In modern vehicles, the layout and structure of various elements play a crucial role in ensuring proper functionality and safety. Each component is meticulously designed and placed to contribute to the overall performance and durability of the automobile. Navigating these systems requires a solid understanding of their structure and arrangement.
Whether it’s the exterior framework or internal mechanisms, identifying and analyzing different elements of the vehicle can help maintain its efficiency. By gaining a clear understanding of how these elements are organized, it becomes easier to troubleshoot issues and make necessary adjustments. This guide provides insights into the positioning and connections between various elements in the vehicle’s framework.
2013 Kia Soul Body Parts Diagram
Understanding the layout and structure of a vehicle’s exterior components is essential for anyone looking to perform repairs or modifications. Each section is interconnected, and knowing how different elements relate to each other helps ensure that maintenance tasks are completed efficiently and accurately.
Exterior structure includes various essential components that form the framework of the vehicle, from panels to crucial attachments that impact its functionality. A clear understanding of these elements is crucial for both professionals and DIY enthusiasts looking to work on their vehicle.
Additionally, the connection points between the structural elements must be considered, as they dictate how securely the outer sections remain intact during operation. Ensuring that each piece is correctly aligned is key to the overall performance of the vehicle.
Overview of Exterior Components
The exterior of any vehicle is composed of various elements that contribute to its structure, appearance, and functionality. Each of these elements plays a crucial role in defining the overall look and ensuring the vehicle’s performance and safety. From the front to the rear, these components work together to provide not only aesthetic value but also critical support to the vehicle’s function on the road.
Key elements include the protective panels, which shield the vehicle from external damage, and lighting fixtures that enhance visibility and communication with other drivers. Additionally, functional components such as mirrors and windows contribute to the overall control and comfort for those inside. These components are designed to withstand environmental challenges while maintaining the vehicle’s sleek and durable exterior.
Key Interior Parts and Layout
The internal design of a vehicle is crucial to providing comfort, accessibility, and functionality. Understanding the arrangement of essential components helps to improve the user experience and optimize the vehicle’s practical use. This section delves into the main elements inside the cabin, offering insight into their positions and roles in creating a cohesive environment.
Dashboard Configuration: At the forefront of the interior lies the control hub, integrating displays, buttons, and switches to give the driver easy access to necessary information and settings. Its layout ensures visibility and ease of use, promoting safety and convenience.
Seating Arrangement: The seating setup is designed to maximize space and comfort. The seats are positioned to allow ample legroom and support for long journeys, with adjustable features to enhance the driving or riding experience.
Storage Compartments:
Understanding the Suspension System
The suspension system plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth and stable ride, absorbing shocks and maintaining the vehicle’s balance. By linking the wheels to the frame, it ensures that the movement of the wheels adapts to road conditions, promoting comfort and safety.
Components and Functionality
Each part of the suspension system is designed to handle specific tasks. Springs, for example, absorb the impact from road surfaces, while shock absorbers reduce the bouncing effect. Other elements, like control arms and bushings, work together to provide precise handling and stability during maneuvers.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular inspection of the suspension system is vital for optimal performance. Worn-out components can lead to a rough ride and decreased safety. Identifying and replacing faulty parts early ensures better control and prolongs the lifespan of the system.
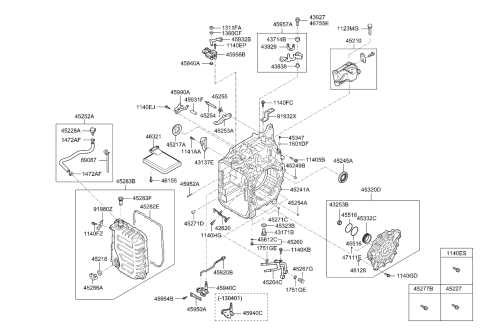
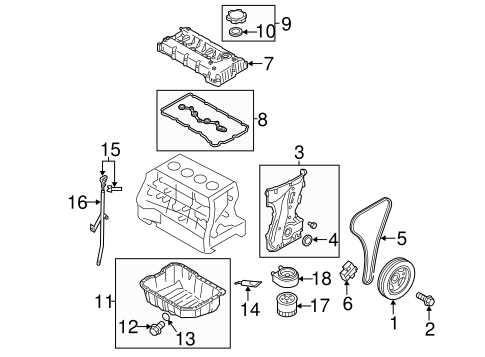
Detailed View of Engine Bay
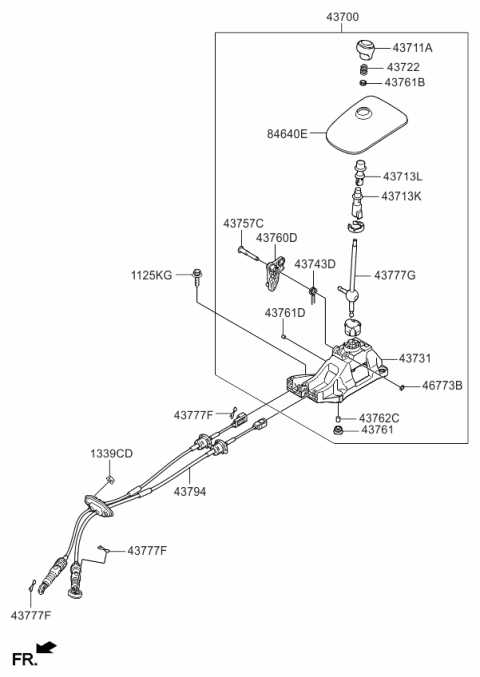
The area beneath the hood houses various crucial elements responsible for the vehicle’s operation. It is essential to understand the layout and the interconnected components that work together to ensure optimal performance. This section provides a closer look at these essential mechanical elements, highlighting their roles in ensuring efficiency and reliability.
Key Components in the Engine Area

- Power source: At the heart of this section is the power unit, which drives the entire vehicle’s motion. It converts fuel into energy, propelling the vehicle forward.
- Cooling system: Essential for regulating temperatures, this system prevents overheating and maintains a stable environment for the power unit to function effectively.
- Intake and exhaust systems: These systems manage airflow into and out of the engine, ensuring optimal combustion and exhaust of gases.
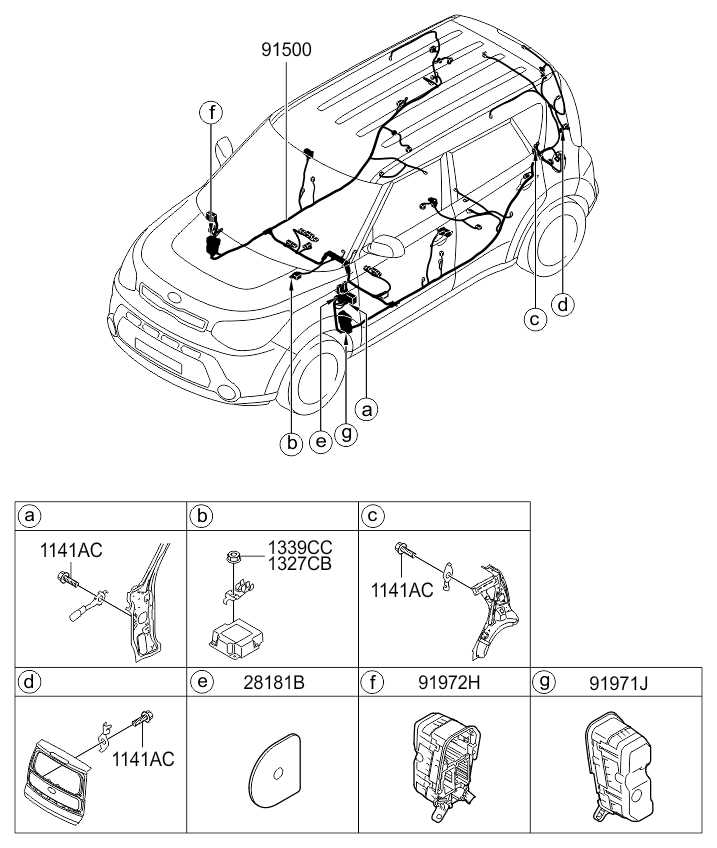
Wiring and Fluid Connections

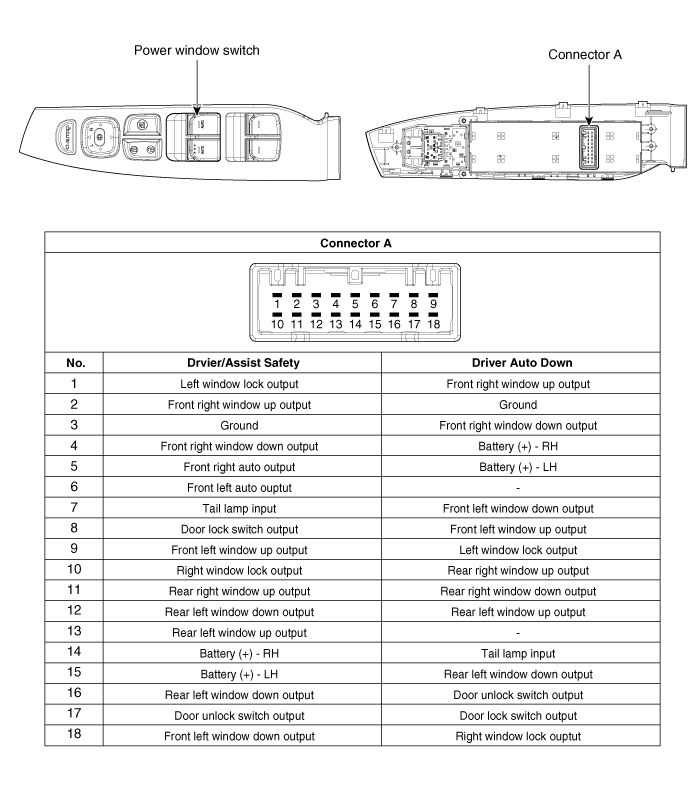
- Exploring the Electrical Wiring Connections
This section delves into the intricate network of electrical links found within vehicles. Understanding these connections is essential for diagnosing issues, enhancing functionality, and ensuring efficient operation. Each wire and terminal plays a critical role in the overall system, facilitating communication between various components.
Key Components of Electrical Wiring

The wiring setup consists of several vital elements that work in harmony to transmit signals and power. These include connectors, fuses, relays, and various wire types, each serving a specific purpose. Familiarizing oneself with these components can simplify troubleshooting and maintenance tasks.
Common Wiring Schematics
To better comprehend the layout of electrical connections, here is a simplified overview of common wiring configurations:
Component Description Connector Joins two or more wires, allowing for easy disconnection and reconnection. Fuse Protects the circuit from overload by breaking the connection when current exceeds safe levels. Relay Acts as a switch to control a larger current using a smaller signal, often for lights or motors. Wire Types Differentiated by gauge and insulation, suitable for various applications within the vehicle. Exhaust System Structure and Placement
The exhaust system is a crucial component of any vehicle, designed to channel harmful gases away from the engine and ensure efficient operation. It comprises several key elements, each playing a significant role in the overall functionality and performance of the automobile. Understanding the configuration and location of these components is essential for maintenance and repair purposes.
At the core of this system is the exhaust manifold, which collects exhaust gases from the engine’s cylinders. These gases are then directed through the catalytic converter, a vital element that reduces harmful emissions by facilitating chemical reactions. Following this, the gases travel through the muffler, which minimizes noise produced by the engine. Finally, the exhaust pipe expels the treated gases into the atmosphere.
Placement of these components is strategically designed to optimize performance while minimizing potential issues. For instance, the exhaust manifold is typically mounted close to the engine, allowing for efficient gas collection. The catalytic converter is positioned along the undercarriage, ensuring adequate heat dissipation and protecting sensitive parts from damage. Understanding this layout aids in troubleshooting and enhances the longevity of the system.
Brake System Components Overview
The brake system is essential for ensuring the safety and efficiency of a vehicle. This intricate assembly consists of various elements working together to provide reliable stopping power. Understanding these components is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and addressing potential issues that may arise during operation.
Key components of the brake system include the following:
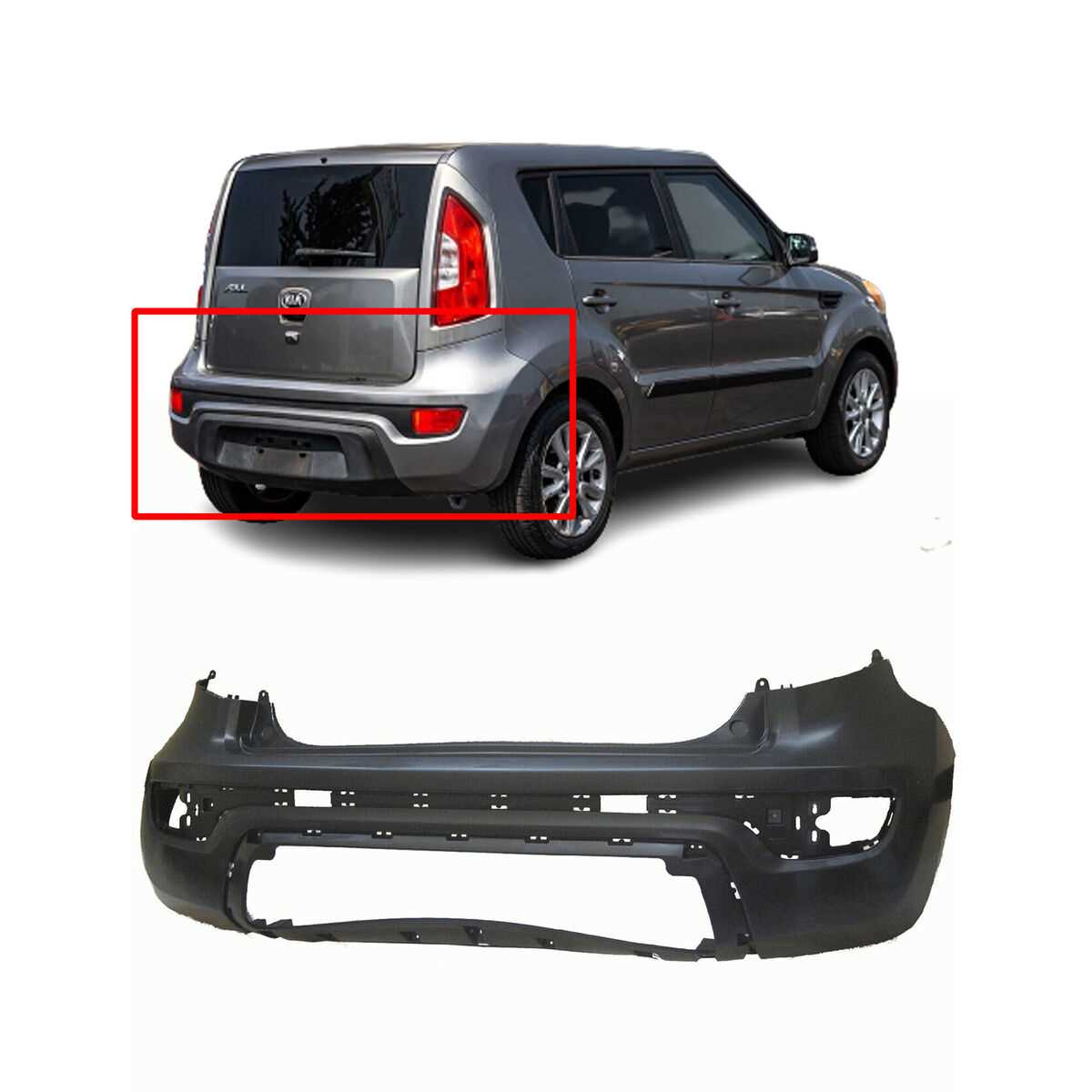
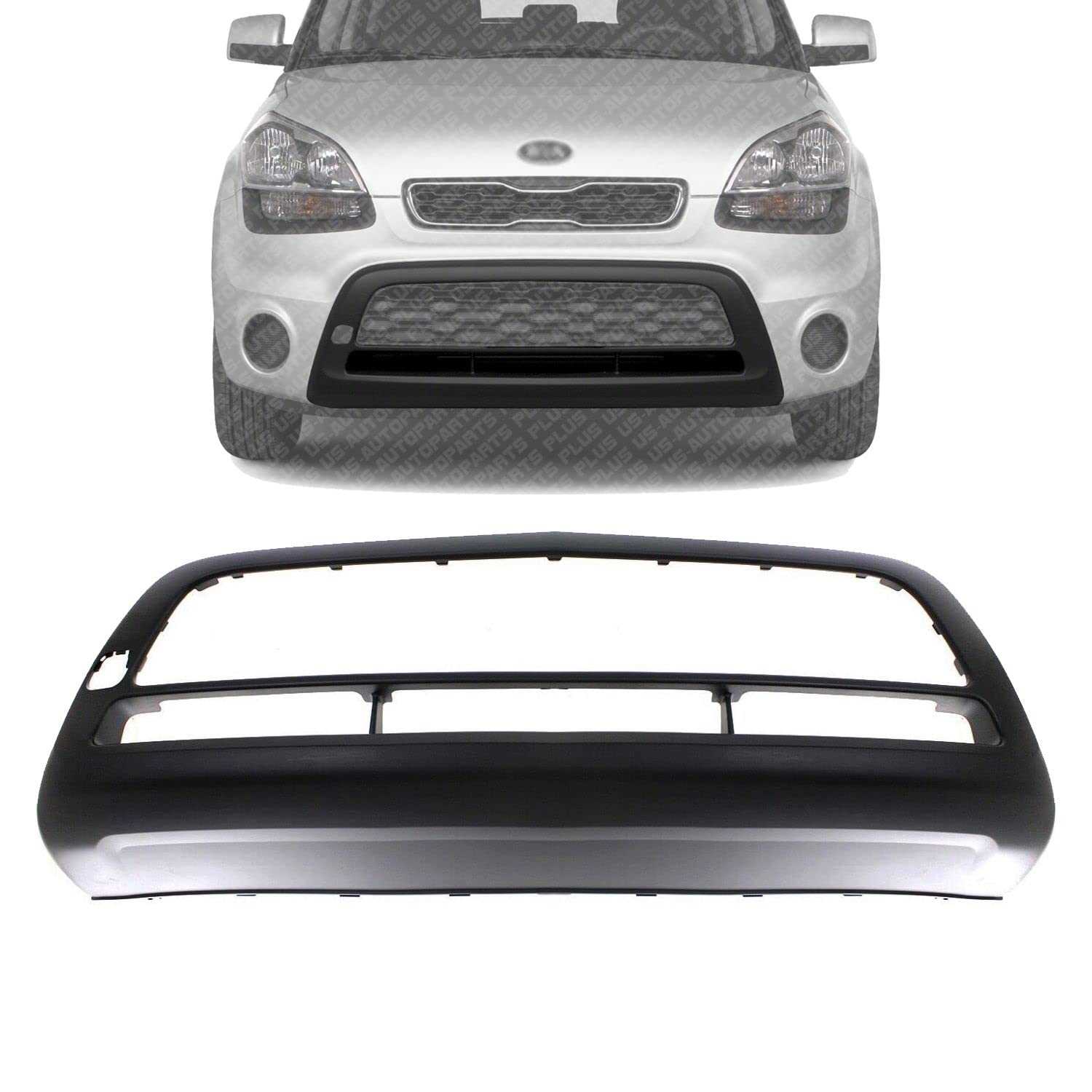
Component Description Brake Pads Friction materials that press against the brake rotor to slow down or stop the vehicle. Brake Rotors Disc-shaped components that the brake pads clamp onto, converting kinetic energy into heat. Brake Calipers Housings that contain the brake pads and are responsible for applying pressure to them. Brake Lines Fluid-filled tubes that transfer hydraulic pressure from the master cylinder to the brake calipers. Master Cylinder The component that generates hydraulic pressure in the brake system when the brake pedal is pressed. Front and Rear Bumper Assembly

The bumper assembly serves as a crucial component of a vehicle’s exterior, providing protection and aesthetic appeal. It is designed to absorb impact, safeguarding the underlying structure and systems from damage during minor collisions. This section delves into the intricacies of the front and rear bumper assembly, highlighting their functionality, structure, and essential components.
Components of the Bumper Assembly
Each bumper assembly comprises several integral components that work together to ensure durability and performance. Understanding these elements can aid in proper maintenance and potential upgrades.
Component Description Bumper Cover The outermost shell that provides a finished look and protects the inner components. Reinforcement Bar A sturdy bar that adds strength and absorbs energy during a collision. Impact Absorbers Materials designed to dissipate force upon impact, reducing damage. Mounting Brackets Hardware that secures the bumper to the vehicle frame, ensuring stability. Reflectors and Lights Enhance visibility and safety by alerting other drivers to the vehicle’s presence. Importance of Regular Inspection
Regular inspection of the bumper assembly is essential to maintain safety and functionality. Damage to any component can compromise the overall integrity of the assembly, making it imperative to address issues promptly. Routine checks can help identify wear and tear, ensuring that all elements are in optimal condition.
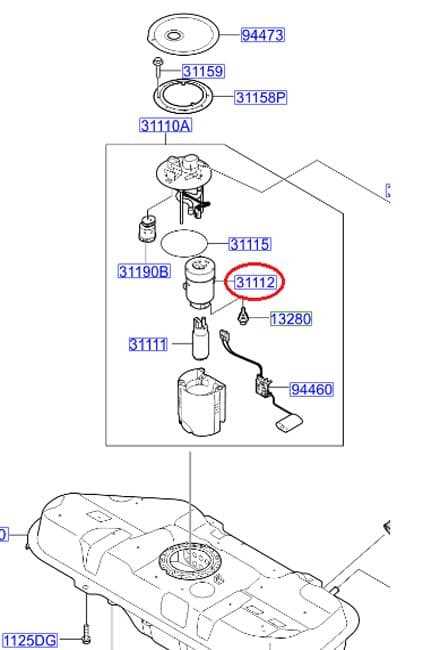
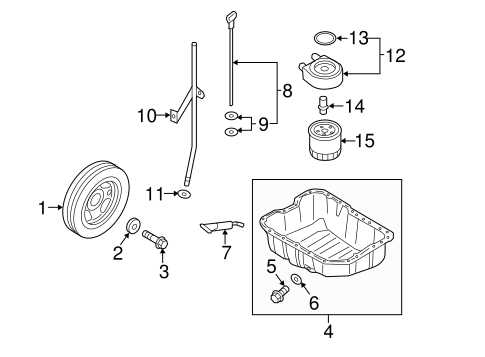
Fuel System and Tank Location

The fuel delivery system plays a crucial role in the performance and efficiency of any vehicle. This intricate setup is designed to store, filter, and transport the necessary energy source to the engine, ensuring smooth operation and optimal performance. Understanding its layout and components can help in diagnosing issues and performing maintenance effectively.
Components of the Fuel Delivery System
This system consists of several key elements, including the fuel tank, pump, filter, and injectors. Each component works in harmony to deliver fuel from the tank to the engine. The tank is typically located at the rear of the vehicle, ensuring safety and proper weight distribution.
Tank Position and Accessibility
Accessing the fuel reservoir can vary based on the vehicle’s design. In most models, the tank is positioned beneath the rear section, often protected by a shield for added safety. Understanding the exact location can facilitate easier access for maintenance or replacement, ensuring that the system functions reliably.
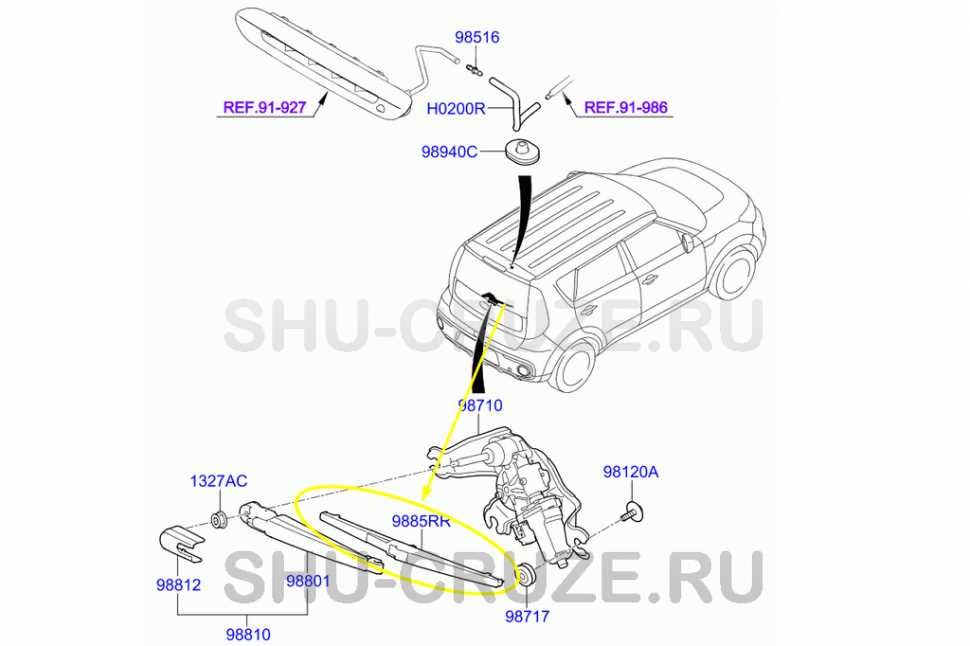
How to Identify Door Mechanisms
Understanding the components that facilitate the opening and closing of vehicle access points is essential for effective maintenance and repairs. These mechanisms play a critical role in ensuring smooth operation and security. By familiarizing yourself with the various types and their functions, you can better diagnose issues and streamline your repair processes.
Several key features can help you recognize different types of door mechanisms. The following table outlines common characteristics and identifiers that differentiate these components:
Type Description Identification Tips Lever Mechanism Utilizes a lever to facilitate door movement. Check for visible levers and linkage attachments. Latch Assembly Holds the door in place when closed. Look for a hook or bolt that secures the door. Locking Mechanism Ensures the door remains secure when closed. Test the operation of the key or electronic fob. Hinge System Allows the door to pivot open and closed. Inspect the hinges for wear and lubrication needs.