
The intricate network of automotive systems requires a clear understanding of how various elements interact and function together. Whether you are performing maintenance, conducting repairs, or simply expanding your knowledge, having a clear visual representation of the internal mechanisms is crucial for achieving accurate results. This guide aims to provide detailed insights into the placement and role of the essential elements that make up the internal structure of a vehicle.
Understanding the arrangement of each component within the vehicle’s framework can enhance the efficiency of any technical work performed on it. With the right overview, you can identify potential issues faster and address them more effectively. Moreover, familiarizing yourself with the layout ensures that every task, from routine upkeep to advanced troubleshooting, is carried out with precision.
Detailed schematics offer a deeper perspective into how each part contributes to the overall functionality of the vehicle. By exploring this layout, you gain the knowledge needed to ensure that all systems operate smoothly and efficiently, reducing
Mercedes-Benz C300 Parts Overview
In this section, we explore the key components of a popular luxury sedan, offering an insight into the vital systems that contribute to its performance, comfort, and reliability. By understanding the essential elements, owners and enthusiasts can better appreciate how each part works together to create a smooth driving experience.
- Engine System: The heart of the vehicle, responsible for converting fuel into mechanical power. It includes various subsystems such as the intake, exhaust, and fuel management components.
- Transmission: A crucial element that ensures the power from the engine is properly delivered to the wheels, allowing seamless shifting between gears.
- Suspension: This setup ensures stability and comfort by absorbing shocks from uneven roads, offering a balanced ride experience.
- Braking System: Responsible for controlling vehicle speed and ensuring safety, it includes components like brake pads, rotors, and calipers.
- Pistons: These move within the cylinders, converting fuel into mechanical energy.
- Cylinders: The chambers where the pistons operate, crucial for compression and power generation.
- Crankshaft: Translates the up-and-down movement of the pistons into rotational motion.
- Camshaft: Controls the opening and closing of valves, coordinating the fuel intake and exhaust processes.
- Valves: Regulate the flow of air and fuel into the cylinders and allow exhaust gases to escape.
- Timing Belt:
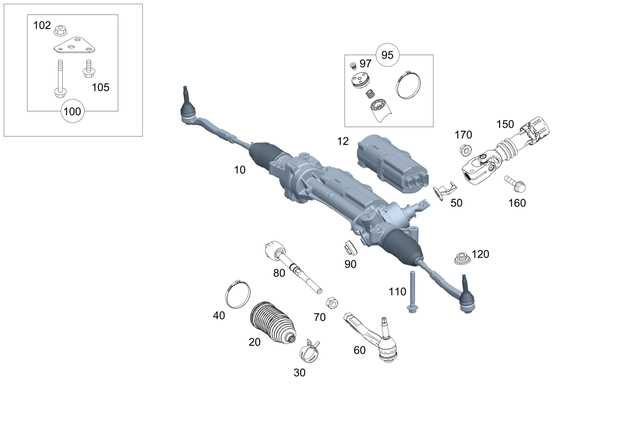
Suspension and Steering Systems
The suspension and steering systems play a critical role in ensuring both comfort and control when driving. These interconnected systems manage how the vehicle responds to road conditions, including bumps, turns, and uneven surfaces. Proper functioning of these systems ensures stability, smoothness, and precise handling during various driving scenarios.
Component Function Shock Absorbers Absorb and dampen impacts from road irregularities to improve ride comfort. Struts Support the weight of the vehicle while maintaining alignment of other suspension components. Steering Rack Converts the rotational movement of the steering Transmission System Parts
The transmission system is a crucial component of any vehicle, responsible for efficiently transferring power from the engine to the wheels. It plays a vital role in ensuring smooth acceleration and optimal performance, whether driving at low speeds or on highways. The system consists of various mechanical and hydraulic elements working together to adjust the speed and torque delivered to the wheels.
- Gearbox – The core of the transmission, responsible for shifting gears and regulating the vehicle’s speed.
- Torque Converter – This part allows the engine to keep running while the vehicle is at a stop, providing smooth power delivery when accelerating.
- Clutch Assembly – Essential for disconnecting the engine from the drivetrain when shifting gears in manual transmissions.
- Driveshaft – A rotating component that transmits power from the gearbox to the differential.
- Differential – Helps in distributing the torque between the wheels, allowing them to rotate at different speeds when turning.
- Transmission Fluid
Brake System Components
The brake system is a vital part of any vehicle, ensuring safe deceleration and control. It consists of several interconnected parts that work together to slow down or stop the car when needed. Understanding these components can help in diagnosing issues and maintaining the system effectively.
Brake Calipers

Brake calipers are essential in applying pressure to the brake pads, which then contact the rotors to slow the vehicle. These hydraulic components convert the force applied by the driver into the necessary clamping force on the discs.
Brake Pads and Rotors
Brake pads are designed to create friction when pressed against the rotors. The rotors, or discs, are attached to the wheels and spin with them. As the pads press on the rotors, they reduce the wheel’s speed, effectively slowing down the vehicle.
Fuel System Structure
The fuel system plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficient delivery and management of fuel within the engine. Its design incorporates various components that work in harmony to facilitate the intake, filtration, and combustion processes. Understanding the structure of this system is essential for diagnosing issues and performing maintenance effectively.
Key Components
Each element within the fuel system contributes to the overall functionality, from the fuel tank to the injectors. Here are the primary components involved:
Component Function Fuel Tank Stores fuel until needed by the engine. Fuel Pump Delivers fuel from the tank to the engine at the required pressure. Fuel Filter Removes impurities and contaminants from the fuel before it reaches the engine. Fuel Injectors Atomizes and sprays fuel into the combustion chamber for efficient combustion. System Operation
The fuel system operates in a sequential manner, where fuel is drawn from the tank and pumped through filters to ensure cleanliness. Once filtered, the fuel is injected into the engine, where it mixes with air and ignites to power the vehicle. Proper maintenance of each component is vital to maintaining the efficiency and performance of the engine.
Exhaust System Diagram
The exhaust mechanism of a vehicle plays a crucial role in managing emissions and optimizing engine performance. Understanding the layout of this system can provide insights into its function and importance. It typically comprises various components that work together to direct exhaust gases away from the engine, reducing noise and minimizing harmful emissions.
Key Components
At the core of the exhaust system are several essential elements, including the manifold, catalytic converter, and muffler. The manifold collects exhaust gases from the engine cylinders and channels them into the exhaust piping. The catalytic converter processes these gases to eliminate pollutants before they exit the system. Finally, the muffler reduces noise produced by the escaping gases, ensuring a quieter driving experience.
Flow Path
The flow of gases begins at the engine and travels through the manifold, into the catalytic converter, and finally exits through the muffler. This path is designed to minimize back pressure, allowing the engine to operate efficiently. Understanding this flow is essential for diagnosing issues related to performance and emissions.
Cooling System Layout
The cooling system is crucial for maintaining optimal engine temperature and performance. It prevents overheating and ensures that the engine operates within the desired thermal range, promoting efficiency and longevity. Understanding the layout and components of this system is essential for diagnosing issues and performing effective maintenance.
Key Components
The main components of the cooling system include the radiator, water pump, thermostat, and hoses. The radiator dissipates heat from the engine coolant, while the water pump circulates the coolant throughout the engine block and radiator. The thermostat regulates coolant flow based on temperature, ensuring the engine warms up efficiently.
Flow Mechanism
The flow of coolant begins at the engine, where it absorbs heat, and then moves to the radiator. As the coolant travels through the radiator, it loses heat to the surrounding air. This cycle continues, maintaining a balance between heat generation and dissipation, which is vital for optimal engine performance.
Electrical System Overview
The electrical framework of a vehicle plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal functionality and performance. It comprises various components and systems that work together to provide power and control for multiple functionalities, including lighting, ignition, and electronic systems. Understanding the layout and operation of this system is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Components
This section highlights the essential elements of the electrical system, outlining their functions and interconnections. Each component contributes to the overall performance and reliability of the vehicle’s electrical architecture.
Component Function Battery Stores and supplies electrical energy for starting the engine and powering electrical systems. Alternator Generates electrical power while the engine is running, recharging the battery and powering the vehicle’s electrical loads. Fuses Protects the electrical circuits by breaking the connection in case of an overload or short circuit. Wiring Harness Connects all electrical components, allowing for efficient power distribution and signal transmission. Electronic Control Unit (ECU) Monitors and manages various systems, including engine performance and emission control. System Functionality
The interaction between the various components in the electrical system is critical for seamless operation. Power generated by the alternator is distributed through the wiring harness, while the ECU processes inputs from different sensors to make real-time adjustments. Regular inspection and understanding of this system can prevent issues and enhance overall vehicle performance.
Body and Exterior Parts
The exterior structure of a vehicle plays a crucial role in both aesthetics and functionality. It encompasses various components that contribute to the overall look, safety, and performance of the automobile. Understanding these elements is essential for maintenance, repairs, and enhancements.
Key Components
- Fenders
- Hoods
- Doors
- Trunk lids
- Grilles
- Bumpers
- Headlights
- Taillights
Functionality and Features
- Protection: Exterior components are designed to shield internal mechanisms from external elements.
- Aerodynamics: The shape and arrangement of these parts contribute to the vehicle’s aerodynamic efficiency.
- Style: A well-designed exterior enhances the visual appeal and marketability of the vehicle.
- Safety: Elements such as bumpers and lights are crucial for ensuring safety during operation.
Interior Component Diagram

This section provides a comprehensive overview of the various elements found within the cabin of a luxury vehicle, emphasizing their arrangement and functionality. Understanding these components is crucial for effective maintenance and customization, allowing owners to appreciate the craftsmanship and design intricacies that enhance comfort and usability.
Key Features
Among the essential elements in the interior are the dashboard, seating, and control interfaces, each designed with both aesthetics and ergonomics in mind. The layout not only contributes to the vehicle’s luxurious appeal but also ensures that all controls are easily accessible to the driver and passengers, facilitating an enjoyable driving experience.
Additional Components
Other notable features include the infotainment system, climate control units, and storage compartments. Each of these components plays a significant role in enhancing the overall functionality of the cabin, contributing to a harmonious blend of technology and comfort that meets the needs of modern drivers.
Lighting System and Wiring

The illumination mechanism in modern vehicles is a crucial aspect that enhances safety and visibility during both day and night driving. This system comprises various components, including headlights, taillights, indicators, and interior lighting. Each element plays a vital role in ensuring that drivers and pedestrians can see and be seen.
Understanding the wiring layout is essential for troubleshooting and maintenance. The electrical connections facilitate the operation of these lighting units, allowing for efficient power distribution. Various wires and connectors link the components to the vehicle’s main electrical system, enabling features like automatic light control and signaling. Proper wiring ensures optimal performance and prevents potential electrical failures.
Regular checks of the lighting system can help identify issues such as blown bulbs or faulty wiring. Maintaining the integrity of this system not only promotes safety but also enhances the overall driving experience. Knowledge of the different components and their configurations empowers vehicle owners to address problems proactively.
Engine Components Breakdown
The internal mechanisms of a vehicle’s engine consist of various elements that work together to deliver power and efficiency. Understanding these components is key to maintaining and diagnosing the engine system. Below is a detailed look at some of the primary elements that make up the heart of the engine.