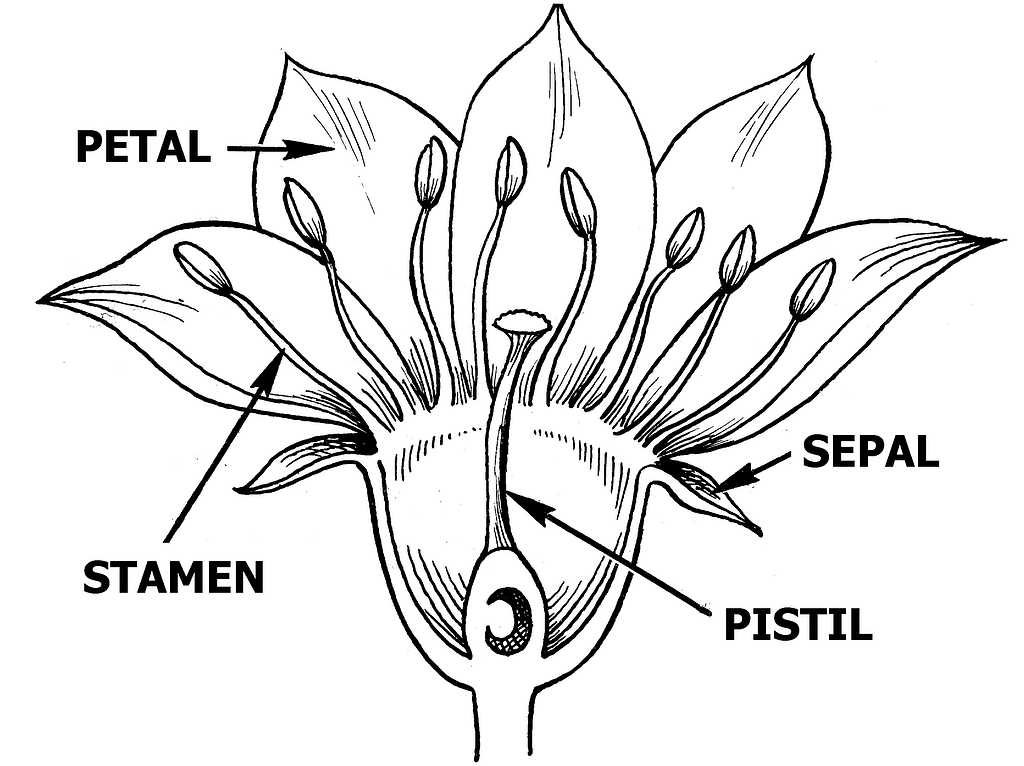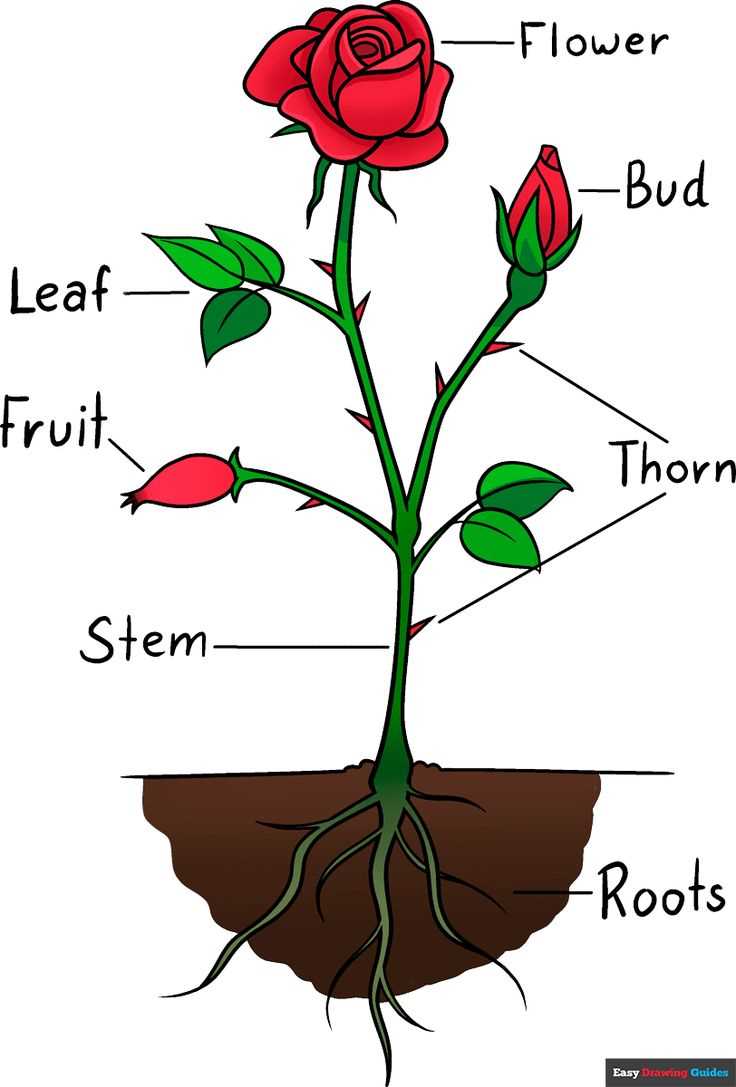
Understanding the structure of a blooming plant reveals fascinating insights into its unique composition. Each section plays a crucial role in the plant’s ability to thrive and reproduce. By examining these components, one can appreciate how intricate and essential each element is in the overall growth process.
The central elements of a bloom are responsible for key processes, including the production of seeds and facilitating the transfer of important biological materials. These structures work together harmoniously to ensure the continuation of the species, showcasing nature’s complexity.
In addition to their practical functions, the various parts contribute to the visual and aromatic appeal of a bloom, attracting pollinators and ensuring successful reproduction. Observing these elements up close provides a deeper connection to the wonders of the natural world.
Anatomy of a Rose Flower
The structure of this well-known plant is intricate and fascinating. Various components work in harmony to support growth, reproduction, and overall function. Each element plays a crucial role in ensuring the plant thrives in its environment.
- The external layers provide protection from external elements, preserving the core of the plant.
- Specialized components help in the reproduction process by interacting with pollinators and dispersing necessary elements for new growth.
- Some sections are designed to attract attention, often through vibrant colors or unique textures, ensuring interaction with other organisms.
These various segments, while unique in function, work together seamlessly
Main Structural Components of a Rose
The composition of this type of plant is defined by several key elements that contribute to its growth, beauty, and reproduction. Each section has its own role, contributing to the overall functionality and aesthetic appeal. Understanding these components helps to appreciate how such a plant thrives in different environments.
| Component | Description | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stem | This part supports the entire organism, transporting nutrients and water from the roots to other sections. | ||||||||||||||||
| Sepals | Small leaf-like structures that protect the developing bud before it opens. | ||||||||||||||||
| Petals |
Rose Petal Arrangement and FunctionThe unique layout of vibrant petals plays a crucial role in the overall structure. Each petal is positioned in a way that enhances both the visual appeal and practical interactions with its surroundings. This harmonious alignment is essential for attracting attention and contributing to important biological processes.
Reproductive Organs of a RoseThe structures responsible for creating new life in this plant work in harmony to ensure its survival and propagation. They are central to the process of transferring essential elements that enable reproduction, a cycle that is critical for sustaining the species. These organs are often enclosed within vibrant, protective layers, ensuring they are shielded from environmental factors while they perform their function. Male Structure: This component generates and releases the crucial material that must be transferred for fertilization to occur. It consists of several smaller elements that work together to carry out this role. Their position within the plant allows for optimal exposure, aiding in the spread of their material. Female Structure: The counterpart, often located deeper within, is designed to receive the material released by its male counterpart. This area also houses the essential components wh The Role of Sepals in Rose Anatomy
Sepals serve as an essential component of the plant’s structure, playing a protective role during its early development. These small, leaf-like structures form a barrier around delicate elements, ensuring safety from external factors such as harsh weather or pests. Their primary function is to provide shelter during the initial stages, creating a stable environment for growth and maturation. Protection and SupportOne of the critical tasks sepals perform is shielding emerging parts from damage before they are ready to flourish. They act as a protective layer, helping maintain the integrity of the plant by preventing harm during crucial stages. Sepals also offer support, holding key elements in place and ensuring they remain intact until they are fully developed. Transition to Maturity
As the plant progresses through its life cycle, sepals undergo changes. Initially How Stamen Contributes to Pollination
The reproductive structure of many plants plays a vital role in the process of transferring pollen. This function is crucial for the continuation of species, as it facilitates the fertilization process necessary for producing seeds. The components responsible for this task are specifically designed to attract pollinators and effectively deliver pollen to other specimens. One key element in this process is the filament, which supports the anther, the part where pollen is produced. This structure not only elevates the anther to an optimal position for transfer but also enables efficient access for visiting insects or other pollinators. The vibrant colors and enticing fragrances associated with these reproductive elements are essential in attracting potential pollinators, increasing the chances of successful pollen transfer. Once a pollinator interacts with the anther, pollen grains adhere to their bodies. As these creatures move from one reproductive structure to another, they inadvertently carry the pollen along, aiding in the fertilization of nearby specimens. This natural mechanism of pollen transfer ensures genetic diversity and the resilience of future generations, showcasing the intricate relationship between plants and their pollinators. Understanding the Pistil in RosesThe pistil plays a crucial role in the reproductive process of plants, serving as the female reproductive organ. It is essential for the development of seeds, ensuring the continuation of species. Composed of multiple components, the pistil facilitates the transfer of pollen and fosters the fertilization process. The structure of the pistil can be broken down into several key elements, each with a specific function:
Each component works harmoniously to ensure successful reproduction. Understanding this structure provides insight into the intricate processes that sustain plant life and biodiversity. Function of the Ovary in Roses
The ovary plays a crucial role in the reproductive process, serving as the location where fertilization occurs and seeds are developed. This structure is essential for the continuation of the species, as it houses the potential for new life. Understanding its functions helps to appreciate the intricacies of plant reproduction. Key functions of the ovary include:
In summary, the ovary’s functions are integral to the reproductive cycle, ensuring successful fertilization, seed development, and the overall survival of the plant’s lineage. Stem and Its Role in Rose GrowthThe central structure of a plant plays a vital role in its overall development and health. This component serves as a support system, elevating the upper parts while providing stability against external forces. Additionally, it acts as a conduit for essential nutrients and water, facilitating their journey from the roots to the rest of the organism. As the main axis, this structure not only supports the weight of leaves and blooms but also influences the plant’s ability to capture sunlight. A robust and healthy stem enables the organism to withstand environmental stresses, ensuring that it can thrive in various conditions. Moreover, it contributes to the plant’s aesthetic appeal, often determining its form and structure. The efficiency of nutrient transportation through the stem is crucial for the vitality of the entire organism. Any damage or disease affecting this central axis can impede growth and reduce overall health. Thus, maintaining the integrity of this structure is essential for the flourishing of the organism and its ability to produce new growth each season. How Nectar Guides Attract PollinatorsNectar guides serve as crucial signals in the natural world, enhancing the interaction between certain organisms and their pollinators. These markings, often visible to various insects and animals, play a vital role in guiding them towards the source of nourishment, ensuring successful reproduction for the plant. Typically, these alluring patterns are designed to be visually striking, attracting potential pollinators through their contrast against the surrounding colors. This attraction is not merely coincidental; it has evolved over time to maximize efficiency in the pollination process.
Through these mechanisms, nectar guides not only facilitate the transfer of pollen but also support the delicate balance of ecosystems, highlighting the intricate relationships between flora and fauna. Relationship Between Rose Thorns and DefenseThe sharp protrusions found on certain plants play a crucial role in their survival. These structures serve as a natural deterrent against potential threats, including herbivores and insects. By understanding their purpose, one can appreciate the evolutionary adaptations that enhance the plant’s chances of thriving in various environments. These protective elements offer multiple advantages:
In addition to their defensive capabilities, these structures can also impact pollination. Some species have developed unique relationships with pollinators, ensuring that the plant attracts beneficial insects while simultaneously protecting itself from harmful ones. This balance highlights the intricate interactions within ecosystems and the role that defense mechanisms play in sustaining life. Understanding the significance of these sharp features not only sheds light on the plant’s defensive strategies but also illustrates the complex web of relationships in nature that contribute to the survival of various species. |