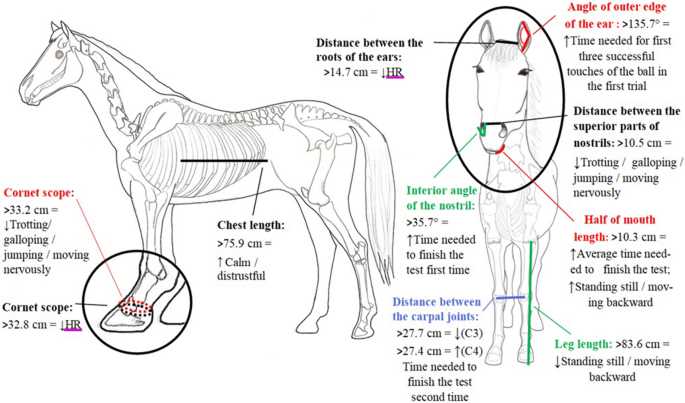
Exploring the intricate structure of equines reveals a fascinating interplay of various elements that contribute to their functionality and movement. A comprehensive examination of this subject not only enhances our appreciation for these magnificent creatures but also serves as a vital resource for those involved in their care, training, and management.
Each segment plays a crucial role in overall performance and health, from the skeletal framework to the muscular arrangements. Gaining insight into these components fosters a deeper understanding of how they interact during different activities, whether in the wild or under human supervision.
Furthermore, knowledge of these anatomical features is essential for veterinarians, trainers, and enthusiasts alike, facilitating better communication and informed decisions in their respective fields. This exploration paves the way for effective practices that can lead to improved well-being and performance in the equine population.
Understanding Equine Anatomy
Gaining insight into the physical structure of these magnificent creatures is essential for anyone involved in their care and management. This knowledge facilitates better handling, training, and healthcare practices. A comprehensive understanding of their anatomy enables enthusiasts and professionals alike to recognize normal functionality and identify potential issues effectively.
Key Components of Structure

The anatomy of these animals comprises several critical systems, including skeletal, muscular, and circulatory. Each system plays a vital role in overall performance and health. The skeletal framework provides support, while muscles enable movement and flexibility. Understanding these systems allows caregivers to tailor training and rehabilitation programs to meet the specific needs of each individual.
Importance of Anatomical Knowledge

Familiarity with anatomical features enhances the ability to detect signs of discomfort or disease. Recognizing the signs of injury or distress can lead to timely interventions, promoting better recovery outcomes. Furthermore, this knowledge aids in the development of effective grooming, feeding, and exercise regimens tailored to the specific physiological requirements of these remarkable animals.
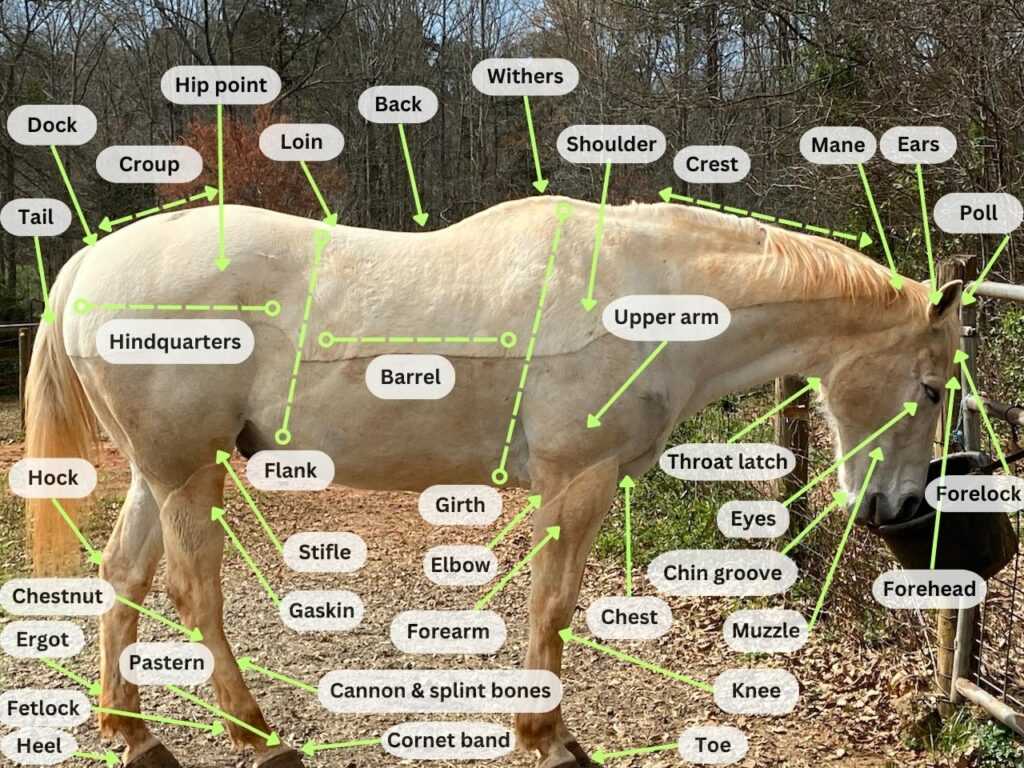
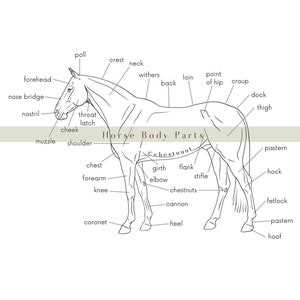
Key External Features of Horses
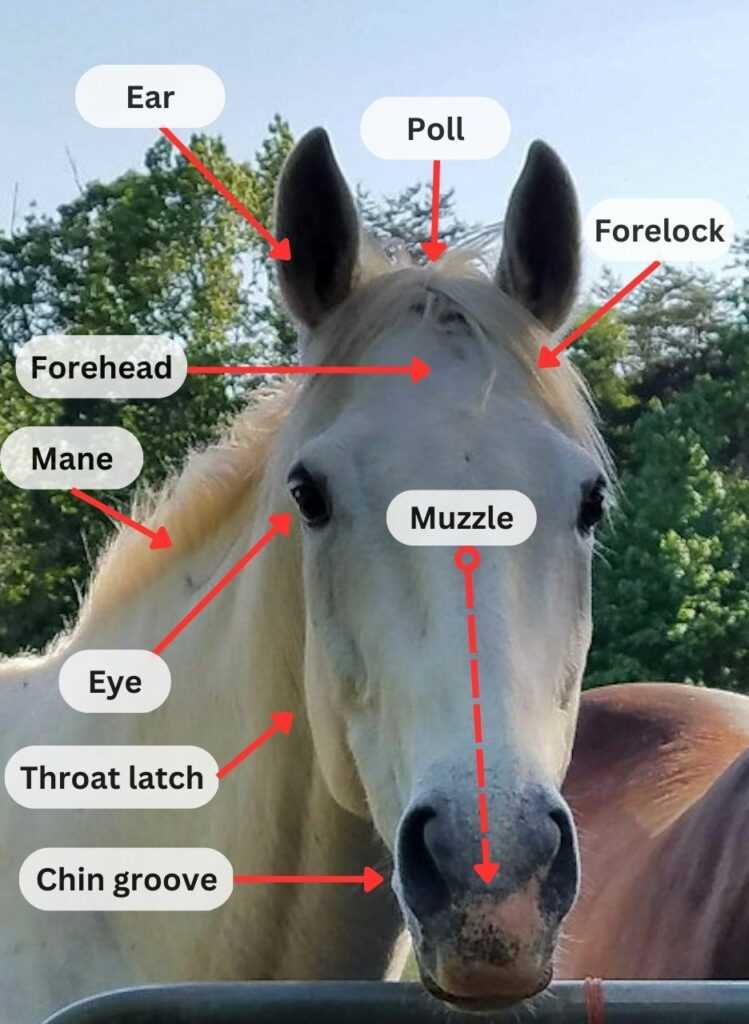
The physical characteristics of these majestic creatures play a crucial role in their function and interaction with the environment. Understanding these attributes not only enhances our appreciation for them but also informs care and management practices.
Distinctive Characteristics
One of the most notable traits is the unique shape of the head, which varies among different breeds. The ears are also particularly expressive, serving as indicators of mood and focus. Additionally, the eyes are positioned to provide a wide field of vision, allowing for awareness of surroundings.
Limbs and Gait
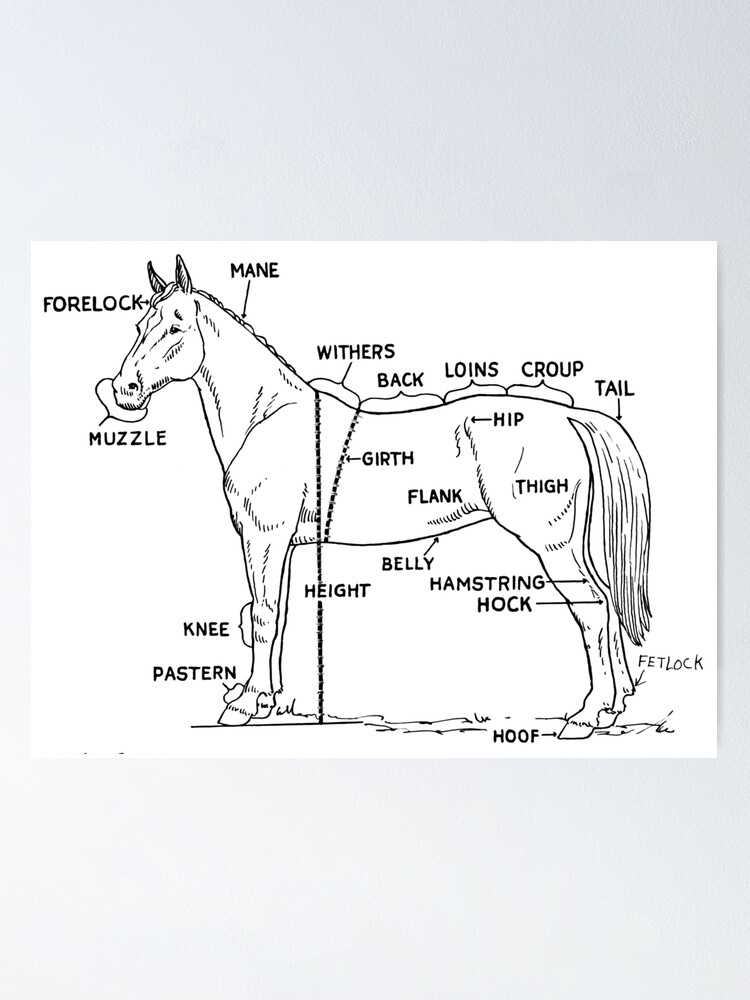
The long, powerful legs are essential for agility and speed. These appendages feature strong muscles and joints, enabling various movements from a gentle trot to an exhilarating gallop. The hooves, specially adapted for different terrains, contribute significantly to overall health and mobility.
Overall, recognizing these external traits is vital for anyone involved in the care or training of these splendid animals. Each feature serves a specific purpose that enhances their adaptability and grace.
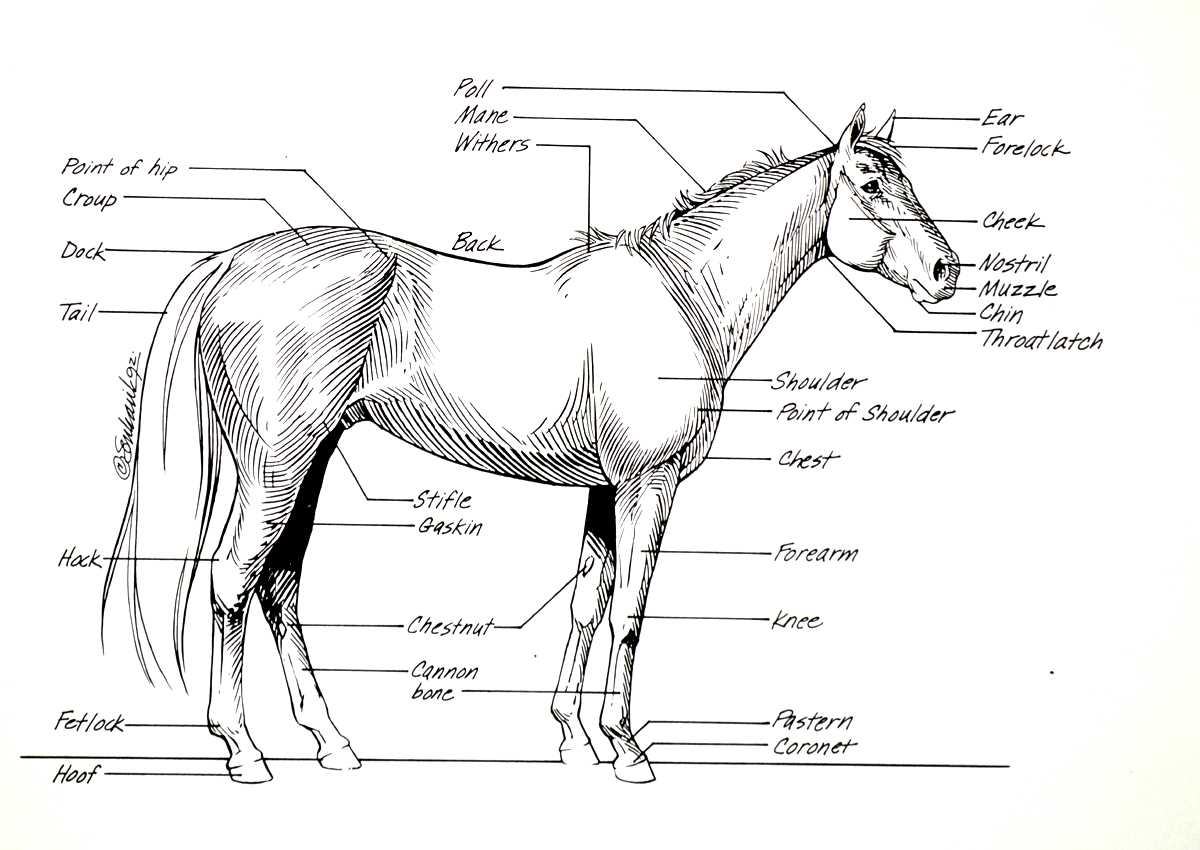
Commonly Recognized Body Parts
This section delves into the widely acknowledged components of equine anatomy, highlighting their significance in various aspects of care, health, and performance. Understanding these elements is crucial for anyone involved in the management and well-being of these magnificent creatures.
- Head: The front section that houses essential sensory organs and plays a vital role in communication.
- Neck: A long and flexible structure connecting the head to the torso, facilitating movement and balance.
- Chest: The area surrounding the heart and lungs, important for respiratory function and overall vitality.
- Back: The central part that supports the saddle and rider, critical for stability and movement.
- Hindquarters: The rear section that contributes to propulsion and power during movement.
These elements serve various functions and are integral to the overall structure and health of the animal. Recognizing and understanding each feature can greatly enhance the ability to provide appropriate care and training.
- Legs: Comprising multiple segments, they provide strength and agility.
- Hooves: The hard covering at the end of each leg, crucial for support and mobility.
- Tail: An extension of the back, serving as a means of communication and protection against insects.
Knowledge of these fundamental components fosters a deeper connection and facilitates effective interaction with these majestic animals.
Importance of Hoof Structure
The integrity of the lower limb structure is crucial for optimal mobility and overall health. Understanding the composition and function of this essential element can significantly impact the well-being and performance of these majestic creatures.
Key aspects of hoof structure contribute to various functions, including:
- Weight Distribution: A well-structured hoof ensures even weight distribution, minimizing the risk of stress and injury.
- Shock Absorption: The flexible components within the hoof play a vital role in absorbing impact, protecting the internal structures during movement.
- Traction: Properly shaped hooves provide adequate grip, enabling stable footing on diverse terrains.
- Circulation: The hoof aids in blood circulation, promoting overall limb health through a pumping action during locomotion.
Neglecting the importance of hoof structure can lead to various complications, such as:
- Increased risk of lameness and discomfort.
- Development of conditions like laminitis or thrush.
- Reduced performance capabilities in competitive activities.
Regular care and attention to hoof health are essential to maintain the structural integrity and functionality of this critical component.
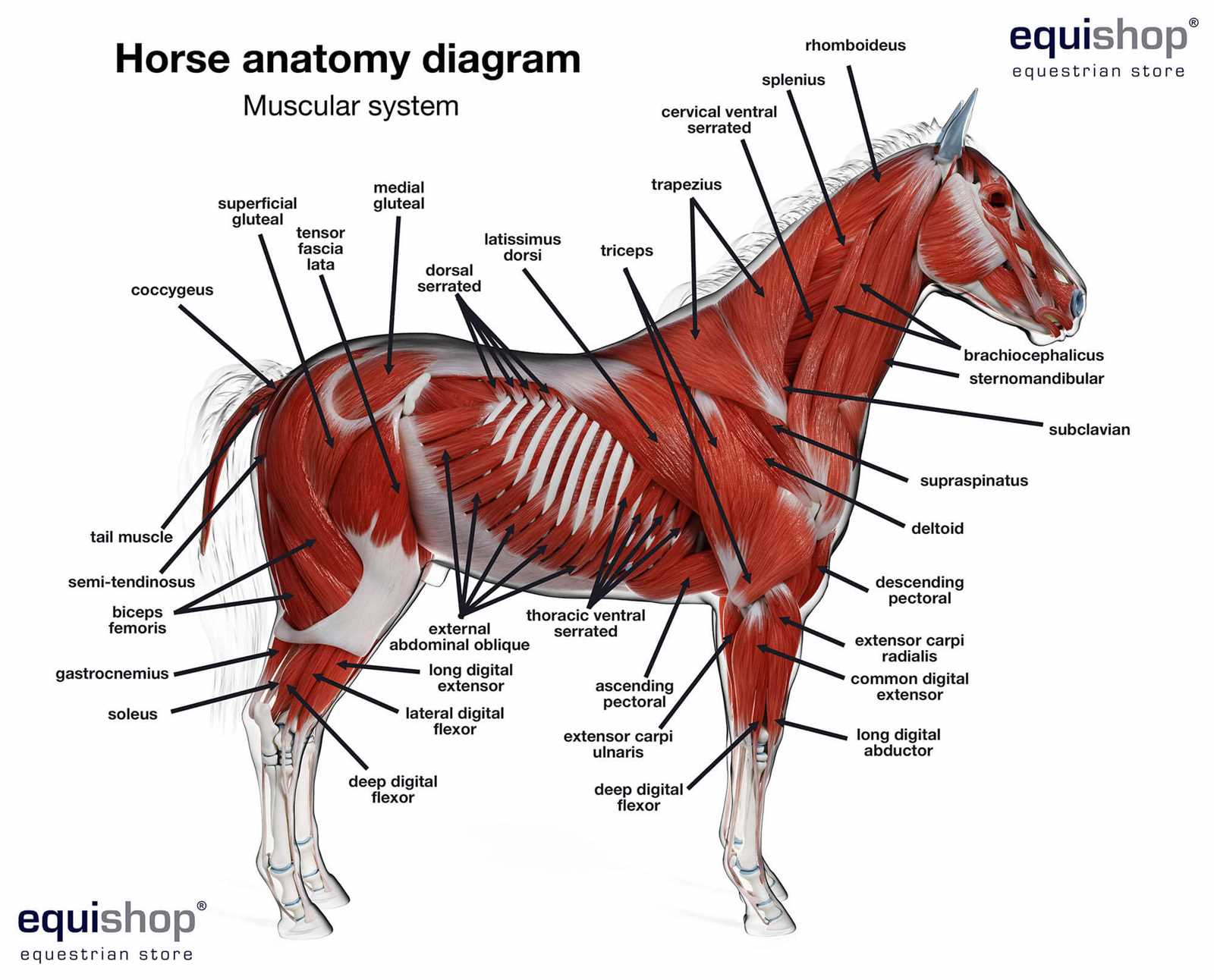
Muscle Groups and Their Functions
The musculature of equines plays a vital role in their movement and overall performance. Understanding the various muscle groups and their specific functions provides insight into how these magnificent creatures achieve agility, strength, and endurance. Each group works in harmony to facilitate locomotion, balance, and physical exertion, contributing to the horse’s athletic capabilities.
Among the primary muscle groups, the forelimb muscles are crucial for movement. They enable the animal to push off the ground and navigate various terrains. These muscles are essential for executing tasks such as jumping, trotting, and galloping, highlighting their significance in equine activities.
The hind limb musculature is equally important, providing the propulsion necessary for forward motion. These muscles not only support acceleration but also assist in maintaining stability and coordination during movement. Their development directly influences performance in disciplines ranging from dressage to racing.
Core muscles contribute significantly to posture and balance, allowing for effective weight distribution and control. A strong core enhances the ability to perform complex movements and adapt to changing conditions while minimizing the risk of injury.
In addition to these major groups, smaller muscles throughout the frame support intricate movements and provide additional stability. Collectively, these muscle systems work in synergy, enabling agility and strength while allowing for a remarkable range of motion essential for various equestrian pursuits.
Internal Organ Overview in Horses
The internal anatomy of these magnificent creatures plays a crucial role in their overall health and performance. Understanding the complex systems that operate within is essential for caretakers, trainers, and
Identifying Different Coat Types
Understanding the various coat varieties is essential for recognizing distinct breeds and their characteristics. Each type showcases unique features that can influence appearance, texture, and maintenance needs. By familiarizing oneself with these categories, enthusiasts can better appreciate the diversity within this equine world.
Common Coat Varieties
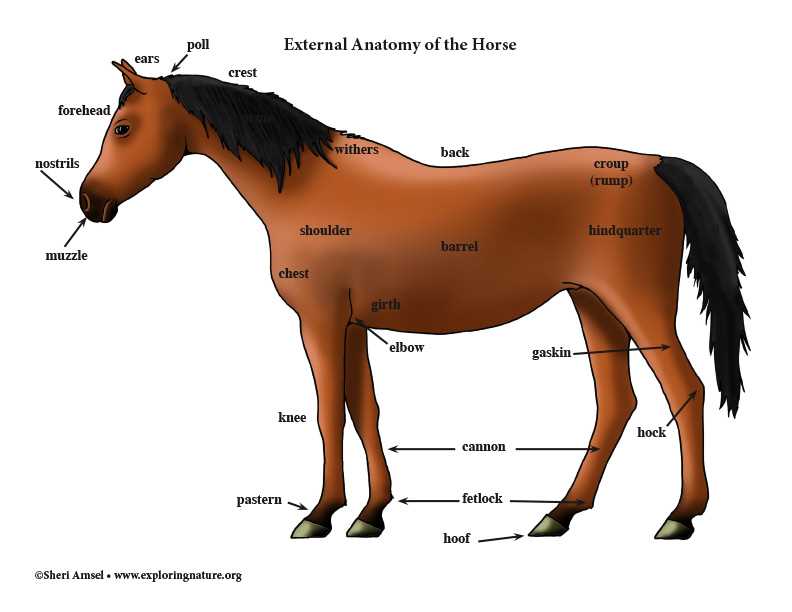
Among the prevalent coat types, solid, pinto, and appaloosa stand out. Solid coats present a uniform color throughout, while pinto patterns feature large patches of white combined with another color. Appaloosa coats are renowned for their distinctive spots, often varying in size and distribution. Recognizing these types aids in the understanding of individual lineage and breed traits.
Texture and Maintenance
The texture of the coat can vary significantly, ranging from sleek and short to long and shaggy. Short-haired varieties generally require less grooming compared to their long-haired counterparts, which may need regular brushing to prevent matting. Awareness of these differences not only enhances care routines but also ensures the overall well-being of these majestic creatures.
Significance of Equine Joints
The importance of articulations in the equine anatomy cannot be overstated. These crucial connections enable movement, flexibility, and overall functionality. Understanding the role of these structures is essential for promoting optimal health and performance in these magnificent creatures.
Functionality and Movement
Articulations are vital for locomotion, allowing for a range of motions that facilitate running, jumping, and turning. Each joint serves a unique purpose, contributing to the animal’s agility and balance. Proper functioning of these connections is essential for peak athletic performance, as any impairment can lead to significant limitations.
Health and Care
Regular monitoring and maintenance of these connections are crucial for preventing injuries and ensuring long-term wellness. Knowledge of common ailments affecting these areas can aid caretakers in implementing preventive measures and seeking timely veterinary assistance when needed.
| Joint Type | Common Issues | Prevention Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Hock | Osteoarthritis | Regular exercise and weight management |
| Knee | Soft tissue injuries | Proper warm-up and cool-down |
| Fetlock | Chip fractures | Routine check-ups and early intervention |
Role of the Horse’s Tail

The tail serves various essential functions that contribute to the well-being and communication of equines. It acts not only as a physical appendage but also plays a vital role in their interaction with the environment and other beings.
Primarily, this feature is crucial for maintaining comfort and health. It aids in protecting against pests, helping to swat away flies and other insects that may cause irritation. Additionally, it plays a significant role in expressing emotions and intentions, conveying subtle signals to other animals and humans.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Pest Control | Helps in keeping away insects, providing relief from bites and discomfort. |
| Communication | Facilitates non-verbal cues, allowing for interaction with peers and handlers. |
| Balance | Aids in maintaining equilibrium during movement, especially at higher speeds. |
Understanding the significance of this appendage enhances the appreciation of its multifaceted role in the life of these magnificent creatures.
Facial Structure and Its Functions
The anatomy of the facial region plays a crucial role in various functions essential for survival and interaction. This intricate arrangement of features enables the organism to communicate, eat, and sense its environment effectively.
At the forefront of this structure are the sensory organs, which are vital for detecting stimuli. The eyes, positioned to provide a wide field of vision, allow for the perception of movement and potential threats. Similarly, the nose is equipped to discern scents, aiding in locating food and recognizing companions.
The mouth serves multiple purposes; it is not only a means of intake for nourishment but also a tool for vocalization. The ability to produce sounds facilitates communication, which is essential for social interactions within groups.
Furthermore, the arrangement of bones and muscles in this area contributes to the overall expression of emotions. Subtle movements can convey feelings such as contentment, fear, or aggression, playing a significant role in social dynamics.
In summary, the configuration of the facial region encompasses sensory input, nutritional intake, vocal expression, and emotional communication, underscoring its importance in daily activities and social engagement.
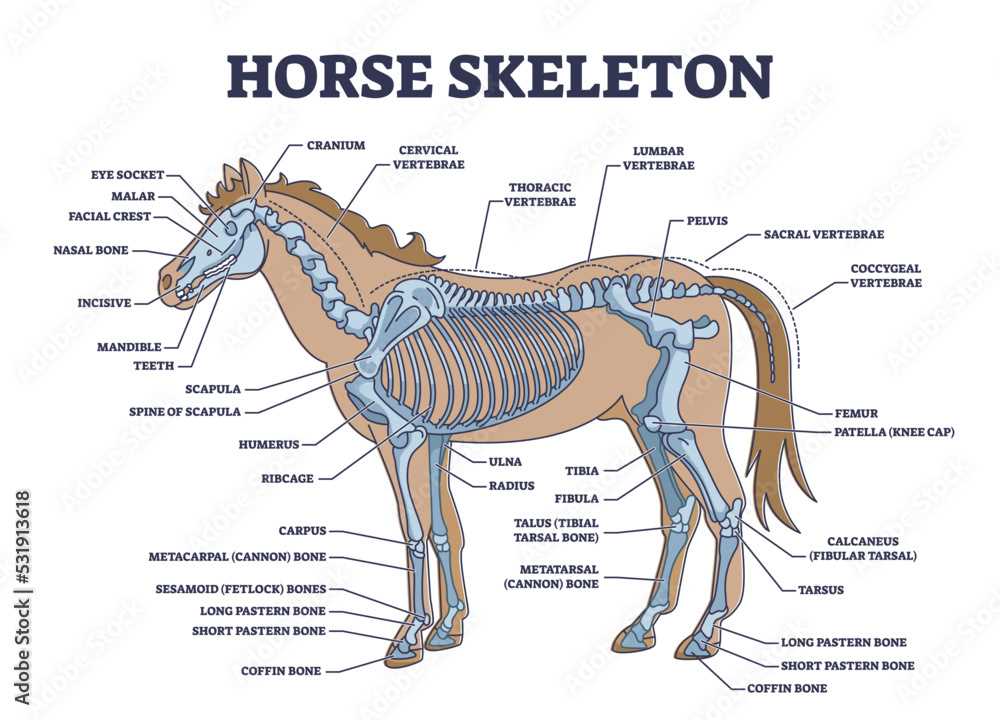
Understanding the Horse’s Skeleton

The framework of equines is a complex structure that provides support, movement, and protection for vital organs. This intricate assembly of bones plays a crucial role in the overall function and performance of these majestic animals.
Equines possess a total of approximately 205 to 207 individual bones, which can be categorized into several main groups:
- Axial Skeleton: Comprising the skull, vertebral column, and rib cage, this section serves as the central support system.
- Appendicular Skeleton: This group includes the limbs and girdles, allowing for mobility and weight-bearing activities.
- Short Bones: Found in the carpal and tarsal regions, these contribute to stability and flexibility.
Understanding the arrangement and function of these structures is essential for anyone involved in equine care and management. Key components of the skeletal framework include:
- Skull: Protects the brain and houses sensory organs.
- Vertebrae: Forms the spine, allowing for flexibility while protecting the spinal cord.
- Ribs: Encases and safeguards the thoracic cavity.
- Limbs: Facilitates movement, with each limb comprised of several bones working in concert.
Each element of this framework not only contributes to the physical capabilities of equines but also plays a significant role in their overall health. An appreciation for the skeletal structure enhances our understanding of their biomechanics and well-being.
Common Health Issues by Region
Understanding prevalent health challenges can significantly enhance the well-being of these magnificent creatures. Various regions exhibit distinct concerns that can affect their overall vitality, influenced by environmental conditions, dietary habits, and common practices in care. Awareness of these regional health issues is crucial for effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Northern Areas
In colder climates, respiratory conditions are often more common due to prolonged exposure to harsh weather and inadequate shelter. Additionally, conditions such as laminitis may arise from changes in diet when transitioning to spring grass after winter. Proper management and regular check-ups can mitigate these risks.
Tropical Regions
In warmer climates, parasites pose a significant threat, leading to a range of gastrointestinal and dermatological issues. Furthermore, heat stress is a concern during peak temperatures, necessitating adequate hydration and shade. Implementing preventive measures is essential to maintain health and productivity in these environments.