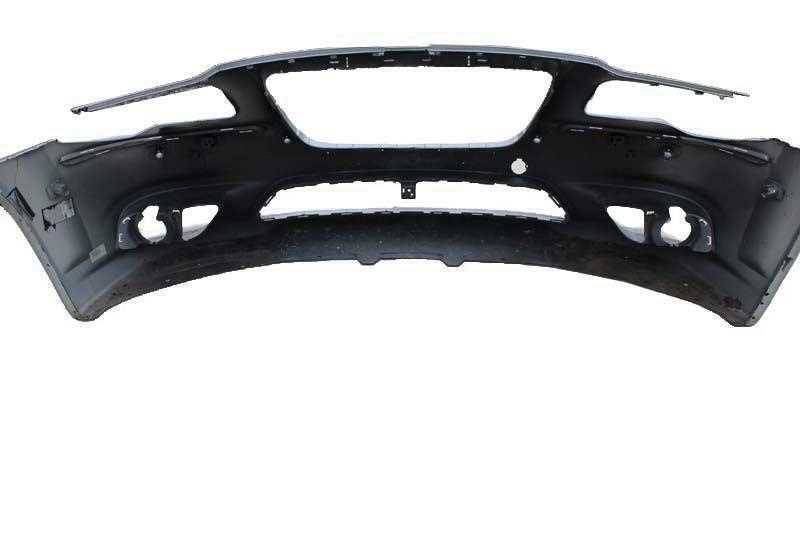
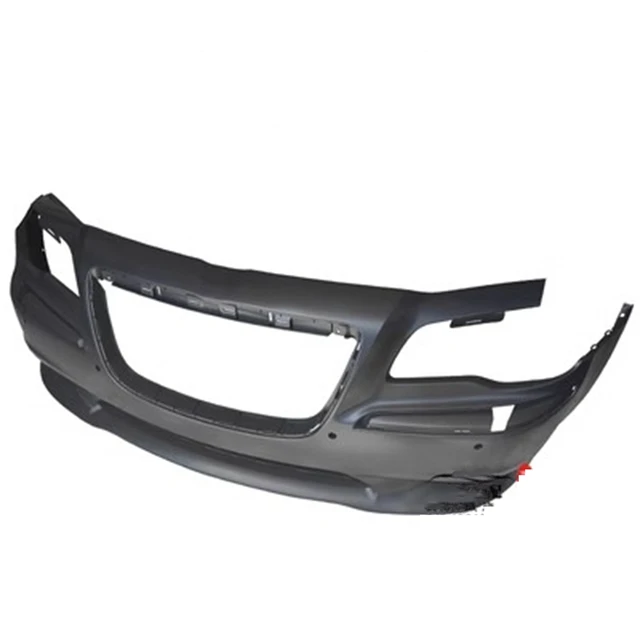
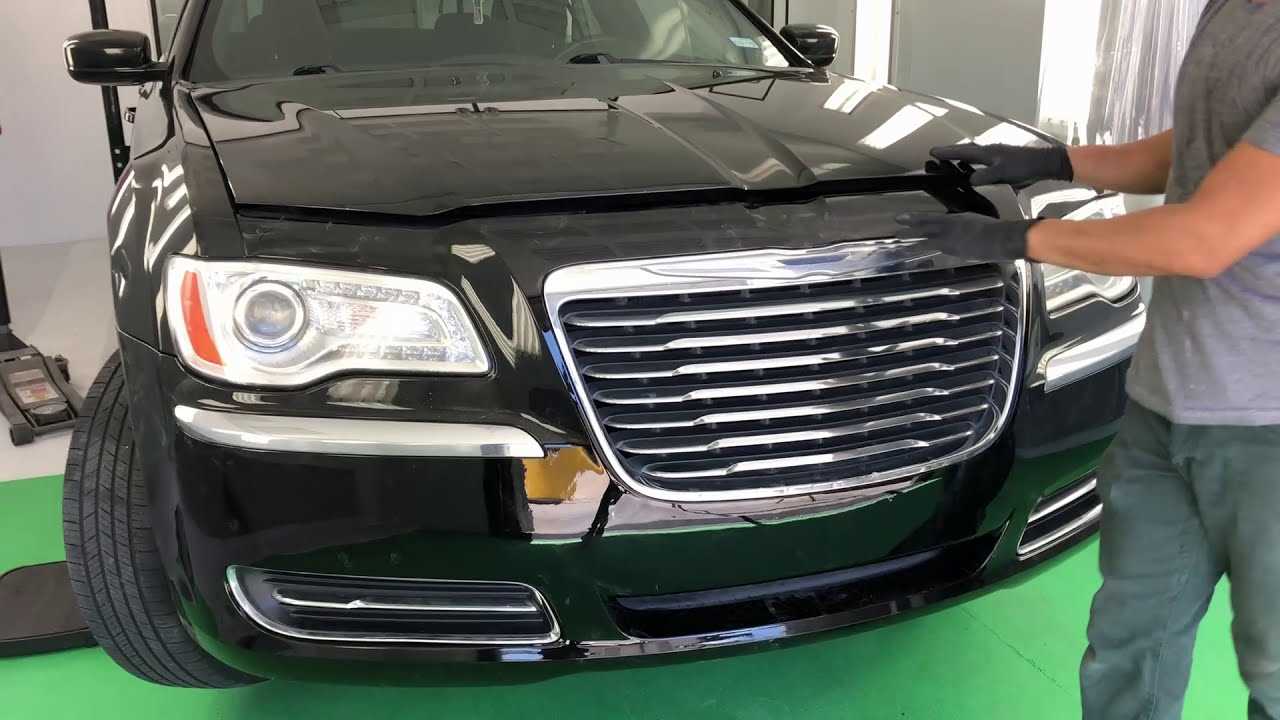
The layout and arrangement of a vehicle’s essential components play a crucial role in its performance, safety, and overall efficiency. Each section is meticulously engineered to meet specific needs, from the frame to the various structural elements that ensure stability and protection. Understanding the interaction between these sections helps in better maintenance and repair practices.
Proper knowledge of how each segment functions within the larger framework is vital for anyone working with or maintaining vehicles. From the internal structure that supports the mechanical components to the outer elements that provide both aesthetic appeal and protection from external forces, every aspect is designed for durability and precision.
Familiarizing yourself with the different zones and their roles can also aid in troubleshooting common issues. Whether dealing with the engine’s housing or the external shell that shields the internal systems, knowing the exact positioning and connections can lead to more effective repairs and improvements. This insight fosters a deeper appreciation for the intricate design of modern vehicles.
Overview of Chrysler 300 Body Structure
The structure of this vehicle is designed to ensure safety, durability, and aesthetic appeal. The overall framework includes various components that serve different functions, from supporting the car’s engine to protecting passengers in the event of a collision. Each part plays a crucial role in providing stability, comfort, and performance under diverse driving conditions.
Key Components and Their Roles
At the core of the frame lies the supporting structure, which maintains the integrity of the vehicle. It includes the chassis that provides the foundation for the engine and transmission. This framework is carefully engineered to balance strength and weight, contributing to both the safety features and fuel efficiency.
Materials and Engineering Considerations
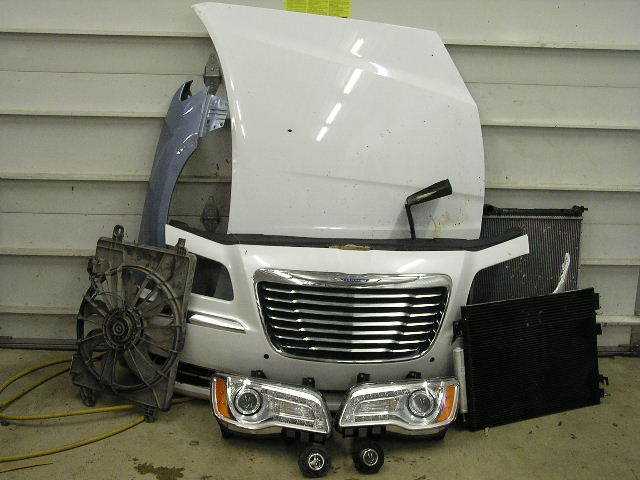

The choice of materials in constructing the frame is critical to the vehicle’s performance. Advanced alloys and steel are used to create a robust yet lightweight design, optimizing the car’s handling and overall stability. The manufacturing process ensures that the vehicle can withstand everyday wear and tear, while also maintaining the smooth aesthetic lines that are a hallmark of its design.
Understanding the Exterior Components
The outer framework of a vehicle encompasses various essential elements that not only contribute to its structural integrity but also define its appearance and functionality. These components work in harmony to provide protection, aerodynamics, and aesthetic appeal. By analyzing each piece, one can gain insight into the engineering and design choices that shape the vehicle’s overall performance and look.
Key Protective Elements
The outer surface is primarily designed to safeguard the internal mechanisms and occupants. Durable shields like the front and rear covers offer resistance against external forces, while also ensuring that environmental elements, such as rain and debris, are kept at bay. These shields are engineered with precision to meet safety standards while maintaining an attractive design.
Aesthetic and Functional Enhancements
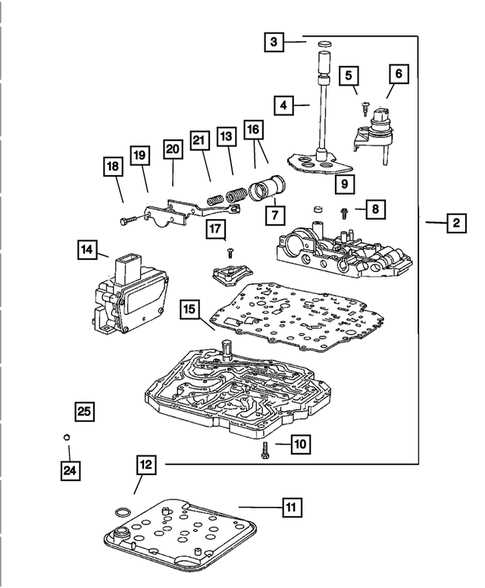
In addition to providing protection, the exterior components also serve to enhance the vehicle’s overall appeal. Sleek lines, curves, and well-positioned openings contribute to both the visual style and functional performance of the vehicle, such as improved air circulation and reduced wind resistance. These features are carefully crafted to balance practicality with visual allure.
Key Front-End Assembly Parts
The front assembly of a vehicle plays a crucial role in ensuring proper alignment, safety, and overall functionality. This section focuses on the primary components that make up the front structure, contributing to both the aesthetic appeal and mechanical performance of the vehicle. These elements work together seamlessly, supporting various systems such as lighting, airflow, and impact absorption.
Main Structural Components
The core structural elements of the front section are vital for maintaining the integrity of the vehicle. These parts are designed to absorb impact and provide stability. Key components include the radiator support, which serves as the mounting base for the radiator and other components, and the bumper reinforcement, designed to protect the front end during a collision. These elements are crucial for ensuring safety and functionality in the event of a minor or moderate impact.
Functional Components
Functional elements that influence the performance of the front section include the grille, which facilitates air intake for engine cooling, and the headlight assembly, responsible for providing visibility during night driving. These components are not only essential for safety but also enhance the vehicle’s aerodynamics and overall performance. Proper installation and alignment of these parts are critical for the optimal functioning of the entire system.
Exploring the Front Bumper and Grille
The front-end features of a vehicle play a crucial role not only in the aesthetics but also in the overall protection and airflow management. Understanding the components of the front bumper and grille can provide insights into their functional and structural importance in modern automobile design.
Key Functions and Design Elements
The front section of a vehicle is engineered to absorb impact while ensuring the protection of critical systems. The combination of the front bumper and grille helps in managing both safety and airflow. Here’s a closer look at their specific roles:
- Impact Absorption: The bumper is designed to mitigate damage during low-speed collisions by absorbing impact energy.
- Airflow Management: The grille plays a key role in directing air to the engine and radiator, promoting cooling efficiency.
- Visual Appeal: The grille design often reflects the brand’s aesthetic and serves as a distinctive feature on the vehicle’s front.
Components and Materials
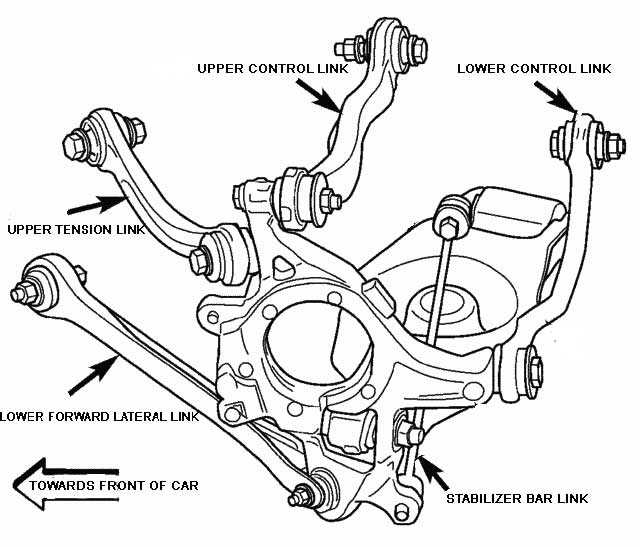
Modern vehicles incorporate a range of materials and construction techniques for these components, ensuring both durability and performance. Commonly used materials include:
- Plastic Composites: Lightweight and cost-effective, commonly used for both bumpers and grilles.
- Aluminum: Known for its strength and corrosion resistance, often used in high-performance models.
- Steel: Provides enhanced protection and strength, particularly in more rugged designs.
Rear Assembly Explained
The rear section of an automobile plays a crucial role in both structural integrity and aesthetics. This area includes several components that contribute to the overall design, function, and safety of the vehicle. From the frame to the exterior panels, each part is designed to protect and support key elements of the car’s rear end. Understanding how these elements come together can provide valuable insights into vehicle maintenance and repair.
Key Components of the Rear Structure
The assembly includes a variety of components, each serving a specific function to ensure proper operation and protection. These elements may include structural supports, reinforcement bars, exterior coverings, and more. Each part contributes to the overall strength and durability of the rear section, making it an essential area of focus for anyone interested in automotive repair or restoration.
Maintenance and Repair Considerations
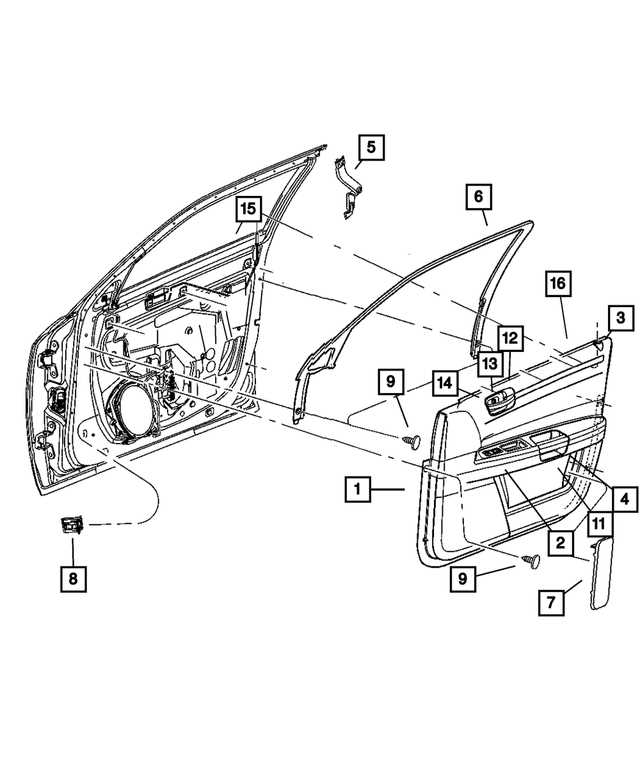
Regular maintenance and timely repairs of the rear section are crucial for maintaining safety and performance. Components such as tail lights, bumpers, and rear panels are subject to wear and tear over time. It is essential to inspect these areas periodically for signs of damage or degradation. Understanding the relationship between the different elements helps in making informed decisions when addressing issues in this section.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Frame Support | Provides structural integrity to the rear section. |
| Reinforcement Bar | Enhances strength and protects against impacts. |
| Rear Panel | Forms the outer surface and helps with aerodynamics. |
| Tail Lights | Provides visibility to other drivers and safety indicators. |
| Bumper | Protects the vehicle during low-speed collisions. |
The Role of the Rear Bumper
The component located at the back of a vehicle plays a critical role in ensuring both safety and structural integrity. It is specifically designed to absorb impact in minor collisions, protecting not only the vehicle’s framework but also reducing potential damage to internal systems.
Protection and Safety
One of the primary functions is to safeguard the rear section from external forces. It mitigates the impact of low-speed collisions, reducing repair costs by preventing deeper damage. Additionally, it plays a role in minimizing injury risks for passengers and pedestrians during incidents.
Aesthetic and Functional Integration
Besides protection, this component contributes to the vehicle’s overall appearance. Its sleek design is crafted to enhance the aesthetic appeal, while also incorporating important features such as sensors and lighting elements
Side Panel and Door Design
The external design of a vehicle’s side sections plays a critical role in both aesthetics and functionality. These components are carefully crafted to ensure sleek integration with the overall framework while providing protection and structural support. In addition, they incorporate elements that enhance safety and access to the interior.
| Component | Description | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outer Surface | The smooth external layer designed to resist environmental impact and contribute to the vehicle’s streamlined appearance. |
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Roof Rails | Provide lateral support and enhance the overall rigidity of the structure. |
| Cross Beams | Distribute load and impact forces across the frame for
Window and Glass ComponentsThe structural design and positioning of various transparent elements in a vehicle play a crucial role in ensuring visibility, safety, and overall comfort. These components are crafted to not only provide a clear view but also to offer protection from external elements such as wind, rain, and debris. Understanding how these elements work together enhances the overall driving experience, contributing to both aesthetic appeal and functional efficiency. Glass Panels and FramesThe large transparent surfaces, such as side panels and front screens, are held in place by a sturdy framework. This construction ensures a tight seal, preventing air and moisture from entering the cabin. These panels are typically designed with special coatings for enhanced clarity and durability, contributing to reduced glare and improved safety. Mechanisms for AdjustmentMost modern systems include mechanisms for raising and lowering glass elements. These mechanisms rely on intricate motor-driven or manual setups that allow for smooth and precise operation. The ease of use and reliability of these systems are critical in ensuring proper ventilation and ease of access to the Types of Side and Windshield Glass
Vehicle windows play a crucial role in both safety and comfort, and understanding the different kinds of glass used in side windows and windshields can help in making informed choices during repairs or replacements. Each type of glass serves a distinct function, offering various levels of protection, durability, and visibility. Side Window Glass
|