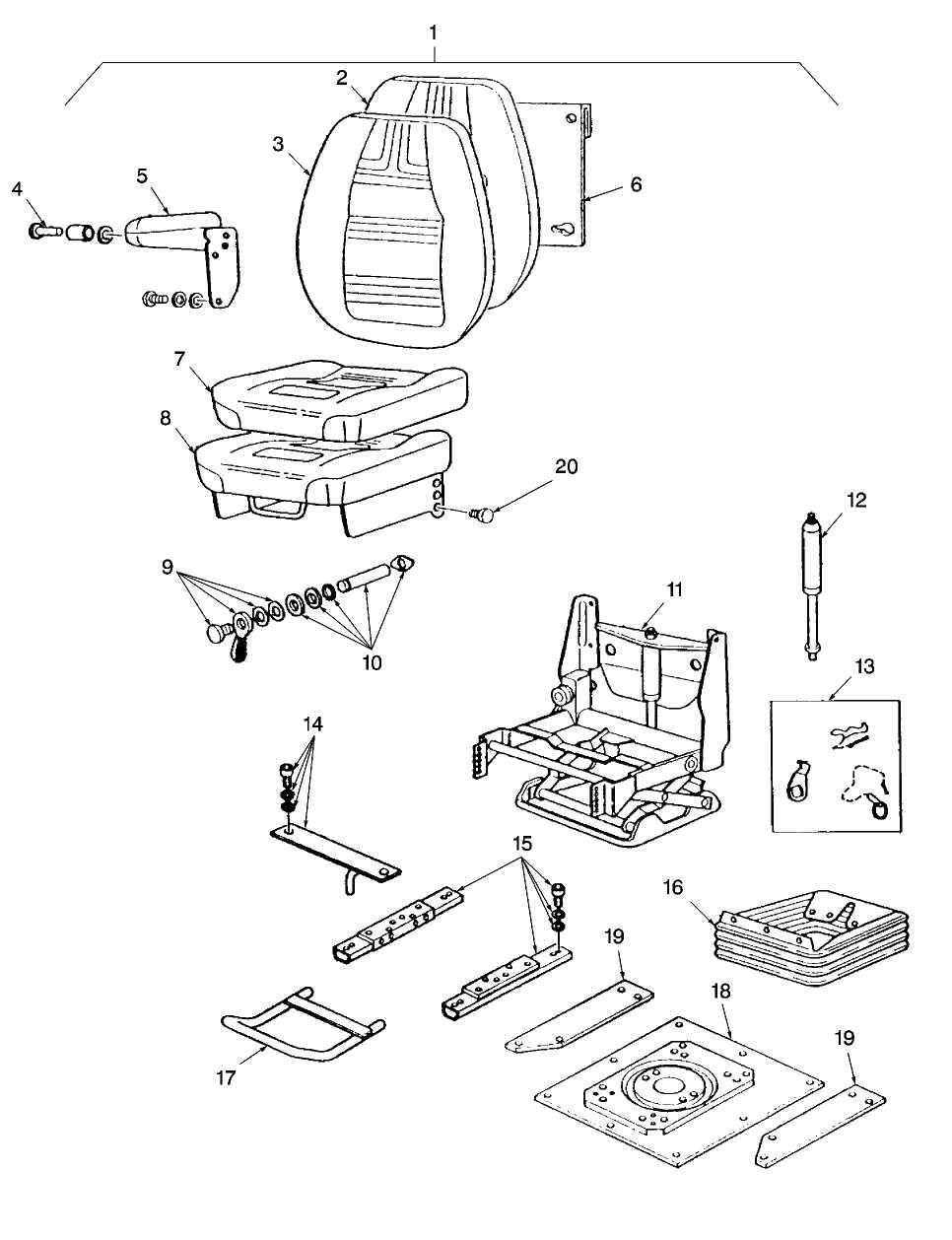
Understanding the structure and arrangement of various elements within machinery is crucial for both maintenance and repair. Each component plays a vital role in the overall performance, making it essential to have a clear understanding of how these elements connect and function together. This section aims to provide clarity on the intricate layout of mechanical assemblies without diving into brand-specific terminology.
Focusing on the relationships between mechanical elements and their positioning, we will explore how the interconnected systems ensure seamless operation. This knowledge can assist in identifying potential issues, improving efficiency, and facilitating smoother troubleshooting processes.
By gaining insight into the spatial configuration of these systems, one can easily navigate through routine inspections and more complex repair tasks, ensuring that each mechanical unit operates optimally.
Overview of New Holland 555E Components

Understanding the various elements of a construction machine is crucial for both operation and maintenance. This type of equipment includes numerous systems that work together to ensure smooth performance. Identifying these core assemblies helps operators maintain the machine’s functionality and address issues more effectively.
Key systems include the hydraulic framework, responsible for fluid power transmission, and the engine block, which supplies mechanical energy. Other vital parts such as the transmission system, steering mechanism, and structural framework contribute to the overall efficiency and stability of the machinery.
Each system is interconnected, ensuring that power, control, and movement are properly distributed throughout the machine. Regular inspection and maintenance of these components are essential to prolong service life and optimize performance in diverse working conditions.
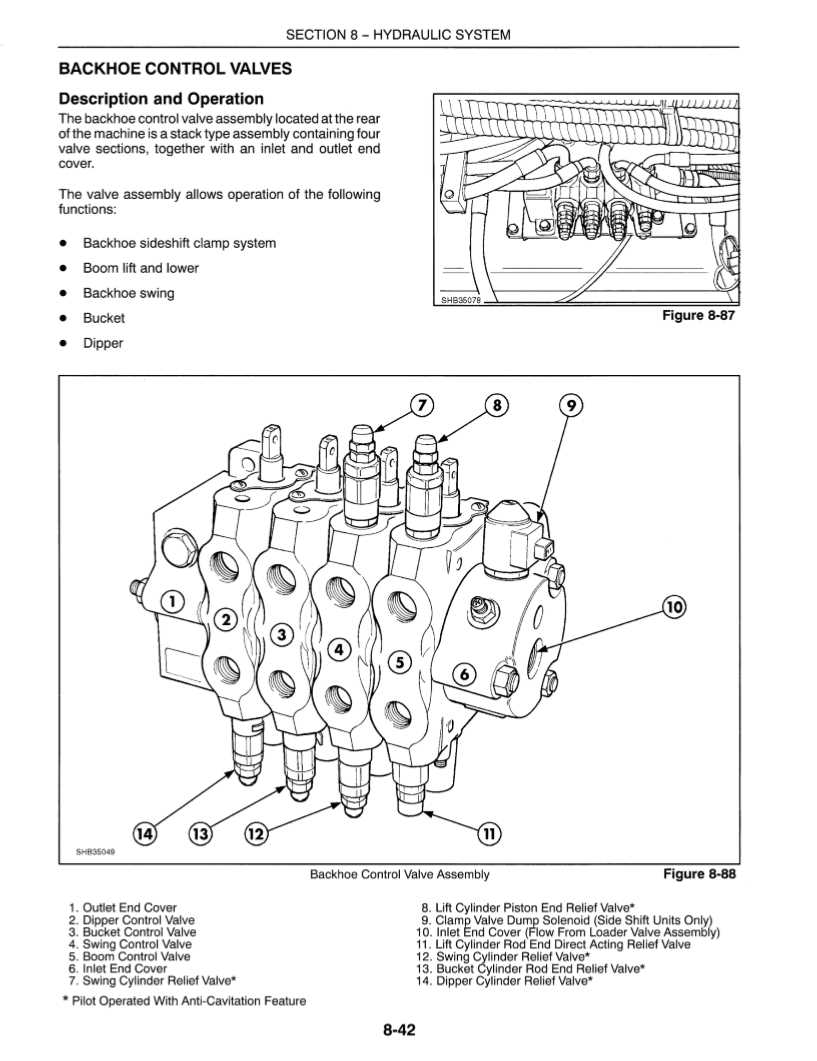
Hydraulic System Breakdown and Key Parts
The hydraulic system plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficient operation of construction equipment. Its main function is to transfer force through fluid, enabling various components to perform heavy lifting, digging, and other critical tasks. Understanding the layout of this system and identifying the core elements is essential for maintaining its reliability and performance.
Below is a breakdown of the primary components involved in the hydraulic system:
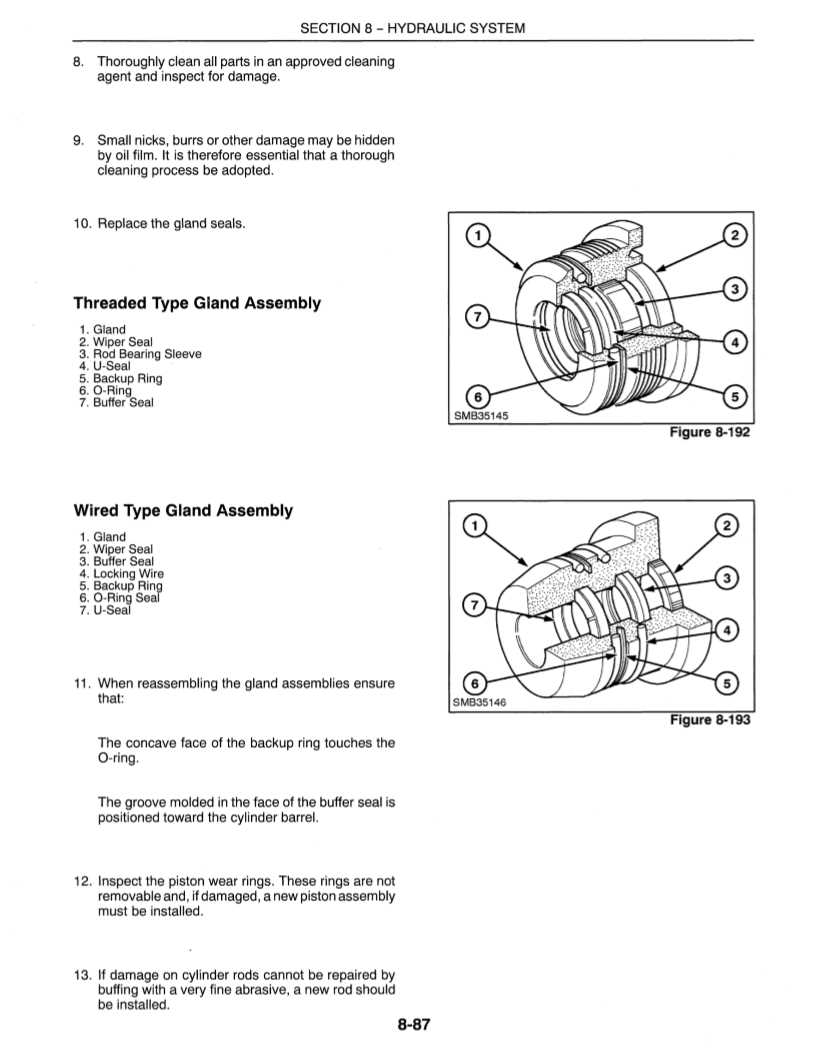
| Component | Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pump | Converts mechanical energy into hydraulic energy, creating the pressure needed to move fluid through the system. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Valves | Regulate, direct, and control the flow of hydraulic fluid, ensuring the right amount of pressure is delivered to various parts of the machine. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Component | Function |
|---|
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Fuel Tank | Stores the fuel needed for engine operation, ensuring a consistent supply. |
| Fuel Pump | Responsible for moving fuel from the tank to the engine, maintaining the necessary pressure. |
| Fuel Filter | Removes impurities from the fuel, preventing damage to the engine components. |
| Injector | Sprays a precise amount of fuel into the combustion chamber for optimal burning. |
| Fuel Lines | Transport fuel between the tank, pump, filter, and engine, designed to withstand high pressure. |
Configuration Insights
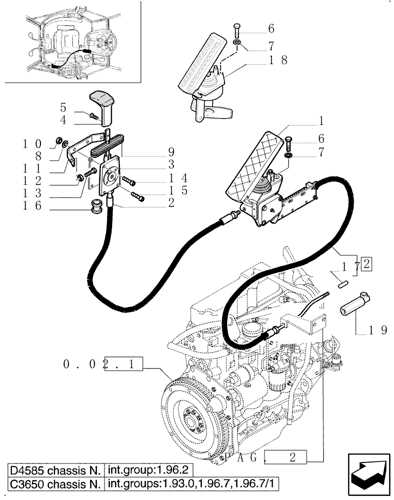
The arrangement of the fuel system components is vital for efficient operation. Proper configuration ensures that fuel flows smoothly and is delivered to the engine at the correct pressure. Regular maintenance of these elements is crucial to prevent fuel system failures and maintain machinery performance.
Brake System Parts and Functions
The braking system of heavy machinery plays a crucial role in ensuring safety and control during operation. This system is composed of various components that work together to provide effective deceleration and stopping power. Understanding the functionality and interplay of these elements is essential for maintaining optimal performance and addressing any potential issues that may arise.
Key Components of the Braking Mechanism
At the heart of the braking system is the brake pedal, which the operator engages to initiate the stopping process. This action sends a signal to the hydraulic system, which amplifies the force applied to the brake components. The brake calipers then clamp down on the brake discs, generating friction that slows down the machinery. Additionally, the brake fluid plays a vital role in transmitting force from the pedal to the calipers, ensuring a responsive braking action.
Functionality and Maintenance Considerations
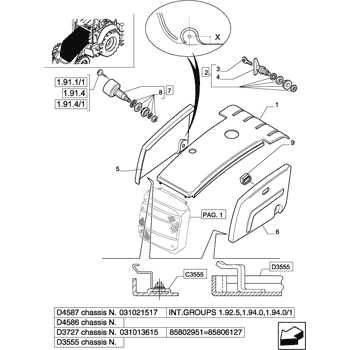
Each element within the braking system has a specific purpose that contributes to overall effectiveness. Regular inspection and maintenance are crucial to prevent wear and tear on components like brake pads and rotors, which can diminish performance over time. Ensuring that the hydraulic fluid levels are adequate and that there are no leaks can significantly enhance the reliability of the braking mechanism. Understanding these functions and performing routine checks can help avoid costly repairs and ensure safe operation.
Cooling System Layout and Key Elements
The cooling system plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures for machinery. Its layout is designed to efficiently dissipate heat generated during operation, ensuring that components remain within safe temperature limits. Understanding the key elements of this system is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Components of the Cooling System
Several essential components work together to facilitate effective cooling. These include the radiator, water pump, coolant reservoir, and thermostat. Each part serves a specific function, contributing to the overall efficiency of the cooling system.
Functionality and Operation
The operation of the cooling system is vital for preventing overheating. The water pump circulates coolant through the engine, absorbing heat. The radiator then dissipates this heat into the atmosphere, while the thermostat regulates coolant flow based on temperature variations.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Radiator | Dissipates heat from coolant |
| Water Pump | Circulates coolant throughout the system |
| Coolant Reservoir | Holds excess coolant |
| Thermostat | Regulates coolant temperature |
Cabin Controls and Instrument Panel Overview

The control systems and instrument panels within a machinery cabin play a vital role in ensuring efficient operation and user comfort. Understanding the layout and functionality of these elements is essential for optimal performance. This section will provide an in-depth examination of the various controls and indicators typically found in heavy equipment cabins, emphasizing their significance in daily tasks.
Control Layout and Functionality
The arrangement of controls in the cabin is designed for accessibility and ease of use. Operators encounter various levers, switches, and pedals, each serving specific functions to manage the machine’s operations. Ergonomics is a key consideration in this design, aiming to minimize fatigue and enhance productivity during prolonged use.
Instrument Panel Features
The instrument panel serves as the command center, providing essential information regarding the machine’s status. Common features include gauges for monitoring engine performance, fluid levels, and operational temperatures. Warning lights and indicators alert the operator to any anomalies, ensuring timely responses to potential issues.
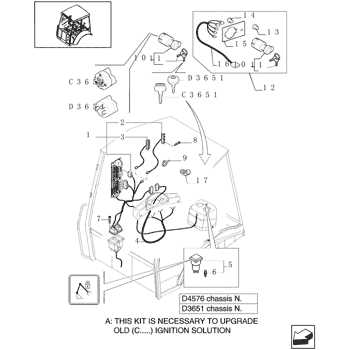
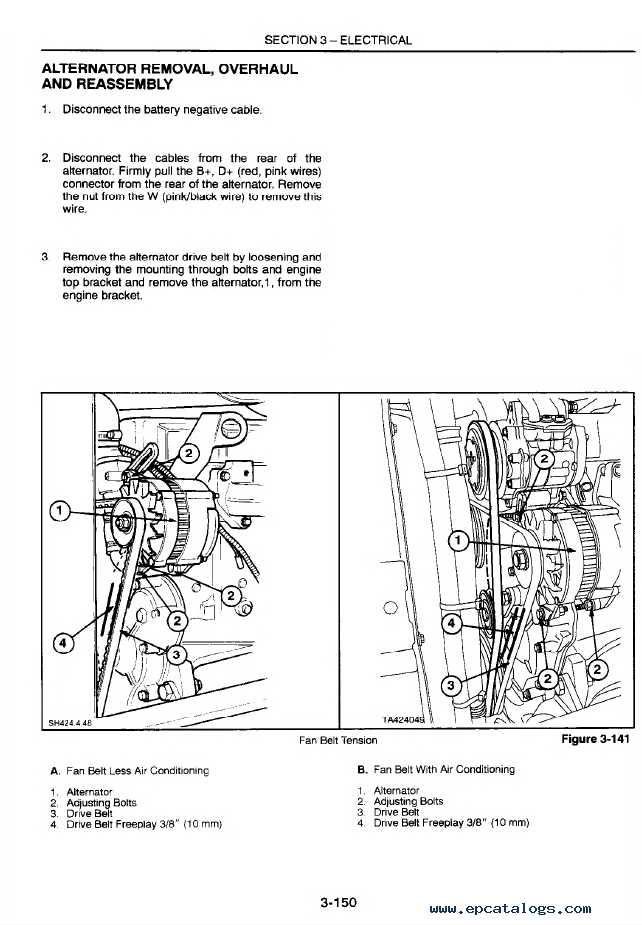
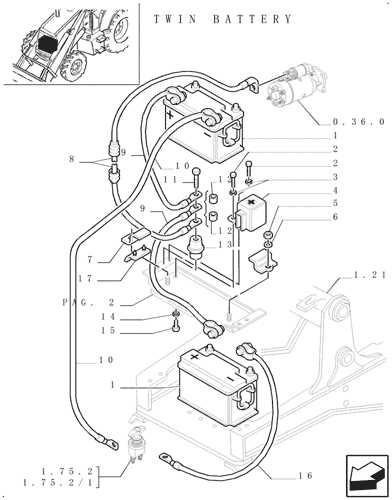
Electrical System: Key Wiring and Components
The electrical framework of heavy machinery plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient operation and control. Understanding the essential wiring and components is vital for proper maintenance and troubleshooting. This section delves into the primary elements that form the backbone of the electrical system.
Wiring Harness: The wiring harness acts as the central nervous system, connecting various electrical components. It ensures that power and signals are efficiently transmitted throughout the machine, facilitating communication between the engine, control panel, and other vital systems.
Fuses and Relays: Fuses and relays are critical safety components that protect the electrical circuit from overloads and short circuits. Fuses act as a safeguard by interrupting the current flow during faults, while relays control the power distribution to different electrical devices, ensuring optimal functionality.
Batteries: The power source for the entire electrical system, batteries provide the necessary energy to start the engine and power auxiliary systems. Regular checks and maintenance of the batteries are essential to prevent unexpected failures and ensure longevity.
Control Switches: Control switches enable operators to manage various functionalities, from lighting to engine start. Their placement and reliability are crucial for safe operation, making them an essential aspect of the electrical system.
Understanding these key components and their interactions is essential for effective troubleshooting and maintenance of the machinery’s electrical system. Proper knowledge can significantly reduce downtime and enhance overall performance.
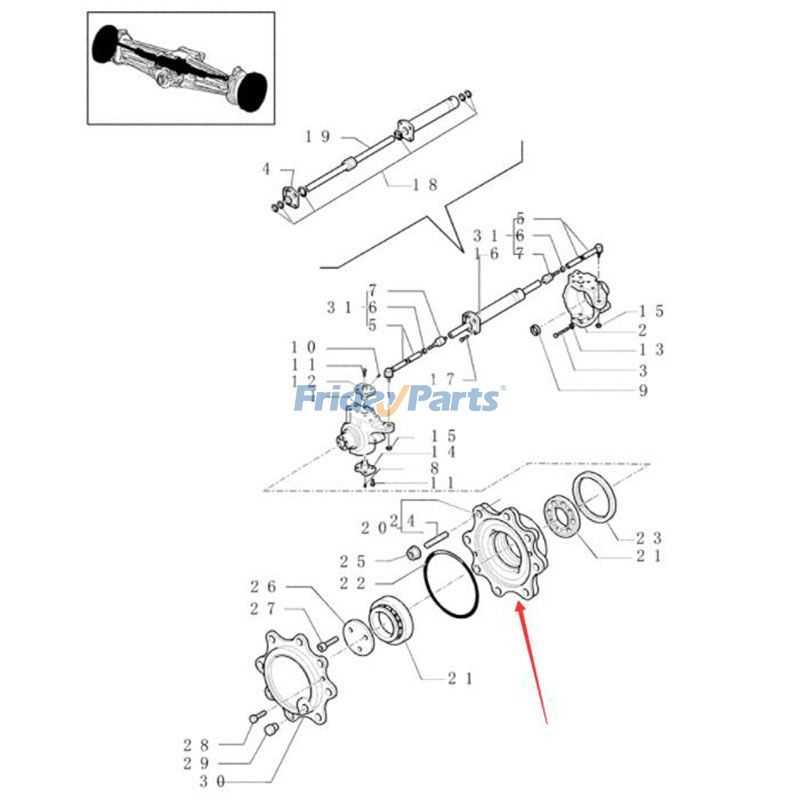
Rear Axle and Driveline Parts Layout
The configuration of the rear axle and driveline components plays a crucial role in the functionality of heavy machinery. Understanding the arrangement and relationships between these elements is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. This section delves into the structural layout, highlighting the key components that facilitate efficient power transmission and stability during operation.
Key Components Overview
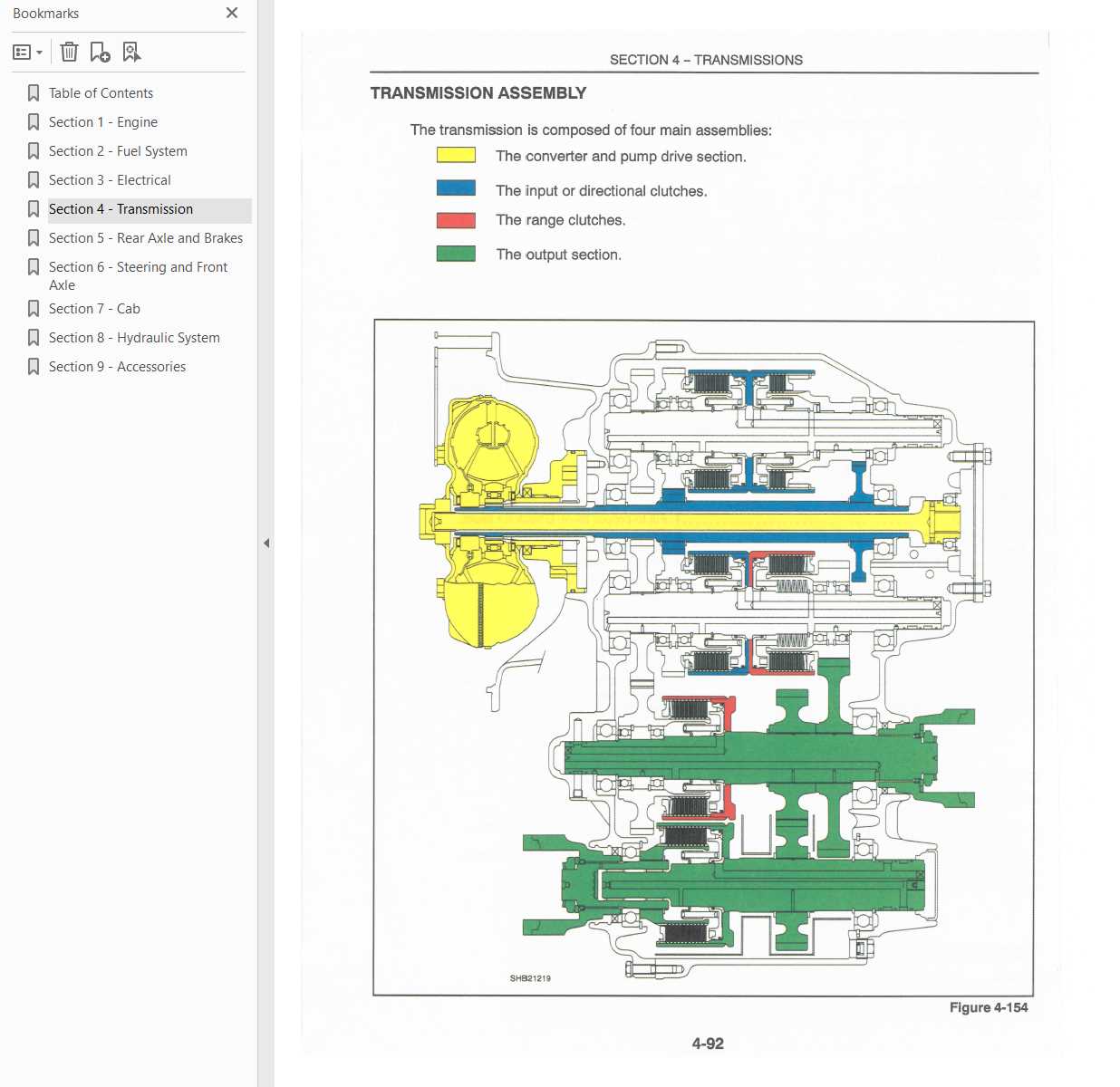
At the core of the rear axle assembly is the differential, which allows for smooth rotation between the wheels during turns. Coupled with the drive shafts, this system ensures the effective distribution of torque to the rear wheels. Additionally, bearings and seals are integrated to minimize friction and protect the internal components from contaminants.
Maintenance Considerations
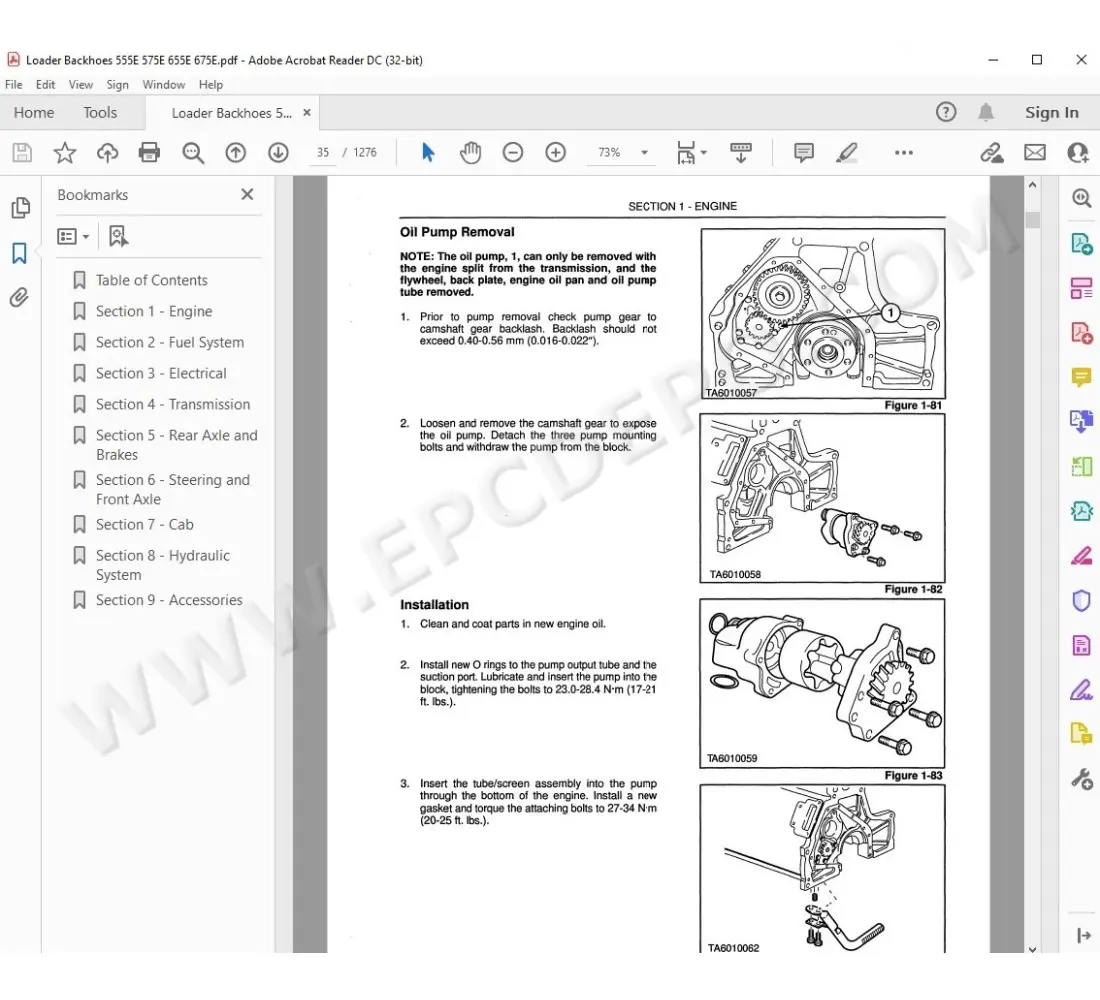
Regular inspection of the driveline elements is vital to ensure optimal performance. Components such as u-joints and yokes should be checked for wear, as they directly influence the transfer of power from the engine to the wheels. Lubrication of the rear axle assembly is also essential to prolong the lifespan of these critical parts and prevent premature failure.