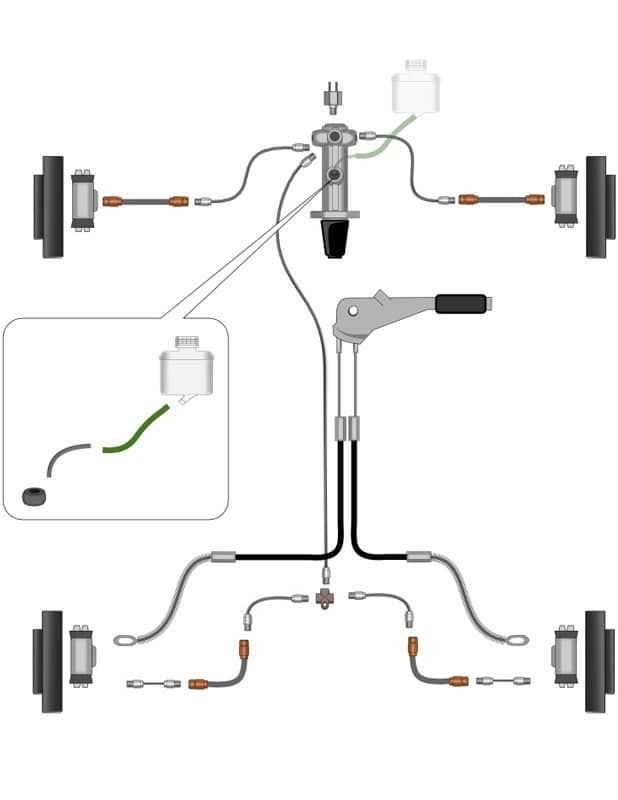
In the realm of vehicle maintenance, comprehending the various elements that contribute to the effective functioning of hydraulic mechanisms is essential. These components work together to ensure optimal performance, providing the necessary support for smooth operation and safety on the road.
Each segment of the hydraulic assembly plays a critical role, from facilitating fluid movement to connecting different sections seamlessly. A clear grasp of these essential elements allows for better maintenance practices and informed decision-making when addressing any issues that may arise.
By exploring the configuration and relationships between these components, one can gain valuable insights into their functionality and importance. This knowledge not only enhances your understanding but also empowers you to engage in more effective troubleshooting and repairs.
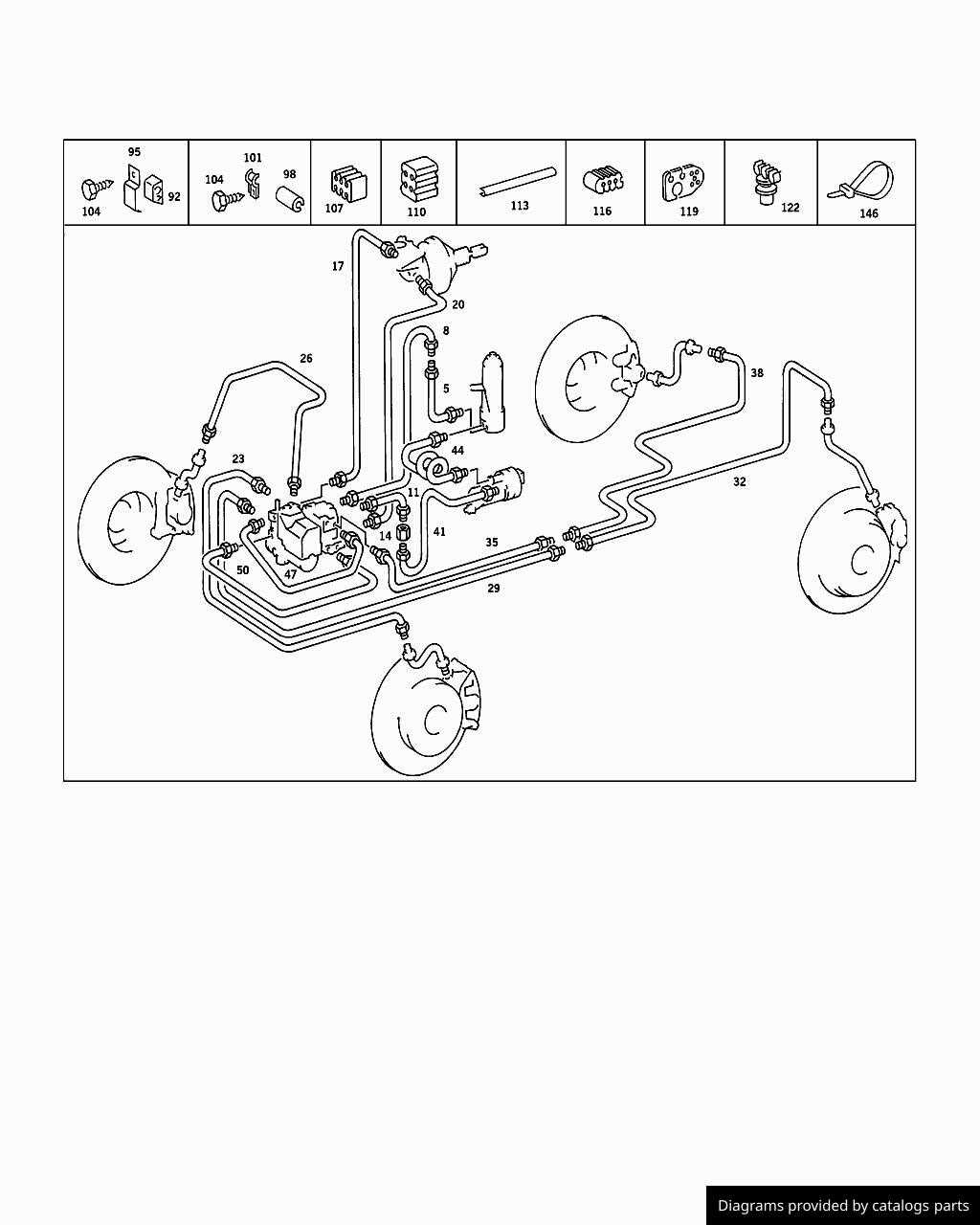
The effective functioning of a stopping system relies on various components, each serving a specific role in ensuring safety and performance. Understanding the purpose of these elements can enhance vehicle maintenance and promote safer driving practices.
Essential Components and Their Roles
-
Master Cylinder:
This device generates hydraulic pressure when the driver applies the stopping mechanism. It converts force from the pedal into fluid pressure, enabling the system to engage effectively.
-
Caliper:
This crucial element houses the friction material and squeezes it against the rotating surface to create friction and slow down the vehicle.
-
Pads:
These are the materials that grip the rotor, providing the necessary friction to halt the motion. Their quality and condition are vital for optimal performance.
-
Rotors:
Rotors serve as the surface against which the pads make contact. Their design and material affect the heat dissipation and overall efficiency of the stopping mechanism.
Supporting Elements

-
Brake Lines:
These conduits carry hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the calipers. They must be intact to maintain pressure and responsiveness.
-
Reservoir:
This container holds the hydraulic fluid, ensuring there is enough fluid for the system to function correctly.
-
ABS Module:
This component helps prevent wheel lock-up during sudden stops, improving stability and control.
Each of these components works in concert to ensure reliable stopping power, underscoring the importance of regular inspections and maintenance for optimal performance.
Common Types of Brake Lines
The essential components responsible for fluid transmission in a vehicle’s stopping mechanism come in various forms, each designed to meet specific requirements. Understanding the distinctions among these elements is crucial for effective maintenance and repairs, ensuring optimal performance and safety on the road.
Flexible Hoses
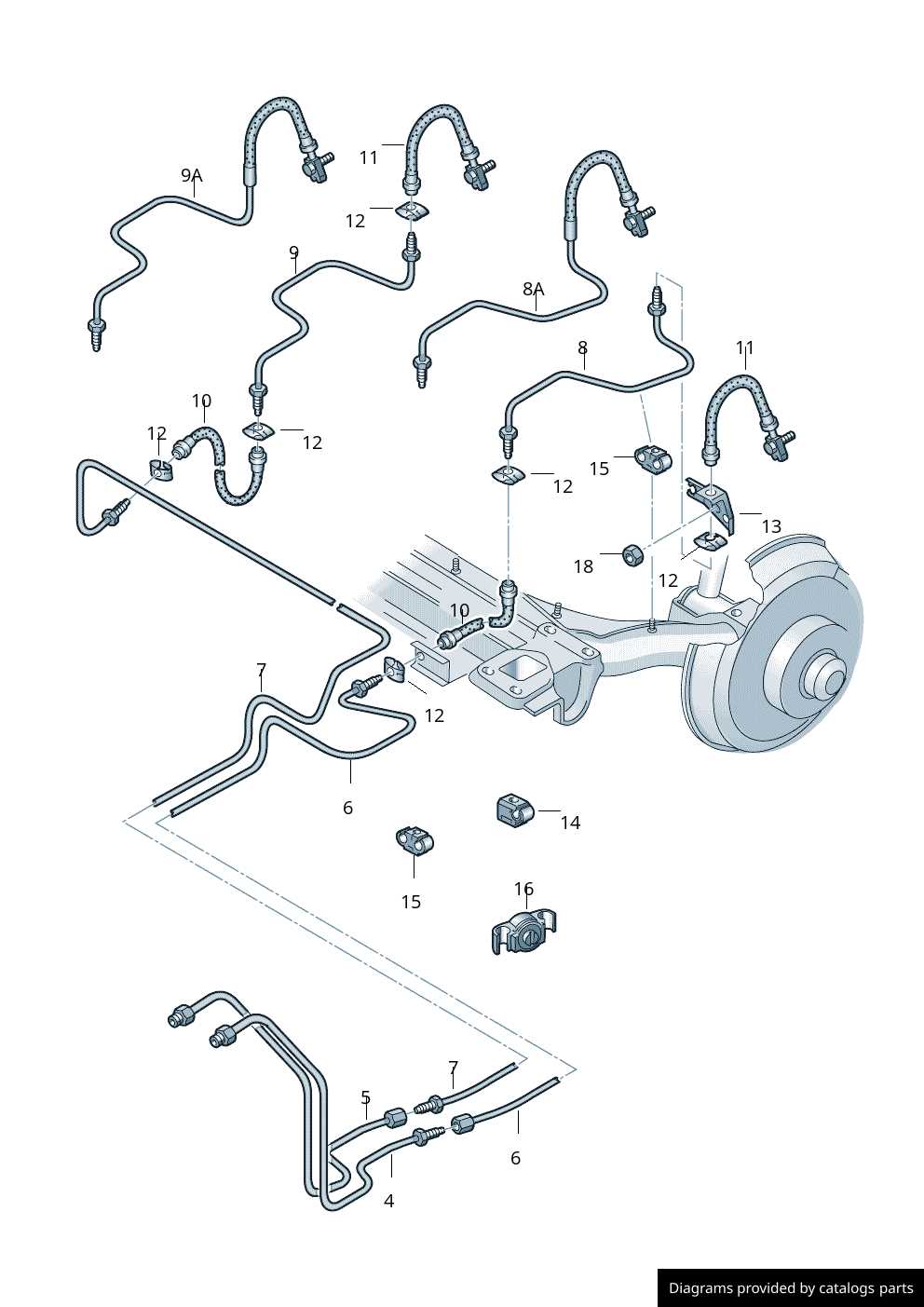
Flexible hoses are made from durable materials that allow for movement and expansion during operation. They are typically used in areas where motion occurs, providing the necessary flexibility to accommodate the dynamics of a vehicle’s suspension system. These hoses are designed to withstand high pressure and resist wear from environmental factors.
Rigid Tubes
Rigid tubes, often constructed from steel or aluminum, offer a more permanent solution for fluid delivery. They are commonly found in fixed locations where flexibility is not needed, providing strength and resistance to external damage. These components are essential for maintaining consistent pressure and reliability throughout the hydraulic system.
How to Identify Brake Issues
Recognizing problems with your vehicle’s stopping mechanism is crucial for safety. Regular monitoring of its functionality can prevent potential hazards. Look for specific signs that may indicate a need for attention, ensuring a smooth and secure driving experience.
Common indicators of malfunction include unusual noises, changes in responsiveness, or visual abnormalities. Here are some symptoms to watch for:
| Symptoms | Possible Causes |
|---|---|
| Squeaking or grinding sounds | Worn friction material or debris |
| Unresponsive or spongy feel | Air in the system or fluid leak |
| Vibrations during operation | Warped rotor or uneven surface |
| Warning lights on dashboard | System malfunction or low fluid level |
| Fluid leaks under the vehicle | Damaged hoses or connections |
Paying attention to these signs allows for timely intervention, ensuring your vehicle operates safely. If any of these issues arise, consulting a professional technician for a thorough inspection is advisable.
Brake System Maintenance Tips
Proper upkeep of your vehicle’s stopping mechanisms is crucial for safety and optimal performance. Regular checks and timely interventions can significantly enhance the longevity of these components while ensuring reliable operation during your travels.
Regular Inspection
- Examine fluid levels frequently to prevent leaks and maintain effectiveness.
- Check for wear and tear on the pads and discs, replacing them when necessary.
- Inspect hoses and connections for any signs of damage or degradation.
Timely Replacement
- Change fluid according to the manufacturer’s recommendations to ensure efficient operation.
- Replace any worn or damaged components promptly to avoid further issues.
- Consider upgrading to higher-quality materials for improved performance and durability.
Tools Needed for Brake Repairs
Performing maintenance on your vehicle’s stopping system requires a specific set of instruments to ensure a thorough and effective process. Having the right equipment at your disposal not only makes the task easier but also enhances safety and efficiency during repairs.
Essential tools include a wrench set for loosening and tightening fittings, along with a socket set for more accessible access to various components. Additionally, a torque wrench is crucial for applying the correct force to ensure secure connections without damaging parts.
To facilitate fluid management, a drain pan is advisable, as it allows for clean collection of any expelled liquids. Furthermore, pliers and a screwdriver set will aid in handling clips and fasteners that hold components in place.
For enhanced visibility and precision, consider using a flashlight or work light, particularly in dimly lit areas. Lastly, a safety kit containing gloves, goggles, and a first-aid kit ensures that you are prepared for any unexpected occurrences during the maintenance process.
Installation Process for Brake Lines
This section outlines the essential steps for effectively securing fluid conduits within a vehicle’s braking system. Proper installation ensures optimal performance and safety, reducing the risk of leaks and failures during operation.
Preparation Before Installation
- Gather necessary tools: wrenches, pliers, and a torque wrench.
- Ensure all components are clean and free from contaminants.
- Review the vehicle’s service manual for specific instructions.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide
- Start by locating the mounting points for the fluid conduits.
- Align the new conduits with the existing fittings.
- Secure the connections hand-tight, ensuring proper seating.
- Use a torque wrench to tighten connections according to specifications.
- Inspect the entire assembly for any misalignments or obstructions.
- Once satisfied, perform a system pressure test to check for leaks.
Safety Precautions During Repairs
Ensuring a secure working environment is essential when undertaking maintenance tasks. Proper measures help prevent accidents and injuries, ensuring both personal safety and the integrity of the equipment involved. Awareness and preparation can significantly reduce the risks associated with mechanical work.
Essential Safety Measures
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and sturdy footwear.
- Ensure the work area is well-ventilated to prevent inhalation of harmful fumes or dust.
- Use tools that are in good condition and appropriate for the task at hand.
- Keep the workspace organized to avoid clutter that can lead to slips or trips.
Proper Handling and Disposal
- Carefully handle all components, avoiding contact with sharp edges or hot surfaces.
- Dispose of any hazardous materials, such as oils or fluids, in accordance with local regulations.
- Never work on the system when it is under pressure or when components are hot.
Upgrading Your Brake System
Enhancing your stopping mechanism is crucial for improving safety and performance. Upgrading can lead to better response times, increased durability, and an overall enhanced driving experience. Whether you’re an avid racer or a daily commuter, investing in superior components is always a wise decision.
Key Benefits of an Upgrade
- Improved stopping power for quicker deceleration.
- Enhanced durability, reducing the frequency of replacements.
- Better heat dissipation, minimizing the risk of overheating.
- Increased pedal feel for more precise control.
Components to Consider
- Rotors: Look for options made from high-performance materials for enhanced longevity and heat resistance.
- Calipers: Upgrading to multi-piston designs can significantly increase force applied to the discs.
- Fluid: High-temperature brake fluid ensures optimal performance under stress.
- Pads: Choosing advanced compounds can enhance friction and reduce fade.
Diagnosing Brake Line Problems
Identifying issues with the fluid transport system is crucial for ensuring safety and performance in any vehicle. When malfunctions occur, they can manifest in various ways, often requiring a systematic approach to diagnosis. Understanding the common indicators can help in pinpointing the underlying causes and determining the necessary corrective measures.
Common Symptoms of Fluid Transport Issues
- Unresponsive or soft pedal feel
- Fluid leakage under the vehicle
- Uneven wear on tires
- Unexpected noises during operation
- Warning lights on the dashboard
Steps for Identifying Problems
- Conduct a visual inspection for any visible leaks or damaged components.
- Check the fluid levels in the reservoir to ensure they are adequate.
- Test the pedal feel by applying pressure and noting any irregularities.
- Listen for unusual sounds when the system is engaged, which may indicate internal issues.
- Consult a professional if symptoms persist, as advanced diagnostics may be necessary.