When it comes to vehicle maintenance and repair, having a clear visual guide for various mechanical systems can be incredibly useful. Knowing how different assemblies and mechanical units fit together helps in troubleshooting and efficient part replacement. Whether you are an experienced mechanic or simply trying to understand the workings of your automobile, access to a well-structured layout is indispensable.
This section provides an in-depth look into the various essential assemblies and mechanisms within your vehicle. By breaking down individual systems, you will gain a deeper understanding of how each element interacts with others to ensure smooth operation. Familiarizing yourself with this arrangement can save time and reduce confusion when performing repairs or upgrades.
Comprehensive Overview of 2017 Chevy Equinox Components
The functionality and performance of this model rely on an interconnected system of various elements. Each of these plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth operation, safety, and overall driving experience. Below is an exploration of key features and their significance in the vehicle’s overall structure.
- Engine System: The power source that drives the vehicle, this system integrates components that manage fuel intake, combustion, and power output.
- Transmission Mechanism: Responsible for managing gear changes, this mechanism ensures that the vehicle operates efficiently across different speeds and terrains.
- Suspension and Steering: These elements contribute to comfort and handling, absorbing road shocks and providing precise control over the vehicle’s direction.
- Brake Assembly: A vital safety feature, the braking system includes elements that work together to decelerate and stop the vehicle under various conditions.
- Cooling and Heating Units: These components regulate the vehicle’s temperature, ensuring that both the engine and passengers maintain optimal conditions during operation.
- Understanding Key Engine Parts and Layout
The structure under the hood of any vehicle is composed of various critical components, each playing a vital role in its overall operation. Familiarity with the essential elements and their arrangement is key to grasping how everything works together seamlessly. Whether it’s providing power, managing airflow, or controlling temperature, each section contributes to the vehicle’s functionality in a unique way.
Component Function Engine Block The core foundation that houses the cylinders and other integral components responsible for power generation. Cylinder Head A part mounted atop the engine block, containing the valves that manage the flow of air and fuel into the engine. Crankshaft Converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational movement, which powers the drivetrain. Essential Transmission Components Breakdown
Understanding the key elements within a vehicle’s transmission system is crucial for maintaining optimal performance. Each part plays a significant role in ensuring smooth operation, power delivery, and longevity of the drivetrain. This section will provide a detailed overview of the most important components that contribute to the functionality and reliability of the transmission system.
Component Description Torque Converter This mechanism connects the engine to the transmission, allowing the vehicle to remain stationary while the engine is running and smoothly transferring power to the drivetrain when acceleration is needed. Planetary Gear Set Responsible for adjusting gear ratios, Exploring the Suspension System Structure
The suspension system plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth and stable ride by connecting the vehicle to its wheels while absorbing road irregularities. It is designed to balance comfort and handling, providing safety and performance under various driving conditions. This intricate setup helps distribute weight and maintain stability, ensuring optimal contact between the tires and the road surface.
Composed of several interconnected elements, the system includes components that manage vertical movement and reduce the impact of uneven terrain. Springs, dampers, and linkages work together to minimize vibrations and provide a controlled driving experience. By adjusting to different forces and road conditions, the suspension system helps maintain vehicle control and passenger comfort.
Diagram of Electrical System and Wiring
The electrical framework of a vehicle is an intricate network that ensures proper functionality of various components. It includes a variety of connections that enable the seamless operation of lighting, control systems, and other vital electronics. Understanding how the wiring is arranged can provide insight into maintenance and troubleshooting when issues arise. This section explores the core elements of the electrical infrastructure and how different circuits are connected throughout the vehicle.
The electrical system includes numerous circuits that are responsible for delivering power from the energy source to specific components. These circuits are protected by fuses and relays to prevent overload and damage. Proper arrangement of cables and connectors ensures that energy flows efficiently, reducing potential risks and ensuring optimal performance. This layout is essential for maintaining the overall health of the vehicle’s electronics, from lighting systems to engine management.
Brake System Parts and Their Roles

The braking mechanism in vehicles is crucial for ensuring safety and performance. Each component plays a vital role in the overall functioning, contributing to effective deceleration and stopping power. Understanding these elements can enhance maintenance efforts and facilitate informed decisions during repairs or upgrades.
Component Function Brake Pads Friction material that presses against the rotor to slow down the wheel. Brake Rotors Disc that the brake pads clamp onto to create friction, enabling stopping. Calipers Holds the brake pads and squeezes them against the rotors when the brake pedal is pressed. Brake Lines Hoses that carry brake fluid from the master cylinder to the calipers. Master Cylinder Converts the force from the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure to activate the braking system. Brake Fluid Transmits the force from the brake pedal to the calipers, enabling the braking action. Fuel System Components in Detail
The fuel system plays a crucial role in the efficient operation of an internal combustion engine. This system is responsible for delivering the correct amount of fuel to the engine, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. Each element within the system works in harmony to facilitate the smooth flow of fuel, maintaining the necessary pressure and purity for combustion.
Key Elements of the Fuel System
At the heart of the fuel system are several essential components, including the fuel pump, filter, and injectors. The fuel pump is tasked with drawing fuel from the tank and delivering it under pressure to the engine. A filter is also critical, as it removes contaminants and impurities that could harm engine performance. Finally, the injectors are responsible for precisely delivering the fuel into the combustion chamber, where it mixes with air for combustion.
Importance of Maintenance
Regular maintenance of the fuel system is vital to ensure longevity and optimal performance. This includes checking the fuel filter for blockages, inspecting the fuel pump for wear, and ensuring that the injectors are functioning correctly. Neglecting these components can lead to decreased fuel efficiency, increased emissions, and ultimately, engine damage.
Cooling System Parts and Functions
The cooling system in a vehicle plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal engine temperature. It prevents overheating and ensures efficient operation by dissipating heat generated during combustion. Understanding the components involved can help in diagnosing issues and maintaining the system effectively.
Main Components

- Radiator: The primary component responsible for dissipating heat. It circulates coolant and releases heat into the air.
- Water Pump: Facilitates the movement of coolant throughout the system, ensuring efficient circulation.
- Thermostat: Regulates the coolant flow based on temperature, maintaining the engine at an optimal operating temperature.
- Coolant Reservoir: Stores excess coolant and allows for easy monitoring of coolant levels.
- Heater Core: Acts as a small radiator for the cabin, providing warmth to the interior of the vehicle.
Functions of the Cooling System
- Maintaining the engine temperature within the designed range.
- Preventing engine components from warping due to excessive heat.
- Ensuring efficient fuel combustion by regulating temperature.
- Providing heat for the vehicle’s interior when needed.
- Facilitating the longevity of engine components through proper thermal management.
Regular maintenance of these components is essential to ensure the cooling system functions efficiently, prolonging the life of the engine and enhancing vehicle performance.
Interior Components and Dashboard Layout
The interior of a modern vehicle is designed with a focus on both functionality and aesthetics. The arrangement of various elements within the cabin significantly contributes to the overall driving experience, offering convenience and comfort. Each component plays a vital role in creating an environment that is not only visually appealing but also practical for everyday use.
Key Elements of the Dashboard
The dashboard serves as the central hub for the driver, housing essential controls and displays. Instrument clusters provide crucial information such as speed, fuel levels, and engine status, ensuring the driver remains informed. Additional features, including infotainment systems, climate controls, and navigation interfaces, are strategically placed for easy access, enhancing the user experience.
Comfort and Convenience Features
Interior design also incorporates various comfort elements, such as seating arrangements, storage solutions, and ambient lighting. Ergonomically designed seats provide support during long drives, while cleverly integrated compartments keep personal items organized. These thoughtful inclusions ensure that occupants enjoy a pleasant journey, making every trip enjoyable.
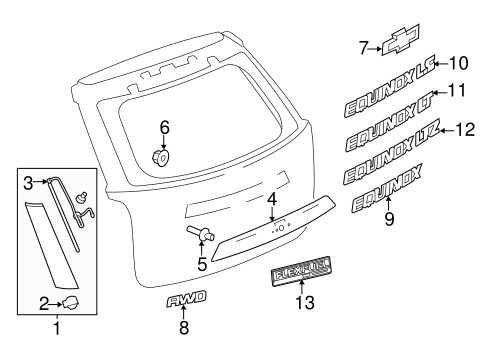
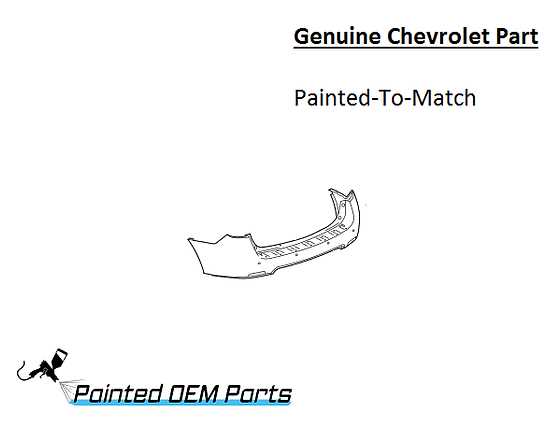
Body and Exterior Panels Explained
The structure and outer surfaces of a vehicle play a crucial role in both aesthetics and functionality. These components not only contribute to the overall design but also serve essential purposes such as protection, aerodynamics, and vehicle integrity. Understanding the various elements that make up the outer shell of an automobile can enhance maintenance practices and inform future upgrades.
Main Components
- Fenders: These sections surround the wheel wells and protect the vehicle from debris while enhancing the overall appearance.
- Hoods: Covering the engine compartment, hoods provide access for maintenance and contribute to the vehicle’s silhouette.
- Doors: Essential for entry and exit, doors are designed for both functionality and security.
- Trunk Lids: These panels facilitate access to the storage compartment at the rear of the vehicle.
- Bumpers: Positioned at the front and rear, bumpers absorb impact and minimize damage during collisions.
Materials Used
Modern vehicles often utilize a variety of materials for their exterior components:
- Steel: Known for its strength and durability, steel is commonly used in body panels.
- Aluminum: Lightweight and resistant to corrosion, aluminum is increasingly popular for various exterior parts.
- Plastic: Used for components such as bumpers and trims, plastic helps reduce weight and cost while offering flexibility in design.
- Fiberglass: This composite material is favored for its lightweight properties and ease of molding into complex shapes.
Exhaust System Diagram and Parts
The exhaust assembly plays a crucial role in the overall performance and efficiency of a vehicle. It is responsible for directing harmful gases away from the engine, reducing emissions, and maintaining optimal engine function. Understanding the components involved in this system can help vehicle owners identify potential issues and facilitate necessary repairs or upgrades.
At the heart of the exhaust setup is the manifold, which collects exhaust gases from the engine cylinders. These gases then travel through the exhaust pipes, which channel them towards the rear of the vehicle. Along the way, they pass through various components, such as catalytic converters that reduce harmful emissions, resonators that fine-tune sound, and mufflers that minimize noise output.
Maintaining a well-functioning exhaust assembly is essential for vehicle longevity and compliance with environmental regulations. Regular inspections can help ensure that each element, from the manifold to the tailpipe, is in good condition, allowing the engine to operate efficiently and quietly.
Steering Mechanism Parts and Functions
The steering system of a vehicle plays a critical role in providing control and maneuverability. Understanding the various components involved in this system and their respective functions is essential for maintaining optimal performance and safety.
Main Components
- Steering Wheel: The primary interface for the driver, allowing for directional control.
- Steering Column: Connects the steering wheel to the mechanism, often housing various controls.
- Rack and Pinion: A type of gear mechanism that converts rotational motion into linear motion, enabling the wheels to turn.
- Steering Gearbox: Houses the gears that assist in converting the driver’s input into wheel movement.
- Power Steering Pump: Provides hydraulic pressure to assist in steering, making it easier to turn the wheel.
Functions of Key Elements
- The steering wheel allows the driver to communicate their intended direction.
- The steering column transmits this input down to the steering mechanism.
- The rack and pinion mechanism translates the circular motion of the steering wheel into the lateral movement of the wheels.
- The steering gearbox amplifies the driver’s input, ensuring smooth and responsive steering.
- The power steering pump reduces the effort needed to turn the wheel, enhancing driver comfort.