake pedal to the calipers or drum assemblies. This fluid pressure forces brake pads or shoes against the rotors or drums, creating the friction necessary to reduce speed. Regular checks of the hydraulic components, such as master cylinders and fluid lines, are essential for proper operation.
Electronic Assistance
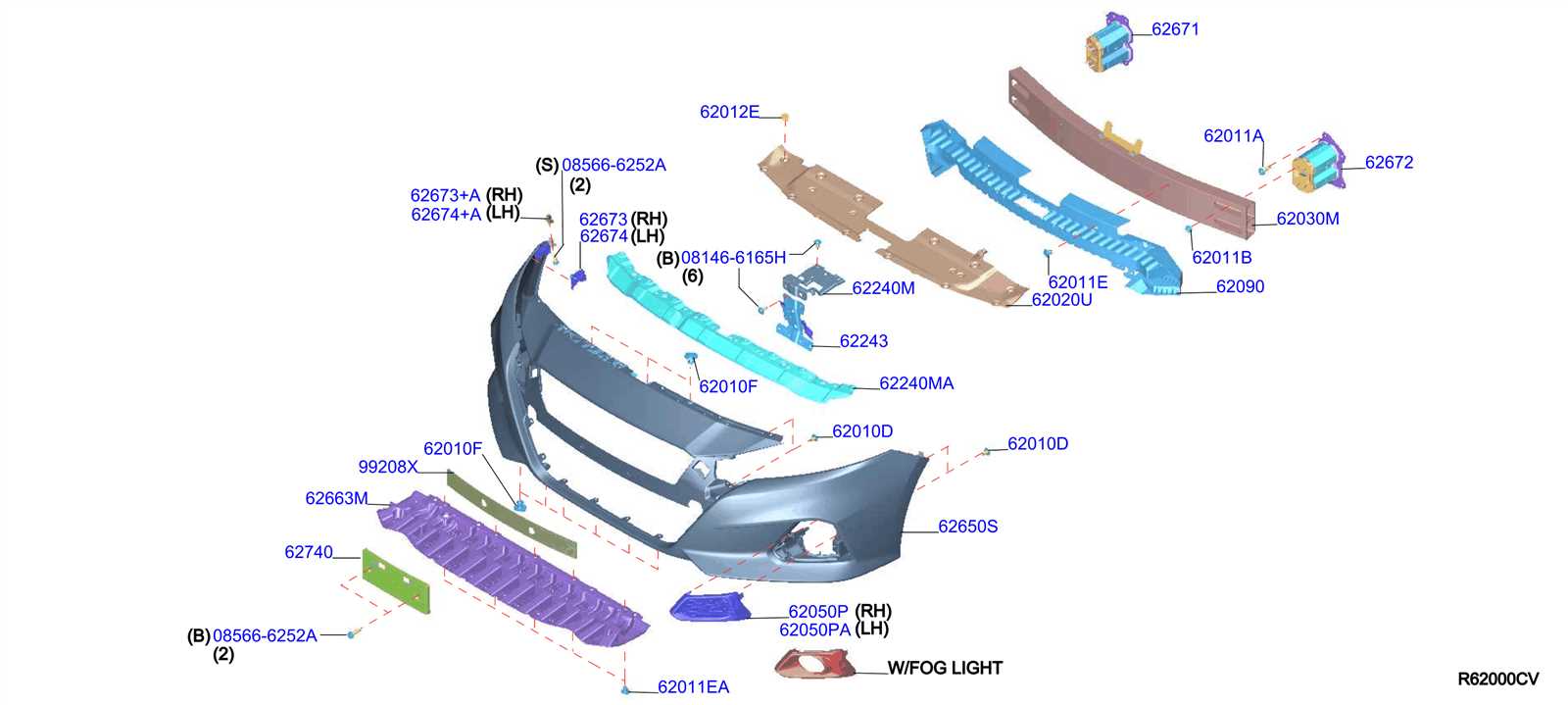
Many contemporary systems include electronic aids that enhance performance and safety. Systems like anti-lock brakes (ABS) and electronic brake-force distribution (EBD) help prevent wheel lock-up and maintain optimal braking force across all wheels. These features work in tandem with the mechanical components to offer improved control during various driving conditions.
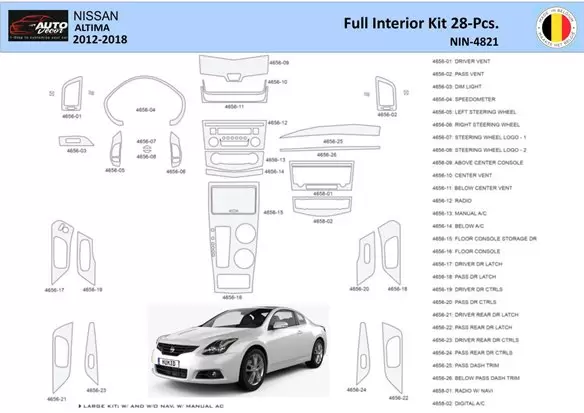
Interior Panel Assembly
The interior panel structure is a crucial component in maintaining both the aesthetic appeal and functionality of a vehicle’s cabin. This section encompasses various elements, providing a seamless blend of design and practical utility. The arrangement ensures that all parts are efficiently integrated, allowing for easy access to controls while enhancing the overall comfort and safety of the passengers.
The assembly is composed of numerous segments, including side panels, door trims, and dashboard coverings. Each piece is meticulously designed to fit perfectly with the rest of the cabin, ensuring a smooth and cohesive appearance. Attention to detail in the manufacturing process guarantees that these panels align properly, minimizing noise and vibration, contributing to a quieter and more comfortable ride.
Furthermore, the panel system not only serves aesthetic purposes but also plays a role in housing important interior mechanisms such as airbags, electrical wiring, and ventilation channels. These elements are carefully concealed behind the panels, maintaining a clean and uncluttered look while ensuring essential systems are easily accessible for maintenance or repairs when needed.
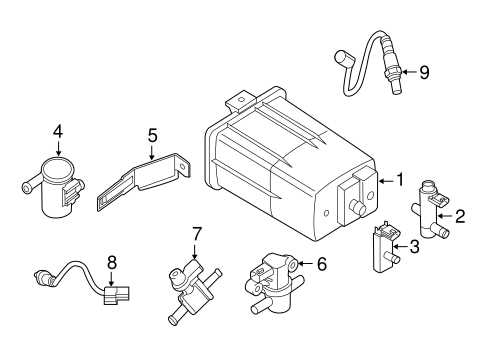
Fuel Delivery System Breakdown
The fuel delivery system is a crucial component in any vehicle’s operation, responsible for transporting fuel from the tank to the engine. Understanding the intricacies of this system can enhance maintenance and troubleshooting efforts, ensuring optimal performance.
This system comprises various elements that work together to facilitate efficient fuel flow and delivery. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring that the engine receives the appropriate amount of fuel under varying conditions.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Fuel Tank | Stores fuel until needed by the engine. |
| Fuel Pump | Transfers fuel from the tank to the engine at the required pressure. |
| Fuel Filter | Cleans the fuel before it reaches the engine, preventing contaminants from causing damage. |
| Fuel Injectors | Sprays the precise amount of fuel into the engine’s combustion chamber. |
| Fuel Pressure Regulator | Maintains consistent fuel pressure within the system for optimal performance. |
Exhaust Structure and Mounting
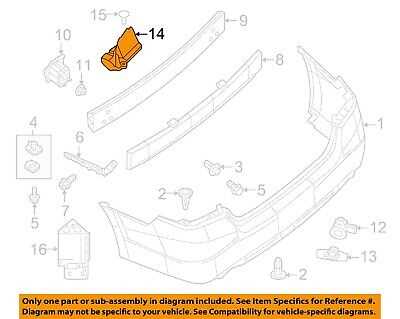
The exhaust system is a crucial component of a vehicle, responsible for directing harmful gases away from the engine and reducing noise. It consists of various elements that work together to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Understanding the configuration and assembly of these components is essential for maintaining the system’s functionality.
Main Components of the Exhaust System
- Exhaust Manifold: This component collects exhaust gases from the engine cylinders and directs them into the exhaust pipe.
- Catalytic Converter: It transforms harmful emissions into less harmful substances before they exit the vehicle.
- Muffler: This part reduces engine noise and helps to control the flow of exhaust gases.
- Exhaust Pipes: These pipes connect various elements of the exhaust system, facilitating the flow of gases.
- Hangars and Mounts: These support the exhaust components, ensuring stability and proper alignment during operation.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Proper installation and regular maintenance of the exhaust system are vital for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Key aspects to consider include:
- Ensure all connections are secure to prevent leaks, which can lead to decreased efficiency.
- Regularly inspect hangars and mounts for wear, as they play a critical role in supporting the system.
- Monitor for unusual noises or vibrations, which may indicate issues within the exhaust structure.
- Consider professional inspection if any components are damaged or if there are performance concerns.
Rear Axle and Suspension Setup
The rear axle and suspension configuration play a crucial role in the overall performance and handling characteristics of a vehicle. This section focuses on the intricate components that contribute to stability, comfort, and control during operation. Understanding these elements allows for better maintenance and potential upgrades to enhance driving experience.
Components of the Rear Suspension
The rear suspension system comprises several key parts, including the axle assembly, shock absorbers, and control arms. Each component works synergistically to absorb shocks from the road, maintain wheel alignment, and provide a smooth ride. Shock absorbers, for instance, are essential for dampening vibrations, while control arms help manage wheel movement during cornering and braking.
Adjustments and Maintenance
Regular inspection and maintenance of the rear axle and suspension system are vital for optimal performance. Adjustments to components can significantly affect handling and ride quality. It is recommended to periodically check for signs of wear, such as unusual noises or uneven tire wear, which may indicate the need for repairs or replacements. Proper alignment and calibration ensure that the vehicle remains stable and responsive on various terrains.
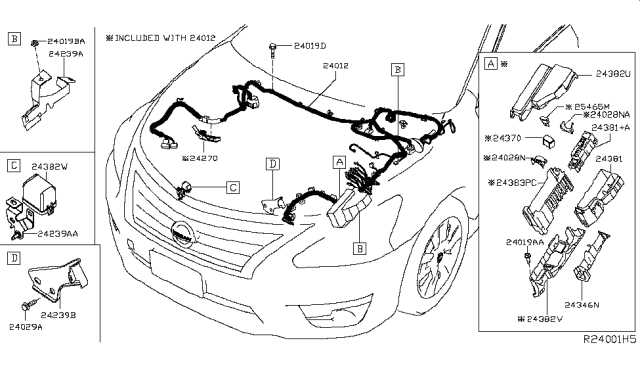
Electrical Wiring and Harness Diagram
The intricate layout of electrical connections and harnesses serves as the backbone of any vehicle’s operational functionality. Understanding the schematic representation of these components is crucial for diagnosing issues, performing repairs, or executing upgrades. This section delves into the essential elements of wiring systems, highlighting their roles in ensuring seamless communication between various electrical units within the automobile.
Electrical harnesses encompass a series of wires bundled together, designed to transmit power and signals throughout the vehicle. Each wire within the harness is meticulously arranged and labeled to facilitate easy identification during maintenance. Additionally, connectors play a pivotal role in linking various electrical components, ensuring robust and reliable connectivity. Familiarity with these elements aids in troubleshooting and enhances overall efficiency in repairs.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of the electrical wiring and harness structures is vital for anyone engaged in automotive maintenance or repair. This knowledge not only streamlines the process of identifying problems but also empowers enthusiasts and professionals alike to implement modifications or upgrades with confidence.
Cooling System Parts and Flow
The cooling mechanism in a vehicle plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal engine temperatures, preventing overheating, and ensuring smooth operation. This system comprises various components that work together to regulate heat dissipation and coolant circulation throughout the engine.
Key elements involved in this intricate process include:
- Radiator: This component dissipates heat from the coolant before it circulates back to the engine.
- Water Pump: Responsible for circulating the coolant through the engine and the radiator, ensuring proper flow.
- Thermostat: This regulates the temperature of the coolant, allowing it to flow into the radiator only when it reaches a certain temperature.
- Coolant Reservoir: Stores excess coolant and allows for expansion as it heats up.
- Hoses: Flexible tubes that transport the coolant between different components of the system.
Understanding the flow of coolant is essential for diagnosing potential issues. The coolant begins its journey from the engine to the radiator, where it is cooled before returning. This continuous cycle ensures that the engine operates efficiently and reduces the risk of overheating.
Transmission and Gearbox Placement
The arrangement of the transmission and gearbox in modern vehicles plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. Proper positioning allows for smooth power transfer from the engine to the wheels, enhancing overall drivability and responsiveness. Understanding the layout can aid in maintenance and potential modifications.
Key Components and Their Functions
- Transmission: Responsible for changing gears, it helps control the vehicle’s speed and torque.
- Gearbox: Houses the gears and various components that facilitate gear changes.
- Driveshaft: Connects the gearbox to the wheels, transmitting power effectively.
Placement Considerations
Placement is influenced by several factors:
- Vehicle Design: The overall structure dictates how components are arranged for optimal space and weight distribution.
- Engine Type: Different engine configurations require unique transmission setups to maintain balance and performance.
- Accessibility: Ease of access for maintenance and repairs is a vital consideration in component placement.
By understanding these elements, vehicle owners can make informed decisions regarding maintenance and upgrades, ensuring longevity and performance of their automobiles.
Body Frame Structure and Support
The frame structure of a vehicle plays a crucial role in its overall integrity and performance. It serves as the backbone, providing essential support for various components while ensuring stability and safety. The design and materials used in the frame not only influence the car’s weight but also its ability to absorb and distribute impact forces during a collision.
Support structures are strategically placed throughout the vehicle to enhance rigidity and durability. These reinforcements are critical in maintaining the vehicle’s shape under stress, allowing for optimal handling and driving dynamics. An effective framework reduces vibrations and noise, contributing to a more comfortable driving experience.
Understanding the framework’s composition is vital for maintenance and repair. Regular inspections can identify potential weaknesses or damages, ensuring longevity and performance. Properly addressing any issues related to the frame structure can prevent further complications, promoting safety and reliability on the road.
Steering Mechanism and Linkages
The steering system is a vital component that ensures precise control over a vehicle’s direction. This mechanism comprises various elements working in harmony to facilitate smooth and responsive handling. Understanding the intricacies of these components can enhance both performance and safety on the road.
Key Components of the Steering System
The steering assembly consists of several critical parts, each playing a specific role in maneuverability. These components include the steering wheel, column, gear, and linkages, which collaborate to transfer driver inputs into effective movement. Proper maintenance of these elements is essential to avoid steering issues that can compromise safety.
Linkage Types and Functionality
Linkages connect the steering wheel to the wheels, translating rotational movement into directional change. Different types of linkages offer unique advantages in terms of responsiveness and stability. Familiarity with these variations can help vehicle owners make informed decisions regarding upgrades or replacements.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Steering Wheel | Provides the interface for the driver to control the vehicle’s direction. |
| Steering Column | Connects the steering wheel to the steering mechanism and houses electrical components. |
| Rack and Pinion | Converts rotational motion from the steering wheel into linear motion for the wheels. |
| Linkages | Transmits movement from the steering column to the wheels, allowing for precise steering. |