
In the world of botany, the study of flora encompasses a wide range of intricate structures that contribute to the life cycle of these beautiful organisms. This section delves into the essential elements that play a vital role in the process of reproduction, facilitating the continuation of plant species. Each structure serves a unique function, working harmoniously to ensure successful propagation and genetic diversity.
By examining the various components involved in the reproductive cycle, we can gain insights into the complexities of plant life. These elements are not only crucial for the survival of individual plants but also for maintaining the balance of ecosystems. The interplay between these structures highlights the remarkable adaptations that have evolved over time, allowing plants to thrive in diverse environments.
Through a comprehensive exploration of these vital structures, we will uncover the intricate relationships that define the reproductive strategies of flowering organisms. Understanding these mechanisms enhances our appreciation of nature’s wonders and underscores the importance of preserving biodiversity for future generations.
Understanding Flower Anatomy

The structure of a bloom is intricate and fascinating, comprising various components that play essential roles in its life cycle. Each element is uniquely adapted to facilitate crucial processes, ensuring the continuity of plant species. By examining these structures, one can gain insight into the complex interactions that occur within the botanical world.
At the core of this study lies the appreciation of how each component functions harmoniously with others. For instance, some elements are designed to attract pollinators, while others are responsible for the production of essential substances needed for reproduction. This symbiotic relationship between the various structures not only supports the individual organism but also contributes to broader ecological systems.
Understanding the anatomy of these blooms enhances our knowledge of their ecology, evolution, and the vital role they play in sustaining life on Earth. Through exploration and study, we can appreciate the diversity and complexity found in these natural wonders.
Overview of Flower Structure
The intricate design of blooming specimens is crucial for their lifecycle and successful reproduction. Understanding this organization can provide insights into the various functions and roles each component plays in the propagation of these organisms.
Key Components
At the heart of the blooming entity lies a complex arrangement of structures, each serving specific functions. The central element often acts as the hub for fertilization, while surrounding elements facilitate pollination and protection. These elements vary widely among species, showcasing the diversity found in nature.
Functional Importance
Every segment contributes to the overall vitality of the organism. The way these elements interact with environmental factors, such as pollinators and climate, significantly impacts the success of reproduction. Recognizing the roles of these segments is essential for comprehending the ecological dynamics at play.
Importance of Reproductive Parts
The significance of the structures responsible for the continuation of plant life cannot be overstated. These components play a critical role in ensuring the survival of various species by facilitating processes that lead to the formation of seeds and fruits, which are essential for propagation. Understanding their functions helps appreciate the intricate relationships within ecosystems.
Several key functions highlight their importance:
- Pollination: The mechanisms involved in transferring pollen are crucial for fertilization, allowing for genetic diversity and stronger offspring.
- Seed Formation: The production of seeds ensures the next generation of plants can grow, contributing to the stability of their environment.
- Fruit Development: Fruits protect seeds and aid in their dispersal, promoting colonization of new areas.
- Attracting Pollinators: Many structures develop vibrant colors and appealing scents to attract pollinators, which are vital for successful reproduction.
In summary, these elements not only support the life cycle of plants but also play a fundamental role in maintaining biodiversity and ecological balance.
Types of Flower Reproductive Organs
The structures involved in the generation of new plants play a crucial role in the life cycle of flowering species. These components are essential for the continuation of genetic material, ensuring diversity and adaptation within ecosystems. Understanding these elements helps in appreciating the complexity of plant biology.
Key Components
The main structures involved in the process of generation include the following:
| Structure | Description |
|---|---|
| Stamen | The male structure responsible for producing pollen, which contains male gametes. |
| Pistil | The female component that houses ovules and is responsible for seed development after fertilization. |
| Petals | Often brightly colored, these structures attract pollinators to aid in the transfer of pollen. |
| Sepals | Green leaf-like structures that protect the bud before it opens. |
Functions and Interactions
The interaction between these structures is vital for successful pollination and fertilization. Each component contributes to a complex process that results in the production of seeds, enabling the propagation of the species. The efficiency of these processes is often enhanced by external factors such as pollinators, which facilitate the transfer of genetic material between different individuals.
Function of Stamen in Pollination
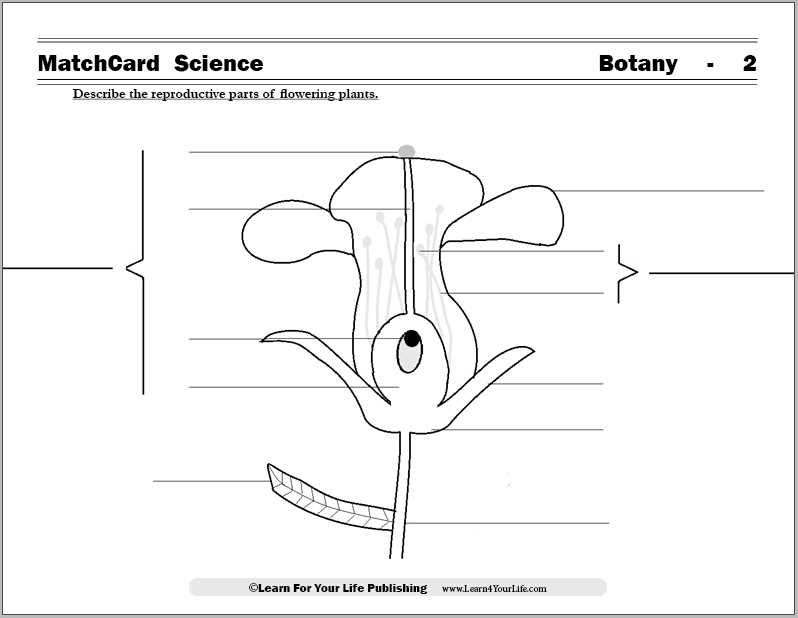
The stamen plays a pivotal role in the process of fertilization by facilitating the transfer of pollen to the receptive structures of other plants. This essential function not only ensures the continuation of plant species but also contributes to the diversity of ecosystems.
Structure and Role: The stamen consists of two main components: the filament and the anther. The filament supports the anther, where pollen grains are produced and stored. Once the anther matures, it releases these grains into the environment, making them accessible for transfer by various agents such as wind, insects, or birds.
Pollination Process: During pollination, the pollen grains must adhere to the stigma, the receptive area of the pistil. This interaction is crucial for the fertilization process to commence, leading to seed formation and, ultimately, the propagation of the species. The efficiency of this process is significantly enhanced by the structural design of the stamen and its strategic placement within the overall framework of the organism.
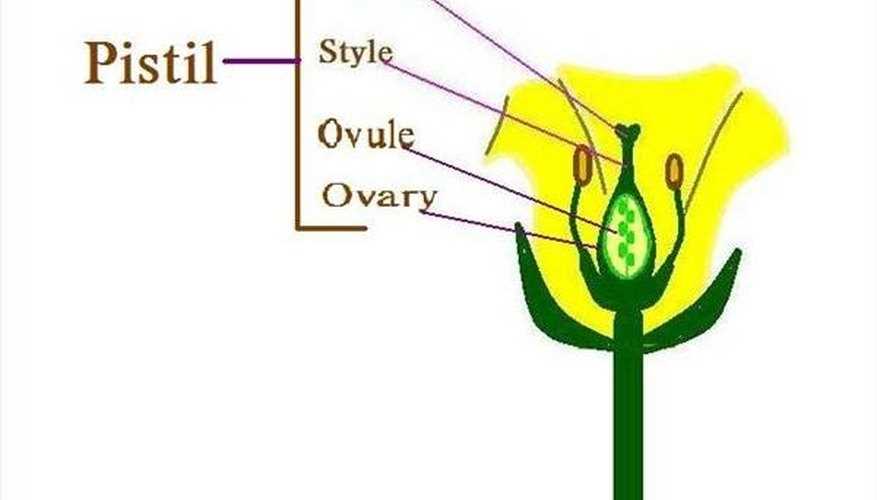
Role of Pistil in Fertilization
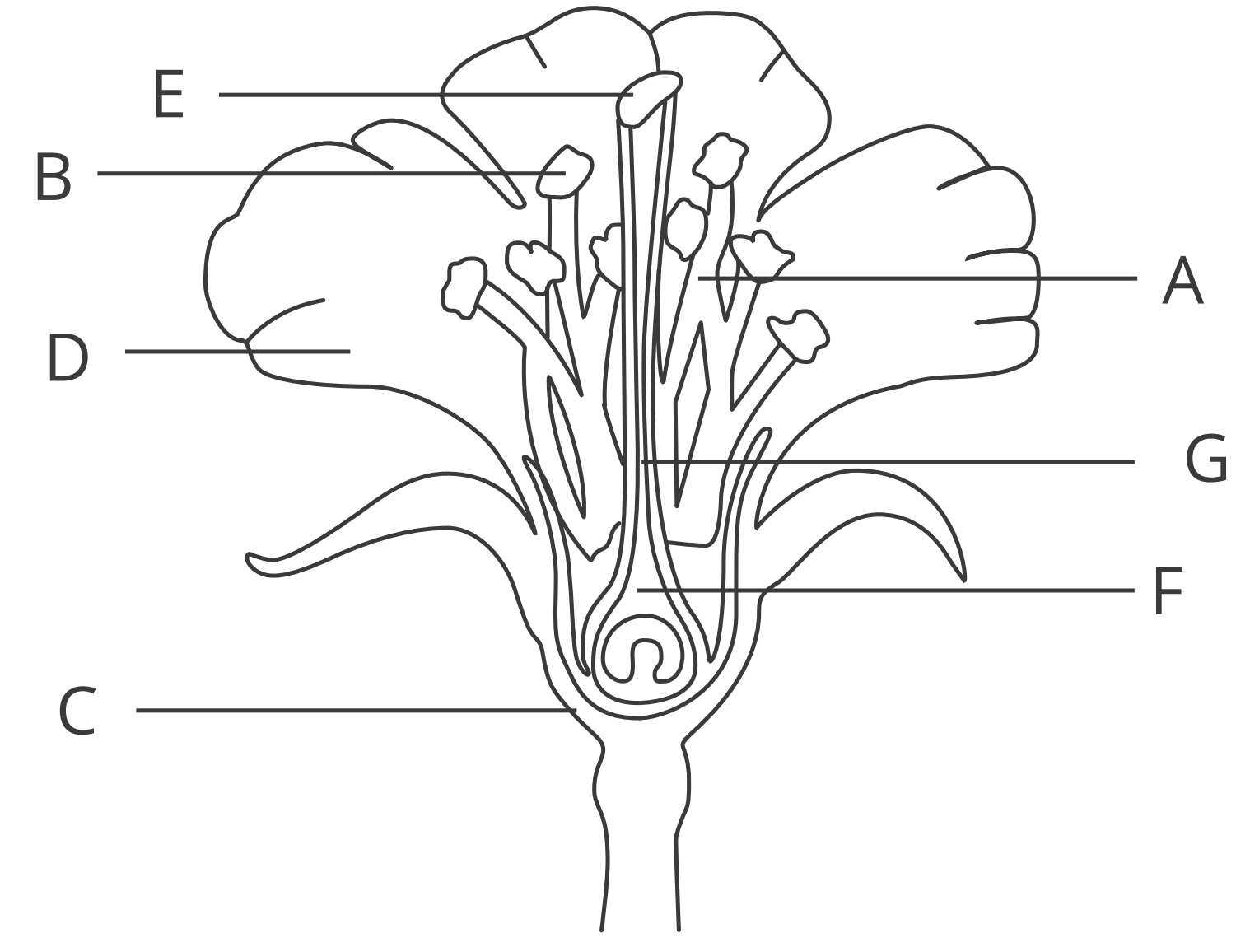
The pistil serves as a crucial component in the process of plant reproduction, facilitating the union of male and female gametes. Its structure is designed to enhance the likelihood of successful fertilization, making it essential for the propagation of various species. This organ plays a significant role in receiving pollen and enabling the development of seeds, ultimately ensuring the continuation of plant life.
Structure of the Pistil
The pistil is composed of three main sections: the stigma, style, and ovary. The stigma acts as the receptive surface for pollen grains, providing a sticky area that captures and holds pollen during pollination. The style serves as a conduit, allowing pollen to travel from the stigma to the ovary, where fertilization occurs. The ovary contains ovules, which develop into seeds once fertilization is successful.
Mechanism of Fertilization
During fertilization, pollen grains germinate on the stigma, forming a pollen tube that extends through the style toward the ovary. Sperm cells travel down this tube to reach the ovules. Once the sperm successfully unites with an ovule, fertilization takes place, leading to the formation of a zygote. This process is essential for the production of seeds, which carry the genetic material for the next generation of plants.
Comparative Analysis of Flower Types
This section delves into the diverse forms of floral structures, highlighting the unique characteristics that differentiate them from one another. By examining these variations, we can gain insights into their ecological roles and evolutionary significance within various plant species.
Diverse Floral Structures
Different plants exhibit a range of floral formations, each adapted to specific pollination strategies and environmental conditions. For example, some may possess vibrant hues and enticing fragrances to attract pollinators, while others have evolved to rely on wind for pollen distribution. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for comprehending plant interactions with their surroundings.
Comparative Table of Floral Characteristics
| Type | Coloration | Pollination Method | Habitat |
|---|---|---|---|
| Orchid | Varied (often bright) | Insect | Tropical and subtropical |
| Daisy | White and yellow | Insect | Grasslands |
| Pine | Green (cones) | Wind | Forests |
| Maple | Red or yellow | Wind | Temperate forests |
By analyzing these various structures, we can appreciate the complexity of plant biology and the intricate relationships that exist within ecosystems. This comparative approach enhances our understanding of biodiversity and conservation efforts.
Pollination Mechanisms in Flowers
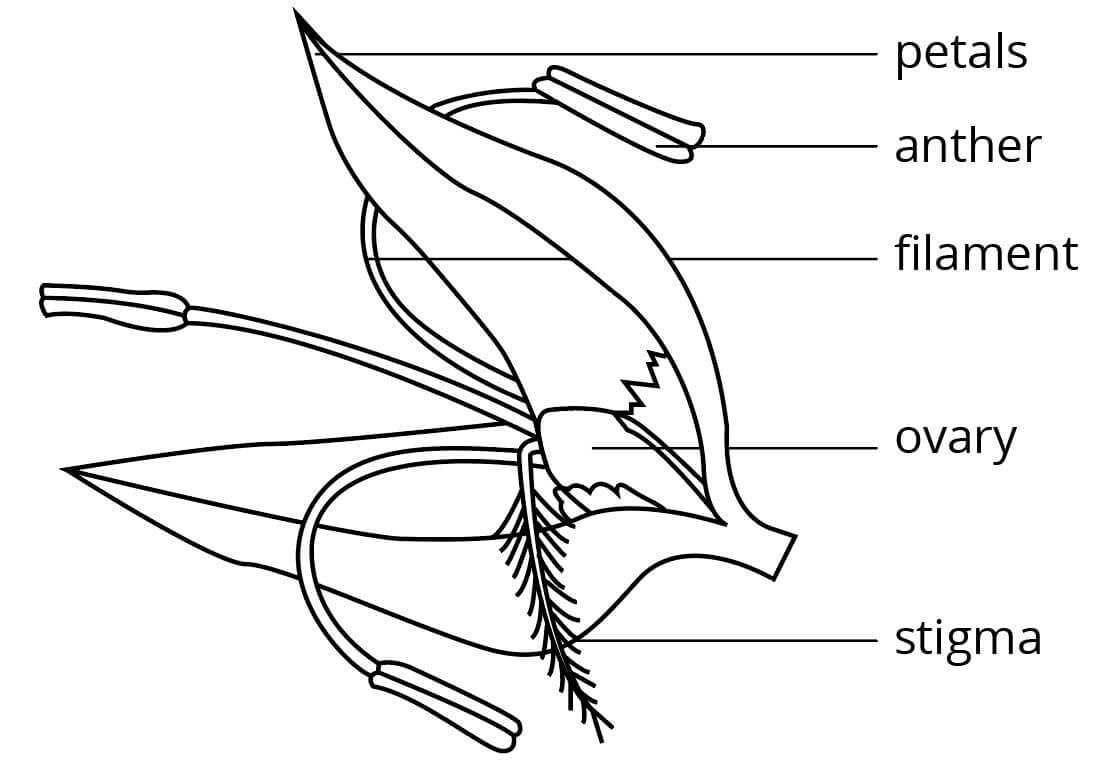
Understanding the ways in which plants achieve fertilization is essential for grasping their life cycles and ecological roles. Various strategies have evolved, enabling these organisms to facilitate the transfer of genetic material. These processes not only ensure the continuation of species but also contribute to biodiversity and ecosystem stability.
Methods of Transfer
Pollination can occur through numerous methods, primarily involving wind, water, or animals. Wind disperses pollen grains over vast distances, while water can facilitate fertilization in aquatic environments. However, the most intricate mechanisms involve animals, particularly insects and birds, which often engage in mutualistic relationships with the plants they visit.
Role of Attractants
To attract pollinators, many plants produce vibrant colors, enticing scents, and nourishing nectar. These features not only allure animals but also guide them toward the specific locations where pollination can occur. This interaction enhances the chances of successful fertilization and promotes genetic diversity within plant populations.
Factors Influencing Flower Reproduction
The process of producing seeds and ensuring the continuation of plant species is affected by various elements in the environment and within the organism itself. Understanding these influences can help in both natural ecosystems and agricultural practices, promoting healthier growth and maximizing yields.
Environmental Influences
- Light Availability: Adequate sunlight is crucial for the development of reproductive structures and successful pollination.
- Temperature: The right temperature range is essential for optimal growth and development, affecting the timing of flowering.
- Soil Nutrients: The availability of essential nutrients in the soil supports overall plant health and impacts the quality of seed production.
- Water Supply: Sufficient moisture levels are necessary for growth and can influence the timing and success of seed formation.
Biological Factors
- Genetic Variability: Different genetic traits can enhance or inhibit the ability of a plant to reproduce effectively.
- Pollinator Availability: The presence of suitable pollinators can significantly impact the success of fertilization.
- Plant Health: Disease resistance and overall vigor affect a plant’s capacity to engage in successful seed production.
- Inter-species Competition: Competition with neighboring plants for resources can limit growth and reduce reproductive success.
Visual Representation of Flower Parts
Understanding the various components of a plant’s structure is essential for grasping its biological functions and interactions within the ecosystem. A clear illustration can significantly enhance comprehension, making the complex relationships among different elements more accessible. This section aims to present an organized view that highlights these essential elements, facilitating a deeper appreciation of their roles and significance.
Key Components Overview
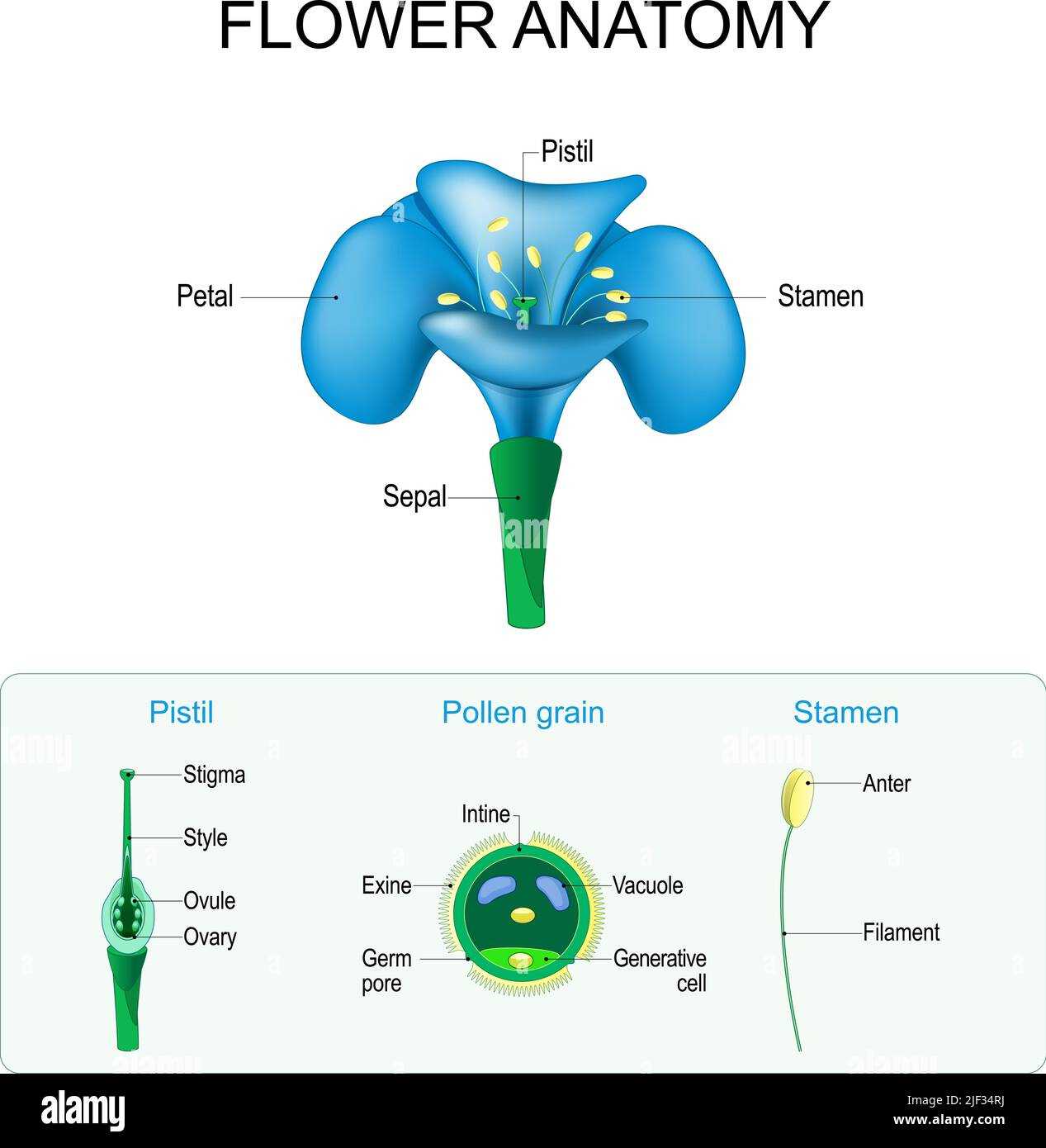
Each component plays a vital role in the lifecycle and reproduction of the organism. The structure is typically divided into several sections, including those responsible for attracting pollinators, protecting developing seeds, and supporting overall growth. A visual guide can aid in recognizing these distinct areas, thereby enriching the learning experience and promoting a greater understanding of plant biology.
Importance of Visual Learning
Visual aids are powerful tools in education, as they help to clarify complex concepts and foster better retention of information. By utilizing illustrative representations, learners can easily identify and relate to the various components, gaining insights into their functions and interconnections. This approach not only enhances academic learning but also inspires a lasting curiosity about the natural world.
Common Examples of Flower Species
This section highlights various types of botanical specimens that exhibit unique characteristics and diverse appearances. These organisms play crucial roles in ecosystems, contributing to pollination and providing habitat and nourishment for various organisms.
Popular Varieties
Some well-known specimens include the vibrant Rosa, commonly recognized for its fragrant blooms and intricate layering of petals. Another example is the Tulipa, celebrated for its striking colors and cup-shaped blossoms that signal the arrival of spring.
Native Species
Additionally, native specimens such as the Sunflower (Helianthus annuus) stand out with their large, sunny faces and towering stalks, while the delicate Lily (Lilium) captivates with its elegant form and enchanting fragrance.
Significance of Flowers in Ecosystems
The various blooming organisms play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance and supporting biodiversity. Their presence contributes to the intricate web of life, providing essential resources for numerous species and fostering healthy habitats.
Key Roles in Nature

- Pollination: Many living beings, including insects, birds, and mammals, rely on these organisms for nourishment, leading to mutualistic relationships that enhance reproduction.
- Habitat Formation: By creating vibrant landscapes, these organisms offer shelter and nesting sites for a variety of fauna, thus promoting species diversity.
- Soil Health: The root systems of these plants contribute to soil stability and fertility, preventing erosion and enhancing nutrient cycling.
Contributions to Human Life
- Aesthetic Value: The beauty of these natural structures enriches human environments and contributes to mental well-being.
- Medicinal Uses: Many species are sources of pharmaceuticals and herbal remedies, underscoring their importance in health and wellness.
- Cultural Significance: These organisms often feature prominently in traditions, celebrations, and art, reflecting their deep connection with human culture.