
In any mechanical system, knowing the location and function of essential elements is crucial for both maintenance and repair. By exploring the structure and connections within a specific model, users can gain valuable insight into how to troubleshoot issues and ensure proper functionality.
Each mechanical structure consists of several interconnected elements, all working together to deliver performance. Identifying the placement and relationships of these elements helps streamline the process of diagnosing issues, whether you’re working with older models or more modern designs.
This guide provides an overview of essential units and their positioning, allowing for easier identification and understanding of how each unit contributes to the overall system. Whether it’s ensuring efficient operation or addressing potential faults, having a clear reference of these elements can save time and improve overall efficiency.
Understanding the Structure of This Agricultural Machine
Comprehending the overall design of this versatile machine is essential for ensuring its long-term efficiency and reliability. The internal framework and various systems work together to handle a wide range of tasks, making it a key asset in agricultural operations. By looking at how the components are arranged, one can gain insight into how the machine operates under different conditions.
Key Systems Overview
- Powertrain: The driving force behind the equipment, responsible for transmitting power to the necessary systems.
- Hydraulics: This system provides the necessary force to manage various attachments and implements effectively.
- Cooling Mechanism: Ensures that the engine remains within optimal temperature limits during extended use.
Structural Elements
- Frame: The backbone that supports all the working parts, ensuring durability and stability.
- Transmission: Facilitates smooth operation by managing the machine’s speed and torque distribution.
- Axles and Wheels
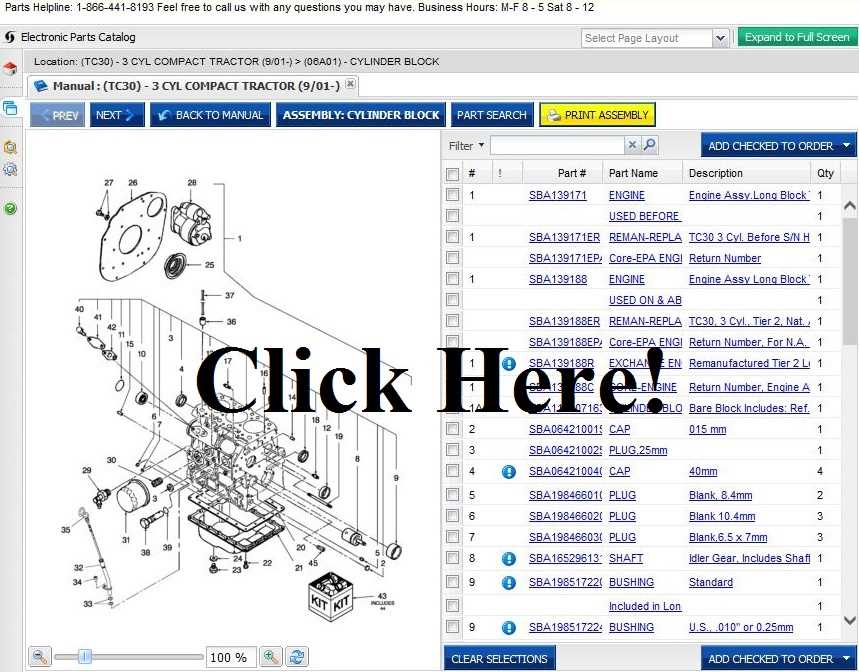
Key Components of the Ford 3930 Engine
The engine of this agricultural vehicle is known for its efficiency and durability, with a combination of crucial elements that ensure smooth operation in various conditions. Understanding the major parts of this engine is essential for maintaining its performance and longevity.
Main Elements Ensuring Engine Operation
- Cylinder Block: This serves as the foundation for the engine, housing the cylinders and associated components responsible for combustion.
- Pistons: These move within the cylinders, converting fuel energy into mechanical motion that powers the vehicle.
- Crankshaft: This part translates the linear motion of the pistons into rotational energy, driving other mechanisms.
Supporting Components for Engine Performance
- Fuel Injection System: Delivers the right amount of fuel into the combustion chamber, ensuring optimal power generation.
- Cooling System: Regulates the temperature of the engine, preventing overheating during extended use.
- Lubrication System: Keeps engine parts moving smoothly by reducing friction and preventing wear.
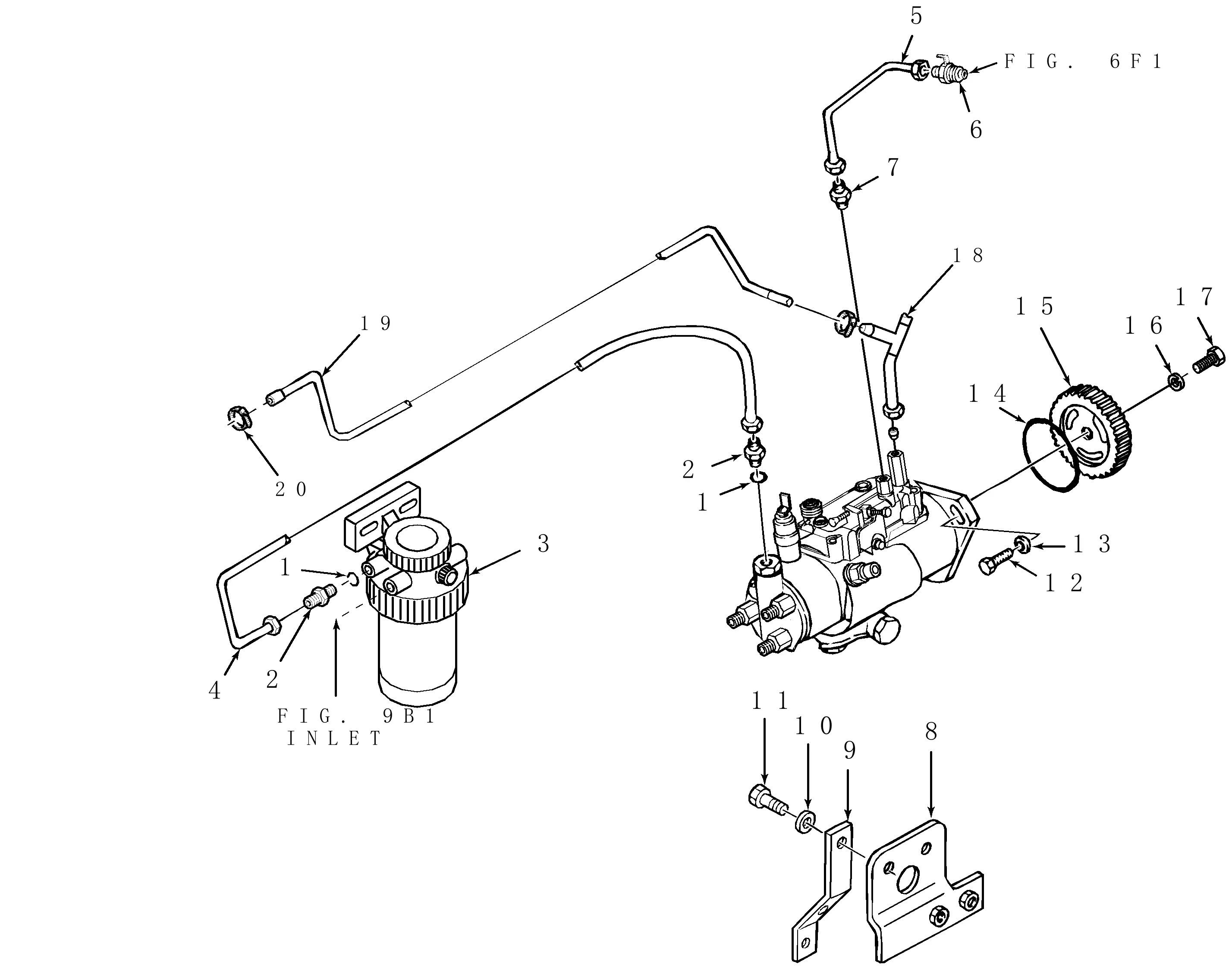
Exploring the Hydraulic System Layout
The hydraulic system serves as a critical component that drives many of the essential functions within machinery. Understanding the arrangement of its elements provides valuable insights into how fluid power is distributed to perform tasks such as lifting or adjusting implements. This layout is designed to ensure smooth operation, with various elements working together to optimize performance.
At the core of the system lies a pump, which generates the necessary pressure to move the fluid. Valves control the flow, allowing operators to direct the power as needed. Additionally, hoses and lines are responsible for transporting the fluid throughout the system, while cylinders translate hydraulic force into mechanical action. Each component plays a role in maintaining efficiency and responsiveness in the equipment’s operation.
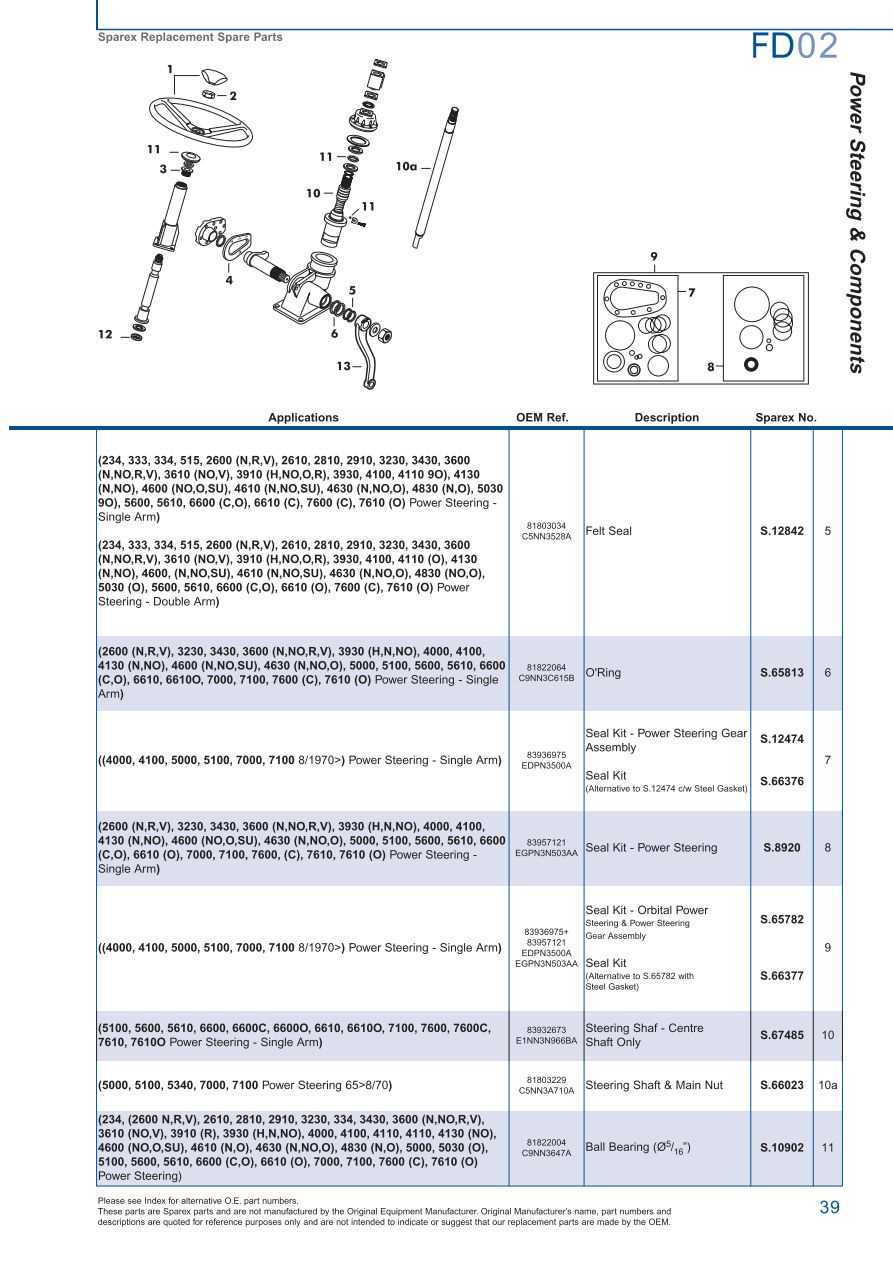
Identifying Steering System Elements
The steering mechanism is a crucial component that allows precise control of direction and stability. Understanding the key elements that make up this system is essential for maintaining smooth operation and ensuring reliable performance in various conditions.
One of the primary components includes the steering wheel, which serves as the main interface for the operator. Connected to it is the steering column, a shaft that transmits the motion to the rest of the system. Additionally, the system incorporates linkages that connect the steering mechanism to the wheels, allowing for responsive and accurate turns.
To complete the steering assembly, there are also essential joints and rods that work together to provide flexibility and durability. Each part must be regularly inspected to avoid issues that can compromise control and handling.
Transmission System Breakdown
The transmission system is a crucial element that ensures the efficient transfer of power from the engine to the wheels. Understanding how this mechanism operates provides insight into the overall functionality and performance of the machine. This section will focus on the key components and their roles in maintaining smooth movement and control.
Main Components Overview
- Gearbox: Facilitates different speed and torque levels, allowing the vehicle to adapt to various driving conditions.
- Clutch: A crucial part that connects and disconnects the engine from the transmission, helping to engage gears smoothly.
- Driveshaft: Transfers rotational power from the transmission to the wheels, playing a vital role in motion.
- Shift Mechanism: Ensures precise gear changes, impacting the overall driving experience and efficiency.
Transmission Maintenance Tips
- Regularly check and change transmission fluid to avoid wear and ensure smooth operation.
- Inspect the clutch system periodically
Examining the Electrical Wiring Overview
This section delves into the fundamental aspects of electrical connections in a specific machinery model. Understanding the layout and functionality of wiring is crucial for efficient operation and maintenance. This overview aims to highlight the primary components and their interrelations within the electrical system.
Key Components of the Electrical System
- Wiring Harness: The central structure that organizes and protects electrical wires, ensuring efficient signal transmission.
- Connectors: Elements that facilitate secure electrical connections, enabling quick assembly and disassembly of components.
- Switches: Devices that control the flow of electricity, allowing operators to manage various functions of the equipment.
- Fuses: Safety devices designed to protect circuits from overload by breaking the connection when current exceeds safe levels.
Understanding Wiring Layout
A clear understanding of the wiring arrangement is essential for troubleshooting and maintenance. The layout typically follows a logical path, linking power sources to various components efficiently.
- Begin by identifying the main power source and its connections to the system.
- Trace the paths leading to critical components, such as the control panel and actuators.
- Examine the protection devices installed along the wiring to ensure circuit integrity.
Familiarizing oneself with these elements and their configurations can significantly enhance the maintenance process and reduce the risk of electrical failures.
Cooling System Parts and Connections

The efficiency of any machinery relies heavily on its ability to manage heat. The cooling mechanism plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures, preventing overheating, and ensuring longevity. Understanding the components and their interconnections is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key elements involved in the cooling mechanism include:
- Radiator: This component dissipates heat from the coolant into the atmosphere, ensuring that the liquid remains at a manageable temperature.
- Water Pump: Responsible for circulating coolant throughout the system, maintaining a consistent flow and pressure.
- Thermostat: Regulates the flow of coolant based on the temperature of the engine, opening and closing to maintain the desired thermal balance.
- Hoses: Flexible tubes that transport coolant between various components, allowing for expansion and contraction as temperatures fluctuate.
- Coolant Reservoir: Stores excess coolant and allows for expansion as the liquid heats up, providing a buffer to prevent overflow.
Connections between these elements must be secure and leak-free to ensure proper functioning. Regular inspections should focus on:
- Checking for signs of wear or damage on hoses and connections.
- Ensuring clamps and fittings are tight to prevent leaks.
- Monitoring the coolant level in the reservoir and adding as needed.
By familiarizing oneself with these components and their relationships, effective maintenance can be achieved, promoting optimal performance and reliability of the machinery.
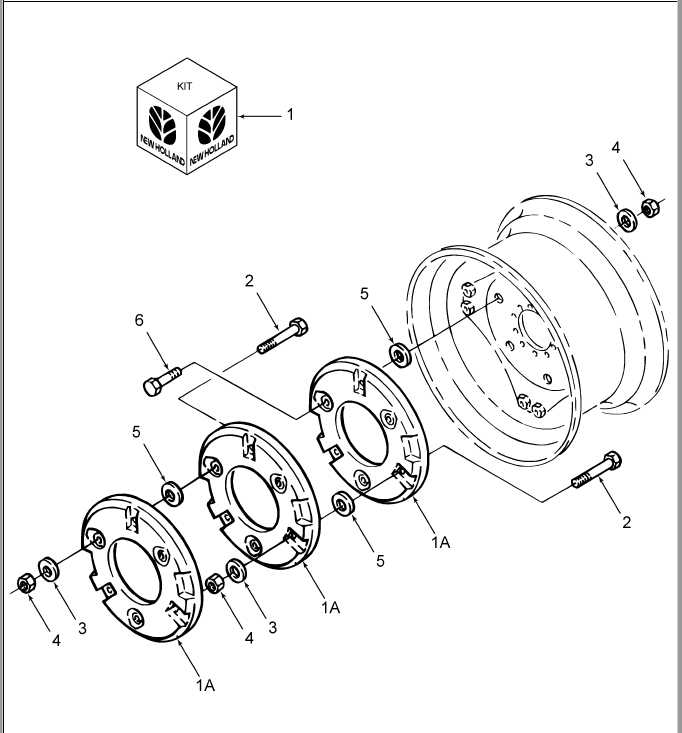
Brake System Diagram Insights
The braking mechanism is a crucial component in any vehicle, ensuring safety and control during operation. Understanding its configuration can enhance maintenance practices and help diagnose potential issues. This section delves into the key elements of the braking setup, highlighting its structure and function.
Key Components and Their Functions
At the heart of the braking setup lies the hydraulic system, which utilizes fluid pressure to activate the brakes effectively. Brake pads and rotors work in tandem, providing the necessary friction to slow down or stop the machine. Additionally, the master cylinder plays a pivotal role by converting force from the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure, facilitating the braking process.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Regular inspections of the braking system can help identify wear and tear on components such as lines and calipers. Symptoms like reduced stopping power or unusual noises may indicate underlying problems that require immediate attention. Addressing these concerns promptly ensures optimal performance and safety.
Fuel System Parts and Functions
The fuel system in machinery plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient engine performance and overall functionality. Each component within this system is designed to manage the delivery and regulation of fuel, facilitating optimal combustion and energy production.
One of the key elements is the fuel tank, which stores the necessary liquid and maintains the required pressure for distribution. Fuel is drawn from the tank by a pump, which sends it through lines to the engine. The filtering mechanism removes impurities, protecting the engine from potential damage.
In addition, the injectors or carburetors mix the fuel with air in precise ratios, essential for efficient combustion. Sensors monitor various parameters, ensuring that the system operates within specified limits. Each component, from the storage to the delivery system, contributes to the overall efficiency and performance of the engine.
Understanding the Clutch Assembly
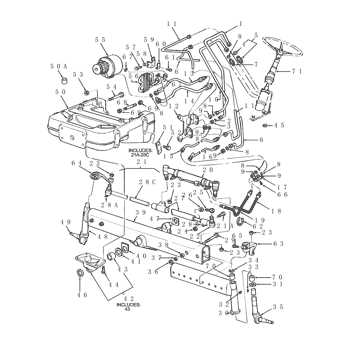
The clutch assembly plays a crucial role in the operation of a vehicle’s transmission system, allowing for the engagement and disengagement of the engine from the drivetrain. This mechanism enables smooth shifting between gears, facilitating effective power transfer from the engine to the wheels. Understanding its components and functionality is essential for anyone involved in maintenance or repair tasks.
Components of the Clutch Assembly

At the heart of the clutch assembly lies several key components that work together to achieve seamless operation. Each part serves a specific function, contributing to the overall effectiveness of the system. Below is a summary of the primary elements:
Component Function Clutch Plate Transfers torque between the engine and transmission when engaged. Pressure Plate Applies pressure to the clutch plate, ensuring it engages properly. Release Bearing Facilitates the disengagement of the clutch when the pedal is pressed. Flywheel Provides a surface for the clutch plate to engage with and helps maintain engine speed. Functionality Overview

When the clutch pedal is pressed, the release bearing moves away from the pressure plate, allowing the clutch plate to disengage from the flywheel. This action interrupts the connection between the engine and transmission, enabling the driver to shift gears smoothly. Once the pedal is released, the pressure plate re-engages the clutch plate with the flywheel, restoring the connection and allowing power to flow from the engine to the wheels.
Rear Axle and Differential Layout
The layout of the rear axle and differential plays a crucial role in the overall functionality of the vehicle’s drivetrain. This assembly is designed to transmit power from the engine to the wheels while allowing for differential rotation, which is essential during turns. Understanding the arrangement and components involved in this system is key to ensuring optimal performance and durability.
The rear axle typically consists of the axle housing, which encases the gears and provides a stable structure for mounting the wheels. Within the housing, the differential is positioned to facilitate the distribution of torque between the two wheels. This component is vital for managing the varying speeds of the wheels, particularly when navigating curves.
Additionally, the gear ratio within the differential determines the balance between torque and speed, influencing the vehicle’s overall performance characteristics. Regular maintenance and inspections of this assembly are important to prevent wear and ensure longevity, as any issues can lead to significant operational problems and costly repairs.