Exploring the intricate elements that contribute to the beauty and functionality of blooming vegetation unveils a fascinating world of structure and purpose. Each segment plays a vital role, supporting the overall health and reproduction of the plant. By gaining insight into these essential constituents, one can appreciate the complexity of nature’s design.
The remarkable interplay among various structures enhances the processes of pollination, growth, and vitality. From vibrant petals to supportive stems, each component is tailored for specific functions, creating a harmonious balance. Understanding these connections allows for a deeper appreciation of the natural world and its myriad forms.
In this discussion, we will delve into the ultimate intricacies of these elements, highlighting their significance and interrelationships. This knowledge not only enriches our understanding but also invites a greater respect for the wonders of the plant kingdom.
Understanding Flower Structure
Exploring the composition of these beautiful organisms reveals the intricate relationships between their various components, each playing a crucial role in their reproductive success and ecological function. By examining these elements, we can appreciate the complexity and beauty inherent in nature.
Main Components
- Petals: Brightly colored structures that attract pollinators.
- Sepals: Protective outer leaves that enclose the developing bloom.
- Stamens: Male reproductive organs responsible for pollen production.
- Carpels: Female reproductive components that house ovules.
Functional Roles
- Pollination: The transfer of pollen from stamens to carpels, facilitating fertilization.
- Attraction: The visual appeal of petals aids in attracting various pollinators.
- Protection: Sepals safeguard the more delicate structures during development.
Components of a Flower Explained
Understanding the structure of a blooming plant reveals the intricate mechanisms that allow for reproduction and growth. Each element plays a vital role, contributing to the overall function and beauty of these natural wonders.
| Element | Function |
|---|---|
| Petals | Attract pollinators with their vibrant colors and scents. |
| Stamens | Responsible for producing pollen, the male reproductive component. |
| Carpels | House the ovary and facilitate fertilization, serving as the female structure. |
| Sepals | Protect the developing bud and support the bloom. |
| Receptacle | Acts as the base, connecting all components and providing structural support. |
Role of Petals in Pollination
Petals serve a crucial function in the reproductive processes of plants, acting as the vibrant and often colorful components that attract various pollinators. Their unique shapes, textures, and colors play a significant role in ensuring successful fertilization by guiding pollinators to the reproductive organs.
Attracting Pollinators
The primary purpose of petals is to lure insects, birds, and other animals. Here are some ways in which they achieve this:
- Color: Bright hues can draw attention from afar, signaling the presence of nectar.
- Patterns: Distinct markings can lead pollinators directly to the source of nourishment.
- Fragrance: Pleasant scents can entice creatures to visit and linger longer.
Facilitating Interaction
Once pollinators arrive, petals also help facilitate the transfer of pollen. Their structure can:
- Provide Landing Platforms: Some petals offer stable areas for pollinators to rest while they gather food.
- Guide Movement: The shape of petals can direct pollinators toward reproductive parts, ensuring effective pollen transfer.
- Protect Reproductive Organs: They can shield delicate structures from environmental elements while attracting visitors.
Through these mechanisms, petals not only enhance the visual appeal of plants but also play an essential role in the continuity of plant species. Their multifaceted contributions are vital in promoting successful reproduction within ecosystems.
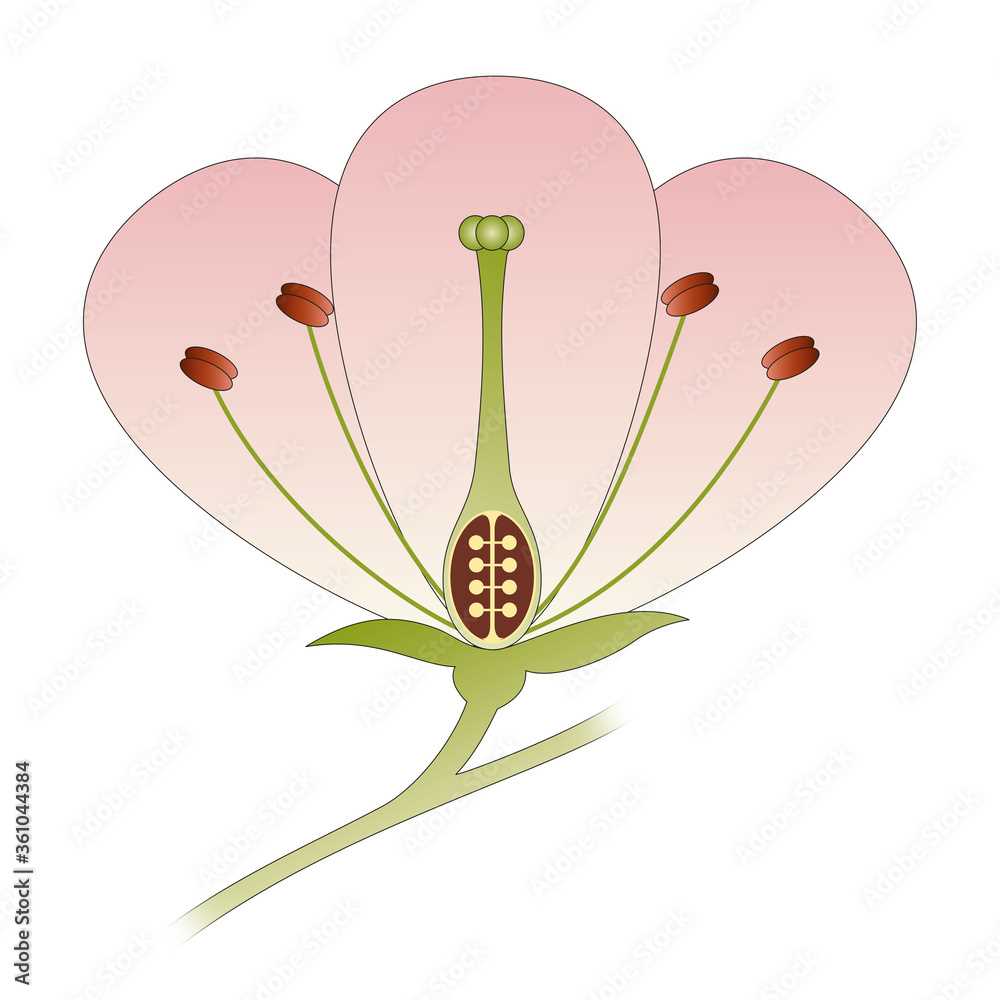
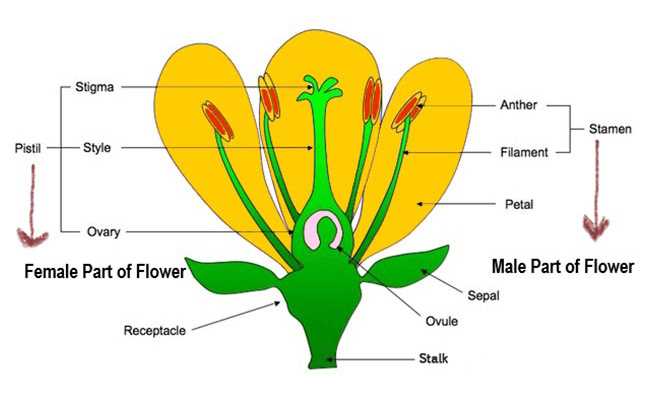
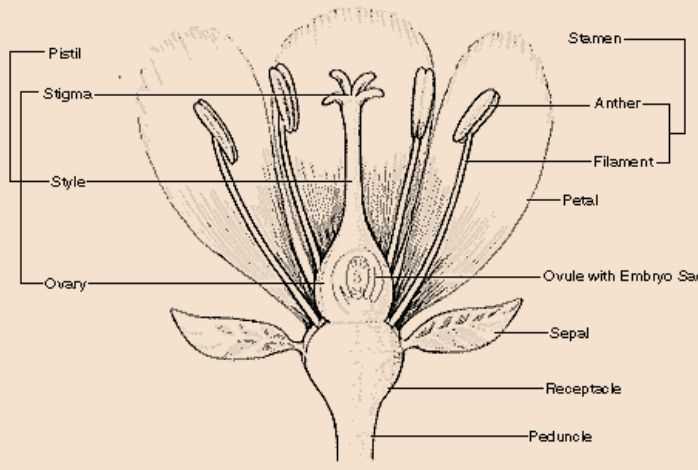
Stamen: The Male Reproductive Part
The stamen plays a crucial role in the reproductive process of many plants, embodying the essence of masculinity in nature. This structure is responsible for producing pollen, which is vital for the fertilization of ovules. Through its specialized components, the stamen ensures the continuation of various species by facilitating the transfer of genetic material.
Composed of two main parts, the anther and the filament, the stamen operates harmoniously to achieve its purpose. The anther serves as the pollen-producing region, releasing grains that can travel to other structures for potential fertilization. Meanwhile, the filament acts as a supportive stalk, elevating the anther to enhance its accessibility to pollinators.
Understanding the significance of the stamen deepens our appreciation for the intricate mechanisms of reproduction in the plant kingdom. Its role is not just functional; it is a testament to the complexity and beauty of life, showcasing how male components contribute to the broader ecological web. Through the stamen, plants exhibit their ultimate purpose: ensuring survival and evolution through generations.
Pistil: The Female Flower Component
The pistil serves as the essential reproductive structure within the reproductive system of a bloom, playing a crucial role in the processes of pollination and fertilization. It typically consists of several key components that work together to ensure successful reproduction and the development of seeds.
Structure of the Pistil
The pistil is primarily composed of three main sections: the stigma, style, and ovary. The stigma is the uppermost part, designed to capture pollen grains, while the style acts as a slender stalk connecting the stigma to the ovary, which houses the ovules. Each of these components plays an ultimate role in the fertilization process.
Function and Importance
The functions of the pistil extend beyond mere reproduction. The effective capture of pollen by the stigma initiates a series of events that lead to the creation of seeds, ensuring the continuation of plant species. This component exemplifies the intricate relationships within nature, emphasizing the vital role it plays in the life cycle of plants.
Function of Sepals in Protection
Sepals play a crucial role in safeguarding the reproductive structures during their development. These outermost components serve multiple protective functions that are essential for the overall health and success of the organism.
Key protective functions of sepals include:
- Shielding delicate inner structures from environmental factors such as pests and extreme weather.
- Preventing desiccation by retaining moisture around developing reproductive elements.
- Facilitating successful pollination by maintaining an optimal environment for attracting pollinators.
Additionally, sepals can contribute to the aesthetic appeal of the reproductive structures, further attracting beneficial agents. Overall, their protective capabilities are vital for reproductive success and the continuity of species.
Types of Flowers and Their Parts
Understanding the various forms and structures of blooms provides insight into their ecological roles and aesthetic beauty. Each species exhibits unique characteristics that serve specific functions in reproduction and pollination, contributing to the diversity of the plant kingdom.
| Type | Description | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Complete | Contains all essential components for reproduction. | Petals, sepals, stamens, pistils |
| Incomplete | Lacks one or more reproductive structures. | May have missing stamens or pistils |
| Perfect | Possesses both male and female organs. | Bisexual with stamens and pistils |
| Imperfect | Contains either male or female structures but not both. | Unisexual, either staminate or pistillate |
| Composite | Consists of multiple smaller flowers grouped together. | Ray and disk florets |
Diagram of Flower Anatomy
This section explores the intricate structure of blooming plants, revealing the essential components that contribute to their beauty and reproductive success. Understanding the configuration of these elements is crucial for botany enthusiasts and anyone interested in the wonders of nature.
Key Components
The structure encompasses several vital elements, including the reproductive organs, which play a pivotal role in the propagation of the species. Additionally, supporting features provide stability and enhance the aesthetic appeal, ensuring these organisms thrive in their environments.
Functions and Importance
Each component serves specific functions, from attracting pollinators to facilitating fertilization. Recognizing the significance of these structures not only deepens appreciation for biodiversity but also underscores their ecological roles in various ecosystems.
Unique Features of Various Flowers
In the world of botanical wonders, different blooms exhibit a fascinating array of characteristics that enhance their beauty and ecological significance. These traits not only contribute to their visual appeal but also play crucial roles in reproduction and survival. Understanding these unique attributes allows us to appreciate the diversity of nature.
Distinctive Characteristics
- Color Variations: Many blossoms display a wide spectrum of hues, often adapted to attract specific pollinators.
- Fragrance: Scent plays a significant role in pollination, with some species emitting strong aromas to lure insects.
- Shape and Structure: The form of each bloom can vary dramatically, influencing how pollinators interact with them.
Adaptive Strategies
- Camouflage: Certain species blend in with their surroundings, providing protection from herbivores.
- Seasonal Changes: Some blossoms undergo transformations based on environmental conditions, ensuring survival in varying climates.
- Mutualistic Relationships: Many plants have developed partnerships with insects, enhancing their reproductive success through co-evolution.
Importance of Flower Parts in Nature
The intricate structures found in blossoms play a vital role in the ecosystem, influencing both the reproduction of plants and the survival of various species. These components are essential not only for the continuation of plant life but also for supporting a diverse array of fauna that rely on them for sustenance and habitat.
Key Functions in Ecosystems
- Attracting Pollinators: Bright colors and enticing scents draw in insects and birds, facilitating the transfer of pollen.
- Seed Production: Successful fertilization leads to the formation of seeds, ensuring the next generation of plants.
- Food Source: Nectar and pollen serve as nourishment for numerous species, contributing to biodiversity.
Impact on Climate and Environment
- Soil Stability: Root structures support the integrity of soil, preventing erosion.
- Carbon Sequestration: Healthy plant life contributes to carbon absorption, aiding in climate regulation.
- Habitat Creation: These structures provide shelter and nesting materials for various animals.
How Flowers Attract Pollinators
The vibrant world of flora employs various strategies to draw in essential visitors for reproduction. These techniques not only enhance the chances of successful fertilization but also create a dynamic relationship between the plants and their animal counterparts. By utilizing colors, scents, and textures, these organisms ensure their survival and continuation of their species.
Color and Visual Appeal
One of the primary methods of attraction involves the use of vivid hues. Brightly colored structures serve as visual signals to potential pollinators. The following aspects are crucial:
- Contrast: Flowers with contrasting colors stand out against their surroundings.
- Patterns: Some species develop intricate patterns that guide insects toward nectar sources.
- UV Reflection: Many plants reflect ultraviolet light, which is visible to certain pollinators like bees.
Fragrance and Chemical Signals
Aromatic compounds play a vital role in enticing visitors. The sweet scents emitted can attract a variety of creatures. Key points include:
- Sweetness: Many fragrances are sweet, signaling the availability of food.
- Timing: Certain plants release scents at specific times to align with the activity patterns of their visitors.
- Chemical Markers: Unique chemical signals can attract specific species, enhancing pollination efficiency.
Through a combination of color, scent, and strategic placement, plants successfully create an inviting environment for their vital partners, ensuring the continuation of their lineage. This intricate dance of attraction illustrates the remarkable interconnectedness of nature.
Relationship Between Flowers and Ecosystems
The intricate connections between blooming plants and their surrounding environments illustrate a vibrant tapestry of life. These botanical structures play a pivotal role in supporting various ecosystems by providing essential resources and fostering interdependent relationships among numerous organisms. Their presence not only enhances biodiversity but also contributes significantly to the ecological balance.
Pollination and Biodiversity
The act of pollination serves as a fundamental mechanism through which these organisms interact with insects, birds, and other animals. This mutualistic relationship ensures the continuation of various species, as pollinators transfer genetic material, facilitating reproduction. Consequently, the diverse array of blooming plants supports a rich community of wildlife, making ecosystems more resilient to changes.
Role in Nutrient Cycling
Blooming species also play a critical role in nutrient cycling within their habitats. Through processes like photosynthesis, they absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen, contributing to the overall health of the atmosphere. Moreover, their decay enriches the soil, promoting the growth of other flora and sustaining various forms of life. This synergy underscores the essential role that these plants hold in maintaining ecological harmony.