
In the realm of two-wheeled transportation, effective deceleration is crucial for both safety and performance. This section delves into the various components that contribute to the mechanism responsible for slowing down and halting movement. An in-depth exploration of these elements will enhance your knowledge of how they function together to ensure a seamless riding experience.
The assembly of these essential elements encompasses a range of features designed for optimal efficiency and reliability. Each component plays a pivotal role, from the initial activation to the ultimate cessation of motion. By understanding the intricate relationships between these features, one can appreciate the engineering that goes into creating a reliable stopping system.
Moreover, this exploration aims to clarify the configuration and interactions within the system. Gaining insights into the specific attributes and functions of each element will empower enthusiasts and riders alike, fostering a greater appreciation for the technology that underpins modern cycling. Equip yourself with knowledge and enjoy a deeper connection with your ride.
Bicycle V Brake Components Overview
This section delves into the essential elements that work in harmony to ensure effective stopping power. Understanding these components is crucial for maintenance and performance optimization.
Main Elements
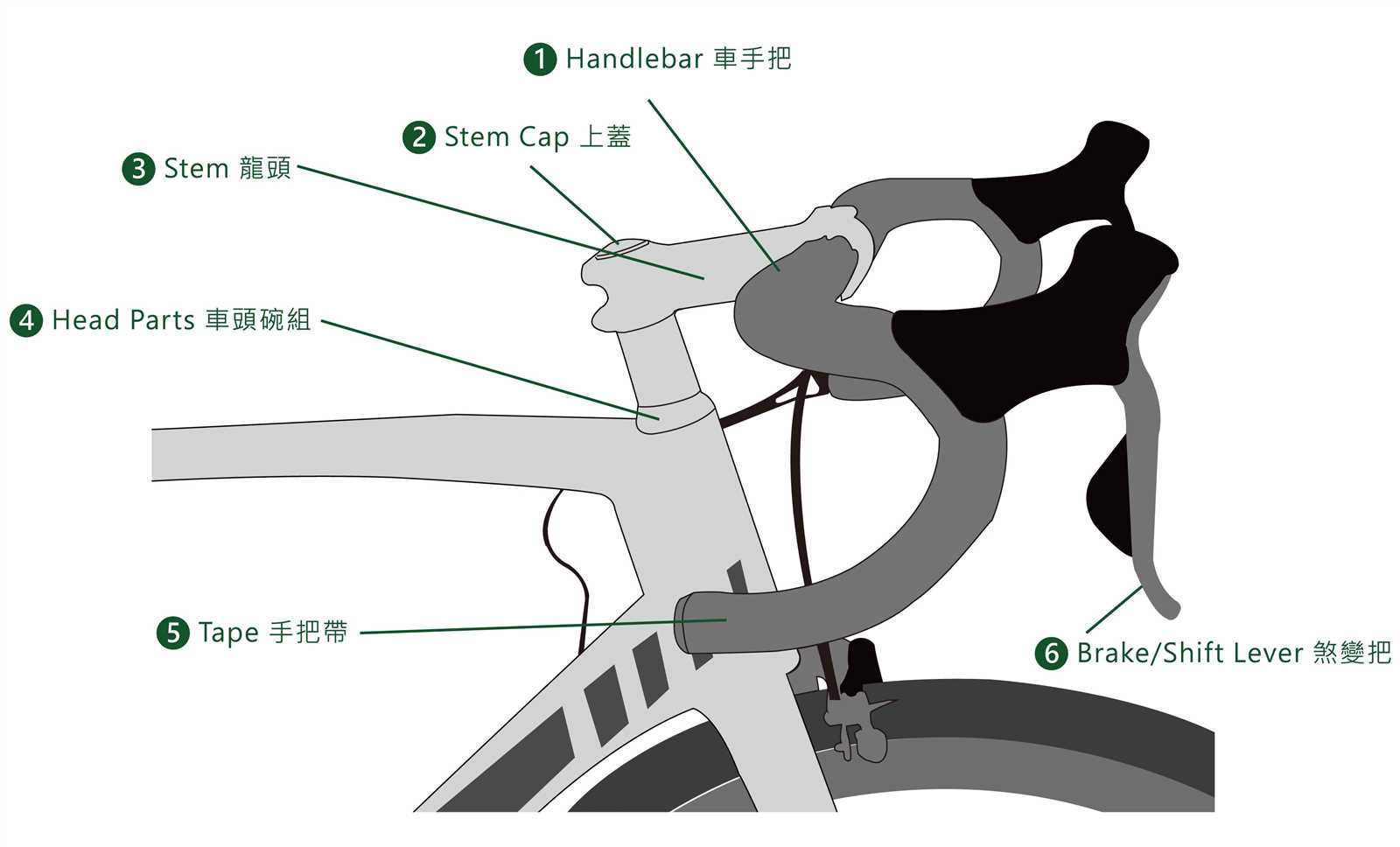
- Cable: A vital component that transmits force from the lever to the stopping mechanism.
- Lever: The mechanism activated by the rider to initiate the stopping action.
- Pads: These provide the necessary friction against the wheel rim to halt motion.
- Arm: This connects the pads to the lever, allowing for the transfer of motion.
- Mounting Bracket: The structure that secures the assembly to the frame or fork.
Functionality
- The lever is pulled by the rider, causing tension in the cable.
- This tension moves the arm, which in turn pushes the pads against the wheel rim.
- The friction generated slows down or stops the vehicle, ensuring safety and control.
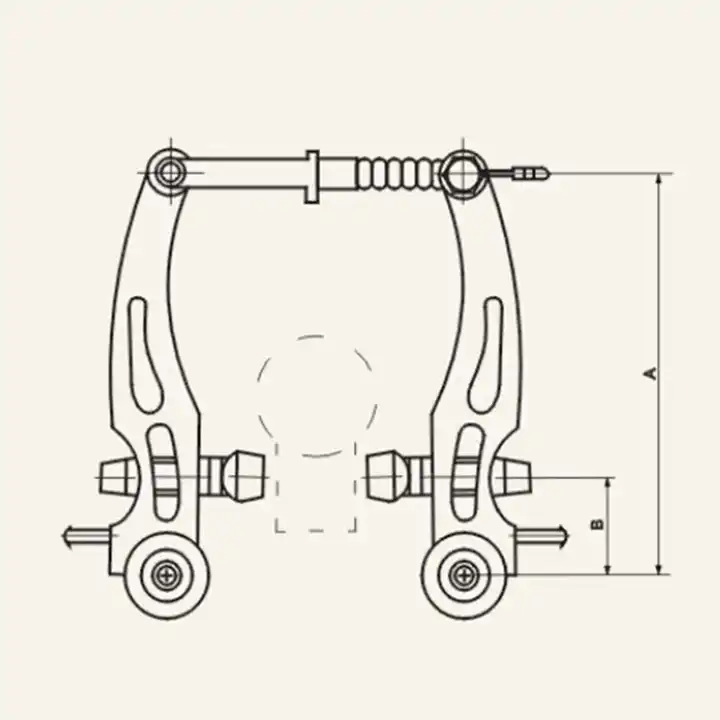
Understanding V Brake Mechanism
The mechanism responsible for decelerating a vehicle involves a unique arrangement that enhances control and stability. This system is designed to provide effective stopping power through a combination of leverage and friction, allowing the operator to maintain safety during movement. By utilizing a simple yet efficient setup, this design contributes to a smoother riding experience.
At its core, the assembly consists of several key elements that work together harmoniously. These components include the lever, arms, and pads, each playing a critical role in the overall functionality. When force is applied to the lever, it triggers a sequence of movements that activate the arms, pushing the pads against the wheel’s surface. This interaction generates the necessary friction to reduce speed.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Lever | The control mechanism that initiates the stopping process. |
| Arms | Linkage that transfers the force from the lever to the pads. |
| Pads | Friction surfaces that contact the wheel, creating resistance. |
Understanding this mechanism is essential for maintaining optimal performance and ensuring safety during operation. Regular inspections and adjustments can help preserve the effectiveness of this system, making it crucial for users to familiarize themselves with its components and functionality.
Key Parts of V Brakes
This section delves into the essential components that contribute to the efficient functioning of a V-style stopping mechanism. Understanding these elements can enhance performance and maintenance, leading to a safer riding experience.
- Arm: This lever-like structure pivots to apply pressure to the stopping surface.
- Pads: Made from friction material, these components come into contact with the wheel to slow down or halt motion.
- Cable: This thin wire transmits force from the hand lever to the arm, allowing for control over the stopping action.
- Mounting Bracket: This secures the assembly to the frame, providing stability during operation.
- Spring: A crucial element that returns the arm to its original position after activation, ensuring quick and responsive action.
Understanding these components can aid in troubleshooting and improving the overall performance of the stopping mechanism. Regular inspection and maintenance of these elements are key to ensuring optimal function and safety on the road.
Installation Guide for V Brakes
Setting up a new stopping system is essential for optimal performance and safety. This guide provides step-by-step instructions to ensure that your system is installed correctly, allowing for efficient and responsive control during rides.
1. Gather Required Tools: Before starting, collect all necessary tools such as a wrench, screwdriver, and any specific mounting hardware. Having everything at hand will streamline the process.
2. Remove Old Components: If replacing existing equipment, begin by detaching the old units. Carefully unscrew and lift them away from their positions to avoid damaging the frame.
3. Install the New System: Align the new units according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Secure them in place with screws, ensuring they are tightened adequately but not overly so, to prevent stripping.
4. Adjust Tension: Once mounted, adjust the tension of the cables. This step is crucial for achieving the desired responsiveness. Ensure that the mechanism moves freely without any hindrance.
5. Test Functionality: After installation, perform a thorough check to confirm that everything is functioning as expected. Take a few gentle test rides, making adjustments as necessary for optimal performance.
Following these steps will help ensure that your new system operates smoothly, enhancing your overall riding experience.
Adjusting Brake Tension Properly

Ensuring optimal tension for your stopping mechanism is crucial for safety and performance. Proper adjustment enhances responsiveness and provides a comfortable riding experience. This section covers the key steps and considerations for fine-tuning this essential component.
Follow these guidelines to achieve the right amount of tension:
- Inspect the Mechanism: Before making adjustments, examine the entire assembly for any signs of wear or damage.
- Loosen the Adjusting Screws: Locate the tension screws on either side of the assembly and gently loosen them to allow for movement.
- Adjust Tension Evenly: Turn the screws clockwise or counterclockwise to increase or decrease tension, respectively. Aim for a balanced feel on both sides.
- Test Responsiveness: After adjustments, perform a quick test by engaging the stopping system to ensure it responds smoothly and effectively.
- Secure the Settings: Once satisfied with the tension, tighten the adjusting screws to secure your settings and prevent any shift during use.
Regular maintenance is vital for longevity. Revisit these adjustments periodically to ensure continued optimal function.
Common Issues with V Brakes
Problems can arise with this essential stopping mechanism, impacting performance and safety. Regular maintenance and awareness of potential complications are crucial for optimal functionality. Here are some frequent challenges encountered by users.
Misalignment of Components
One common issue is the misalignment of the various elements involved in the stopping process. When components are not properly positioned, it can lead to uneven pressure distribution, resulting in inefficient operation. Ensuring that all elements are aligned correctly is vital for achieving smooth and effective engagement.
Worn-Out Materials
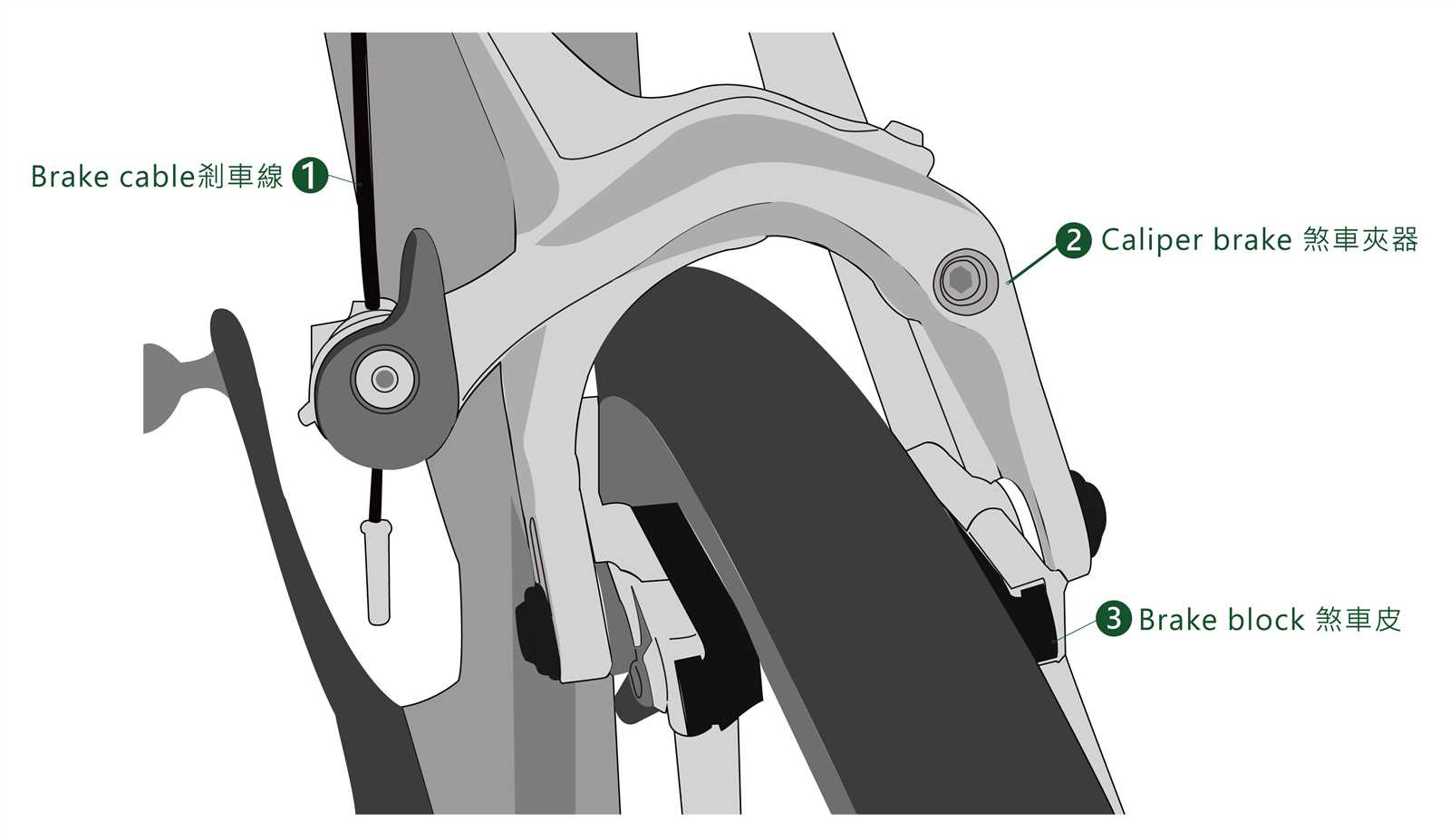
Another prevalent concern is the degradation of essential materials over time. Components like pads and cables can wear out, diminishing their effectiveness. Regularly inspecting and replacing these materials when necessary is essential for maintaining the overall performance and safety of the system.
Maintaining Your V Brake System
Regular upkeep of your stopping mechanism is crucial for optimal performance and safety. Ensuring that all components are in good condition will not only enhance responsiveness but also prolong the life of the entire assembly. This section outlines essential practices to keep your stopping system functioning smoothly.
Start by routinely inspecting the main components for wear and tear. Pay special attention to the friction surfaces, as they can degrade over time. Additionally, ensure that the cables are properly tensioned and free from fraying. Cleaning the surfaces can significantly improve contact and overall effectiveness.
Here’s a simple maintenance checklist:
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Inspect pads for wear | Monthly | Replace if less than 1mm thick |
| Check cable tension | Every ride | Adjust as necessary |
| Clean surfaces | Weekly | Use a soft cloth and mild cleaner |
| Lubricate pivot points | Every 3 months | Use a light grease |
| Inspect the lever | Monthly | Ensure smooth operation |
By following this maintenance schedule, you can ensure that your stopping mechanism operates at peak efficiency, providing a safe and smooth experience.
Replacing V Brake Pads Effectively
Maintaining optimal stopping power is essential for a safe and smooth riding experience. One of the key components that require periodic replacement is the friction material, which plays a crucial role in slowing down or stopping movement. Understanding how to efficiently replace these elements can greatly enhance performance and ensure safety on the road.
To successfully change the friction materials, follow the steps outlined in the table below:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Gather necessary tools, including a wrench and a replacement set of friction materials. |
| 2 | Loosen the securing mechanism that holds the current friction materials in place. |
| 3 | Carefully remove the old components, taking care not to damage adjacent elements. |
| 4 | Align the new friction materials correctly and secure them firmly using the wrench. |
| 5 | Check alignment and adjust as necessary to ensure even contact. |
| 6 | Test functionality by applying pressure gently before a full ride. |
By following these steps, you can ensure that your stopping components remain in optimal condition, providing reliable performance during your journeys.
Choosing the Right Brake Cables
Selecting appropriate cables is crucial for optimizing the performance of your stopping system. The right cables enhance responsiveness, ensuring a smooth and effective operation. When choosing, it’s essential to consider various factors such as compatibility, material quality, and environmental conditions.
Types of Cables
Different types of cables are available, each designed for specific applications. Here’s a brief overview:
| Type | Description | Best Use |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | Basic construction, suitable for everyday use. | Casual riding |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion-resistant, providing durability and longevity. | Wet or humid environments |
| Compressionless | Designed for precise control, minimizing slack during operation. | Performance cycling |
Factors to Consider
When making your choice, consider the following elements:
- Compatibility with your system’s specifications
- Length of the cables to ensure proper fitting
- Quality of materials for improved performance
Tools Required for Brake Maintenance

Proper upkeep of stopping mechanisms is essential for safety and performance. Having the right tools on hand not only facilitates efficient maintenance but also enhances the longevity of these critical components. This section outlines the necessary instruments to ensure effective care and adjustments for optimal functionality.
Essential Tools
To perform routine maintenance, a selection of basic instruments is required. These tools enable adjustments, replacements, and thorough inspections to ensure all elements are in prime condition.
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Adjustable Wrench | For loosening and tightening nuts and bolts. |
| Screwdriver Set | To adjust screws and fasteners on the mechanism. |
| Allen Keys | For hex screws often found in assembly. |
| Cleaning Brush | To remove dirt and grime from surfaces. |
| Lubricant | To ensure smooth operation and prevent corrosion. |
Additional Recommendations
For more comprehensive tasks, consider investing in specialized tools such as torque wrenches and calipers. These can help achieve precise adjustments and measurements, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
Upgrading Your Brake System
Improving your stopping mechanism can significantly enhance your riding experience, ensuring greater safety and control. Whether you’re an avid rider or a casual enthusiast, investing in higher-quality components can make a noticeable difference in performance. This section will explore various enhancements you can implement to elevate the efficiency of your stopping system.
Choosing High-Performance Components
When considering an upgrade, selecting superior elements is crucial. Look for options that offer better modulation and responsiveness. High-quality materials, such as aluminum or carbon fiber, can provide both durability and weight savings. Additionally, examine the compatibility of new components with your existing setup to ensure seamless integration.
Regular Maintenance Practices
Maintaining your stopping system is as essential as upgrading. Regular checks and adjustments can prevent wear and tear, ensuring consistent performance. Clean and lubricate the mechanisms regularly to enhance their lifespan and functionality. Adopting these practices will complement your upgrades, providing a reliable and effective stopping system.
Safety Tips for V Brake Use
Ensuring a smooth and secure riding experience requires attention to certain safety measures when utilizing the stopping mechanism. Proper maintenance and awareness can significantly enhance performance and reliability.
Regularly inspect the components for wear and tear. Check for frayed cables, worn pads, and any signs of corrosion. Timely replacement of these elements is crucial for optimal functionality.
Adjust the mechanism to ensure even pressure on both sides. Misalignment can lead to uneven wear and reduced stopping power. A well-calibrated system not only enhances control but also increases safety.
Make sure to keep the surfaces clean and free from debris. Contaminants can interfere with the effectiveness of the stopping mechanism, leading to longer stopping distances. A simple wipe can make a significant difference.
Familiarize yourself with the technique of applying pressure. Gradual engagement rather than abrupt force can help maintain stability and avoid skidding. This practice is particularly important in wet or slippery conditions.
Lastly, always wear appropriate safety gear. Protective equipment such as helmets, gloves, and reflective clothing can provide additional security while navigating various terrains.