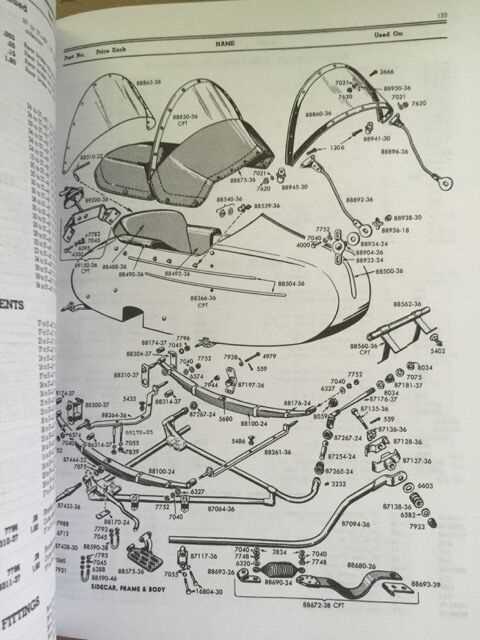
Understanding the intricate assembly of two-wheeled vehicles is essential for enthusiasts and mechanics alike. Detailed visual representations of each element can enhance knowledge, making it easier to identify components and comprehend their functions within the overall system.
Such illustrations provide a comprehensive overview, showcasing how various elements interconnect and operate. These visual aids serve as invaluable resources for maintenance, upgrades, and customization, allowing individuals to gain insights into the engineering behind these machines.
By studying these schematics, riders can better appreciate the craftsmanship involved, fostering a deeper connection with their vehicles. This knowledge empowers them to undertake repairs with confidence and encourages a more profound understanding of the mechanics at play.
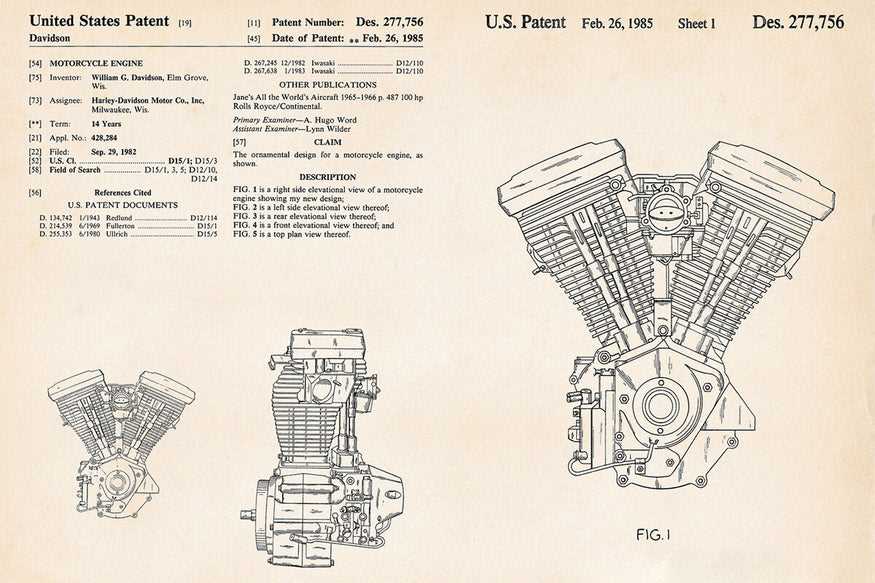
Essential Components of Harley Engines
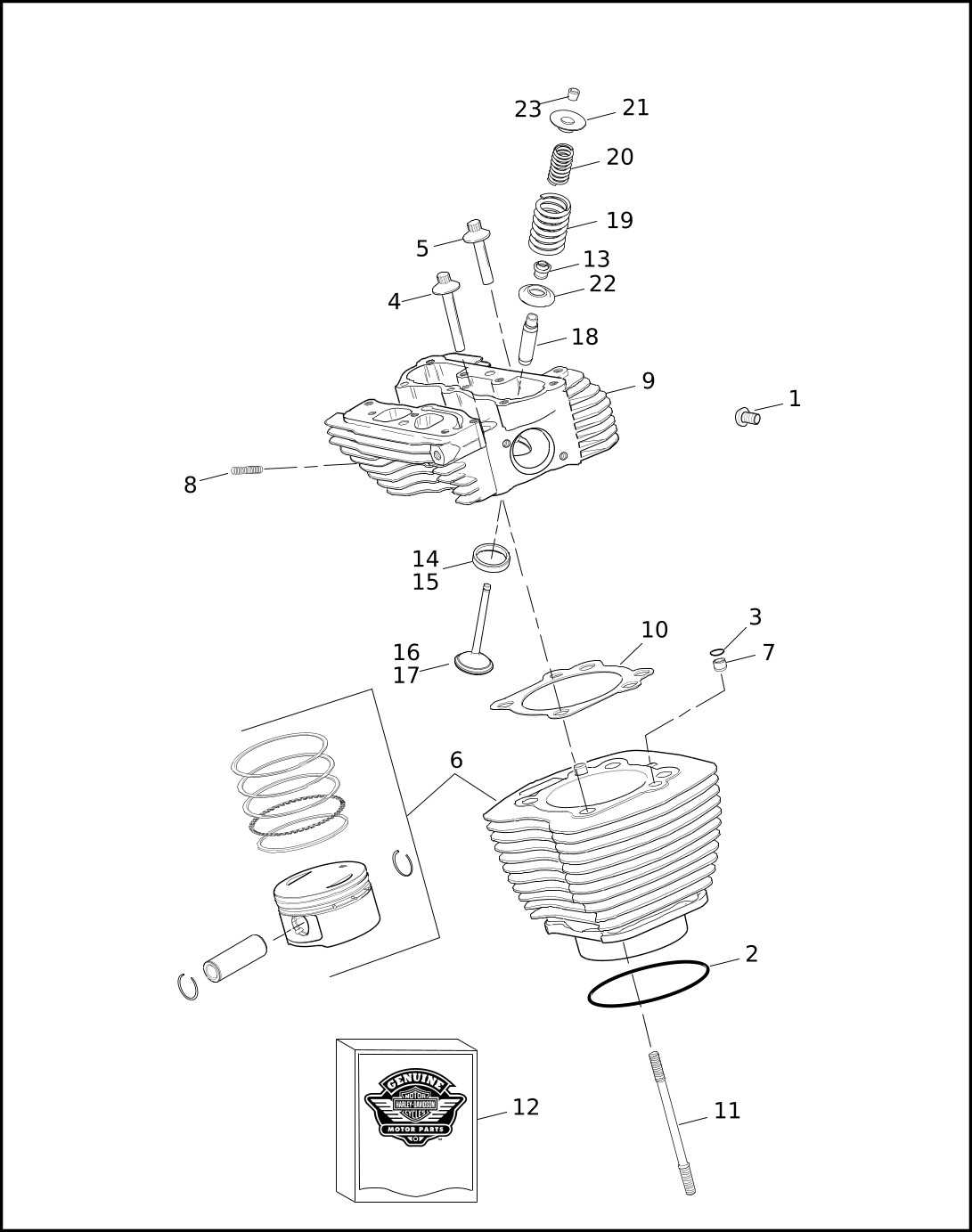
The core structure of these powerful machines consists of several critical elements that work in harmony to ensure optimal performance. Understanding the fundamental aspects of these units is crucial for anyone looking to maintain or enhance their functionality. Each component plays a specific role in delivering the impressive capabilities that enthusiasts have come to appreciate.
Key Functional Elements

Among the most vital components are the cylinders, which house the combustion process. These structures are designed to withstand intense pressure and temperature, facilitating the transformation of fuel into energy. Additionally, the crankshaft is essential, as it converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational force, powering the entire vehicle.
Supporting Structures
Equally important are the valve train and ignition system, which ensure proper airflow and timely combustion. The valve train regulates the intake and exhaust of gases, while the ignition system initiates the combustion process, playing a pivotal role in engine responsiveness. Together, these components create a robust framework that defines the experience of operating these exceptional machines.
Understanding the Electrical System
The electrical system is a critical component that ensures the proper functioning of various systems within the vehicle. It encompasses a network of wires, connections, and devices that work together to provide power and control functionalities.
Key elements of the electrical system include:
- Batteries: These are the main source of electrical energy, storing power for starting the engine and running accessories.
- Wiring Harness: A collection of wires that transmit electrical signals and power between different components.
- Alternator: This device generates electricity while the engine is running, replenishing the battery and powering the electrical systems.
- Ignition System: Responsible for starting the engine, it includes components like spark plugs and ignition coils.
- Lighting System: Ensures visibility and safety by providing illumination through headlights, taillights, and turn signals.
Understanding these elements is essential for troubleshooting issues and ensuring optimal performance.
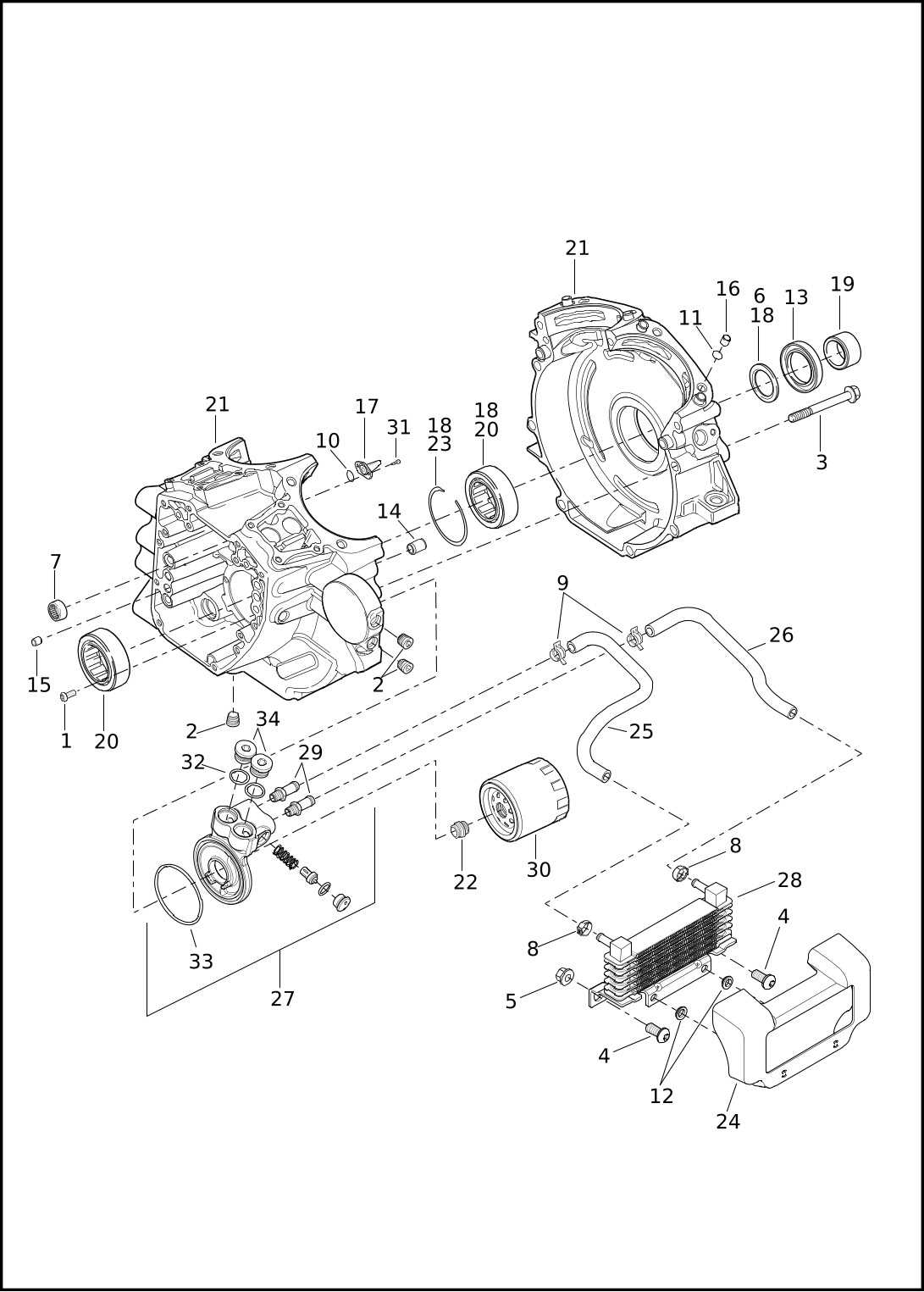
Transmission and Drivetrain Insights

The interplay between the transmission and drivetrain is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and efficiency in two-wheeled vehicles. Understanding their components and functionality can greatly enhance the riding experience, allowing enthusiasts to make informed decisions regarding maintenance and upgrades.
Key Components of the Transmission

- Gearbox: Responsible for changing gear ratios, which affects acceleration and speed.
- Clutch: Engages and disengages power from the engine to the transmission, allowing for smooth shifting.
- Sprockets: Essential for transferring power from the engine to the rear wheel.
Drivetrain Functions
- Power Delivery: Transmits engine power to the wheels, impacting acceleration and handling.
- Torque Management: Helps in controlling the amount of power sent to the wheels during different riding conditions.
- Efficiency Optimization: Proper tuning of the drivetrain components ensures maximum energy utilization, enhancing fuel efficiency.
Fuel System Anatomy Explained
The fuel system plays a crucial role in the performance and efficiency of any internal combustion engine. Understanding its components and their interactions helps enthusiasts and mechanics ensure optimal operation. This section delves into the essential elements that contribute to the effective delivery of fuel, ensuring that the engine runs smoothly and efficiently.
Key Components: The primary elements of the fuel system include the fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel filter, and injectors. Each part serves a distinct function, from storing fuel to delivering it precisely to the combustion chamber. Proper maintenance of these components is vital for maintaining performance and preventing issues.
Fuel Delivery Process: Fuel is drawn from the tank by the pump, which generates the necessary pressure to move the fuel through the lines. The fuel filter ensures that any contaminants are removed before the fuel reaches the injectors. Finally, the injectors atomize the fuel for efficient mixing with air, facilitating optimal combustion.
Conclusion: A well-functioning fuel system is essential for the overall health of the engine. Regular checks and maintenance can help identify potential issues before they escalate, ensuring longevity and performance.
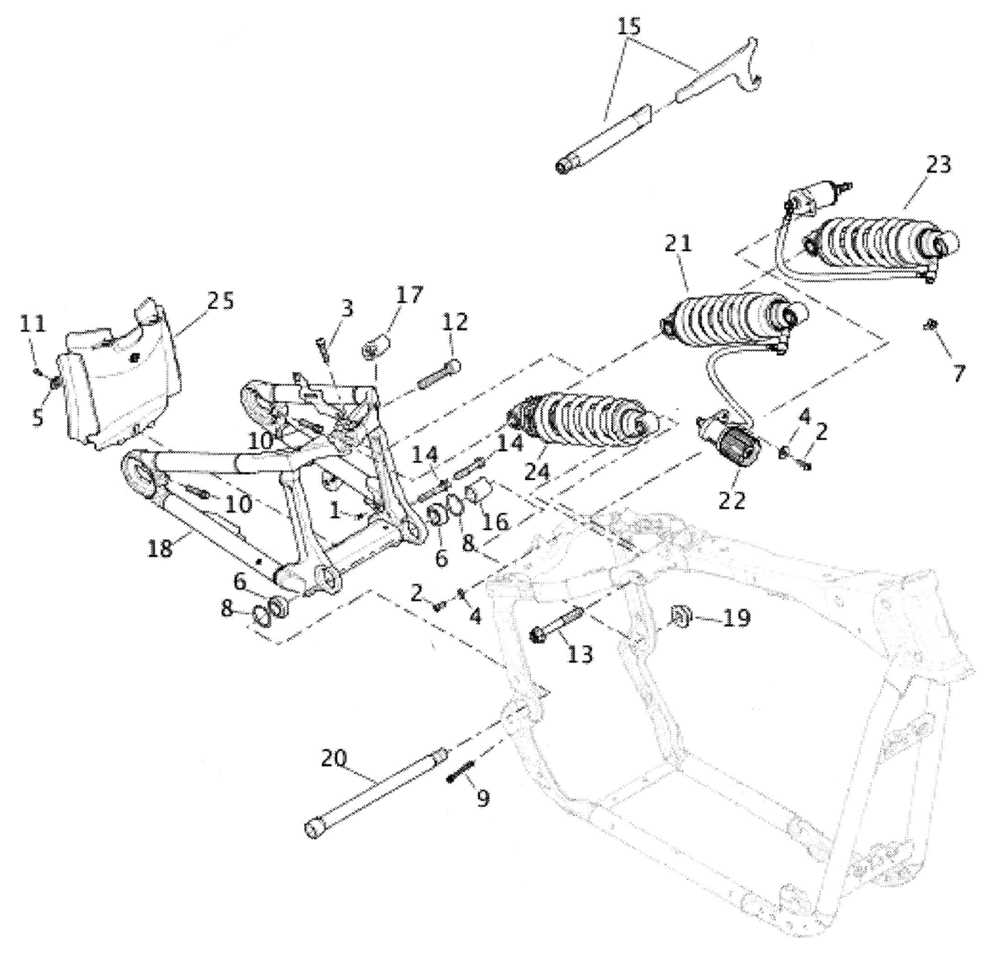
Suspension Parts and Functionality
The suspension system plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth and controlled ride by absorbing shocks and maintaining contact between the wheels and the road surface. It comprises various components designed to work together, enhancing stability, comfort, and overall performance. Understanding these elements and their functions is essential for optimizing vehicle handling and ensuring safety on the road.
Key Components of the Suspension System
Several essential elements contribute to the effective functioning of the suspension system. Each component has a specific role, from providing support to absorbing impacts and allowing for adjustments in ride height and stiffness.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Shock Absorber | Dampens the oscillations of the springs and stabilizes the ride. |
| Spring | Absorbs shocks from the road and supports the weight of the vehicle. |
| Control Arm | Connects the suspension system to the vehicle’s frame and allows for vertical movement. |
| Strut | Combines the functions of a shock absorber and a spring, providing structural support and damping. |
| Sway Bar | Reduces body roll during turns and enhances stability. |
Importance of Maintenance
Regular inspection and maintenance of the suspension system are vital for optimal performance. Worn or damaged components can lead to decreased handling, increased tire wear, and compromised safety. Addressing issues promptly can enhance ride quality and extend the lifespan of the system.
Braking System Breakdown
The braking mechanism of a vehicle is crucial for ensuring safety and control while on the road. A thorough understanding of its components and functionality can significantly enhance maintenance and performance.
Key elements of the braking system include:
- Brake Pads: These components create friction against the rotor, allowing the vehicle to slow down or stop.
- Rotors: The discs that the brake pads press against to generate the necessary force for deceleration.
- Calipers: The devices that house the brake pads and apply pressure to them against the rotors.
- Brake Lines: These conduits carry hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the calipers.
- Master Cylinder: The heart of the braking system, it converts the force applied to the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure.
Each of these components plays a vital role in the overall effectiveness of the braking system. Regular inspection and timely replacement of worn parts can ensure optimal performance and safety.
Considerations for maintaining the braking system include:
- Routine inspection of brake pads for wear and tear.
- Checking the condition of rotors for warping or scoring.
- Ensuring brake fluid levels are adequate and free from contamination.
- Inspecting calipers for leaks and proper operation.
- Monitoring the performance of the master cylinder for any signs of failure.
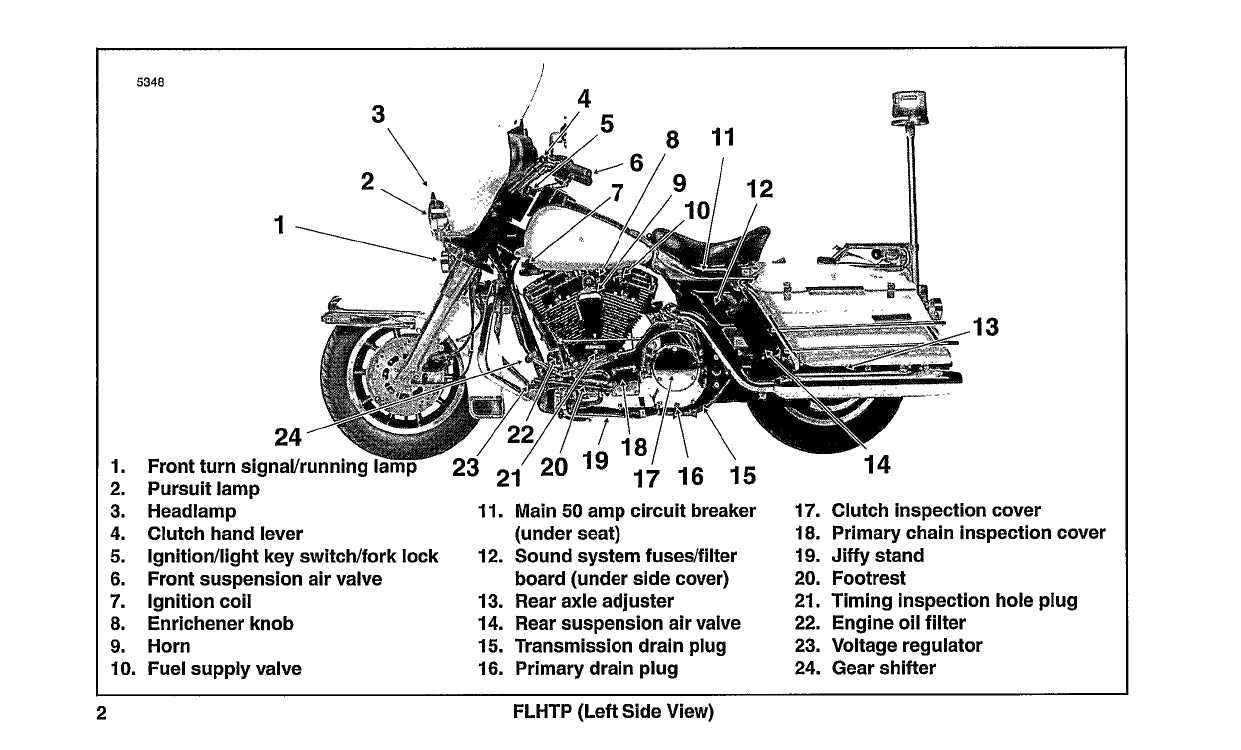
Chassis and Frame Structure

The framework of a two-wheeled vehicle serves as its backbone, providing essential support and stability. A well-designed chassis not only enhances performance but also contributes to rider comfort and safety. This section explores the key components and configurations that define the structure of these powerful machines.
- Frame Design: The frame is typically constructed from steel or aluminum, offering a balance between strength and weight.
- Suspension System: This includes front forks and rear shock absorbers, which work together to smooth out the ride over various terrains.
- Engine Mounting: Secure placement of the engine is crucial for optimal weight distribution and handling.
- Footpeg and Handlebar Placement: These components are strategically positioned to enhance rider ergonomics and control.
- Rear Swingarm: This part connects the rear wheel to the frame, allowing for wheel movement during suspension compression.
Understanding these elements is vital for enthusiasts looking to modify or restore their vehicles, ensuring that any adjustments maintain the integrity of the overall structure.
Maintenance Tips for Motor Parts
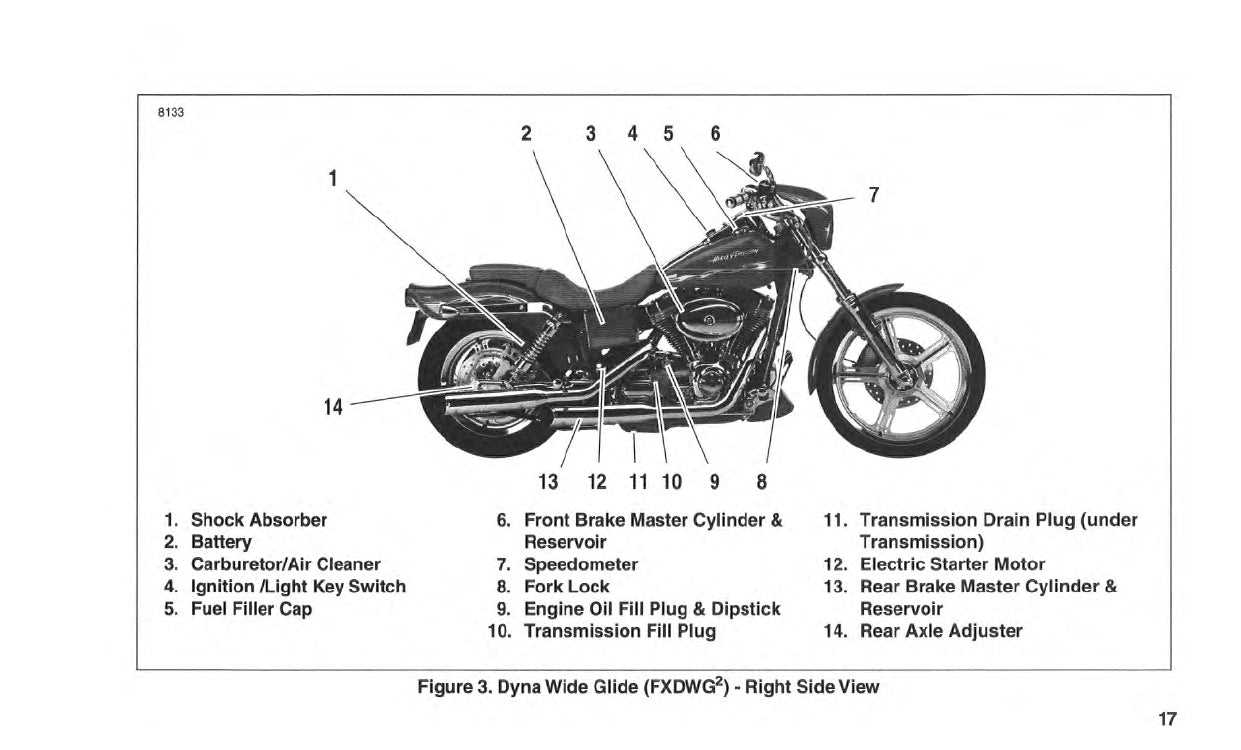
Proper upkeep is essential for the longevity and performance of any vehicle. Regular inspections, timely replacements, and appropriate care can significantly enhance the reliability of various components. Adopting a systematic approach to maintenance can prevent unexpected failures and ensure a smoother operation over time.
Regular Inspection
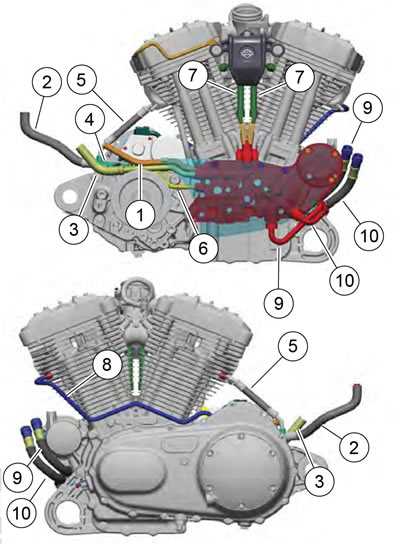
Conduct frequent assessments to identify wear and tear early. Check for leaks, unusual noises, and any signs of corrosion. Regularly scrutinizing critical components helps in taking proactive measures, ensuring everything functions correctly.
Clean and Lubricate
Keeping components clean is vital for their optimal performance. Accumulated dirt and debris can cause malfunctions. Ensure to clean surfaces and apply suitable lubricants to minimize friction and prolong the life of mechanical parts.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Inspection for wear | Monthly | Look for leaks and unusual signs |
| Cleaning components | Every 3 months | Remove dirt and grime buildup |
| Lubrication | Every 6 months | Use appropriate lubricants for parts |
Common Modifications and Upgrades
Enhancing the performance and aesthetics of two-wheeled vehicles has become a popular pursuit among enthusiasts. Riders often seek to customize their machines to improve handling, increase power output, or simply to achieve a more personal look. This section explores various widely adopted alterations that can elevate the overall riding experience.
Performance Enhancements
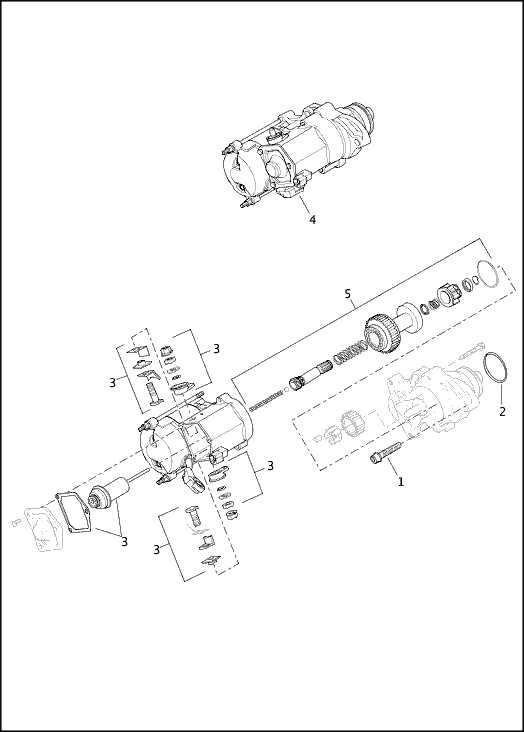
One of the most sought-after improvements involves upgrading the engine components to boost horsepower and torque. This can be achieved by installing high-flow air filters, aftermarket exhaust systems, or tuning the engine’s electronic control unit (ECU). Such modifications not only enhance acceleration but also provide a more exhilarating auditory experience while riding.
Aesthetic Customizations
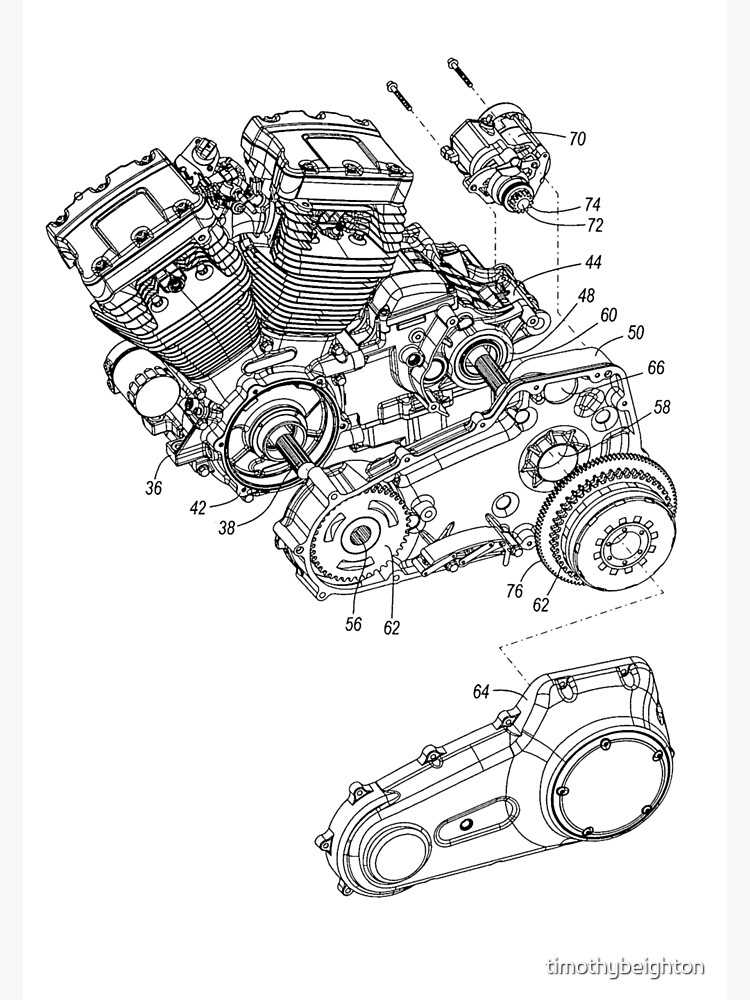
In addition to performance upgrades, visual enhancements play a crucial role in personalizing two-wheeled vehicles. Changing the paint color, adding custom decals, or installing unique lighting systems can significantly transform the overall appearance. Riders often opt for distinctive handlebars, seats, or grips to create a unique style that reflects their personality and preferences.
Visual Resources for Part Identification
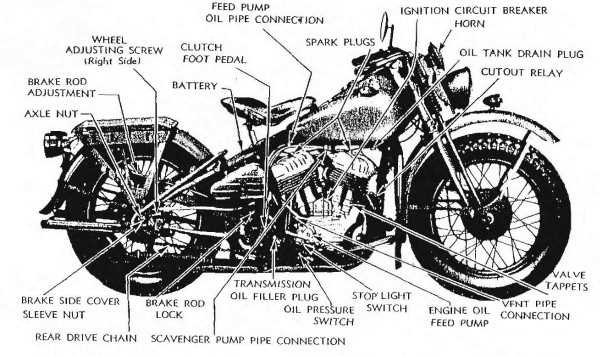
Effective identification of components is essential for maintaining and repairing vehicles. Utilizing various visual aids can greatly enhance the understanding of different elements, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in work. These resources can range from detailed illustrations to comprehensive guides, each offering valuable insights into the intricacies of assemblies.
Illustrative Guides
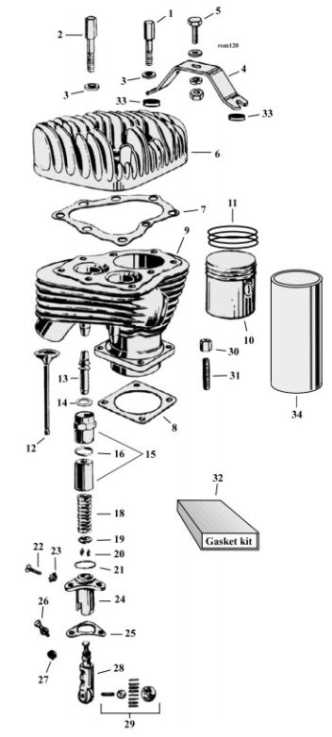
Illustrative guides provide clear and concise images that highlight specific elements within a system. They serve as excellent references for individuals looking to familiarize themselves with the layout and functionality of various components. By studying these guides, users can quickly pinpoint the parts they need, streamlining the repair or maintenance process.
Online Databases
Online databases are invaluable tools that compile extensive information about different components. These platforms often feature high-resolution images and interactive diagrams, allowing users to explore each part in detail. Access to such resources can significantly improve one’s ability to identify and source necessary items, making it easier to undertake repairs or modifications.