Understanding the intricate details of various agricultural machinery is essential for efficient operation and maintenance. This section provides an in-depth exploration of the key elements that ensure optimal performance and reliability in the field. Knowing how different mechanical systems work together can help in diagnosing issues and performing necessary repairs.
Each piece of equipment is composed of multiple interconnected systems that must function harmoniously to achieve desired results. These components, often hidden beneath the surface, play a critical role in maintaining the durability and functionality of the machine. A clear understanding of their arrangement and interaction simplifies troubleshooting and upkeep.
In this guide, we focus on the crucial mechanical assemblies and how each part contributes to the overall efficiency. From tension controls to feeding mechanisms, every element serves a purpose in the larger system. By familiarizing yourself with these mechanisms, you can ensure the longevity and productivity of your equipment.
Overview of New Holland 269 Baler Components

The various elements of this agricultural machine work together to efficiently compress and bundle materials, ensuring seamless performance during harvesting. Understanding the individual components and their roles is essential for maintaining operational reliability and optimizing functionality.
Key Mechanical Parts
- Compression Chamber – The area where materials are compacted into dense units.
- Tie Mechanism – Ensures that the compressed units are securely fastened.
- Feeding System – Facilitates the consistent flow of materials into the machine for processing.
Structural and Supporting Elements
- Frame Assembly – Provides stability and support to the machine’s core structure.
- Axles and Wheels – Allow for smooth movement across the field during operation.
- Control Levers – Enable the operator to manage and adjust various machine settings.
Key Mechanical Parts of the 269 Baler
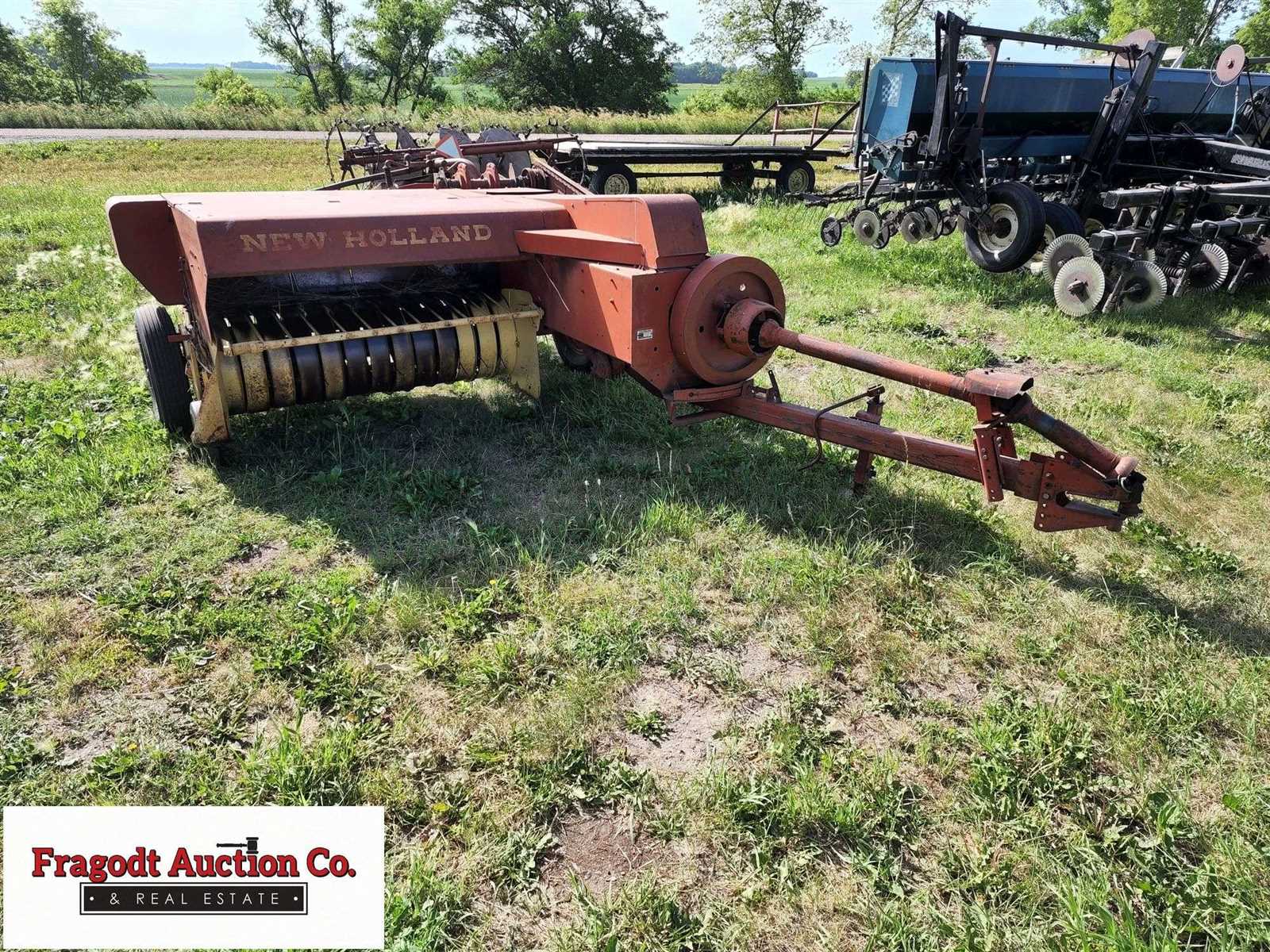

The core mechanical components of this agricultural machine are essential for its efficient operation in the field. These elements work together to ensure that the equipment functions smoothly and consistently, providing a reliable way to handle materials. Understanding the key elements of this machine allows operators to maintain performance and troubleshoot potential issues effectively.
One of the primary components is the pickup mechanism, which gathers materials from the ground and feeds them into the system. The feed system then moves these materials toward the compression chamber. In this chamber, the materials are compacted into dense units, ensuring proper shaping and handling.
Another critical component is the knotting system. This intricate assembly is responsible for tying the compressed units, securing them for transport. Proper adjustment of this system is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the finished product.
In addition to
Understanding the Knotter System Functionality
The knotter mechanism plays a crucial role in ensuring the proper tying of materials during the baling process. It ensures that the gathered material is securely fastened, allowing for efficient handling and transport. A clear understanding of how this system operates is essential for maintaining optimal performance.
The process involves several moving components that work together in precise synchronization. As the material reaches the tying stage, the knotter engages and wraps the twine or string around the bundle. The mechanism then creates a secure knot, ensuring that the load remains intact until it is released.
Key elements of this system include components responsible for gripping, cutting, and forming the knot. Each part must function correctly to avoid malfunctions such as missed ties or incomplete knots. Regular inspection and proper maintenance of these elements are vital for ensuring smooth operation.
By understanding the core functionality of the knotter system, users can better troubleshoot common issues and perform necessary adjustments to ensure consistent results.
Pickup Mechanism and Its Role in Baling
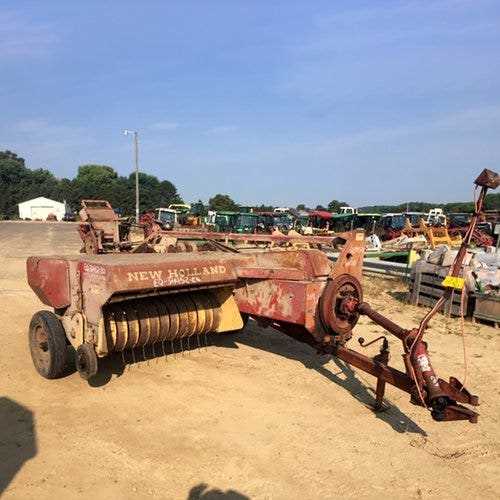

The pickup mechanism is essential for efficiently gathering loose materials from the ground and feeding them into the baling system. This component ensures smooth operation and plays a pivotal role in the baling process by enabling the collection of scattered crops or other materials. Its functionality directly influences the overall productivity of the equipment, as it controls the initial phase of material intake.
- Ensures even collection of materials from the field
- Feeds gathered materials into the compression system
- Helps maintain consistent flow to prevent clogs
- Plays a critical role in optimizing time and energy during the baling cycle
Without a properly functioning pickup system, the gathering process would become inefficient, leading to uneven bale formation and potential delays. Maintaining this mechanism is crucial for smooth and effective operation.
Plunger Assembly: Structure and Operation
The plunger assembly is a crucial component in the overall mechanism of the machine, responsible for compressing and shaping material into compact bundles. Its design combines multiple interconnected elements that work together to ensure smooth and efficient operation. Understanding how the various parts within the assembly interact is essential for maintaining optimal performance.
The structure of the plunger consists of a robust frame, which supports the compression plate and guiding components. The guiding tracks ensure precise movement along a predetermined path, minimizing friction and wear. Additionally, the driving mechanism, typically powered by mechanical or hydraulic force, ensures consistent and powerful strokes during the operation cycle.
During the operation, the plunger moves rhythmically, pushing material through a confined space, where it undergoes a series of compressions. The timing and synchronization of the plunger with other components are critical for achieving uniformity in the output. Proper lubrication and regular maintenance of the moving parts help prevent operational inefficiencies and mechanical failures.
Bale Chamber Components and Their Maintenance
The chamber responsible for forming the bales plays a crucial role in the efficiency and performance of the equipment. Understanding the various elements that constitute this section is essential for optimal functioning. Proper care and regular maintenance of these components not only enhance the machine’s longevity but also ensure the quality of the output. This section delves into the main elements of the bale chamber and the best practices for their upkeep.
Key Elements of the Chamber
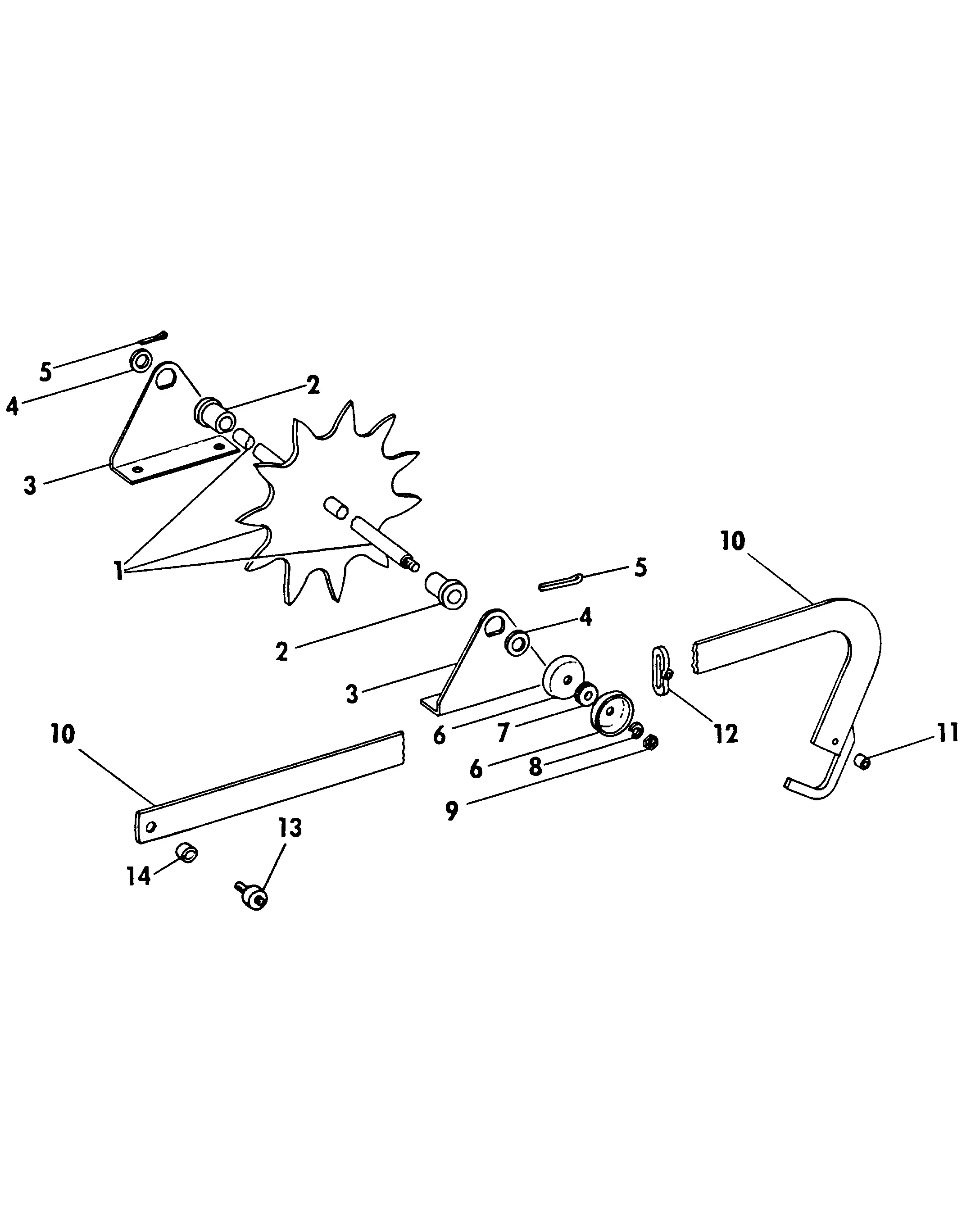
Several essential components work together within the chamber to facilitate the compression and tying of the material. These include the rollers, plunger, and tying mechanisms. Each of these elements must operate smoothly to ensure effective baling. Any wear or damage can lead to inefficiencies and increased downtime, making it vital to regularly inspect and service these parts.
Maintenance Practices
Regular maintenance involves inspecting the chamber for signs of wear, cleaning any accumulated debris, and lubricating moving parts. Checking the alignment of the rollers and ensuring the tying mechanisms are functioning correctly are also critical tasks. Addressing minor issues promptly can prevent major repairs and ensure consistent performance during operation.
Function of the Feeder Forks in Baling
The feeder forks play a crucial role in the process of collecting and transporting plant material into compression machinery. Their design and operation are essential for ensuring an efficient workflow and optimizing the overall performance of the equipment. By guiding the crop material smoothly into the system, these components help maintain consistent feeding, which is vital for effective compression and packaging.
Importance of Proper Functionality
When functioning correctly, the feeder forks facilitate the even distribution of material, preventing clogs and ensuring a steady flow. This not only enhances the machine’s efficiency but also reduces the likelihood of mechanical failures caused by uneven feeding. A well-maintained fork system contributes to increased productivity and improved end product quality.
Maintenance Considerations

Regular inspection and maintenance of the feeder forks are essential for optimal performance. Wear and tear can lead to misalignment, affecting their ability to gather material effectively. Ensuring that these components are in good condition helps to sustain the operational efficiency of the entire system.
| Component | Function | Maintenance Tip |
|---|---|---|
| Feeder Forks | Guide crop material into the compression chamber | Inspect regularly for wear and alignment |
| Hydraulic Cylinders | Control the movement of the forks | Check for leaks and proper fluid levels |
| Drive Chain | Transfers power to the forks | Lubricate periodically to prevent rust |
Twine System and Its Importance

The twine mechanism plays a crucial role in the efficiency and reliability of agricultural equipment designed for hay and forage management. This system is responsible for securely binding the harvested material, ensuring proper bales for storage and transport. A well-functioning twine setup not only enhances productivity but also minimizes waste, contributing to overall operational success.
Understanding the components of the twine system and their functions can help operators maintain optimal performance. Regular inspection and maintenance are essential to prevent breakdowns and ensure that the binding process is seamless.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Twine Holder | Holds and feeds twine during the binding process. |
| Twine Tensioner | Maintains appropriate tension to ensure secure binding. |
| Knife Assembly | Cuts the twine after binding is complete. |
| Wrap Arm | Wraps the twine around the bale during the binding cycle. |
| Control Mechanism | Regulates the entire binding operation, ensuring accuracy and efficiency. |
Proper operation and maintenance of the twine system are vital for achieving high-quality bales. By ensuring that all components are functioning correctly, operators can prevent issues that may lead to production delays or reduced quality in the final product.
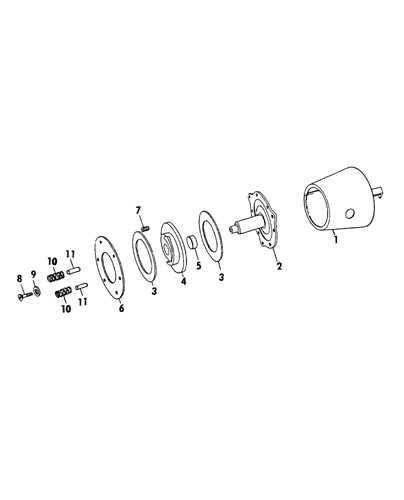
Gearbox Layout in the 269 Baler
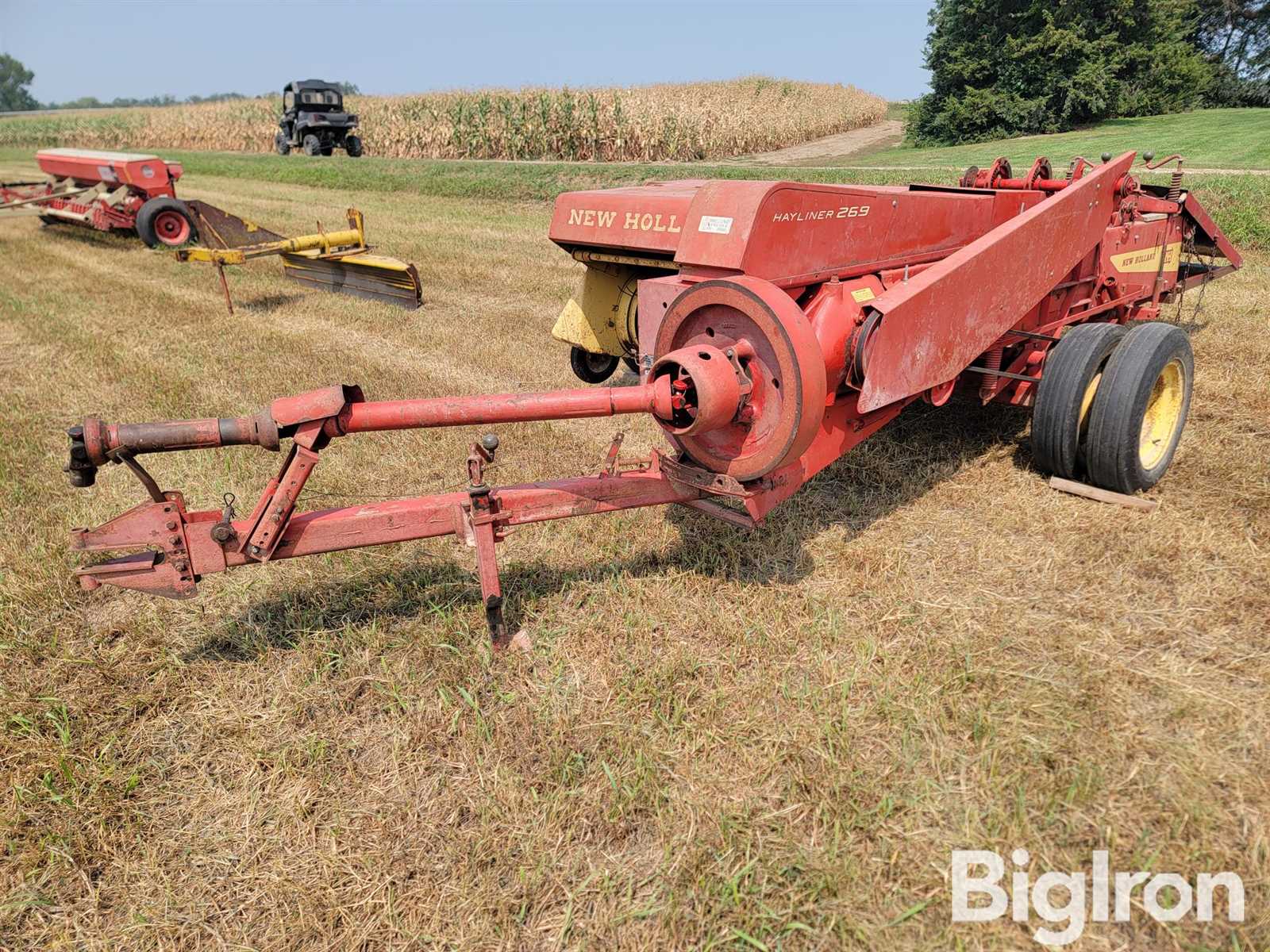

The gearbox configuration plays a critical role in the efficient operation of agricultural machinery. Understanding its arrangement helps operators and technicians diagnose issues, perform maintenance, and ensure optimal performance during use. The layout encompasses various components that work in harmony to transfer power effectively, contributing to the overall functionality of the equipment.
Key Components of the Gearbox

Within the gearbox assembly, several essential elements contribute to its performance. The gears, shafts, and bearings are strategically positioned to facilitate smooth power transmission. Each gear is designed to mesh precisely, allowing for the appropriate torque and speed adjustments needed for effective operation. Regular inspection of these components is vital to prevent wear and maintain reliability.
Maintenance Considerations
Proper maintenance of the gearbox layout is crucial for longevity. Regular lubrication of the gears and bearings ensures smooth operation and minimizes friction. Monitoring for unusual sounds or vibrations can indicate potential issues, prompting timely interventions. Keeping the gearbox in optimal condition directly affects the efficiency and productivity of the machinery.
Flywheel and Shear Bolt Functions
The flywheel and shear bolts play crucial roles in the operational efficiency and safety of agricultural machinery. These components work together to ensure smooth functioning while protecting the machine from potential damage during heavy workloads. Understanding their functions can help operators maintain optimal performance and reduce the risk of malfunctions.
The flywheel serves several important purposes:
- Energy Storage: It accumulates rotational energy, which helps maintain a consistent speed during operation.
- Vibration Dampening: The flywheel helps absorb vibrations, leading to a smoother running experience.
- Power Transmission: It facilitates the transfer of power from the engine to the operational components, ensuring efficient performance.
On the other hand, shear bolts are designed to protect the machinery from excessive strain:
- Overload Protection: They act as a safety mechanism by breaking under extreme stress, preventing damage to more expensive components.
- Simple Replacement: Shear bolts are easy to replace, allowing for quick repairs and minimal downtime.
- Cost-Effective Solution: Utilizing shear bolts helps avoid costly repairs that could arise from a failure of other machine parts.
In conclusion, the interplay between the flywheel and shear bolts is vital for ensuring the effective operation of agricultural equipment. Proper understanding and maintenance of these components contribute significantly to overall machine longevity and performance.
Best Practices for Replacing Baler Parts
Ensuring the efficient operation of agricultural machinery requires regular maintenance and timely replacements of essential components. Understanding the recommended procedures can greatly enhance performance and prolong the lifespan of the equipment. Here are some effective strategies to follow when undertaking replacements.
1. Preparation and Planning
- Review the equipment manual to identify the necessary components and specifications.
- Gather all required tools and replacement items before starting the process.
- Set up a clean and organized workspace to prevent any damage or loss of parts.
2. Follow Safety Protocols
- Always disconnect power sources to prevent accidental activation during the replacement process.
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves and safety glasses.
- Be cautious of sharp edges and heavy components, ensuring proper lifting techniques are employed.
By adhering to these best practices, operators can effectively manage the replacement process, leading to improved functionality and reduced downtime of the equipment.