Every vehicle consists of numerous elements that work together to ensure smooth operation. When it comes to maintaining or repairing a vehicle, it’s important to have a clear understanding of how these individual components interact within the system. Whether you’re focusing on the engine, suspension, or electrical systems, knowing the details of each part and its function is essential for effective maintenance.
In this section, we will explore the various systems that make up your vehicle and how they are interconnected. Understanding this layout can help in troubleshooting issues, performing repairs, and ensuring that all the components are functioning efficiently. With the right approach, keeping your vehicle in optimal condition becomes much easier and more manageable.
2005 Buick Rendezvous Parts Overview
This section offers a detailed look into the various components and systems that make up the vehicle, providing a comprehensive understanding of its mechanical structure. We’ll explore key assemblies and essential elements necessary for proper functionality, ensuring a smooth and efficient driving experience. By understanding the intricacies of each component, you can maintain optimal performance and address any potential issues effectively.
Main Structural Components
From the framework that supports the vehicle to the suspension system responsible for a comfortable ride, every element plays a vital role. The bodywork, including panels and doors, protects the interior while ensuring safety. Additionally, the chassis and undercarriage offer stability and contribute to the vehicle’s overall durability.
Engine and Transmission Systems
The powertrain serves as the heart, converting fuel into motion with the help of the engine and gearbox. Each part within these systems is crucial for generating power, delivering torque, and shifting smoothly. These elements work in tandem to ensure reliability and efficiency throughout various driving conditions.
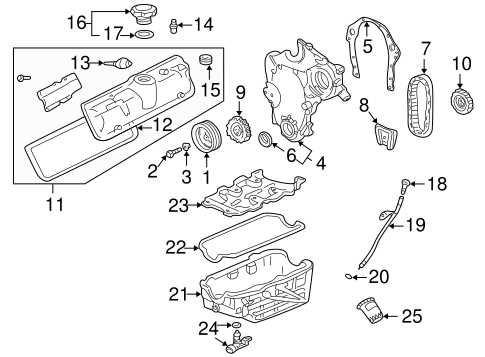
Engine Components and Layout
The arrangement and structure of the various elements within the engine play a crucial role in ensuring efficient performance. Understanding the placement and function of these components helps in maintaining the system’s overall functionality.
Below is an outline of the essential elements that form the foundation of the engine’s internal configuration:
- Combustion Chamber – The area where fuel and air mix to create the energy that powers the vehicle.
- Pistons – Cylindrical elements that move within the combustion chamber to transfer energy from the combustion process.
- Crankshaft – Converts the piston’s vertical motion into rotational motion that drives the vehicle forward.
- Valves – Control the intake of air and fuel and the release of exhaust gases.
- Camshaft – Works in sync with the crankshaft to open and close the valves at the correct times.
The precise coordination of these components is vital for smooth operation. Each part must function together to maintain optimal engine performance, ensuring reliability and longevity of the system.
Suspension System Breakdown
The suspension system is crucial for ensuring a smooth and stable ride, as it absorbs shocks from uneven surfaces and helps maintain control over the vehicle. This system works by distributing the weight evenly and keeping the tires in constant contact with the ground, which improves both comfort and safety.
Key components of the suspension include springs, shock absorbers, and control arms. Each of these elements plays an essential role in supporting the vehicle’s structure and ensuring proper alignment. Springs handle the weight distribution, while shock absorbers reduce the impact of road irregularities, and control arms guide the movement of the wheels.
By maintaining the suspension system in optimal condition, drivers can ensure a stable, comfortable ride and enhance the overall performance of the vehicle.
Electrical System Diagram and Key Parts
The electrical layout in a vehicle plays a crucial role in ensuring all components function effectively. This section provides an overview of how the wiring and key elements work together to maintain seamless electrical flow throughout the system.
Main Wiring Components
- Battery: The main power source that supplies energy to the entire electrical system.
- Alternator: Converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, recharging the battery and powering essential systems.
- Fuse Box: Protects circuits from overloads, ensuring the safe distribution of electricity.
Crucial Connectors and Relays
Connectors and relays act as intermediaries between various systems, ensuring reliable communication between electrical parts.
- Relays: Serve as switches that manage high-power components, such as headlights or fans, by using low-power signals.
- Connectors: Link different sections of the wiring system, allowing for efficient transmission of electrical signals.
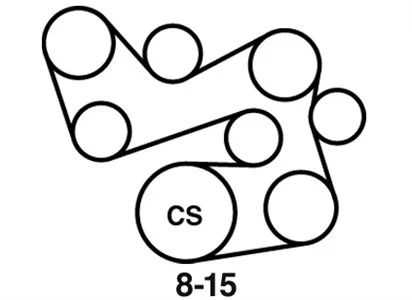
Transmission Assembly Details
The transmission system is a critical component that ensures the vehicle’s ability to transfer power from the engine to the wheels efficiently. This complex mechanism consists of multiple interconnected elements, each designed to handle specific functions within the system. Proper understanding of how these elements work together is essential for maintaining performance and prolonging the lifespan of the vehicle’s drivetrain.
Key components within the transmission include the gear sets, clutches, and fluid lines, all working in unison to provide smooth shifting and optimal power distribution. Regular maintenance and timely inspection of these elements can help prevent common issues, ensuring reliability and smooth operation on the road.
Additionally, the integration of modern technologies, such as electronic control units, has enhanced the precision and efficiency of the transmission system, allowing for better fuel economy and improved driving dynamics.
Brake System Structure and Components
The brake system is a critical safety feature in any vehicle, designed to slow down or stop the motion effectively. It consists of various interconnected components that work together to ensure reliable and efficient braking performance. Understanding the structure and function of these elements is essential for proper maintenance and troubleshooting.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Brake Pedal | Initiates the braking process when pressed by the driver. |
| Master Cylinder | Converts the force applied on the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure. |
| Brake Lines | Transfer hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the brake calipers or wheel cylinders. |
| Brake Calipers | Houses the brake pads and applies pressure to them, creating friction against the rotors. |
| Brake Pads | Friction material that contacts the brake rotor to slow down the vehicle. |
| Brake Rotors | Metal discs that are squeezed by the brake pads to stop the wheels from turning. |
| Wheel Cylinders | Used in drum brake systems to push the brake shoes against the drum. |
| Brake Shoes | Friction materials that press against the drum in drum brake systems. |
Cooling System Parts and Functionality
The cooling mechanism of a vehicle is essential for maintaining optimal operating temperatures and preventing overheating. It consists of various components that work in unison to ensure that the engine runs efficiently and remains within a safe temperature range. Understanding the individual roles of each component helps in diagnosing issues and ensuring longevity.
Key Components
The main elements of the cooling mechanism include the radiator, water pump, thermostat, and cooling fans. The radiator dissipates heat absorbed by the coolant, while the water pump circulates the coolant throughout the system. The thermostat regulates the flow of coolant based on the engine’s temperature, ensuring that the engine warms up quickly and operates at its ideal temperature. Cooling fans assist in drawing air through the radiator to enhance heat dissipation, especially during low-speed conditions.
Functionality Overview
Each component plays a crucial role in the overall efficiency of the cooling system. When the engine generates heat, the coolant absorbs it and flows to the radiator, where it releases heat into the atmosphere. The thermostat monitors the engine temperature and controls the coolant flow, ensuring that the engine does not overheat. If any of these components fail, it can lead to significant overheating issues, resulting in engine damage. Regular maintenance and inspections are vital to ensure that the cooling system operates smoothly and effectively.
Fuel System Components Explained
The fuel system plays a critical role in the overall performance and efficiency of a vehicle. Understanding its various components can help in diagnosing issues and ensuring optimal functionality. Each part contributes to the effective delivery and management of fuel, which is essential for engine operation.
Here are the key components typically found in a fuel system:
- Fuel Tank: This is where the fuel is stored before being sent to the engine. It is designed to hold various types of fuel safely and securely.
- Fuel Pump: The fuel pump is responsible for transporting fuel from the tank to the engine. It ensures that the right amount of fuel is delivered under the necessary pressure.
- Fuel Filter: This component removes impurities and contaminants from the fuel before it reaches the engine. A clean fuel filter is vital for maintaining engine performance.
- Fuel Injectors: Fuel injectors spray the fuel directly into the engine’s combustion chamber. Their precision is crucial for achieving optimal fuel-air mixture and combustion efficiency.
- Fuel Lines: These are the conduits through which fuel flows from the tank to the engine. They must be durable and resistant to corrosion and leaks.
Each of these elements works together to ensure that the engine receives the fuel it needs, contributing to smooth operation and efficient performance.
Interior Controls and Dashboard Layout
The arrangement of controls and instruments within the cabin plays a crucial role in the overall driving experience. A well-designed dashboard enhances usability and ensures that essential functions are easily accessible to the driver and passengers alike. Understanding the layout and functionality of various elements is key to maximizing comfort and convenience during travel.
- Control Placement: The positioning of controls should prioritize ease of access. Essential features, such as climate control and infotainment systems, are strategically located within reach of the driver.
- Instrumentation Cluster: This area typically houses key indicators such as speed, fuel level, and engine temperature, providing vital information at a glance.
- Multimedia System: Many vehicles incorporate advanced technology that includes touchscreens or buttons, allowing for seamless interaction with navigation, audio, and connectivity features.
Designing a user-friendly dashboard involves balancing aesthetics with functionality. Thoughtful organization of controls and clear labeling contribute to a more intuitive experience, ultimately enhancing safety and enjoyment on the road.
Steering Mechanism and Parts
The steering system is a crucial component of any vehicle, enabling precise control and direction. It encompasses various elements that work in harmony to facilitate smooth handling and responsiveness. Understanding the configuration and function of these components is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Components of the steering assembly include the steering wheel, steering column, and the rack and pinion system. The steering wheel allows the driver to guide the vehicle, while the steering column connects the wheel to the rest of the mechanism. The rack and pinion setup translates the rotational motion of the wheel into lateral movement of the tires.
Regular inspection of the steering mechanism is vital to ensure safety and optimal performance. Worn-out or damaged components can lead to steering difficulties and compromise the vehicle’s handling. Keeping an eye on fluid levels and ensuring that all connections are secure can prevent potential issues and extend the lifespan of the system.
Exhaust System Parts Overview
The exhaust system plays a crucial role in the overall functionality of a vehicle, ensuring that harmful gases are effectively expelled from the engine while enhancing performance. Understanding the components that make up this system can help in maintaining optimal operation and improving longevity.
- Muffler: This component reduces noise produced by the engine, allowing for a quieter ride.
- Exhaust Manifold: This part collects gases from the engine cylinders and directs them into the exhaust pipe.
- Catalytic Converter: A vital component that converts harmful emissions into less toxic substances before they exit the vehicle.
- Exhaust Pipe: These pipes transport gases from the manifold to the rear of the vehicle, facilitating proper venting.
- Resonator: Often located near the muffler, it fine-tunes the sound of the exhaust system, contributing to a pleasant auditory experience.
Maintaining these elements in good condition is essential for performance and compliance with environmental regulations. Regular inspections and timely replacements can prevent potential issues and enhance the efficiency of the exhaust system.
Lighting System and Wiring Diagram
The illumination mechanism in vehicles plays a crucial role in ensuring safety and visibility during operation, especially in low-light conditions. Understanding the configuration and interconnections of the lighting components is essential for effective troubleshooting and maintenance. This section outlines the various elements of the lighting system and the corresponding wiring layout.
Components of the Illumination System
The illumination setup consists of several critical components, including headlights, taillights, turn signals, and interior lights. Each of these elements is designed to serve a specific function, enhancing the overall visibility of the vehicle. Headlights provide primary illumination for the road ahead, while taillights signal the presence of the vehicle to those behind. Turn signals are essential for indicating directional changes, and interior lights enhance visibility within the cabin.
Wiring Configuration

The wiring network connects these components to the vehicle’s electrical system, allowing for efficient operation. Each light fixture is linked to a dedicated circuit, which facilitates power distribution and ensures that all lighting elements function correctly. Understanding the layout of these connections can aid in diagnosing issues, such as blown fuses or faulty wiring, ultimately leading to more effective repairs and maintenance.
Body and Exterior Panels Layout
This section provides a comprehensive overview of the arrangement and configuration of the outer structure of the vehicle. Understanding the layout of various components is essential for maintenance and repairs, ensuring that each part fits seamlessly with the overall design. Proper alignment and functionality of these elements contribute significantly to the aesthetics and performance of the automobile.
The exterior panels serve not only as protective barriers against environmental factors but also play a crucial role in the vehicle’s appearance. The following table outlines the key components involved in the outer shell of the automobile.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Front Fenders | Located on both sides of the front section, these panels cover the wheel wells and contribute to the car’s aerodynamic profile. |
| Hood | The hinged cover that rests over the engine compartment, providing access for maintenance while enhancing the vehicle’s design. |
| Doors | Access points to the interior, these panels vary in style and design, offering convenience and security for passengers. |
| Rear Quarter Panels | Situated behind the rear doors, these panels complete the side profile and often house windows or taillights. |
| Tailgate | The rear panel that provides access to the trunk or cargo area, designed for easy loading and unloading. |
| Bumpers | Located at the front and rear, these components absorb impact and protect the vehicle’s body from damage during low-speed collisions. |