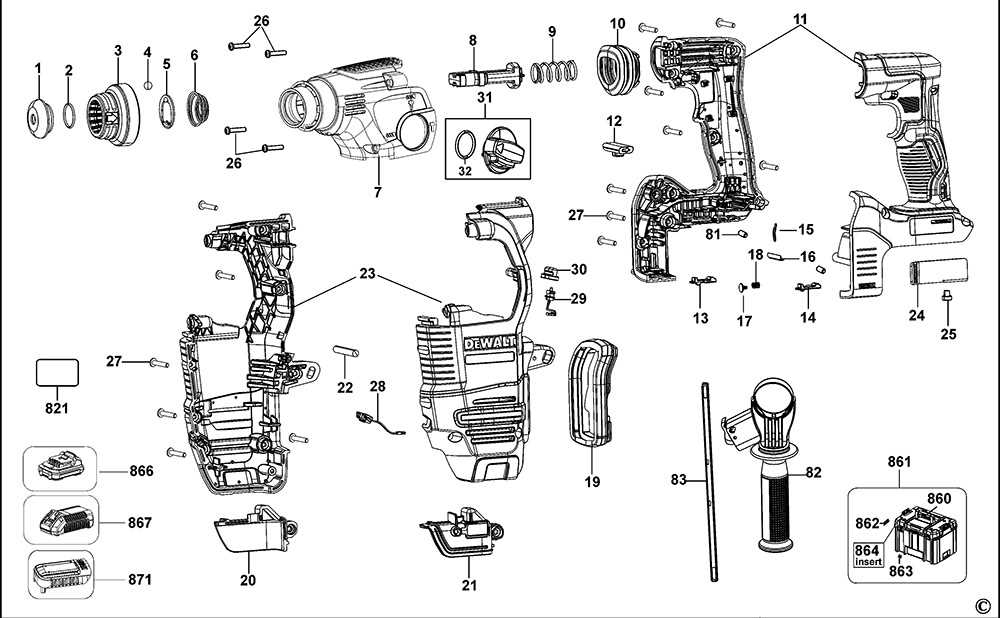
In the realm of power tools, having a clear grasp of the various elements that constitute the machinery is essential for effective maintenance and operation. This section aims to illuminate the intricate makeup of a specific model, offering insights into its functionality and design. By dissecting the individual components, users can enhance their understanding and troubleshooting skills.
Proper maintenance relies on recognizing each part’s role, ensuring longevity and optimal performance of the equipment. Familiarity with the layout of these components aids in diagnosing issues and executing repairs efficiently. Such knowledge empowers users, enabling them to confidently manage their tools.
Furthermore, accessing a visual representation of the assembly allows for a comprehensive overview, highlighting how each piece interacts within the whole. This approach not only simplifies the repair process but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the engineering behind these powerful devices.
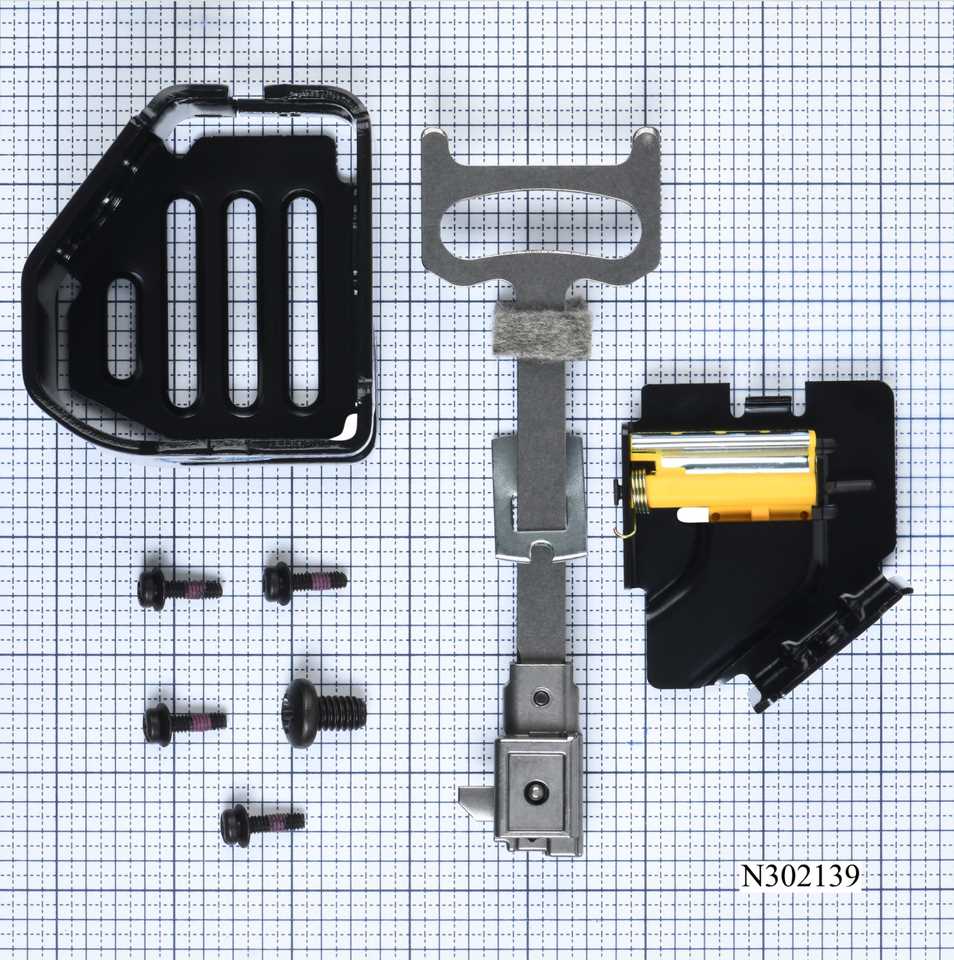

Understanding the illustrations that represent component layouts is essential for efficient assembly and maintenance. These visual guides provide clarity on how each piece fits together and aids in identifying individual elements. By familiarizing yourself with the structure and notation used in these representations, you can enhance your comprehension and troubleshooting skills.
Key Elements to Consider
- Labels and Numbers: Each component is usually accompanied by a unique identifier, making it easy to reference specific items.
- Connection Points: Look for indications of how parts connect or interact with one another.
- Orientation: Pay attention to the direction of components, as this can affect functionality.
Tips for Effective Reading

- Start by identifying the main assembly and its associated components.
- Familiarize yourself with the legend or key that explains the symbols used in the illustration.
- Take notes of any components that appear frequently, as they may be crucial for various setups.
- Practice with various diagrams to build confidence in interpreting different layouts.
Finding Replacement Parts
When it comes to maintaining your equipment, sourcing the right components is essential for optimal performance. Identifying suitable replacements ensures that your tools function correctly and efficiently. Here are some strategies to help you locate the necessary items.
- Manufacturer’s Website: Check the official website for a dedicated section on components. Many manufacturers provide a comprehensive list of available items and their specifications.
- Local Retailers: Visit nearby hardware stores or specialized retailers that might stock the required components. Staff can often assist in finding the correct parts for your tool.
- Online Marketplaces: Utilize online platforms where various sellers offer spare components. Look for reputable vendors with good reviews to ensure quality.
- Forums and Communities: Join online forums or social media groups focused on tool maintenance. Engaging with experienced users can lead to recommendations for where to find specific items.
- Third-party Suppliers: Explore options from third-party suppliers who specialize in aftermarket components. These can often be more affordable while maintaining acceptable quality.
By exploring these avenues, you can enhance your chances of successfully finding the necessary replacements to keep your equipment running smoothly.
Safety Precautions During Repairs
When performing maintenance on power tools, it is essential to prioritize safety to prevent accidents and injuries. Following specific guidelines can significantly reduce the risk of harm, ensuring that the repair process is efficient and secure.
Before starting any repair work, familiarize yourself with the equipment and understand its components. Always disconnect the tool from its power source to avoid accidental activation. Wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as safety goggles, gloves, and hearing protection, is crucial to shield yourself from potential hazards.
| Precaution | Description |
|---|---|
| Disconnect Power | Ensure the tool is unplugged or the battery is removed before starting repairs. |
| Use PPE | Wear safety glasses, gloves, and ear protection to guard against injuries. |
| Work in a Clear Area | Maintain a tidy workspace to prevent trips and falls. |
| Read the Manual | Refer to the user manual for specific safety instructions and repair guidelines. |
| Inspect Tools | Check tools for damage before use to ensure they are safe to operate. |
By adhering to these precautions, you can significantly enhance your safety while performing repairs. Remember that taking the time to prepare properly will lead to a more successful and secure maintenance experience.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When working with power tools, encountering problems is not uncommon. Understanding how to identify and resolve these issues can greatly enhance performance and prolong the lifespan of the equipment. Below are some typical challenges users may face and suggestions for addressing them.
- Tool Not Starting
- Check the power source to ensure it is functioning correctly.
- Inspect the switch for any signs of damage or malfunction.
- Verify that the battery or power cord is securely connected.
- Overheating
- Allow the tool to cool down before resuming use.
- Ensure that ventilation holes are not blocked.
- Examine the motor for any signs of wear or obstruction.
- Unusual Noises
- Listen for grinding or rattling sounds, which may indicate loose parts.
- Check for debris caught in the mechanism.
- Consult the user manual for guidance on internal components.
- Poor Performance
- Assess the sharpness of blades or bits; dull tools can cause inefficiency.
- Review the settings and ensure they are appropriate for the task.
- Consider the quality of materials being used, as inferior products can lead to subpar results.
Repair vs. Replacement Decisions
When faced with a malfunctioning tool, the choice between repairing and replacing it can be daunting. Understanding the benefits and drawbacks of each option is crucial in making an informed decision. Factors such as cost, availability of components, and the extent of damage play significant roles in determining the best course of action.
Assessing the Condition
Before deciding, it is essential to evaluate the current state of the equipment. Minor issues may be easily fixed with little investment, while extensive damage might warrant a complete replacement. Analyzing the repair costs compared to the price of a new unit can provide clarity on the most economical solution.
Long-Term Considerations
Another important aspect is the longevity and reliability of the repaired unit. If the tool has been dependable in the past, repairing it might extend its life without significant costs. However, if the equipment has frequently needed repairs, it may be more practical to invest in a new model, ensuring better performance and reduced downtime in the future.
Resources for Further Information
For those seeking additional details and guidance on repair and maintenance, various resources are available. These can help users navigate through the intricacies of their equipment and ensure optimal performance.
- Manufacturer Websites: Official sites often provide manuals, specifications, and troubleshooting tips.
- Online Forums: Community discussions can offer insights and shared experiences from other users.
- Instructional Videos: Platforms like YouTube feature tutorials that visually guide users through repairs and maintenance tasks.
- Retailer Support: Many retailers provide customer service assistance, including technical help and advice on compatible accessories.
- Professional Repair Services: Local or online repair services can offer expert assistance for more complex issues.
Utilizing these resources can enhance understanding and facilitate effective problem-solving, ensuring equipment remains in excellent working condition.