Modern personal transport vehicles offer convenience and mobility, providing a swift and efficient way to navigate through urban environments. The integration of various mechanical and electrical elements ensures their smooth operation and performance. Each component plays a critical role in delivering the best user experience, from power delivery to movement control.
To maximize the functionality of these vehicles, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of the key elements that contribute to their design. These systems work together seamlessly, with each part serving a specific function. A detailed overview of the mechanisms involved can help users maintain and optimize the device for long-term use.
By familiarizing yourself with the essential components, you’ll gain deeper insight into how the vehicle operates. This knowledge will not only aid in troubleshooting issues but also in upgrading or customizing the device to fit your needs.
Understanding Electric Scooter Components
Modern personal transporters are made up of various interconnected elements that work in harmony to ensure smooth and efficient operation. Each component plays a crucial role in achieving the desired performance, mobility, and user experience. By understanding how these key elements function together, riders can ensure optimal care and troubleshoot issues effectively.
One of the main components includes the power source, which provides the necessary energy to drive the system. This is typically paired with a control unit that regulates the distribution of power to different parts. Other essential parts include mechanical support systems, which maintain stability, and navigation controls that allow for user interaction and direction adjustments.
Each of these systems is designed to be both durable and efficient, contributing to the overall safety and ease of use. Understanding their interactions helps in maintaining longevity and maximizing performance.
Key Parts of an Electric Scooter
Modern personal transporters consist of various essential components working together to provide smooth and efficient travel. Understanding the core elements that enable these vehicles to operate is crucial for both maintenance and optimal use. These key components contribute to the overall functionality and performance of the vehicle, ensuring reliability and safety on the road.
Motor and Drive System
The motor serves as the heart of the vehicle, converting electrical energy into motion. It works in conjunction with the drive system, which includes gears and chains, transferring power to the wheels. Together, these elements determine the speed and efficiency of the ride.
Battery and Power Management
The battery is the source of energy, storing power that fuels the motor. Efficient power management systems ensure that energy is used optimally, helping to extend the range and lifespan of the vehicle. This system monitors power usage, controlling charging and discharging to maintain peak performance.
Motor and Battery Interaction Explained
The collaboration between the propulsion system and the energy source is crucial for efficient movement. These components work together to ensure smooth operation and effective performance. The power generated by the battery is transferred to the motor, which then converts it into mechanical force. Understanding the connection between these two elements helps optimize performance and longevity.
Power Transfer and Efficiency
The battery serves as the energy reservoir, releasing stored power when needed. As the motor receives this energy, it transforms it into rotational motion, which propels the vehicle forward. This process must be finely tuned to ensure the vehicle operates at peak efficiency, balancing power output with energy consumption.
Factors Affecting Performance
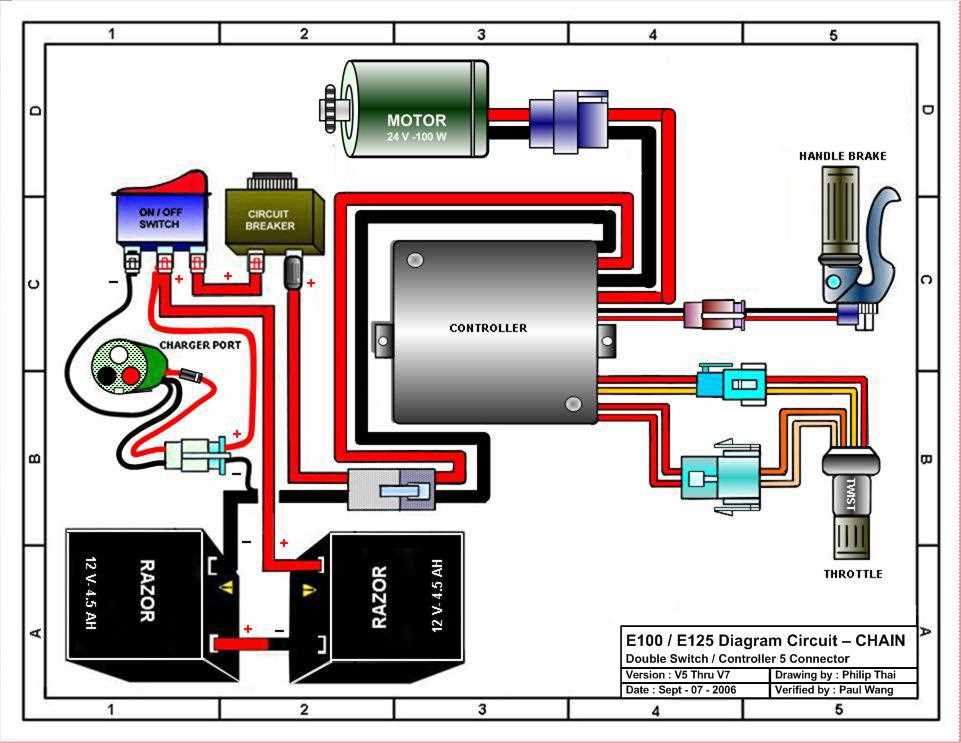
How the Controller Regulates Power
The controller plays a crucial role in managing the flow of energy within the system, ensuring that the motor receives the correct amount of power based on the user’s commands. By adjusting the electrical signals, the controller governs the speed and acceleration, optimizing the balance between performance and energy consumption.
Regulation Mechanisms
The regulation of power is achieved through a series of complex processes that involve monitoring the rider’s input and adjusting the output to the motor. These adjustments are made by modulating the voltage and current supplied to the motor, which directly impacts the movement and efficiency of the vehicle.
Power Distribution and Control
Power distribution is managed by the controller through its connection with other components. By dynamically distributing the energy, the system can ensure smooth transitions between speeds while also preventing overloads that could damage the motor or battery. This balance allows for a safer and more responsive experience for the rider.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Controller | Regulates power to the motor based on user input |
| Battery | Supplies the electrical energy needed for operation |
| Motor | Converts electrical energy into mechanical movement |
| Throttle | Controls the amount of power being drawn by the motor |
Brakes and Suspension in Scooters
Effective stopping and smooth rides are essential for ensuring safety and comfort in personal transportation devices. The braking system and suspension play a key role in controlling speed and handling uneven terrain, offering riders greater stability and confidence. Understanding their function is crucial for both maintenance and optimal performance.
Brake Types and Functionality
The braking system is responsible for reducing the device’s speed and bringing it to a stop. There are various brake mechanisms used, each with its own characteristics. From basic mechanical to more advanced systems, choosing the right one depends on factors such as speed, terrain, and rider preference.
| Brake Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Disc Brake | Strong stopping power, reliable in wet conditions | Can be noisy, requires more maintenance |
| Drum Brake | Durable, less affected by weather | Less responsive, harder to repair |
| Foot Brake | Simple to use, low maintenance | Limited stopping power, less effective on steep inclines |
Suspension Systems for Comfort
The suspension system absorbs shocks and vibrations caused by uneven surfaces. It ensures that riders experience a smoother ride, reducing fatigue and providing better control. Depending on the model, different suspension setups are used to suit various riding conditions.
| Suspension Type | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Front Suspension | Improves stability, absorbs bumps effectively | Can add weight, may reduce maneuverability |
| Rear Suspension | Enhances comfort during long rides | May increase cost, requires regular upkeep |
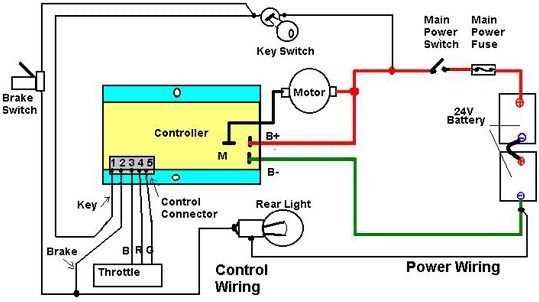
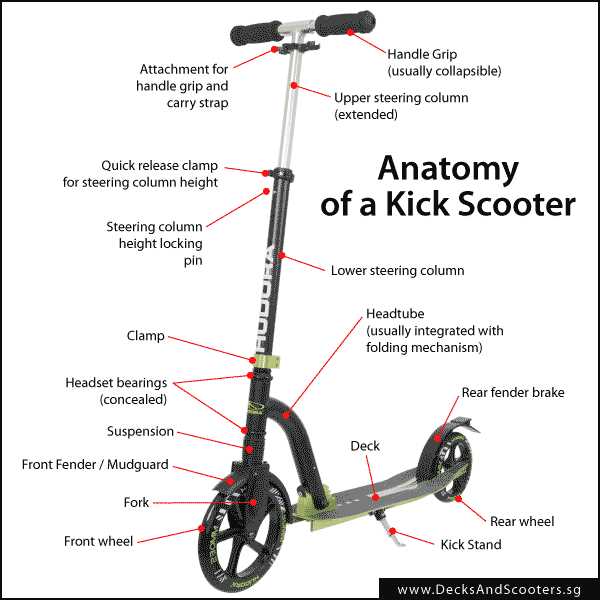
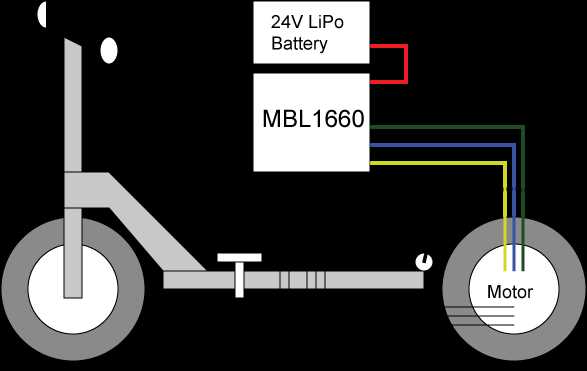
Understanding the Wiring System
Comprehending the internal wiring is crucial for proper maintenance and troubleshooting of battery-operated two-wheelers. The electrical connections form the foundation for the efficient operation of the entire vehicle, enabling communication between different components like the motor, battery, and control unit.
Key Components in the Wiring System
- Battery: Supplies power to the entire system, ensuring smooth operation.
- Controller: Acts as the brain, regulating the flow of electricity to different parts.
- Throttle: Adjusts the speed by controlling the power sent to the motor.
- Motor: Converts electrical energy into mechanical motion, propelling the vehicle forward.
Why Proper Wiring is Essential
- Safety: Faulty wiring can lead to short circuits, posing safety hazards.
- Efficiency: Proper wiring ensures that the system operates at its best, maximizing battery life.
- Durability: Well-maintained wiring prolongs the life of all electrical components.
Role of the Throttle in Vehicle Operation
The throttle is a key component that regulates the speed and power of the vehicle. By controlling the amount of energy provided to the motor, it allows the rider to adjust the vehicle’s movement according to the desired pace. Its smooth operation ensures the vehicle responds efficiently to rider inputs, contributing to overall control and safety.
How the Throttle Affects Movement
The throttle controls the flow of electricity to the motor, dictating how fast the vehicle accelerates. When the throttle is engaged, the motor receives more power, causing the vehicle to speed up. Conversely, releasing the throttle reduces the power supplied, allowing the vehicle to decelerate or stop. This interaction is essential for maintaining a comfortable and responsive riding experience.
Types of Throttle Controls
- Twist Grip Throttle: This type requires the rider to twist the grip to increase speed. The more the grip is twisted, the more power is delivered to the motor.
- Thumb Throttle: Operated by pushing a button or lever with the thumb, this throttle style is often seen in smaller, compact models.
In both cases, the throttle ensures that the vehicle can accelerate or decelerate based on the rider’s needs, providing full control over the movement.
Battery Maintenance for Longevity
Maintaining the battery of your personal transport device is crucial for maximizing its lifespan and ensuring reliable performance. Proper care can prevent early wear and tear, improve efficiency, and reduce the frequency of replacements.
Key Tips for Prolonging Battery Life
- Charge the battery at regular intervals, avoiding deep discharges.
- Store the battery in a cool, dry place when not in use for extended periods.
- Avoid exposing the battery to extreme temperatures, both hot and cold.
- Use the correct charger and avoid using third-party, non-recommended options.
- Regularly check for any signs of wear or damage and replace the battery if necessary.
Charging Practices
It’s essential to develop a good charging routine. Overcharging or undercharging can lead to faster degradation. Ideally, the battery should be kept between 20-80% charge for optimal longevity.
Environmental Considerations
- Store the battery away from heat sources, such as direct sunlight or radiators.
- Avoid storing the battery in freezing conditions, as extreme cold can impair its functionality.
How Wheels and Tires Impact Performance
The choice of wheels and tires directly influences the overall efficiency and handling of a vehicle. Their design and composition affect how the vehicle interacts with various surfaces, impacting speed, stability, and comfort.
Key factors include:
- Size: Larger wheels tend to offer better stability but may reduce acceleration. Smaller wheels may increase agility but could compromise smoothness over uneven terrain.
- Material: Tires made of softer compounds provide better grip, whereas harder materials may enhance durability but reduce traction.
- Inflation: Proper tire inflation ensures optimal performance, as under-inflated tires can cause friction and reduce efficiency, while over-inflated tires may lead to poor grip and increased wear.
Understanding these aspects helps in optimizing the vehicle for different conditions, ensuring a balance between performance and safety.
Charging System and Its Components

The charging mechanism plays a vital role in maintaining the energy levels of a personal mobility device. It ensures the smooth transfer of power to the internal energy storage unit, allowing the vehicle to function efficiently over longer periods. This system is essential for optimizing performance and extending the operational lifespan.
Battery is the core element of this setup, storing the electricity required for operation. The capacity and type of this component significantly affect the range and charging time. Coupled with the controller, it regulates the flow of energy, ensuring safe and effective charging without overloading the system.
Additionally, the charger converts the external power source into a suitable form for the battery, adjusting the voltage and current to avoid damage. This component is often equipped with indicators to show the status of the charging process.
Overall, these interconnected elements work together to maintain the vehicle’s power efficiency, ensuring reliable and convenient usage over time.
Importance of the Vehicle Frame Structure
The frame is the backbone of any two-wheeled transport, providing the necessary foundation for all other components. It plays a critical role in ensuring the overall stability, strength, and safety of the vehicle. Without a robust and well-engineered structure, the entire system would be prone to failure, reducing performance and increasing risks during operation.
Key Functions of the Frame
- Support: It supports the weight of the rider, battery, and other components, distributing the load evenly.
- Durability: A sturdy frame ensures that the vehicle can withstand harsh conditions, including rough terrains and impacts.
- Handling: A well-designed structure helps with maneuverability, offering better control and responsiveness on various surfaces.
Materials Used for the Frame
- Aluminum: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, making it ideal for mobility.
- Steel: Known for its strength and durability, although heavier than aluminum.
- Carbon Fiber: Provides high strength with minimal weight, often used in high-performance models.